Oxidative DNA Damage Is Elevated in Renal Patients Undergoing Haemodialysis ()
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of mortality in patients undergoing haemodialysis (HD) [1] -[3] with an increased frequency of atherosclerosis, heart attacks and strokes, perhaps related to an increase in oxidative stress and damage [4] . Elevated markers of inflammation and disordered calcium and phosphate metabolism have also been shown to influence the incidence of atherosclerosis in this patient group [1] . Frequency of cancer is also increased in patients with end stage renal disease [5] .
Oxidative stress results when the natural balance between antioxidants (responsible for protecting cells and tissue from possible damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS)) and pro-oxidants is perturbed [6] . Moreover, the interaction between the HD patient’s blood and the semipermeable membranes contained in the haemodialysis apparatus increases levels of oxidative stress in these patients [7] . Indeed, during this interaction, circulating neutrophils are responsible for generating ROS, such as superoxide, which further enhances levels of oxidative stress [8] . In addition, HD patients have a very restricted diet and malnutrition occurs in approximately 40% - 50% of cases; this may lead to a restriction or exclusion of certain food categories which may also add to the elevated levels of oxidative stress, due to under nutrition and a lack of endogenous antioxidants to combat the elevated levels of ROS [9] .
The resulting increased levels of oxidative stress can lead to an increased incidence of DNA damage in patients receiving HD. Impairment of the DNA repair system has been observed including point mutations due to base oxidation, simple and double strand breaks, and genomic instability [10] . This would help to explain the increased incidence in mortality and cancer in HD patients compared to the healthy population [11] [12] . This view is supported by a ten-year prospective study in HD patients that suggests that both the incidence and the prevalence of renal cell carcinoma are high in this patient group [13] . Some researchers have proposed that the potential mechanisms responsible for this reported increase in cancer incidence to be due to impairment DNA repair mechanisms experienced during long-term HD [5] .
Oxidative DNA damage is a valuable tool for the measurement of oxidative stress and may represent an optimal index of measurement of the potential risk of cancer development in this cohort. Additionally, the most accurate means of measuring oxidative DNA damage has been shown to be the comet assay [14] . This assay as first described by Singh et al. [15] measures strand breaks and alkali-labile sites, which includes apurinic and apyrimidinic sites which arise from the loss of a damaged base, leaving a base-less sugar in the backbone. Therefore, in order to measure specific oxidative DNA damage an enzymatic step identifying oxidised DNA bases has been included in the modified comet assay [4] . This involves the use of the bacterial enzymes endonuclease III (Endo III) and formamidepyrimidine DNA glycosilase (FPG) first described by Collins et al. in 1993 [16] . These two enzymes are of important value in our experiment in the sense that they recognise pyrimidinepyrimidine breaks (Endo III) and 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-guanine, purine-purine breaks (FPG).
In this investigation, baseline oxidative DNA damage of 8 healthy controls and 38 patients receiving HD has been determined using the modified comet assay.
2. Participants and Methods
2.1. Recruitment and Consent
Thirty eight individuals (mean age 63.7 ± 9.7 years) undergoing HD at the Western Health and Social Care Trust (WHSCT) were recruited following informed consent. Ethical approval was obtained from the Office of Research Ethics Northern Ireland and Research Governance from WHSCT. All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000. Exclusion criteria included smokers, known alcohol abuse and malignancy. Eight healthy females (mean age 60.38 ± 4.73 years) were recruited from the University of Ulster, also subject to informed consent. Exclusion criteria in the Control group included smoking, any significant underlying health conditions and any current medication. On recruitment, each participant was issued with a unique study identifier. Identification of the study participants was limited to this unique identifier and all data were treated in a confidential manner.
2.2. Chemicals
Normal melting point agarose (NMA), low melting point agarose (LMA), Trizma® Base (Tris), calcium and magnesium free phosphate buffered saline (PBS), Triton® x-100 (Triton-X), and Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate (Na2-EDTA) were purchased from Sigma (Poole, UK). Sodium hydroxide pellets (NaOH) and sodium chloride (NaCl) were purchased from AnalaR (Normapur). Endo III, Endo III buffer and FPG were purchased from Biolabs (UK).
