A multiwavelength study of a nearby dust lane early-type galaxy IC 5063 is presented. The objectives are to investigate dust extinction properties and the association of interstellar dust with other phases of ISM. The color-index maps as well as the extinction maps derived from the analysis of deep CCD observations in optical passbands revealed a prominent dust lane along its optical major axis in the inner region. In addition, two more fainter and extended dust patterns are apparent in the color index map as well as extinction maps. These features are also evident in the smooth model subtracted residual maps. The
extinction curve derived for this galaxy revealed that dust grains in it are identical to the canonical grains in the Milky Way with the dust grains little larger than the canonical grains. The total extinction measured in the V band extinction map enabled us to quantify the dust content of this galaxy to be equal to
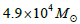
, an order of magnitude shorter than that estimated using the IRAS flux densities at 60 and 100
μm. A Multiphase ISM study revealed a surprising similarity in the morphologies of the Hα emitting ionized gas distribution and X-ray emitting gas. Systematic analysis of high resolution X-ray observations using
Chandra telescope enabled us to detect 18 discrete X-ray sources within optical D
25 region of IC 5063, out of which 17 sources were separated out as the low mass X-ray binaries and one as the high mass X-ray binary source in the X-ray color-color plot.