Numerical Simulation of Unsteady Friction in Transient Two-Phase Flow with Godunov Method ()
1. Introduction
Friction in pressurized flows can be decomposed into two components: static friction in steady flows and dynamic friction in transient flows. Transient flows present fairly important dynamic frictions that can significantly modify system behavior. Several types of model are used to calculate the dynamic friction component. One of the first types is the convolution-based model developed by Zielke [1], which uses the local acceleration and weight functions to calculate the unsteady friction component for laminar flow. The integration procedure in the Zielke model requires lots of memory and is very time-consuming. Others such as Suzuki et al. [2] and Schohl [3] suggested improvements in the determination of the unsteady friction component. Later, Vardy and Brown [4,5], Prashanth Reddy et al. [6] and Vitkovsky et al. [7] proposed an extension of the Zielke convolution model for smooth and rough pipes with turbulent flow. Another type of model called the instantaneous accelerations-based model is noted in the literature. It attributes the attenuation of flow amplitudes to local  and convective instant acceleration
and convective instant acceleration  [6,8,9]. In instantaneous accelerations-based model, the friction coefficient
[6,8,9]. In instantaneous accelerations-based model, the friction coefficient 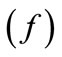 is decomposed into a static friction component
is decomposed into a static friction component  and an unsteady friction component
and an unsteady friction component  (Equation (1)).
(Equation (1)).
 (1)
(1)
with:
 (2)
(2)
where  is the Brunone coefficient,
is the Brunone coefficient,  is the pipe diameter,
is the pipe diameter,  is the water velocity,
is the water velocity,  is the pressure wave celerity,
is the pressure wave celerity,  is the time and
is the time and  is the abscissa.
is the abscissa.
Bergant et al. [10] improved this formulation by introducing  instead of
instead of , to better reproduce the attenuation of flow acceleration and deceleration. For producing good accuracy in case of an upstream valve closing, second improvement was considered by the sign of the velocity and its acceleration or deceleration
, to better reproduce the attenuation of flow acceleration and deceleration. For producing good accuracy in case of an upstream valve closing, second improvement was considered by the sign of the velocity and its acceleration or deceleration  [11-13].
[11-13].
For solving transient flows with the dynamic friction, several numerical methods are proposed in the literature and two approaches are generally used. The first approach involves calculating the local and convective acceleration in the source term  (see Equation (4)) as treated by Bergant et al. [10], Brunone et al. [14] and Bughazem and Anderson [15]. The second one transfers acceleration or one part of acceleration in the variables and the flux terms (see Equation (4)), as illustrated by Bughazem and Anderson [16], Wylie [17] and Vítkovský et al. [11]. The first approach uses finite differences, while the second employs the method of characteristics that is a graphical procedure for the integration of partial differential equations (PDEs) [18]. Prashanth Reddy et al. [6] used the second type of resolution with the characteristic equations developed by Vitkovsky et al. [11] to calculate the dynamic friction component. The formulation of the dynamic friction component in the instantaneous accelerations-based model has been tested with finite difference techniques and the method of characteristics. However, there is a lack of literature on the use of the finite volume technique in instantaneous accelerationsbased models.
(see Equation (4)) as treated by Bergant et al. [10], Brunone et al. [14] and Bughazem and Anderson [15]. The second one transfers acceleration or one part of acceleration in the variables and the flux terms (see Equation (4)), as illustrated by Bughazem and Anderson [16], Wylie [17] and Vítkovský et al. [11]. The first approach uses finite differences, while the second employs the method of characteristics that is a graphical procedure for the integration of partial differential equations (PDEs) [18]. Prashanth Reddy et al. [6] used the second type of resolution with the characteristic equations developed by Vitkovsky et al. [11] to calculate the dynamic friction component. The formulation of the dynamic friction component in the instantaneous accelerations-based model has been tested with finite difference techniques and the method of characteristics. However, there is a lack of literature on the use of the finite volume technique in instantaneous accelerationsbased models.
Finite volume techniques, particularly those using the Godunov method (as presented by Toro [19] and Guinot [20]) are now widely used for transient flow in sewers (as in León et al. [21], Vasconcelos and Wright [22] and Sanders and Bradford [23]) but without unsteady friction. This paper presents and applies the instantaneous accelerations-based model including a numerical method based on Godunov approach. Four specific objectives are targeted: i) to modify the single equivalent two-phase flow equations, ii) to consider air content, i.e. some compressibility, in the equations, iii) to propose a numerical method, and iv) to compare numerical and experimental results.
