1. Introduction
Detailed description of the subjects treated in this paper may be found in the two books recently published by Berman in 2012 [1,2]). Additional paper references are Berman in 2007 [3]; in 2011 [4,5]; in 2012 [6]) and with co-authors Costa, (Berman and Costa in 2012 [7]) and with Gomide {Berman and Gomide in 2012 [8] and [9]- (version of the year 2010)} and book form as a Chapter in an edited book [10], by Berman and Gomide.
Anderson et al., in 2008 [11], and Lämmerzahl et al., in 2006 [12], have alerted the scientific community about the fly-by anomaly: during Earth gravity assists, spacecraft has suffered from an extra-energization, characterized by a positive extra speed, such that, measured “at infinity”, the hyperbolic orbiting object presented an empirically calculated  around
around  A formula was supplied,
A formula was supplied,
 (1.1)
(1.1)
where , R and c stand for the angular speed and radius of the central mass, and the speed of light in vacuo. T. L. Wilson, from NASA, (Houston) and H.-J. Blome (Aachen), delivered a lecture in Montreal, on July 17, 2008, and called the attention to the fact that the most trusted cause for both this anomaly, and the Pioneers, would be “rotational dynamics” (Wilson and Blome, in 2008 [13]). One of us, had, by that time, published results on the Pioneers Anomaly, through the rotation of the Universe (Berman, in 2007 [3]). Now, we shall address the three anomalies.
, R and c stand for the angular speed and radius of the central mass, and the speed of light in vacuo. T. L. Wilson, from NASA, (Houston) and H.-J. Blome (Aachen), delivered a lecture in Montreal, on July 17, 2008, and called the attention to the fact that the most trusted cause for both this anomaly, and the Pioneers, would be “rotational dynamics” (Wilson and Blome, in 2008 [13]). One of us, had, by that time, published results on the Pioneers Anomaly, through the rotation of the Universe (Berman, in 2007 [3]). Now, we shall address the three anomalies.
The Pioneers Anomaly is the deceleration of about  cm·s–2 suffered by NASA space-probes travelling towards outer space. It has no acceptable explanation within local Physics, but if we resort to Cosmology, it could be explained by the rotation of the Universe. Be cautious, because there is no center or axis of rotation. We are speaking either of a Machian or a General Relativistic cosmological vorticity. It could apply to each observed point in the Universe, observed by any observer. Another explanation, would be that our Universe obeys a variable speed of light Relativistic Cosmology, without vorticities. However, we shall see later that both models are equivalent. Thermal emission cannot be invoked, for it should also decelerate elliptical orbiters, but the deceleration only affects hyperbolic motion. It does not explain fly-bys, either. A secondary Pioneers anomaly refers to spinning down of the spacecraft, when they were not disturbed. Again, thermal emission cannot explain it.
cm·s–2 suffered by NASA space-probes travelling towards outer space. It has no acceptable explanation within local Physics, but if we resort to Cosmology, it could be explained by the rotation of the Universe. Be cautious, because there is no center or axis of rotation. We are speaking either of a Machian or a General Relativistic cosmological vorticity. It could apply to each observed point in the Universe, observed by any observer. Another explanation, would be that our Universe obeys a variable speed of light Relativistic Cosmology, without vorticities. However, we shall see later that both models are equivalent. Thermal emission cannot be invoked, for it should also decelerate elliptical orbiters, but the deceleration only affects hyperbolic motion. It does not explain fly-bys, either. A secondary Pioneers anomaly refers to spinning down of the spacecraft, when they were not disturbed. Again, thermal emission cannot explain it.
In previous papers (Berman and Gomide in 2010, updated for this Journal in 2012 [9]; in 2012 [10]), by considering an exact but particular solution of Einsteins field equations for an expanding and rotating metric, found, by estimating the deceleration parameter of the present Universe, as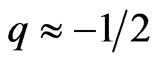 , that the Universe appeared to possess a field of decelerations coinciding approximately with the Pioneers anomalous value (Anderson et al. in 2002 [14]). We now shall consider the condition for an exact match with the Pioneers deceleration,with a large class of solutions in General Relativity. Sections 5 and 6, treat the second Pioneers anomaly, and the fly-by. In Section 7, an alternative cosmological model will be presented, following an idea by Godlowski et al. in 2004 [15], which allows us to work with a non-modified RWs metric.
