Association of retinoblastoma with clinical and histopathological risk factors ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Retinoblastoma, a rapidly developing cancer and which also be inherited, arises from the immature neural retinal cells of retina. Genetic mutation involving “Retinoblastoma gene 1 (Rb1) at chromosome 13 affects has a significant role in its etiology [1]. RB inherited as autosomal dominant trait, with 40% of worldwide cases belonging to this category, needs mutation in both the alleles for the disease to occur [2]. Irrespective of the gender and race the mean age-adjusted incidence of RB in the USA is 11.8 per million children aged 0 - 4 years [3].
It is the commonest paediatric intraocular tumor in children under 5 years of age, occuring in approximately 1 in every 20,000 live birth, was first reported by Benedict [4].
A heritable form where both eye are involved (bilateral retinoblastoma) or sometimes only in one eye, and a non-heritable form where only one eye is involved (unilateral retinoblastoma) [5-7].
The clinical presentation of RB is variable and depends upon the stage at which the child is brought to the hospital. At early stage the usual presentation is with Leucocoria, however patients may present with strabismus, inflammed or painful red eye. Presentation of late cases varies from proptosis to fungating mass with secondaries. Depending on the position of the tumors, they may be visible during a simple eye exam using an ophthalmoscope. A positive diagnosis is usually made only with an examination under anesthesia and with the help of B Scan & CT Scan [8].
Retinoblastoma occuring in about 3 percent of registered cancers in children < 15-year-old, and in 1 in 18,000 live births, may assume an endophytic pattern, in which the growth is predominantly into the vitreous cavity, or an exophytic pattern, in which the tumor grows into the subretinal space, often detaching the overlying retina. The growth pattern is not prognostic for survival but can have implications for management. The important histopathogical progostic factors for RB are the optic nerve invasion, extraocular extension and choroidal invasion. Ten percent mortality has been reported with superficial invasion of the nerve head, 29 percent with involvement of the lamina, 42 percent with extension posterior to the lamina, and 78 percent with tumor cells to the surgical resection line [9,10].
2. MATERIAL AND METHODS
This was a retrospective descriptive analytical study. The records of the Institute of Ophthalmology, King Edward Medical University/Mayo hospital, Lahore, Pakistan for more than 1100 cases of orbital lesions from January 2006 to December 2011 will be analyzed. Five years’ biopsies of the retinoblastoma, from the Pathology Department, were retrieved to see optic nerve involvement in all the retrieved specimens. In addition, the evaluation of slides for invasion of the anterior chamber, iris, ciliary body, choroid, sclera and extraocular extension were done.