2. Methodology
The first section of the paper proposes the governing equations and the second a numerical method adapted from Guinot’s [20] traffic flow model. The third section presents two case studies in which numerical and experimental results are analyzed. The proposed model is governed by the single-equivalent two-phase flow equations. The dynamic friction component refers to the instantaneous accelerations-based model formulation and the resolution scheme uses the Godunov approach. This formulation of equations considers some compressibility of the fluid with variable density and pressure wave celerity. The model results are compared to experimental measurements from Adamkowski and Lewandowski [24] and Bergant et al. [25].
3. Governing Equations
The pressurized flow Equations (3) and (4) are those presented by Guinot [20] for the calculation of waterhammer in the presence of a two-phase fluid with an air content.
 (3)
(3)
Vectors ,
,  and
and  correspond, respectively, to the variables, flux and source term defined by Equation (4).
correspond, respectively, to the variables, flux and source term defined by Equation (4).
 (4)
(4)
where:  and
and  represent the time and the abscissa,
represent the time and the abscissa,  the flow cross-section,
the flow cross-section,  the flow discharge,
the flow discharge,  the fluid density,
the fluid density,  the mass of fluid per unit length of the pipe,
the mass of fluid per unit length of the pipe,  the mass discharge,
the mass discharge, 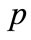 the pressure,
the pressure,  the pipe slope,
the pipe slope,  the friction slope calculated by Dary-Weisbach formula as following
the friction slope calculated by Dary-Weisbach formula as following ,
,  acceleration of gravity, and
acceleration of gravity, and  the water velocity.
the water velocity.
The friction coefficient is determined by considering local and convective instantaneous accelerations as in the model by Brunone et al. [8,9] that was modified by Bergant et al. [10] as in Equation (5).
 (5)
(5)
where the Brunone coefficient  depends on
depends on  expressed in Equation (6).
expressed in Equation (6).
 (6)
(6)
Friction  is therefore first decomposed into static
is therefore first decomposed into static  and dynamic
and dynamic  components as shown in Equation (5). The dynamic friction component is transformed according to the variables flow
components as shown in Equation (5). The dynamic friction component is transformed according to the variables flow  and
and  in Equation (7):
in Equation (7):
 (7)
(7)
In which:
 (8)
(8)
The Brunone coefficient  is determined as in Bergant et al. [10] by:
is determined as in Bergant et al. [10] by:
 (9)
(9)
where  (Equation ) depends more on the flow regime (Reynolds number
(Equation ) depends more on the flow regime (Reynolds number ).
).
 (10)
(10)
The contributions of the dynamic friction acceleration  in the vector variable
in the vector variable  and in the flux vector
and in the flux vector  (Equation (4)) allows to obtain Equation (11), in which
(Equation (4)) allows to obtain Equation (11), in which  is the friction slope due to the dynamic friction component.
is the friction slope due to the dynamic friction component.
 (11)
(11)
In vectorial form Equation (11) become Equation (12), where the sought variables are  and
and . The other variables
. The other variables  will be determined by considering the Equations (24), (25) and
will be determined by considering the Equations (24), (25) and .
.
 (12)
(12)
with:
 (13)
(13)
and
 (14)
(14)
Equations (12) and (13) are equivalent to Equations (3) and (4) if the dynamic friction component is not considered (i.e., ).
).
The next proposes a numerical method for solving these equations for each internal cell. The exterior cells will be determined by the boundary conditions formalized in each case. Since a variable is known for each pipe end, one of the Riemann invariants will be used to calculate the second variable. For example, for a known discharge or pressure to the left boundary, the second Riemann invariant is used to calculate the second variable (discharge or pressure). When it is the right boundary, the first Riemann invariant is used. Details of the calculation will be discussed in the next section.
4. Procedure for Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations (PDEs)
Equations (12) and (13) resemble the Guinot’s [20] traffic flow model, in which the acceleration/deceleration of a vehicle influences the speed of the preceding vehicle. Solving this non-conservative system of balance equations with the Godunov approach by using the solution of the Riemann problem, involves four steps:
The first step is to make the solution of the Riemann problem of Equation (15) to express the conservation component of Equation (12):
 (15)
(15)
The second is to analyze the solution of the Riemann problem of the second hyperbolic part (Equation (16)):
 (16)
(16)
The third is to obtain the solution of the Riemann problem of the source term  corresponding to Equation (17):
corresponding to Equation (17):
 (17)
(17)
The fourth step is to obtain all parameters (as velocity  and pressure
and pressure  in each cell) needed to determine the flow. The next time
in each cell) needed to determine the flow. The next time  step is calculated by taking into account the Courant condition:
step is calculated by taking into account the Courant condition: ,
,  corresponding to the spatial step.
corresponding to the spatial step.