, that the Universe appeared to possess a field of decelerations coinciding approximately with the Pioneers anomalous value (Anderson et al. in 2002 [14]). We now shall consider the condition for an exact match with the Pioneers deceleration,with a large class of solutions in General Relativity. Sections 5 and 6, treat the second Pioneers anomaly, and the fly-by. In Section 7, an alternative cosmological model will be presented, following an idea by Godlowski et al. in 2004 [15], which allows us to work with a non-modified RWs metric.
The key result for all these subjects, is that hyperbolic motion, extends towards infinity, and, thus, qualify for cosmological alternatives, and boundary conditions. The fly-bys, and the Pioneers, are in hyperbolic trajectories, when the anomalies appear, so that Cosmology needs to be invoked.
Ni in 2008 [37] and 2009 [38], has reported observations on a possible rotation of the polarization of the cosmic background radiation, around 0.1 radians. As such radiation was originated at the inception of the Universe, we tried to estimate a possible angular speed or vorticity, by dividing 0.1 radians by the age of the Universe , obtaining about 10–19 rad·s–1. Compatible results were obtained by Chechin in 2010 [33], Su and Chu in 2009 [41], Godlowski in 2011 [35] and Chechin in 2012 [34].
The numerical result is very close to the theoretical estimate, by Berman in 2007 [3],
 (1.2)
(1.2)
where c, R represent the speed of light in vacuum, and the radius of the causally related Universe.
When one introduces a metric temporal coefficient g00 which is not constant, the new metric includes rotational effects. The metric has a rotation of the tri-space (identical with RWs tri-space) around the orthogonal time axis. This will be our framework, except for Section 7.
2. On the Four Kinds of Rotation in Relativistic Cosmology
The purpose of this Section is basically to focus on new rotational formulations in Relativistic Cosmology, the first, due to Berman [1-10]; based on a seminal metric that was proposed by Gomide and Uehara [36] when the purpose of those two authors was something else, unrelated to rotation, and the second, was an idea by Godlovski et al. [15], developed in several articles by Berman (see for instance papers [2,4] and books [1,2].
Consider the metric line-element:
 (2.1)
(2.1)
If the observer is at rest,
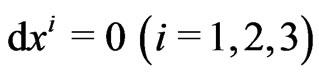
while,
 (2.2)
(2.2)
This last equality defines a proper time; we called cosmic time, in Cosmology.
From the geodesics’ equations, we shall have:
 (2.3)
(2.3)
We then find:
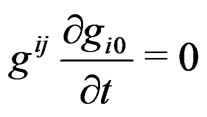 (2.4)
(2.4)
This defines a Gaussian coordinate system, which in general implies that:
 (2.5)
(2.5)
We must now reset our clocks, so that, the above condition is universal (valid for all the particles in the Universe), and then our metric will assume the form:
 (2.6)
(2.6)
If we further impose that, in the origin of time, we have:
 (2.7)
(2.7)
then by (2.5), we shall have:
 (2.8)
(2.8)
The above defines a Gaussian normal coordinate system.
For a commoving observer, in a freely falling perfect fluid, the quadrivelocity  will obey:
will obey:
 (2.9)
(2.9)
while, if we normalize the quadrivelocity, we find, from the condition:
 (2.10)
(2.10)
that,
 (2.11)
(2.11)
Though later we shall discuss the case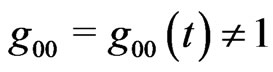 , it is usually imposed:
, it is usually imposed:
 (2.12)
(2.12)
When dealing with Robertson-Walker’s metric, this is the usual procedure. By this means, we have a tri-space, orthogonal to the time axis.
Gaussian coordinate systems, in fact, imply that, with , there are no rotations in the metric, and in each point we may define a locally inertial reference system.
, there are no rotations in the metric, and in each point we may define a locally inertial reference system.
Gaussian normal coordinates were called “synchronous”; in an arbitrary spacetime, when we pick a spacelike hypersurface , and we eject geodesic lines orthogonal to it, with constant coordinates
, and we eject geodesic lines orthogonal to it, with constant coordinates  and
and , while
, while , where
, where  on
on , then t is the proper time, whose origin is
, then t is the proper time, whose origin is 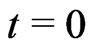 on
on  (see MTW in 1973 [16]).
(see MTW in 1973 [16]).
In the above treatment, cosmic time is “absolute”, so that the measure of the age of the Universe, according to this “time”, is not subject to a relative nature.
