High Rate Algal Pond (HRAP) was constructed and operated using a mixer device to investigate its capability in treating greywater for reuse in gardening. Physico-chemical and microbiological parameters were monitored. With a hydraulic retention time of 7.5 days and a solid retention time of 20 days, the average removal efficiencies (ARE) were 69% and 62% for BOD5 and COD respectively. The ARE for
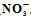
,
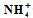
and

were 23%, 52% and 43% respectively. The removal of suspended solids (SS) was unsatisfactory, which could be attributed to the low average algal settling efficiencies of 9.3% and 16.0% achieved after 30 and 60 minutes respectively. The ARE of fecal coliforms, Escherichia coli and enterococci were 2.65, 3.14 and 3.17 log units respectively. In view of the results, the HRAP technology could be adapted for greywater treatment in sahelian regions. However, further studies on the diversity of the algal species growing in the HRAP unit are necessary in order to increase the removal of SS. Hazards of a reuse of the effluents are discussed on the basis of the various qualitative parameters. The residual content of E. coli was varying from <1 to 1.77 × 10
4 CFU per 100 mL. Based on WHO guidelines for greywater reuse in irrigation, the effluents could be used for restricted irrigation (E. coli < 105 CFU per 100 mL). Furthermore, the reuse potential is discussed on the basis of FAO guidelines using SAR (3.03 to 4.11), electrical conductivity (482 to 4500 μS/cm) and pH values (6.45 to 8.6).