4.1. Step 1: Solution of the Riemann Problem for the Conservation Part
The conservative part is close to the two-phase flow of the equation presented by Guinot [20] and León et al. [21]. The only difference is the factor  in the second line of the flux
in the second line of the flux 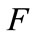 regarding Equation (13). If the dynamic friction component (i.e.,
regarding Equation (13). If the dynamic friction component (i.e., ) is not considered, the equations are those usually used when only the static friction component is considered. Considering
) is not considered, the equations are those usually used when only the static friction component is considered. Considering , the Jacobian matrix of
, the Jacobian matrix of 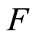 respecting the matrix
respecting the matrix ,
,  can be found in Equation (18):
can be found in Equation (18):
 (18)
(18)
After processing and arrangement, the eigenvalues of the matrix  are given by Equation (19).
are given by Equation (19).
 (19)
(19)
With:
 (20)
(20)
The eigenvalues, corresponding to the eigenvectors for the matrix , are
, are 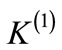 and
and  as seen in Equation (21).
as seen in Equation (21).
 (21)
(21)
4.1.1. Riemann invariants of the Conservative Solution
The Riemann invariants along each characteristic  are given by Equation (22).
are given by Equation (22).
 (22)
(22)
Equation (22) can be integrated respectively between  and
and  following approximation according to the trapezoidal rule, as with static friction.
following approximation according to the trapezoidal rule, as with static friction.  represents the variables to the left of the region of the constant state,
represents the variables to the left of the region of the constant state,  the region of the constant state and
the region of the constant state and  those to the right of the constant state region. The resulting equation (Equation (23)) is solved by the Newton Raphson method for determining
those to the right of the constant state region. The resulting equation (Equation (23)) is solved by the Newton Raphson method for determining  i.e.
i.e.  and
and .
.
 (23)
(23)
Note that the celerity , which depends on
, which depends on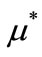 , is related to other parameters through Equation (24), as presented by Guinot [26].
, is related to other parameters through Equation (24), as presented by Guinot [26].
 (24)
(24)
With  fluid density,
fluid density,  the volume fraction of air at the reference pressure
the volume fraction of air at the reference pressure ,
,  the polytropic coefficient of air (
the polytropic coefficient of air ( for isothermal conditions and
for isothermal conditions and  for adiabatic conditions). The pressure waves celerity
for adiabatic conditions). The pressure waves celerity  in water is calculated as suggested by Wylie and Streeter [27].
in water is calculated as suggested by Wylie and Streeter [27].
The solution of Equation (23) yields:  and
and  i.e.
i.e.  and
and  used for calculating the mass discharge
used for calculating the mass discharge  and the vector variable
and the vector variable . The pressure force
. The pressure force  is obtained by solving Equation (25) [20].
is obtained by solving Equation (25) [20].
 (25)
(25)
4.1.2. Boundary Conditions Calculation of the Conservative Part
The approach assumes half-virtual cells at  and
and  as suggested by Guinot [20], using a reference pressure/velocity depending on the boundary conditions type.
as suggested by Guinot [20], using a reference pressure/velocity depending on the boundary conditions type.
Prescribed pressure at the left boundary
If the pressure is prescribed, i.e. known at the left boundary, then Equation (25) is used to determine . Therefore Equation (24) can be used to determine
. Therefore Equation (24) can be used to determine  from
from . The Riemann invariant along
. The Riemann invariant along  (Equation (23)) yields the velocity
(Equation (23)) yields the velocity (Equation (26)) with
(Equation (26)) with  corresponds to flow parameter
corresponds to flow parameter  at cell 1 at time
at cell 1 at time .
.
 (26)
(26)
Prescribed discharge at the left boundary
If the discharge is known, then the velocity Riemann invariant (Equation (27) along
Riemann invariant (Equation (27) along is combined with Equations (24) and (25) yields
is combined with Equations (24) and (25) yields  and
and .
.
 (27)
(27)
Prescribed pressure at the right boundary
If the pressure is prescribed at the right boundary, Equations (25) and (24), and Riemann invariant along  (Equation (28) or (29)) provide
(Equation (28) or (29)) provide  and
and  with
with  corresponding to flow parameter
corresponding to flow parameter  at cell
at cell  at time
at time .