Now, we might ask whether the tri-space, orthogonal to the time axis, could rotate relative to this axis. Berman in 2008 [17,18], has exactly defined this original idea, by identifying this rotation, which is different from all others, as will shall show bellow, with a time-varying metric coefficient . In the next Section, we relate the angular speed of the tri-space, relative to the time axis, with
. In the next Section, we relate the angular speed of the tri-space, relative to the time axis, with  by means of,
by means of,
 (2.13)
(2.13)
In the above, we still may have a perfect fluid model. Book treatments can be found in Berman [1,2].
Other type of rotation, is Raychaudhuri’s vorticity [19- 21], which is attached to non-perfect fluids (see, for instance, Berman in 2007 [19]). A third type of rotation, is what we usually call rotation of the metric, and is defined by non-diagonal terms, in the metric. For instance, Kerr’s metric [22-24].
A fourth kind of rotation, is also attached to a perfect fluid model, like Berman’s one: it is the Godlowski et al. in 2004 [15] idea, which is developed in Section 7 below. See also Berman [1,2,4-7].
3. Field Equations for Gomide-Uehara-R.W.-Metric
Consider first a temporal metric coefficient which depends only on t. The line element becomes:
 (3.1)
(3.1)
The field equations, in General Relativity Theory (GRT) become:
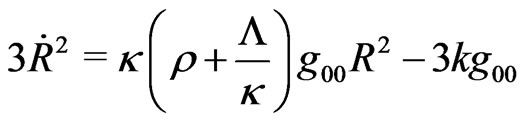 (3.2)
(3.2)
and,
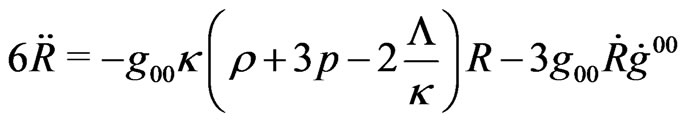 (3.3)
(3.3)
Local inertial processes are observed through proper time, so that the four-force is given by:
 (3.4)
(3.4)
Of course, when , the above equations reproduce conventional Robertson-Walker’s field equations.
, the above equations reproduce conventional Robertson-Walker’s field equations.
In order to understand Equation (3.4) , it is convenient to relate the rest-mass m, to an inertial mass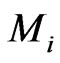 , with:
, with:
 (3.5)
(3.5)
It can be seen that Mi represents the inertia of a particle, when observed along cosmic time, i.e., coordinate time. In this case, we observe that we have two acceleration terms, which we call,
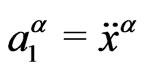 (3.6)
(3.6)
and,
 (3.7)
(3.7)
The first acceleration is linear; the second, resembles rotational motion, and depends on  and its timederivative.
and its timederivative.
If we consider  a centripetal acceleration, we conclude that the angular speed
a centripetal acceleration, we conclude that the angular speed 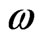 is given by,
is given by,
 (3.8)
(3.8)
The case where  depends also on
depends also on ,
,  and
and 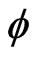 was considered also by Berman in 2008 [18] and does not differ qualitatively from the present analysis, so that, we refer the reader to that paper.
was considered also by Berman in 2008 [18] and does not differ qualitatively from the present analysis, so that, we refer the reader to that paper.
4. The Exact Solution to the Pioneers Anomaly
Consider the possible solution for the rotating case. We equate (1.2) and (3.8). We try a power-law solution for R, and find,
 (A = constant).
(A = constant).
The scale-factor assumes a power-law, as in constant deceleration parameter models (Berman in 1983 [25]; and Gomide in 1988 [26])
 (4.1)
(4.1)
where, m, D = constants, and,
 (4.2)
(4.2)
where q is the deceleration parameter. We may choose q as needed to fit the observational data.
We find,

If we now solve for energy-density of matter, and cosmic pressure, for a perfect fluid, the best way to present the calculation, and the most simple, is showing the matter energy-density  and the
and the 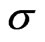 -or gravitational density parameter, to be defined below. We find
-or gravitational density parameter, to be defined below. We find


For the present Universe, the infinite time limit makes the above densities become zero.