2.1. Study Design
Analytical Descriptive.
2.2. Study Population
Patients with retinoblastoma who visited the Institute of Ophthalmology from 2006 to 2011.
2.3. Study Settings
Patients who came to Ophthalmology Department, Mayo Hospital, King Edward Medical University, Lahore.
2.4. Approval of Ethical Committee
The study plan was approved from ethical committee of King Edward Medical University.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All collected data will be entered in SPSS version 17 and data will be analyzed by using the same software. The qualitative data will be presented in form of frequency table (%) and appropriate graphs. The quantitative data will be presented in form of mean ± S.E. We will also use Standard Deviation to see the variability of the quantitative data. The following analysis will be used to meet the objectives of the study.
We will calculate prevalence for descriptive study design and Chi-square analysis will be used to see the association between qualitative data. Fisher exact test will be used when expected count will be less than 5.
3. RESULTS
There were 52 cases, retrieved from the previous record (2007-2011), 3 cases were from children Hospital and one case was from Service Hospital Lahore while remaining all cases were from Mayo Hospital Lahore.
3.1. Age
The minimum age was 1 year while maximum age was 10 years (Age Range 1 - 10 years) while the mean age was 3.54 ± 1.686 years. The maximum numbers of cases with retinoblastoma eye were of 3 years 18/52 (34.6%) while one case was found with seven years and 10 years group (Table 1).
3.2. Laterality
There were 15 cases of bilateral retinoblastoma and 37 cases with unilateral neoplasms. The age range of bilateral tumors was 2 - 6 years while the range in unilateral tumor was 1 - 10 years (Table 2). Among 52 cases, 37 (71.2%) patients were unilateral retinoblastoma and 15 (28.28%) patients were with bilateral disease. In Unilateral cases, 20 (38.5%) patients were from right eye and 17 (32.7) cases were of left eye (Table 3).
3.3. Gender
There 32 females and 20 males suffering from Retinoblastoma and male to female ratio was 1:1.5. Male were 38% and females were 61.5% (Table 4).
3.4. Clinical Presentation
On clinical examinations, 28 patients presented with proptosis of (it was the most common presenting sign in our patients, accounting for about 53.8% of cases), 20 cases presented with leucocoria eye (leukocoria or white pupillary reflex or cat’s eye reflex, was the second most common presenting sign, accounting for about 38.5% of cases), 3 cases (5.8%) with strabismus (Strabismus,
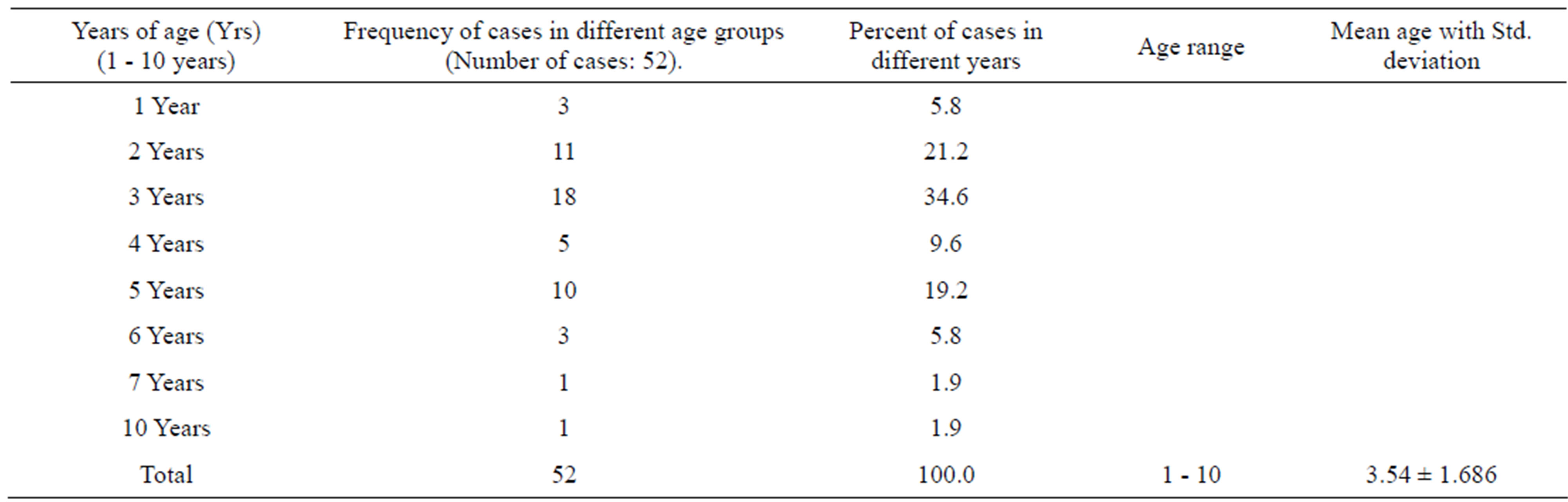
Table 1. Descriptive statistical analysis of all cases of retinoblastoma eye studied 2007-2011.