.
 (28)
(28)
 (29)
(29)
Prescribed discharge at the right boundary
When discharge  is prescribed, Riemann invariant (Equation (28)) along
is prescribed, Riemann invariant (Equation (28)) along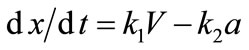 , combined with Equations (24) to (25), yields
, combined with Equations (24) to (25), yields ,
,  and
and  as shown in Equation (30):
as shown in Equation (30):
 (30)
(30)
4.1.3. Balance over the Cells
The conservative part yields the homogeneous solution (Equation (31)) at each cell without the source term as presented by Guinot [20]:
 (31)
(31)
The flux  will be calculated by Equation (32):
will be calculated by Equation (32):
 (32)
(32)
The provisional values  will be corrected in two successive stages, integrating the second hyperbolic part
will be corrected in two successive stages, integrating the second hyperbolic part  and the source term
and the source term .
.
4.2. Step 2: Solution of the Riemann Problem of the Second Hyperbolic Part
Equation (16) is solved by seeking the eigenvalues and vectors of  (Equations (33)).
(Equations (33)).
 (33)
(33)
Given that eigenvalues and vectors of  differ depending on the sign of
differ depending on the sign of , each case of Equations (33) is treated separately in sections 4.2.1 for
, each case of Equations (33) is treated separately in sections 4.2.1 for  and in section 4.2.2 for
and in section 4.2.2 for .
.
4.2.1. Resolution of Case 1
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors of  for Case 1 are depicted in Equations (34) and (35), respectively:
for Case 1 are depicted in Equations (34) and (35), respectively:
 (34)
(34)
 (35)
(35)
Considering the validity of the eigenvectors in Equation (35), along each characteristic line, solution of the Riemann problem (Equation (36)) is obtained.
 (36)
(36)
Using the trapezoidal rule, as in Equation (37), the velocity  of the constant state is calculated by Equation (38).
of the constant state is calculated by Equation (38).
 (37)
(37)
 (38)
(38)
After the determination of  and
and , the vector variable
, the vector variable  is determined for each inter face. The new variable
is determined for each inter face. The new variable  considering the second hyperbolic part is then calculated by applying the Riemann invariants principle [19,20]:
considering the second hyperbolic part is then calculated by applying the Riemann invariants principle [19,20]:
 (39)
(39)
4.2.2. Balance over the Cells
The following formulation (Equation (40)) is obtained when  is integrated over the cell for
is integrated over the cell for .
.
 (40)
(40)
4.2.3. Resolution of Case 2
In Case 2 , eigenvalues (
, eigenvalues ( and
and ) and eigenvectors (
) and eigenvectors ( and
and ) of
) of  are respectively Equations (41) and (42):
are respectively Equations (41) and (42):
 (41)
(41)
 (42)
(42)
As in Case 1, the Riemann invariant is expressed by Equation (43).
 (43)
(43)
The second part of the solution of the Riemann problem (Equation (43)) is used to calculate the velocity  of the constant state (Equation (44) or (45)).
of the constant state (Equation (44) or (45)).
 (44)
(44)
 (45)
(45)
The quantities  and
and  yield the vector variable
yield the vector variable
 .
.
The new variable  taking into account the second hyperbolic part is then calculated by applying the principle of Riemann invariants:
taking into account the second hyperbolic part is then calculated by applying the principle of Riemann invariants:
 (46)
(46)
4.2.4. Balance over the Cells
Integrating Equation (46) over the cell yields  for
for :
:
 (47)
(47)
4.2.5. Boundary Conditions
The last cell is calculated by considering either the first component of Equation (37) for  or the second component of Equation (44) for
or the second component of Equation (44) for . Each of the resulting Equations (48) or (49) is combined with the known flow condition:
. Each of the resulting Equations (48) or (49) is combined with the known flow condition:
 (48)
(48)
 (49)
(49)
with  dependant respectively on
dependant respectively on  and
and .
.
4.3. Step 3: Solution of the Riemann Problem of the Source Term
The source term is solved by Equation (50) to estimate the variable vector  of each cell depending on
of each cell depending on , as presented by Guinot [20] and Toro [19].
, as presented by Guinot [20] and Toro [19].
 (50)
(50)
where  indicates that
indicates that  is used to evaluate the source term
is used to evaluate the source term  of the Equation (13).
of the Equation (13).