2.3. Routine Blood Sampling
The HD patients provided a routine monthly blood sample for biochemistry in parallel, 8 ml of blood were collected into lithium heparin coated vacutainers® (Becton-Dickinson, UK) for the analysis of DNA damage; control volunteers also provided 8 ml of Lithium Heparin blood. This blood was immediately stabilized with 8 ml of a 20:80 mixture of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and RPMI 1640 cell culture medium, according to the method of Hininger et al. [17] . Aliquots of these samples were progressively frozen to −70˚C until analysis.
2.4. Preparation of Cells
After rapid immersion of the specimen in a 37˚C water bath, cell viability was determined using the Trypan blue exclusion technique. A 4 ml blood suspension was then centrifuged at 220 × g for 3 min at 4˚C. The cell pellet was washed twice and re-suspended in calcium and magnesium free PBS to obtain approx. 100,000 cells in 20 l, and stored on ice in the dark for use the same day in the modified comet assay.
2.5. The Comet Assay
The comet assay was performed according to the method described by Singh et al. [17] with modifications described in detail by Dusïnska and Collins [18] . Briefly, approximately 100,000 cells were mixed with 75 μl of 0.5% low melting agarose at 37˚C and pipetted onto normal melting agarose pre-prepared slides. A total of five slides were prepared per volunteer. When solidified the slides were immersed in freshly prepared lysis solution (2.5M NaCl, 10 mM Na2-EDTA, 10 mM Tris and 1% Triton-X) for 1 h at 4˚C in the dark. Slides were then washed three times for 5 min each with calcium and magnesium free PBS and treated with 20 ml of: buffer; Alkaline Comet; FPG; Endo III and FPG plus Endo III together for 45 min at 4˚C. The slides were then horizontally submerged in cold alkaline electrophoresis solution (300 mM NaOH and 1mM EDTA, pH 13) in an electrophoresis tank for 20 min to allow unwinding of the DNA with exposure of alkali-labile sites. Electrophoresis was then conducted at 25 V and 300 mA for 20 min. After electrophoresis, the slides were removed from the tank and washed three times for 5 min each with neutralising solution (0.4 M Tris, pH 7.5). The slides were stained with 20 μl of ethidium bromide (20 g/ml) and coverslips placed on the slides prior to analysis.
2.6. Calculation of Net Oxidative Damage
The score from the buffer-alone slides were subtracted from the FPG and Endo III score and this figure was reported as net oxidative specific DNA damage.
2.7. Image Analysis
The slides were viewed within the 1h of ethidium bromide staining and cells were observed at 40× magnification using an Ophtiphot compound microscope (Nikon) fitted with a Nikon Fluor objective of 0.85 of numerical aperture and an epifluorescence mercury lamp (barrier filter 590 mm and 515 mm wide band excitation filter) and using the Komet 5.5 Image Analysis System (Kinetic Imaging Ltd., Liverpool, UK). Results were expressed as percentage of DNA in the tail (% tail DNA) for the quantification of DNA damage. Slides were assessed in duplicate and a total of 50 randomly chosen cells per slide analysed.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the PC version 17.0 of the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Participants characteristics are presented as mean ± standard deviation. All other data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. Student’s t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were applied as appropriate to compare means of normally distributed data and Pearson’s product-moment coefficient to assess correlation. A p-value < 0.05 was set to be statistically significant.
3. Results
Volunteer characteristics are presented in Table 1. There were no significant difference in age and BMI in the HD group compared to the control group.
DNA damage (Figure 1) assessed as alkaline (total) DNA damage (no enzymes) was significantly elevated in the HD group (19.46% ± 1.37% tail DNA) compared to (3.86% ± 1.36% tail DNA) in the control group; p < 0.001.
For oxidative specific DNA damage, FPG and Endo III were significantly higher (p < 0.001) in the HD group (23.50% ± 1.56% and 23.46% ± 1.50% tail DNA, respectively), compared to the control group (4.36% ± 1.55% and 5.11% ± 1.81% tail DNA, respectively).