Table 2. Age distribution of unilateral and bilateral retinoblastoma.

Table 3. Distribution of retinoblastoma in both eyes (Side involvement).

Table 4. Frequency and distribution of gender with retinoblastoma of eye.
which occurred as a result of visual loss, was the third most common mode of presentation. This was performed by funduscopic examination through a well-dilated pupil in all cases of childhood strabismus). Retinoblastoma caused secondary changes in the eye, including glaucoma and 1 case (1.9%) presented with sec glaucoma. The clinical findings in all the stages of retinoblastoma were numerous and varied (Table 5).
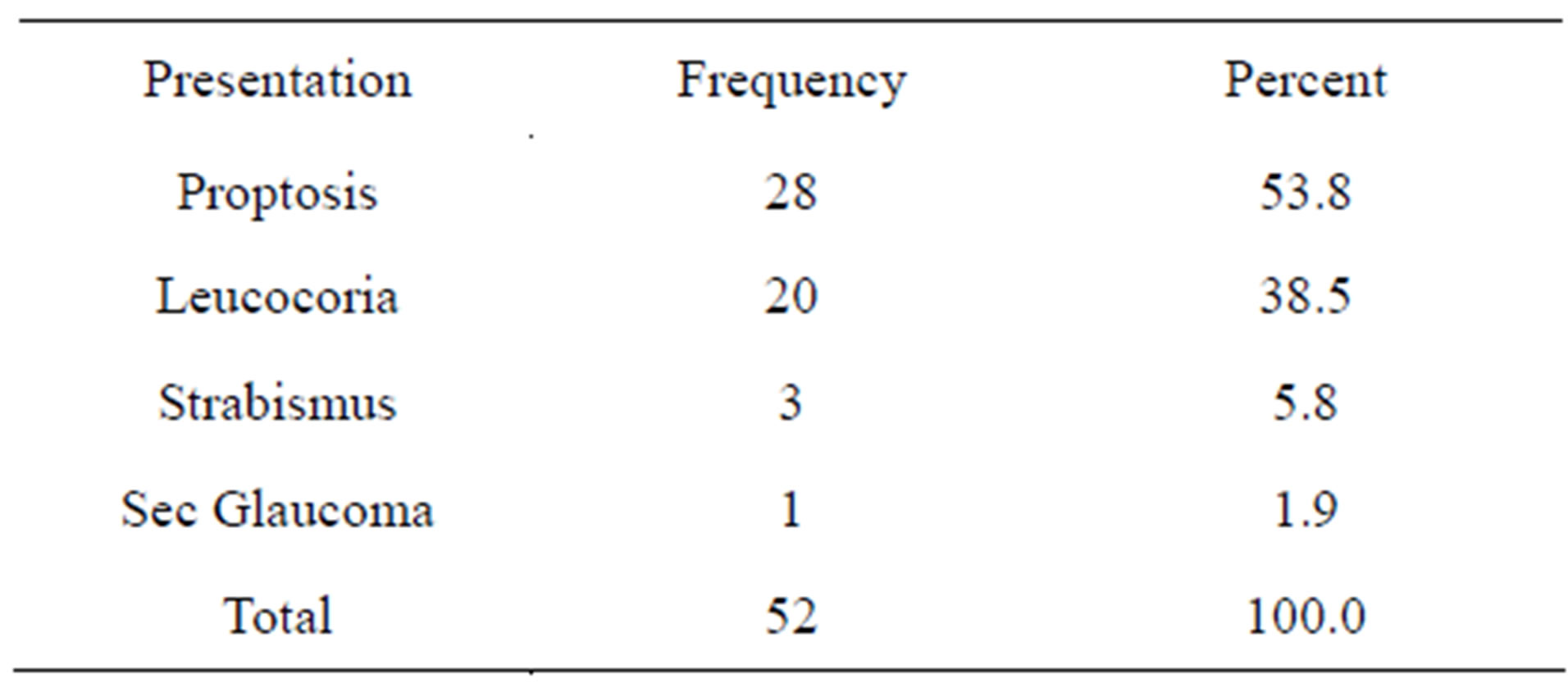

Table 5. Clinical presentation of the patients suffering from retinoblastoma eye.
3.5. Regarding Optic Nerve (ONI)
Prognostic factors of the lesion, 29/52 patients showed involvement of optic nerve (ONI), 17 were from 1 - 3 years age and 12 were from 4 - 6 years. Statistically there was no difference in the involvement of ONI with the age of patients (p = 0.217). Eleven (11) males and 18 females showed ONI. There was also no statistical difference seen in gender for ONI (p = 0.578). 11 retinoblastoma on right side, 9 on left side and 9 bilateral lesions showed optic nerve involvement, again statistically no significance was determined for ONI with respect to side of origin (Tables 6 and 7). However 9/15, bilateral lesions showed ONI as compared to 20/37 unilateral lesions showing ONI. No association (p = 0.108) was seen with unilateral or bilateral retinoblastoma and ONI (Table 7). A strong to strongest association was seen with patient’s presentation, symptoms and size of the tumors and ONI. 7/52 endophytic and 21/52 exophytic lesions showed

Table 6. Distribution of optic nerve, optic disc and extra ocular involvement in different ages, gender and side of the retinoblastoma in different patients.

