Calculation of Mass Stopping Power and Range of Protons as Well as Important Radiation Quantities in Some Biological Human Bodyparts (Water, Muscle, Skeletal and Bone, Cortical) ()
ABSTRACT
In this work, the electronic
mass stopping power and the range of protons in some biological human body
parts
(Water, Muscle, Skeletal and Bone, Cortical) were calculated in the energy
range of protons 0.04 to 200 MeV using the theory of Bethe-Bloch
formula as giving in the references. All these calculations were done using Matlab program. The data
related to the densities, average atomic number to mass number 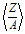 and excitation energies for the present
tissues and substances were collected from ICRU Report 44 (1989). The present results
for electronic mass stopping powers and ranges were compared with the data of
PSTAR and good agreements were found between them, especially at energies
between 1 - 200 MeV for stopping power and 4 - 200 MeV for the range. Also in this study, several
important quantities in the field of radiation, such as thickness, linear
energy transfer (LET), absorbed dose, equivalent dose, and effective dose of
the protons in the given biological human body parts were calculated at protons energy 0.04 - 200 MeV.
and excitation energies for the present
tissues and substances were collected from ICRU Report 44 (1989). The present results
for electronic mass stopping powers and ranges were compared with the data of
PSTAR and good agreements were found between them, especially at energies
between 1 - 200 MeV for stopping power and 4 - 200 MeV for the range. Also in this study, several
important quantities in the field of radiation, such as thickness, linear
energy transfer (LET), absorbed dose, equivalent dose, and effective dose of
the protons in the given biological human body parts were calculated at protons energy 0.04 - 200 MeV.
Share and Cite:
Almutairi, A. and Osman, K. (2022) Calculation of Mass Stopping Power and Range of Protons as Well as Important Radiation Quantities in Some Biological Human Bodyparts (Water, Muscle, Skeletal and Bone, Cortical).
International Journal of Medical Physics, Clinical Engineering and Radiation Oncology,
11, 99-112. doi:
10.4236/ijmpcero.2022.112009.