The aim of this research is a better understanding of the quantization in physics. The true origin of the quantization is the existence of the quantized kinetic momentum of electrons, neutrinos, protons and neutrons with the
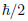
value. It is a consequence of the extended relativistic invariance of the wave of fundamental particles with spin 1/2. This logical link is due to properties of the quantum waves of fermions, which are functions of space-time with value into the

and End(
Cl3) Lie groups. Space-time is a manifold forming the auto-adjoint part of
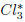
. The Lagrangian densities are the real parts of the waves. The equivalence between the invariant form and the Dirac form of the wave equation takes the form of Lagrange's equations. The momentum-energy tensor linked by Noether's theorem to the invariance under space-time translations has components which are directly linked to the electromagnetic tensor. The invariance under
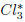
of the kinetic momentum tensor gives eight vectors. One of these vectors has a time component with value
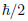
. Resulting aspects of the standard model of quantum physics and of the relativistic theory of gravitation are discussed.