Research on the Impact of Blockchain Technology on Real Earnings Management of Listed Companies ()
1. Introduction
Today, with the rapid development of information technology, blockchain technology has come into being, triggering a new round of technological trends around the world. The Outline of the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan clearly states that blockchain should be one of the seven key industries of digital economy in the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan. China has entered a period of a new round of scientific and technological revolution and industrial revolution represented by the Internet, which also puts forward higher requirements for various economic and social fields, and blockchain, as an important carrier of “digital economy” and “digital China”, will surely play an increasingly important role in the process of digital industrialization and industrial digitization. As an important carrier of “digital economy” and “digital China”, blockchain will play an increasingly important role in the digital industrialization and industrial digitization, promote the deep combination of digital technology and the real economy, empower the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries, and strengthen the new engine for economic development. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the promotion and application of blockchain technology in China.
In recent years, the management of listed companies such as Kangdexin and Kangmei Pharmaceuticals have frequently engaged in myopic behaviour, which has seriously affected the development of the capital market and the rights and interests of investors. In fact, since the principal-agent theory was put forward, the short-sighted behaviour of the management has become a major problem in the theoretical and practical circles, but it has not been well solved so far. Short-sighted behaviour at the cost of the company’s sustainable development will not only affect principals and agents, but also bring negative effects to stakeholders such as regulators, creditors and employees. In short, management’s short-sighted behaviour is not fully restrained and curbed at present, which remains a major problem in corporate governance and urgently needs to be explained from a scientific perspective. And the real earnings management activity is a very typical management short-sighted behaviour, which manages the earnings by adjusting the company’s production, investment and financing activities, which will make the investors as well as the company’s interests suffer. Therefore, how to effectively curb real earnings management behaviour through sound corporate governance mechanisms has become an important issue of common concern in both theoretical and practical circles. This paper introduces blockchain technology to test whether it can play a certain role in curbing the real earnings management of the company.
The research contributions of this paper: firstly, while most of the existing literature studies the integration mechanism between blockchain technology and various industries from a theoretical perspective, this paper investigates the impact of blockchain on real earnings management from an empirical perspective, enriching the research on the implementation effect of blockchain technology. Secondly, this paper explores the impact of the proportion of independent directors and the proportion of institutional investors’ shareholding on the relationship between blockchain and real earnings management from the perspective of internal and external corporate governance respectively, and the findings provide some insights into the application of blockchain technology in corporate governance. Thirdly, the conclusions of this paper are of reference value for improving the short-sighted behaviour of real earnings management of listed companies and constructing a high-level corporate governance structure.
2. Literature Review and Research Hypotheses
2.1. Literature Review
2.1.1. Studies Related to the Management of Real Earnings
The real earnings management that penetrates the earnings manipulation in the real activities is highly hidden, the regulator is not easy to detect, and even after detection, it is not easy to be investigated and punished, and it has become a earnings manipulation method adopted by more and more managers, and the specific manipulation methods at present are: sales manipulation ( Li & Zhang, 2010 ), expense manipulation ( Cheng, 2004 ), production manipulation, and asset disposal manipulation ( Roychowdhury, 2006 ). For enterprises, the implementation of real earnings management will increase the future operational risk and affect the allocation efficiency of the capital market as well as the sustainable development of the company, so how to curb the real earnings management behaviour of corporate management is of great importance. Existing empirical studies on how to curb management’s real earnings management behaviour: Cao et al. (2014) found that auditing behaviour can inhibit real earnings management. Hu et al. (2016) argued that technologically independent directors can increase management’s emphasis on R&D expenses, thus improving the quality of the company’s earnings information. Liu et al. (2013) found that institutional investors have an inhibitory effect on management’s real earnings management, and the inhibitory effect of institutional investors in non-SOEs on real earnings management is significantly stronger than that of SOEs. It remains to be further researched by academics as to what other means can effectively curb real earnings management and thus reduce its damage to the long-term interests of the company.