It is possible to define,
 (negative energy-density of the gravitational field)
(negative energy-density of the gravitational field)
Now, let us obtain the gravitational energy of the field,
 (4.3)
(4.3)
5. The Second Pioneers Anomaly
The universal angular acceleration, is given by
 (5.1)
(5.1)
The spins of the Pioneers were telemetered, and as a surprise, it shows that the on-board measurements yield a decreasing angular speed, when the space-probes were not disturbed. Turyshev and Toth in 2010 [27], published the graphs (Figures 2.16 and 2.17 in their paper), from which it is clear that there is an angular deceleration of about 0.1 RPM per three years, or,
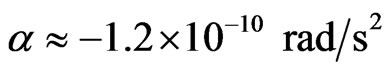 (5.2)
(5.2)
As the diameter of the space-probes is about 10 meters, the linear acceleration is practically the Pioneers anomalous deceleration value ,in this case,  cm·s–2. The present solution of the second anomaly, confirms our first anomaly explanation.
cm·s–2. The present solution of the second anomaly, confirms our first anomaly explanation.
I have elsewhere pointed out that we are in face of an angular acceleration frame-dragging field, for it is our result (5.1) above, for the Universe, that causes the result (5.2), through the general formula,
 (5.3)
(5.3)
where l is the linear magnitude of the localized body suffering the angular acceleration frame-dragging. For subatomic matter, this angular acceleration can become important.
6. The Solution of the Fly-By Anomaly
Consider a two-body problem, relative to an inertial system. The additional speed, measured at infinity, relative to the total speed, measured at infinity, is proportional to twice the tangential speed of the earth, 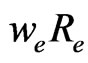 , divided by the total speed
, divided by the total speed  taken care of the Universe angular speed. In fact, we write
taken care of the Universe angular speed. In fact, we write
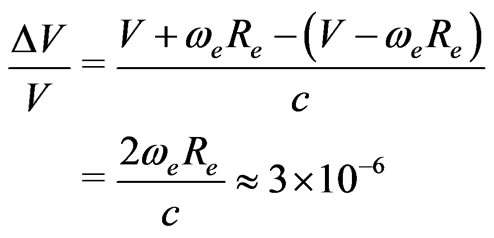 (6.1)
(6.1)
The trick, is that infinity, in a rotating Universe, like ours, has a precise meaning, through the angular speed Formula (1.2).
7. The Godlowski et al. Rotation
We, now, shall follow an idea by Godlowski et al. in 2004 [15], and supply another General Relativistic model, of an expanding and rotating Universe. Their idea, is that the homogeneous and isotropic models, may still rotate relative to the local gyroscope, by means of a simple replacement, in the Friedman-RWs equations, of the kinetic term, by the addition of a rotational kinetic one.
Einsteins field equations, for a perfect fluid with perfect gas equation of state, and RWs metric, are two ones. The first, is an energy-density equation, the second is a definition of cosmic pressure, which can be substituted by energy momentum conservation. But, upon writing the  term, we shall add an extra rotational term, namely
term, we shall add an extra rotational term, namely , in order to account for rotation. If we keep (3.1), the field equations become, for a flat Universe
, in order to account for rotation. If we keep (3.1), the field equations become, for a flat Universe
 (7.1)
(7.1)
with
 (7.2)
(7.2)
and
 (7.3)
(7.3)
The usual solution, with Bermans constant deceleration parameter models, render (Berman in 1983 [25]; and Gomide in 1988 [26]),
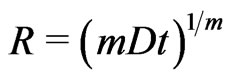 (7.4)
(7.4)
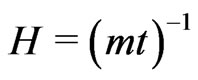 (7.5)
(7.5)
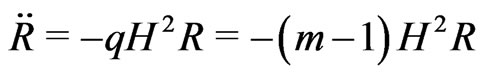 (7.6)
(7.6)
Notice that we may have a negative deceleration parameter, implying that the Universe accelerates, probably due to a positive cosmological “constant”, but, nevertheless, it is subjected to a negative rotational deceleration, a kind of centripetal one, that acts on each observed point of the Universe, relative to each observer, given by relation (1.2), so that,
 (7.7)
(7.7)
We now supply the necessary relations among the constants, so that the above equations be observed, namely,

 (7.8)
(7.8)
 (7.9)
(7.9)
8. Final Comments
If we calculate the centripetal acceleration corresponding to the above angular speed (1.2), we find, for the present Universe, with 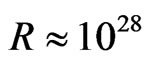 cm and
cm and  cm/s,
cm/s,
 (8.1)
(8.1)
Our model of Section 4 has been automatically calculated alike with (1.2) and (8.1). This value matches the observed experimentally deceleration of the NASA Pioneers’ space-probes. Equation (3.3) shows that one can have a positive cosmological lambda term accelerating the Universe, i.e.,  along with a centripetal deceleration that is felt by any observer, relative any observed point, given by (8.1). Berman and Gomide, in 2010, update for this Journal in 2012 [9], had obtained a Machian General Relativistic solution, though particular. We call it Machian, because it parallels the semirelativistic Machian solution by Berman in 2007 [3].
along with a centripetal deceleration that is felt by any observer, relative any observed point, given by (8.1). Berman and Gomide, in 2010, update for this Journal in 2012 [9], had obtained a Machian General Relativistic solution, though particular. We call it Machian, because it parallels the semirelativistic Machian solution by Berman in 2007 [3].