4.4. Step 4: Flow Parameter Calculation
After determining the variables  and
and , velocity
, velocity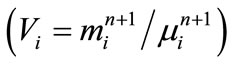 , density
, density , pressurewave celerity
, pressurewave celerity  by Equation (24), and pressure
by Equation (24), and pressure  by Equation (25) are determined for each cell.
by Equation (25) are determined for each cell.
5. Results and Discussion
Two case studies ((1) a closed downstream valve and (2) a closed upstream valve) are performed, and numerical results compared to the experimental results.
5.1. Case Study 1: Closed Downstream Valve Analysis
5.1.1. Experimental Setup of the Case Study 1
The used experimental results are from the study of Adamkowski and Lewandowski [24]. The experiments were conducted at a test rig composed of a 98.11 m long copper pipe with an internal diameter of 0.016 m and a wall thickness of  The pipe slope is
The pipe slope is  over the horizontal plan. A steel cylinder with a diameter of about 1.6 m is used as an upstream reservoir. A quick-closing ball valve is installed at the downstream end of the pipe. Four absolute pressure semiconductor transducers are mounted on the pipe at 0.25 L, 0.5 L, 0.75 L and L from the reservoir. The test procedure consists in an instant closing of the valve. During the tests, the steady head-water level in the upstream reservoir is
over the horizontal plan. A steel cylinder with a diameter of about 1.6 m is used as an upstream reservoir. A quick-closing ball valve is installed at the downstream end of the pipe. Four absolute pressure semiconductor transducers are mounted on the pipe at 0.25 L, 0.5 L, 0.75 L and L from the reservoir. The test procedure consists in an instant closing of the valve. During the tests, the steady head-water level in the upstream reservoir is . The water temperature is 22.6˚C and the kinematic viscosity coefficient is
. The water temperature is 22.6˚C and the kinematic viscosity coefficient is 
 m2/s. The pressure wave celerity calculated according to the pipe characteristics is
m2/s. The pressure wave celerity calculated according to the pipe characteristics is  m/s. The initial velocity in the pipe before closing of the valve is
m/s. The initial velocity in the pipe before closing of the valve is .
.
5.1.2. Discussion of Case Study 1 Results
Comparison of numerical results with measured results needs to consider several parameters such as the rate of air (Equation (24)) and the static friction. As shown by Wylie and Streeter [27], the rate of air reduces pressure wave celerity. This reduction is reflected in the numerical model by an increase in the pressure-oscillation period. This analysis was used to estimate the rate of air. Simulations were performed to find the value of the rate of air for better correspondence between measured and calculated oscillations. The rate of air is then considered to be 0.02%. The static friction  is selected from Axworthy et al. [28], who compared their numerical results to the experimental results of Adamkowski and Lewandowski [24]. The polytropic coefficient is considered as
is selected from Axworthy et al. [28], who compared their numerical results to the experimental results of Adamkowski and Lewandowski [24]. The polytropic coefficient is considered as . After several simulations, this value, corresponding to adiabatic conditions, seemed to yield best results.
. After several simulations, this value, corresponding to adiabatic conditions, seemed to yield best results.
Comparison between simulated and measured results (Figure 1) shows good correlation with the frequency of oscillations. The period of frequency is slightly larger in the case without taking into account the dynamical friction component. There is a slight overestimation of pressure when the dynamical friction is not taken into account, which may reach a maximum of 3 m at the downstream end of the pipe. For pressure amplitudes, the difference between measured and simulated results increases over time. This indicates that the dissipation of the numerical model is not sufficient; in other words, the friction coefficient is underestimated. This may be due either to the static friction component or the dynamic friction component. Moreover, the increased gap between numerical results and measurements may be due to the Brunone coefficient calculation by Equations (9) and (10). Indeed the difference becomes important beyond 2.5 s, i.e. when the Reynolds number in the peak pressure falls below 6000. This shows that when the flow dissipates or becomes less turbulent, the coefficient  becomes less accurate.
becomes less accurate.
5.2. Case Study 2: Closed Upstream Valve Analysis
5.2.1. Experimental Setup of the Case Study 2
The experimental tests used to examine the unsteadyflow, in case of a closed valve installed upstream just after the pump are taken from Pezzinga and Scandura [29]. These results are extracted from the paper by Prashanth Reddy et al. [6]. The tests were carried out on experimental installation composed of a zinc-plated steel pipeline (length 143.7 m, diameter 53.2 mm, thickness 3.35 mm, modulus of elasticity 2.06 × 1011 N/m2, roughness 0.1 mm) fed by a centrifugal electropump. A 1 m3 pressure tank is located at the downstream end of the pipe. Closing the upstream valve generates an interesting transient flow useful for analyzing dynamic friction.