Net oxidative specific DNA damage for FPG and Endo III was significantly higher in the HD group (5.81% ± 1.08% and 6.04% ± 1.00% tail DNA, respectively), Figure 2, compared to the control group (1.23% ± 0.43% and 1.98% ± 0.70% tail DNA, respectively). We observed a significant positive correlation with duration of HD and net oxidative specific Endo III DNA damage (p = 0.041).
4. Discussion
This study was designed to measure levels of oxidative leucocyte DNA damage in patients receiving HD treatment for ESRD and age and gender matched apparently healthy control volunteers using a modification of the comet assay. The comet assay is a fast, simple and sensitive technique for the analysis of DNA damage. It is able to detect a wide range of additional types of DNA, single and double strand breaks. The modified assay can measure oxidative DNA damage by including lesion specific enzymes such as End III and FPG since the DNA is readily digested. FPG recognises the common oxidised purine-7, 8-dihydro-8-oxo-guanine and ring opened purines; Endo III converts oxidised pyrimidines to strand breaks [18] .

Table 1. Volunteer characteristics.
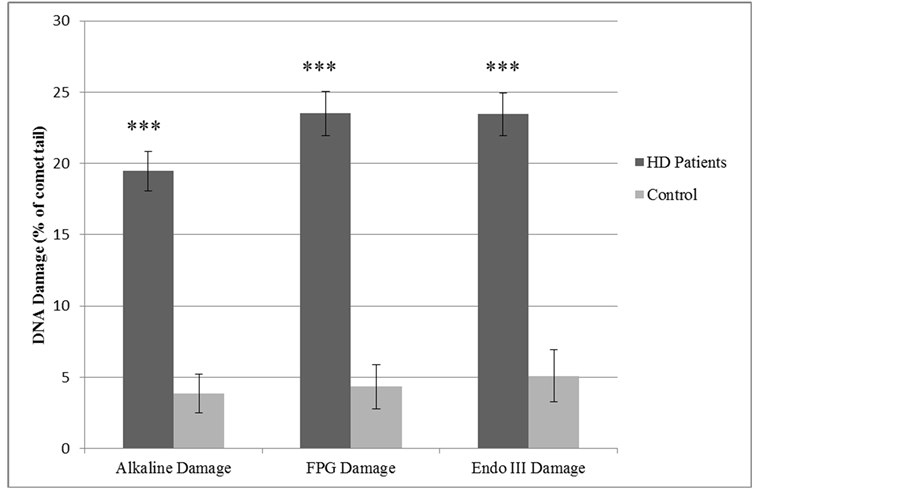
Figure 1. DNA damage in haemodialysis patients and control groups.

Figure 2. Net oxidative specific DNA damage in haemodialysis patients and control groups.
The main finding of this study was that individuals receiving HD have increased alkaline DNA damage and oxidative specific DNA damage and the duration of HD is positively correlated with Endo III specific DNA disruption. To date, only one study has used Endo III and FPG in the modified comet assay for evaluation of oxidative DNA damage in whole blood from HD patients [4] . Our study is however the first to include a healthy control in parallel with HD patients.
In our study, alkaline DNA damage was significantly higher in patients receiving HD compared to controls. Alkaline DNA damage includes all types of genomic damage therefore given the established link between oxidative stress and DNA damage [10] as well as increased incidence of cancer [5] [12] [13] , we introduced specific endonucleases to determine whether the generic (Alkaline) damage detected was oxidative in nature.
Our results show that oxidative disruption, both Endo III damage (representative of a pyrimidine-pyrimidine break) and FPG damage (representative of a purine-purine break), was significantly higher in the patient group compared to the control group. We therefore suggest that this result shows a link between HD treatment (and/or renal disease) and increased levels of oxidative damage compared to the general population.
