The chemical and physical characteristics of PM2.5, especially their temporal and geographical variations, have been explored in metropolitan Hangzhou area (China) by a field campaign from September 2010 to July 2011. Annual average concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 during non-raining days were 106 - 131 μg.m-3 and 127 - 158 μg.m-3, respectively, at three stations in urban breathing zones, while corresponding concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 at an urban background station (16 mabove ground level in a park) were 78 and 104 μg.m-3, respectively. For comparison, the annual average PM10 concentration at a suburban station (5 mAGL) was 93 μg.m-3. Detailed chemical analyses were also conducted for all samples collected during the campaign. We found that toxic metals (Cd, As, Pb, Zn, Mo, Cu, Hg) were highly enriched in the breathing zones due to anthropogenic activities, while soluble ions (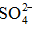 ,
, 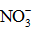 ,
,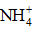 ) and total carbon accounted for majority of PM2.5 mass. Unlike most areas in China where sulfate was several times of nitrate in fine PM, nitrate was as important as sulfate and highly correlated with ammonium during the campaign. Thus, a historical shift from sulfate-dominant fine PM to nitrate-dominant fine PM was documented.
) and total carbon accounted for majority of PM2.5 mass. Unlike most areas in China where sulfate was several times of nitrate in fine PM, nitrate was as important as sulfate and highly correlated with ammonium during the campaign. Thus, a historical shift from sulfate-dominant fine PM to nitrate-dominant fine PM was documented.