2.1.2. Studies Related to the Digital Economy in the Field of Corporate Governance
Currently, scholars have conducted extensive research on the relationship between the development of digital economy and corporate governance. Li (2014) pointed out that technological innovation in the mobile Internet era brings about governance changes such as the reduction of corporate governance costs, the broadening of external governance subjects, the reorganisation of governance power, the innovation of governance models, and the weakening of information asymmetry in the governance chain. Tan et al. (2016) found that Internet information communication helps to improve the level of information efficiency in the stock market. Qi et al. (2020) demonstrated that the digital economisation of enterprises improved the level of corporate governance through two paths: improving information transparency and prompting management to make more rational and scientific decisions. Liu et al. (2020) found that the popular application of digital technology in modern enterprises improves the information transparency of enterprises in processes such as financial management and internal control, which is conducive to cutting down the organisational agency costs and inducing organisational downward empowerment. Luo and Wu et al. (2021) showed that the firm-wide application of digital technology can inhibit the real surplus management activities of firms by enhancing resource operation efficiency and information transparency. Wu et al. (2021) empirically examined the positive effects of deeper digitalisation of firms in improving information asymmetry, enhancing R&D and innovation performance, stabilising finances and enhancing value, and increasing stock liquidity levels. In summary, existing research on the impact of digital economic development on corporate governance mainly focuses on the perspective that digitalisation accelerates real-time information interaction and improves business performance, and deduces that the development of digital economy is conducive to reducing information asymmetry, lowering corporate agency costs, and promoting corporate governance.
2.1.3. Research Related to Blockchain Technology in the Field of Corpo Rate Governance
Against the background of the rapid development of information technology, blockchain technology has made up for the shortcomings of traditional technology with its own advantages in meeting the needs of the information age, and has set off a new wave of technology worldwide. Blockchain technology is an important new type of infrastructure, and China has laid out a layout for its development at the national strategic level and has given strong support in terms of policy, which has made the development of blockchain technology enter a policy dividend period.
Foreign scholars have conducted in-depth discussions on the application of blockchain in corporate governance from the aspects of internal business process optimisation and external transformation of supply chain management, from establishing relevant framework models, conceptualising specific implementation plans to exploring opportunities and challenges in practice, and carrying out relevant case studies in the context of energy, construction, textile and other industries. Domestic scholars’ research in this field mainly focuses on improving supply chain management and optimising internal corporate governance. For the application of blockchain to enterprise supply chain management, Yang and Li (2021) found that blockchain technology can effectively improve the degree of supply chain data sharing. Sheng (2021) conducted an in-depth study on the application of blockchain in supply chain management based on blockchain technologies such as smart contract, distributed ledger and consensus mechanism, which provided a flexible and portable information resource sharing platform for enterprises. Yang and Tan (2018) , on the other hand, argued that the use of blockchain for supply chain management can achieve the purpose of cost reduction and quality improvement. Regarding the application of blockchain technology to internal corporate governance, Yao (2019) proposed that combining blockchain technology and cloud computing can create a new type of financial sharing system. Yang et al. (2020) concluded that listed companies applying big data and blockchain will have increased risks when facing material misstatements, at which time auditors need to increase relevant audit procedures, which will increase the company’s audit fees.
In summary, in recent years, academics have conducted extensive research on the specific application of blockchain technology in the process of corporate governance, and explored in depth the opportunities and challenges that it may face in the process of practical application. However, from the perspective of corporate governance, empirical research on blockchain technology and its application effects through regulated large samples is still lacking. Therefore, this paper investigates the impact of blockchain technology on real earnings management from the perspective of corporate governance structure.
2.2. Research Hypotheses
Blockchain technology allows for the establishment of a decentralised, open and transparent ledger system to record corporate financial transactions and information flows, achieving data traceability and non-tamperability. This technology eliminates intermediaries and redundant audits, greatly improves the efficiency of information sharing, enhances the transparency and credibility of information disclosure, and management’s opportunistic behaviour is effectively supervised and restrained, thus inhibiting management’s motivation and ability to implement real earnings management.
Firstly, blockchain technology inhibits management’s incentives to implement real earnings management by alleviating financing constraints. Myers and Majluf (1984) points out that information asymmetry makes firms face the problem of adverse selection, which leads to difficulties in corporate financing. In China’s capital market, due to the crisis of trust of external capital in the information of the company’s real situation, the cost of external financing is higher than the cost of internal financing, which is unable to meet the company’s financing needs. Blockchain technology with its characteristics of decentralisation and openness can alleviate the problem of information asymmetry to a certain extent and provide a good credit environment for financing constraints, thus alleviating the financing constraints ( Wan & Chen, 2021 ). Distributed computing unique to blockchain technology enables multi-party verification and real-time synchronisation between companies on the same node and between various departments of the company, which in turn improves the quality of information. As a result, managers are able to make timely judgements based on high-quality information, which improves the company’s decision-making ability and operational efficiency, and attracts more external financing for the company. The advantage of the whole process traceability of blockchain technology can improve the transaction problems in a weak trust environment, thus strengthening the communication and collaboration between the company and financial institutions, and broadening the financing methods and approaches for enterprises, which can effectively alleviate the financing constraints faced by the management of the company ( Wei et al., 2014 ) and inhibit the motivation of the management of the company to implement real earnings management.
