This study is performed to know the contamination level of heavy metals
on the surrounding agricultural soils at the site of Barapukuria Coal Mine
Company Limited (BCMCL). Total concentrations of eight heavy metals (Cu, As,
Cd, Zn, Pb, Cr, Ni and Mn) were measured in that soil. To calculate the
contamination level, the enrichment factor (
EF),
geoaccumulation index (
Igeo)
and Hakanson potential ecological risk index were done.
Igeo values indicated that the study areas at all
stations were suffering from moderate contamination with As. The results of
enrichment factor revealed that soils in all stations were in extremely high
enrichment condition by As metal. Under
Hakanson potential ecological risk index, the contamination coefficient (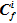 ) and potential
ecological risk index (
) and potential
ecological risk index (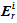 ) were calculated.
The degree of contamination at BCMCL area reflects moderate contamination. By considering the ecological risk index of a
particular heavy metal, the order is as follows: Cd > As > Cu > Pb >
Ni > Cr > Zn and Cd has the highest risk index and poses the greatest
damage to the BCMCL area’s soil. EF, Igeo values and potential
ecological risk index indicate that there is considerable As and Cd pollution,
mainly caused by coal mine drainage water.
) were calculated.
The degree of contamination at BCMCL area reflects moderate contamination. By considering the ecological risk index of a
particular heavy metal, the order is as follows: Cd > As > Cu > Pb >
Ni > Cr > Zn and Cd has the highest risk index and poses the greatest
damage to the BCMCL area’s soil. EF, Igeo values and potential
ecological risk index indicate that there is considerable As and Cd pollution,
mainly caused by coal mine drainage water.