A cosmologist has made very important criticisms on our work. First, he says why do not the planets in the solar system show the calculated deceleration on the Pioneers? The reason is that elliptical orbits are closed, and localized. You do not feel the expansion of the universe in the sizes of the orbits either. In General Relativity books, authors make this explicit. You do not include Hubbles expansion in Schwarzschilds metric. But, those space probes that undergo hyperbolic motion, which orbits extend towards infinity, they acquire cosmological characteristics, like, the given P.A. deceleration. Second objection, there are important papers (Rievers and Lämmerzahl in 2011 [28]; Francisco et al. in 2011 [29]; Cuesta in 2011 [30]) which resolve the P.A. with non-gravitational Physics. Our answer, that is OK, we have now alternative explanations. However, in the Introduction of this paper, we have responded why thermal emission is no good an explanation because it does not explain the other two anomalies neither why the elliptical orbiters did not suffer the same deceleration; as to Cuesta in 2011 [30] he also has no explanation for the other two anomalies. This does not preclude ours. Third, cosmological reasons were discarded, including rotation of the Universe. The problem is that those discarded cosmologies, did not employ the correct metric. For instance, they discarded rotation by examining Godel model, which is non expanding, and with a strange metric. The two kinds of rotating and expanding metrics we employ now, were not discarded or discussed by the authors cited by this cosmologist. Then, the final question, is how come that a well respected author, dismissed planetary Coriolis forces induced by rotation of distant massesby means of the constraints in the solar system. The answer is the same above, and also that one needs to consider Machs Principle on one side, and the theoretical meaning of vorticities, because one is not speaking in a center or an axis of rotation or so. When we say, in Cosmology, that the Universe rotates, we mean that there is a field of vorticities, just that. The whole idea is that Cosmology does not enter the Solar System except for nonclosed orbits that extend to outer space. For the Gomide Uehara RWs metric, it is the tri-space that rotates relative to the orthogonal time-axis.
Another cosmologist pointed out a different “problem”. He was discussing the prior paper, to the present one (Berman and Gomide in 2010, updated in 2012 for this Journal [9]). He objects, that the angular speed formula of ours, is coordinate dependent. Now, when you choose a specific metric, you do it thinking about the kind of problem you have to tackle. After you choose the convenient metric, you forget tensor calculus, and you work with coordinate-dependent relations. They work only for the given metric, of course. It must be stressed once more, what has been discussed in several prior papers by these authors, or by Berman alone, that the point most important that is taken into consideration remains the zero-total energy of the Universe, whose pioneer pseudo-tensor calculation has been made in an unpublished Master of Science Thesis by Berman, in 1981 [31], which was advised by the second author of this paper and became the seminal zero-energy calculation on the Universe’s energy.
The solutions of Section 4, and Section 7, are in fact a large class of solutions, for they embrace any possible deceleration parameter value, or, any power-law scalefactor. Our solution with the rotation of the Universe, is the only unified explanation that applies to the three NASA anomalies.
As stated in the Abstract of this paper, detailed description of the subjects treated here, may be found in the two books recently published by Berman in 2012 [1] and [2]. Additional paper references are Berman in 2007 [3]; in 2011 [4,5] and in 2012 [2]) and with co-authors Costa, (Berman and Costa, in 2010 updated for this Journal in 2012 [7]) and with Gomide (Berman and Gomide, in 2010, updated in 2012 [9]; in 2011, updated in 2012 for this Journal, in the present paper [8,9]).
9. Acknowledgements
One of the authors (MSB) thanks Marcelo Fermann Guimarães, Nelson Suga, Mauro Tonasse, Antonio F. da F. Teixeira, and for the important incentive offered by Miss Solange Lima Kaczyk, now, a brand new advocate, continued during the last five years of his research in Cosmology.