Figure 1. Comparison between calculated and measured pressure (measures reported in Adamkowski and Lewandowski [24]): a) at pipe middle; b) at pipe end.
The pressure variation is measured by pressure transducers located at the upstream valve and at the middle of the pipe. The average temperature of the water during the tests was 15˚C; the values of the kinematic viscosity  and of the elastic modulus K were assumed to be 1.14 × 10−6 m2/s and 2.14 × 109 N/m2, respectively. The theoretical pressure wave celerity considered by the authors [29] is equal to 1360 m/s. As with the downstream valve in Case Study 1, a low rate of air into the water is assumed. Several simulations are performed with different rates of air to find out which allows for a better comparison between calculated and measured pressure oscillations. The initial velocity in the pipe, before closing of the valve, is
and of the elastic modulus K were assumed to be 1.14 × 10−6 m2/s and 2.14 × 109 N/m2, respectively. The theoretical pressure wave celerity considered by the authors [29] is equal to 1360 m/s. As with the downstream valve in Case Study 1, a low rate of air into the water is assumed. Several simulations are performed with different rates of air to find out which allows for a better comparison between calculated and measured pressure oscillations. The initial velocity in the pipe, before closing of the valve, is , and the static friction component is considered equal to
, and the static friction component is considered equal to .
.
5.2.2. Discussion of Case Study 2 Results
Figure 2 shows the comparison between calculated and measured pressure values. The best superposition of oscillations is obtained with a rate of air of 0.01% and a polytropic coefficient considered equal to . The calculated frequencies of oscillations coincide perfectly with those measured at the valve and at the middle of the pipe. Consideration of the static friction component or dynamic friction component shows that they tend to dissipate energy. The inclusion of the dynamic friction
. The calculated frequencies of oscillations coincide perfectly with those measured at the valve and at the middle of the pipe. Consideration of the static friction component or dynamic friction component shows that they tend to dissipate energy. The inclusion of the dynamic friction

Figure 2. Comparison between calculated and measured pressure by Pezzinga and Scandura [29]: a) at the valve location; b) at the middle of the pipe.
component enables a better agreement between calculated and measured pressure values. The maximum difference obtained is 6%, and is greatest at the valve position. This difference may be due to the boundary condition calculation. The difference between measured and calculated pressure values is very low in the first pressure peaks, i.e., just after the valve closure. These pressure peaks are the most damaging to water plants. Overall, the numerical results tend to overestimate pressure values, especially at the valve position, which may be due to the choice of static friction, the initial flow condition before the valve closure, the boundary condition calculation, or the early stage of computing. Another factor that might affect the quality of results is the choice of the rate of air. The choice of the polytropic coefficient may also influence the quality of results. Experiments are rarely realized under ideal adiabatic  or isothermal
or isothermal  conditions. Thus, tests with a uniform measure of the rate of air are needed to better calibrate the model.
conditions. Thus, tests with a uniform measure of the rate of air are needed to better calibrate the model.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
This paper focuses on the resolution of unsteady friction using the Godunov approach in a finite volume method with single-equivalent two-phase flow equations. The calculated results show good agreement with experimental measurements, especially for the first pressure peaks, which are the most dangerous for pipe safety. However, dissipation is found to be lower in the calculated than in the measured results. The differences between simulated results with a dynamic friction component and those with a static friction component are more important in the case of a closed upstream valve than a closed downstream valve. It would appear that taking the dynamic friction component into account is more relevant in the case of upstream valve closure. This could be due partly to the formalization of the dynamic friction component, and in particular, the inclusion of acceleration and deceleration, as well as direction of flow. The difference could also be due to the calculation of boundary conditions, which are different in the two case studies. These results demonstrate that the proposed approach allows dynamic friction to be taken into account in finite-volume models, using the increasingly popular Godunov approach. The results also point to the possibility of considering the effect of air in order to improve the quality of simulation models. The model requires further improvements to more accurately reproduce the pressure values in cases of upstream valve closure. Searching for an adequate solution should address the determination of boundary conditions, the formalization of the dynamic friction component and the choice of the polytropic coefficient and experiments in which all parameters are adequately defined.