Secondly, blockchain technology reduces management’s ability to implement real earnings management by improving internal controls. The use of blockchain technology can construct a distributed physical network with complete equality and decentralisation of each node, which can achieve the purpose of information sharing without the need to introduce intermediate links. The effective use of blockchain consensus mechanism can construct a true, reliable and tamper-proof multi-node distributed accounting information recording system, which can provide convenience for the company to unify the internal control track and dynamically track the internal control activities ( Huang & Liu, 2018 ). In addition, the timestamp function of blockchain technology makes it more difficult to tamper with information that has been recorded for a longer period of time, which provides a technical guarantee for the traceability of internal control responsibilities and rights. The blockchain technology smart contract enables the company to compile a list of responsibilities according to relevant regulations and construct an intelligent early warning system, which helps the company discover internal control risks in a timely manner, reduces the space for rent-seeking of power, and forces the main body exercising the power to enhance the awareness of responsibility, so that the level of the company’s control of power can be improved ( Yang et al., 2020 ). The improvement of the effectiveness of internal control can not only better alleviate the principal-agent conflict, enhance the transparency of accounting information, and timely detect the damage of management’s real earnings management behaviour to the company’s value, especially the long-term value, but also form a better regulation of management’s opportunistic behaviour, which in turn restrains the management’s ability to carry out the real earnings management behaviour. In summary, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
H1: Subject to other conditions, the application of blockchain technology can inhibit real earnings management activities of listed companies.
The agency problem arising from information asymmetry has an important impact on the firm’s earnings management decisions, and management is likely to use private information to engage in opportunistic behaviour when shareholders do not have full control over management’s actions. The lower the degree of information asymmetry, the more it can restrain the opportunistic behaviour of management and the more it can restrain the earnings management behaviour of management. In the process of applying blockchain technology to listed companies, the degree of information asymmetry is reduced due to the decentralised, tamper-proof, smart contract and other characteristics of blockchain technology, and at the same time, corporate governance mechanisms that have been proved to be effective, such as independent directors and institutional investor shareholding, also act as a disincentive to earnings management activities.
According to the principal-agent theory, independent directors, as a third party, should supervise management’s implementation of earnings management, act as guardians of the company’s contractual rules, protect shareholders’ interests and improve the quality of the company’s accounting information. As a key role in corporate governance, independent directors can play a role in monitoring and restraining management’s real earnings management activities ( Chen et al., 2019 ). The specific impacts are as follows: Firstly, independent directors can independently and prudently assess the company’s financial statements, and can actively expose and criticise the real earnings management activities to ensure the transparency and authenticity of the company’s financial statements. Secondly, as a member of the company’s board of directors, independent directors can, through participation in the board of directors and the relevant audit and finance committees and other organisations, carry out comprehensive supervision and gate-keeping of the company’s internal control and business operations, so as to reduce the occurrence of real earnings management. Thirdly, independent directors are mostly industry leaders who are familiar with professional knowledge, and can provide independent advice and recommendations based on their professional knowledge and experience in performing their duties to review and supervise management’s earnings management decisions, so as to make management’s decisions more pragmatic and robust. In general, independent directors play an important role in restraining and supervising the management’s real earnings management activities, which helps to ensure the transparency and authenticity of the company’s financial statements, and enhances investors’ confidence and motivation to participate. Based on the above theories, this paper gives the following assumptions:
H2: The higher the proportion of independent directors, the stronger the inhibitory effect of listed companies’ application of blockchain technology on real earnings management.