Stoyanova et al. [4] recently assessed a population of 253 patients with chronic kidney disease, including 77 receiving HD. HD patients had higher levels of DNA damage than those not currently on HD. Quoting reference data from Müller et al. [7] the authors concluded that their findings represented a significant increase in oxidative DNA damage. The study also defined a positive correlation between DNA damage and creatinine and protein levels in plasma. Our results are in agreement with these studies and also in accordance with a study by Stopper et al. [19] who showed a significant increase of oxidative DNA damage in individuals undergoing HD treatment.
Oxidative stress is one of the most widely accepted reasons for an increase in oxidative DNA damage in ESRD individuals and the enhanced risk of cancer observed in individuals receiving dialysis treatment [11] -[14] could perhaps be attributable to this phenomenon. Moreover, genetic instability because of attenuated ability to repair DNA lesions may amplify a genetic predisposition to cancer and has been reported in various studies involving patients with chronic kidney disease [20] -[23] . HD treatment status has also been associated with greater telomere shortening, reflecting cumulative DNA exposure to oxidative stress [24] .
Although previous studies have on the one hand measured levels of genomic damage in both healthy volunteers and in HD patients [10] [21] [25] and, on the other, have determined levels of oxidative specific DNA disruption in patients with kidney disease [4] , no previous work has used oxidative specific endonucleases (Endo III and FPG) to assess oxidative DNA damage simultaneously in HD patients and healthy controls. Even though the unmodified comet assay allows for the measure of overall alkaline DNA damage, the use of these two enzymes is most valuable as they recognise oxidative damage [18] . Others have measured levels of oxidative DNA damage using 8-hydroxy-2’deoxyguanosine in chronic peritoneal dialysis patients and have shown these levels to be associated with chronic kidney disease and accentuated by HD treatment [10] .
There could be several reasons for such a significant increase in these specific oxidative DNA damage indices. In first instance, chronic kidney disease in its own right promotes oxidative stress, perhaps related to increased markers of inflammation with enhanced free radical production as well as suppressed antioxidant status. This situation is aggravated by exposure of blood to dialysis membranes, provoking metabolism of oxygen in blood by circulating neutrophils with generation of ROS such as superoxide, thus enhancing oxidative stress. The degree of biocompatibility of the dialysis membrane strongly influences the severity of this phenomenon, with modern biocompatible membranes much less likely to promote generation of ROS than older non-biocompatible materials. Hollow fibre membranes have been shown to generate relatively little ROS during HD [26] , especially if coated with the anti-oxidant vitamin E [27] [28] .
Moreover, dietary restriction in HD patients may also result in increased levels of oxidative stress due to under nutrition and reduced intake of antioxidant vitamins and/or trace elements required for antioxidant enzyme systems [9] . In addition, an impairment of the DNA repair system in HD patients [21] will further confound the elevated levels of DNA damage reported here.
Finally, we also calculated oxidative specific DNA damage by subtracting the DNA damage measured in the buffer from the Endo III and FPG DNA damage. This was also significantly higher than in the control group.
The duration of HD treatment status and its role in genomic damage is still unclear. Indeed, there have been conflicting reports: some have shown no association between time on dialysis and extent of genomic damage [22] [23] , while others have reported a significant reduction when vitamin E-modified, regenerated cellulose membranes are used [27] . In our study we report, for the first time, a positive correlation between the duration of HD treatment and Endo III specific DNA damage, which would suggest that genomic damage resulting from HD treatment, is cumulative and characterised by pyrimidine-pyrimidine DNA strands damage.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study reports a significant increase in alkaline and oxidative DNA damage in leucocytes from HD patients compared to the control group. We have in addition shown a relationship between duration of HD treatment status and an increase in oxidative Endo III specific DNA damage compared to a healthy control group. The elevated levels of DNA damage reported here together with the previous reports of ineffective repair systems in HD patients suggest that as treatment continues, DNA damage accumulates, which may in turn result in genomic instability leading to the increased rates of cancer observed in HD patients.
We would recommend that in order to ameliorate the incidence of cardiovascular disease and cancer in this vulnerable patient group, intervention studies are conducted in HD patients to determine if levels of oxidative stress and DNA damage can be minimised.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the volunteers for taking part in the study and the Irish Nephrology Society and the Western Health and Social Care Trust for financial support.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.