Institutional investors, whose financial strength and ability to collect and analyse information are much stronger than that of ordinary investors, can better identify and interpret the company’s financial information, and through in-depth analysis of the company’s financial situation, they can discover the management’s real earnings management and financial falsification phenomenon in a timely manner, so as to carry out control and inhibit the management’s motivation to implement the real earnings management behaviour more effectively ( Feng & Wei, 2022 ). Moreover, institutional investors can transmit various information about the company’s operating conditions through the media of newspapers, the Internet and television, making it easier for external investors to receive the relevant information disclosed by the company, thus playing a supervisory role over the financial information of listed companies to a certain extent. This study argues that blockchain technology can effectively restrain management from manipulating its own interests due to its own decentralisation, high security and traceability. Companies with a higher shareholding ratio of institutional investors tend to satisfy the needs of institutional investors by disclosing more comprehensive information, which weakens the management’s freedom to make decisions on daily operating activities, and thus reduces the space for management to manipulate the company’s profits, and this positive effect will be more effective in the companies applying blockchain technology, which will play a stronger role in the management’s real earnings management behaviour. Based on the above analysis, this paper gives the following assumptions:
H3: The higher the shareholding ratio of institutional investors, the stronger the inhibitory effect of listed companies’ application of blockchain technology on real earnings management.
3. Research Design
3.1. Sample Selection and Data Sources
In this paper, the listed A-share companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2012 to 2022 are selected as samples, considering that China’s blockchain industry has stepped into the stage of rapid development since 2016, so it is reasonable to choose the samples between 2012 and 2022 as the research object. The missing data, ST and financial companies are excluded, and all continuous variables are subjected to before and after 1% shrinking tail treatment, and 25,960 observations are obtained. The data are mainly from CSMAR database and annual reports of listed companies.
3.2. Variable Design and Measurement
3.2.1. Explanatory Variable: Blockchain Technology
Referring to the measurement method of Xu et al. (2022) , the application of blockchain by listed companies in China is portrayed through text analysis and word frequency statistics. The annual reports of listed companies are collected, and then Python language is used to analyse the text of the annual reports, and the word frequency of keywords such as “blockchain, decentralisation, distributed computing, smart contracts” is used as a proxy indicator to measure the application of blockchain by enterprises. Drawing on the methodology of Pan et al. (2020) , as well as the white papers of the sample companies and other relevant public information, this paper assigns a value of 1 to the samples that have applied blockchain technology, and 0 otherwise; for the time segmentation problem, the first year of the implementation and each subsequent year are assigned as 1.
3.2.2. Explained Variable: Real Earnings Management
Referring to Roychowdhury’s (2006) methodology, the level of real earnings management of the company is measured from three perspectives: abnormal production costs, abnormal cash flows and abnormal manipulative expenses. The measurement model is as follows:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
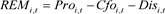 (4)
(4)
where i denotes the company, t denotes the year, Cfo is the net cash flow from operating activities; Pro is the production cost; Dis is the abnormal discretionary expense; REM is the real earnings management level; TA is the total assets at the end of the period; Sales is the operating income; ΔSales is the amount of change in the operating income; α0, β0 and γ0 are the intercept terms; α1 and α2, β1 to β4, γ1 and γ2 are the coefficient; ε, σ and ω are the residual terms. The regression of Equations (1) to (3) by industry and year, the obtained ε is Cfo, σ is Pro, and ω is Dis. Eventually, this paper obtains the explanatory variable real earnings management through the calculation of Equation (4), and the larger the absolute value of REM is, the larger the degree of real earnings management is.
3.2.3. Adjusting Variable: Corporate Governance Structure
In this paper, the proportion of sole directors and the proportion of institutional investors’ shareholding are selected as moderating variables to represent the internal and external corporate governance structure, respectively. 1) Proportion of sole directors: the proportion of the number of independent directors to the number of all directors in the enterprise. 2) Institutional investor shareholding ratio: the ratio of the number of shares held by institutional investors to the number of shares outstanding at the end of the year. The reason for choosing these two indicators is mainly based on the degree of influence of corporate governance structure on real surplus management. On the one hand, enterprises with a larger proportion of sole directors have their corporate management power concentrated in the hands of directors who are independent and objective in their judgemental relationships, and the objectivity will be conducive to the introduction of corporate blockchain technology; on the other hand, companies with a higher proportion of institutional investor shareholdings tend to satisfy the needs of institutional investors through disclosure of more comprehensive information, which weakens the management’s discretionary power of decision-making on daily operational activities, and thus reduces the management’s ability to manipulate the space for the company’s profits.
3.2.4. Control Variable
See Table 1 for specific variable definitions.
3.3. Regression Equation
To test H1 and H2, the following regression model was set up in this study:
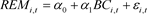 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
 (7)
(7)
 (8)
(8)
In the above model, Controli,t denotes all control variables.
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
The results are shown in Table 2, the mean (0.115) and median (0.087) of the
real earnings management of the sample implementing blockchain technology are smaller than the mean (0.132) and median (0.093) of the sample not implementing blockchain technology, which to a certain extent reflects the fact that the company’s application of blockchain technology can inhibit its real earnings management.
4.2. Regression Analysis
4.2.1. Baseline Regression
The results are shown in Table 3. Model 1 is the regression model of blockchain technology on real earnings management, and model 2 is the regression model with control variables added on the basis of model 1. As can be seen from Table 3, the regression coefficients of blockchain technology are all significantly negative, indicating that the company’s implementation of blockchain technology can inhibit its real earnings management, and H1 is verified.
4.2.2. Adjusting Effect
The results are shown in Table 3. The regression coefficients of the interaction term BC × INST in Model 3 are significantly negative at the 1% level, and the regression coefficients of the interaction term BC × Indep in Model 4 are significantly negative at the 5% level, which implies that the higher the proportion of institutional investor’s shareholding and the proportion of independent director, the better the blockchain technology suppresses the real earnings management, which is in line with the hypotheses H2 and H3.
4.2.3. Robustness Testing
1) Robustness test for one period lagging
As blockchain technology may have a lagged effect, this paper regresses the core explanatory variables one period lagged, and the regression results are similar to the original regression, and the results are shown in Table 4.
![]()
Table 3. OLS multiple regression and regulating effect regression results.
![]()
Table 4. Robustness test for one period lagging.
2) The placebo test.
In order to test whether the regression results are caused by hard-to-observe omitted factors, a placebo test is conducted by drawing on the method of Yang and Yang (2023), where the sample is reallocated randomly and 1000 regression tests are conducted, and from this, a kernel density plot of t-statistics of the coefficients of the blockchain technology indicators is constructed (Figure 1). The empirical results found that most of the t-statistics of the blockchain technology indicators are concentrated around the value of 0 and no regression coefficients with t-values (in absolute value) greater than the t-statistic in the baseline regression (−5.54) were observed. This suggests that the dampening effect of blockchain technology on real earnings management is not shaped by random chance events and that there is no statistically significant causal association between this relationship and other unknown random disturbances. Thus, the core findings of this paper are once again validated.
3) Propensity score matching (PSM)
To avoid sample selection bias, the samples after matching using PSM were regressed again. In this paper, three methods of radius matching, kernel matching, and intra-caliper 1:4 nearest-neighbour matching are used for matching, and the regression results of the matched samples are shown in Table 5. The regression results are highly consistent with Table 3 and Table 4.
a) Co-support domain and PSM matching results. As can be seen from Figure 2, the overlap range of the density function after PSM matching is obviously
![]()
Figure 1. Placebo test (1000 simulations).
![]()
Table 5. Robustness test for propensity score matching.
![]()
Figure 2. Kernel density function plot before and after matching.
increased compared with that before matching, which indicates that the quality of matching is better. The sample loss results are examined in Table 6, there is no loss of samples in the treatment group under the three matching methods, and the control group samples lose up to 2084 samples, the final matching
![]()
Table 8. PSM mean treatment effects.
results are good.
b) Balance test. The results, as shown in Table 7, show that PSM matching effectively reduces the difference in the distribution of explanatory variables in the experimental and control groups and eliminates sample self-selection bias.
c) Average treatment effects of PSM multiple matching methods. As shown in Table 8, the results of the three methods are similar, indicating good robustness of propensity score matching.
5. Further Analysis
5.1. Heterogeneity Test
5.1.1. Impact of the Nature of Property Rights
China’s unique economic system determines that state-owned enterprises (SOEs) have special resource endowments and governance structures, thus forming a unique management model. Therefore, this paper argues that SOEs and non-SOEs will have different strategic plans when facing the new innovative technological means of blockchain. Based on this, this paper conducts group regressions for SOEs and non-SOEs, and Table 9 shows the regression results. Models 17 to 19 show the regression results for the non-SOE samples, with blockchain technology being significantly negative at the 1% level, the interaction term BC × INST being significantly negative at the 1% level, and the interaction term BC × Indep being significantly negative at the 5% level. Models 20 to 22 are regressed on the sample of SOEs, and the results show that blockchain technology is negative or insignificant at the 10% significance level, and the coefficients of the interaction term BC × INST and the interaction term BC × Indep are also insignificant, which suggests that the extent of inhibition of real earnings management by blockchain technology is weakened in SOEs.
5.1.2. Impact of the Level of Urban Internet Development
The higher the internet development level of the city where the company is located, the higher the possibility of applying blockchain technology. Referring to the study of Yang et al. (2020) , the variable of internet development level CITY is used for grouping study, when the company is located in 10 cities such as Hangzhou, Guangzhou and Zhuhai CITY = 1, otherwise CITY = 0. The results of Table 9 show that when CITY = 1, listed companies’ implementation of blockchain technology significantly inhibits their real earnings management at 1% level of significance; whereas, when CITY = 0, it only inhibits its real
![]()
Table 9. Regression results for subgroups on the nature of property rights and subgroups on the level of urban Internet development.
earnings management at 10% level of significance. This implies that the increase in the level of urban Internet development can enhance the inhibiting effect of blockchain technology on real earnings management.
5.2. Adjusting Effects of the Degree of Digital Transformation
Referring to the study of Zhang et al. (2021) , the ratio of digitisation-related intangible assets to total intangible assets in the year-end financial reports of listed companies was selected to measure the degree of digital transformation (intangible). In the process of implementing blockchain technology, the degree of digital transformation of listed companies plays a decisive role, which has a direct impact on the implementation effect of blockchain technology and determines the upper limit of the constraints imposed by the application of blockchain technology on the management’s real earnings management behaviour. Digital transformation provides the basic software and hardware foundation for the application of new information technologies, including blockchain, thus accelerating the application process of blockchain technology and enabling it to exert more significant effects. The empirical results are shown in Table 10, the coefficient of real earnings management and blockchain technology is −0.019 and significantly correlated at 1% level and the cross-multiplier term of blockchain technology and the degree of digital transformation is −0.038 and highly
![]()
Table 10. Regression results for the regulating effect of the degree of digital transformation.
significant. From the above results, it can be seen that the digital transformation of listed companies strengthens the binding effect of blockchain on real earnings management.
6. Conclusions and Implications
Since 2016, China’s blockchain technology has begun to develop rapidly and has been gradually applied in the fields of e-government, finance and depository, etc., and the effect of its implementation and the factors affecting it have also received extensive attention from the academic community. Against this background, this paper selects a sample of China’s A-share listed companies in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2012 to 2022 for empirical research, defines dummy variables by whether blockchain technology is applied in that year, and econometrically analyses the impact of the implementation of blockchain technology by listed companies on the management of the real earnings, as well as the adjusting effect of the proportion of institutional investor shareholding and the proportion of independent director. The empirical results show that blockchain technology is negatively correlated with the real earnings management of listed companies. In this negative correlation, the proportion of institutional investors’ shareholding and the proportion of independent director both play a positive adjusting role. Further research finds that the implementation of blockchain technology by non-state-owned enterprises and enterprises with a higher level of urban Internet development has a better inhibiting effect on real earnings management, and digital transformation strengthens the inhibiting effect of blockchain on real earnings management. The conclusions of this paper remain stable after robustness tests using lagged one-period regression, placebo test and propensity score matching method. The findings of this paper have implications for listed companies, investors and regulators.
First of all, listed companies should follow the pace of China’s digital development and new infrastructure construction, pay active attention to the technology of blockchain, take blockchain technology as an important breakthrough in innovation to accelerate their own transformation, and promote the coordination of macro policies with their own micro-economic effects, so as to bring economic benefits to enterprises; the implementation of blockchain technology by listed companies is also conducive to the improvement of the quality of information disclosure and information transparency, thus inhibit management from implementing real earnings management behaviour and attract more investors.
Secondly, for investors, on the one hand, it increases the ways for investors to pay attention to enterprises, and they can judge the investment value of the company from different perspectives, so as to reduce the investment risk and achieve highly efficient investment; on the other hand, investors should, on the basis of supervising listed companies through traditional channels in the past, make use of digital platforms to achieve information communication with other investors, strengthen supervision of management’s short-sighted behaviour, and promote the corporate governance system to a higher level.
Finally, regulators should improve the legal system, increase the punishment for false accounting information disclosure, and establish and implement the “blacklist” system to strengthen the governance of accounting information, so as to ensure the quality of earnings; for the highly hidden short-sighted behaviour of the management, it is difficult to detect and stop it in time with the traditional supervision methods, and the combination of digital technology should be used. For highly hidden management short-sightedness, it is difficult to detect and stop it in a timely manner with the traditional regulatory methods, while the use of regulatory means combined with digital technology can detect the hidden information of the management in a more timely and effective manner.