Table 7. Distribution of optic nerve, optic disc and extra orbital involvement on B Scan presentation, patients symptoms and tumor size of the retinoblastoma in different patients.
association of ONI (p = 0.041), 21/52 patients with proptosis, 5/52 patients with Leucocoria, 2/52 cases with strabismus and one with secondary glaucoma, showed association of ONI (p = 0.001). Greater the size of tumor, more the ONI (p = 0.005) (Tables 6, 7 and Figure 1(B)).
3.6. Regarding Optic Disc Invasion (ODI)
With the lesion, 28/52 patients showed ODI, 19 were from 1 - 3 years age and 9 were from 4 - 6 years. Statistically there was no difference in the involvement of ODI with the age of patients *(p = 0217). 12 males and 16 females showed ODI. There was also no statistical difference seen in gender for ODI (p = 0.578). 11 retinoblastoma on right side, 7 on left side and 10 bilateral lesions showed optic disc involvement, again statistically no significance was determined for ODI with respect to side of origin (0.376) (Table 7). However 10/15, bilateral lesions showed ODI as compared to 18/37 unilateral lesions showed ODI. No association (0.192) was seen with unilateral or bilateral retinoblastoma and ODI (Table 7). A strong to strongest association was seen with patient’s presentation, symptoms and size of the tumors and ODI. 21/52 endophytic and 6/52 exophytic lesions showed association of ODI *(p = 0.043), 20/52 patients with proptosis, 5/52 patients with Leucocoria and 3/52 cases with strabismus showed association of ODI (p = 0.001). Greater the size of tumor, more the ODI (p = 0.001) (Tables 6, 7 and Figure 1(C)).
3.7. Regarding Extra-Ocular Extensions (EOE)
With the retinoblastoma lesion, 18/52 (35%) patients showed EOE, 10 were from 1 - 3 years age and 8 were from 4 - 6 years. Statistically there was no difference in the EOE with the age of patients (p = 0.437). 7 males and 11 females showed EOE. There was also no statistical difference seen in gender for optic disc involvement (p = 1.00). 7 retinoblastoma on right side, 6 on left side and 5 bilateral lesions showed EOE, again statistically no significance was determined for EOE with respect to side of origin (1.000) (Table 7). However 5/18, bilateral lesions showed EOE as compared to 13/18 unilateral lesions that showed EOE. A significant association (0.009) was seen with unilateral or bilateral retinoblastoma and EOE (Table 7). A strong to strongest association was seen with patient’s presentation, symptoms and size of the tumors and EOE. 13/52 endophytic and 4/52 exophytic lesions showed association of EOE (p = 0.016) (Table 7 and Figures 1(A), 2).
3.8. Figures
Gross, B Scan and histological photomicrographs are shown in Figures 1(A)-(D) and 3.

Figure 1. (A) Exophytic retinoblastoma with histological picture involving extra ocular extension (EOE) muscles, arrow showing tumor cells (H & E stain 10×); (B) Retinoblastoma with optic nerve involvement, Arrow showing tumor cells (H & E stain 10×); (C) Retinoblastoma with optic Disc involvement, Arrow showing tumor cells (H & E stain 10×); (D) Photomicrograph of endophytic retinoblastoma with histological picture involving anterior chamber. Vitreous and cells coming inside, arrow showing scleral of the eye (H & E stain 10×).

Figure 2. Photograph showing optic nerve, optic disc involvement with retinoblastoma and extra ocular extension of disease.
4. DISCUSSION
In United Kingdom, most children are diagnosed before the age of five years. Bilateral cases usually present within the first year with the average age at diagnosis being 9 months and age of unilateral cases peaks between 24 and 30 months [1].
In our study the minimum age was 1 year while maximum age was 10 years (age range 1 - 10 years) with mean age of 3.54 ± 1.686 years. The maximum numbers of cases with retinoblastoma eye were of 3 years 18/52 (34.6%) while one case was found with seven years and 10 years group. There were 15 (28.8%) cases of bilateral retinoblastoma and 37 (71.2%) cases with unilateral neo-
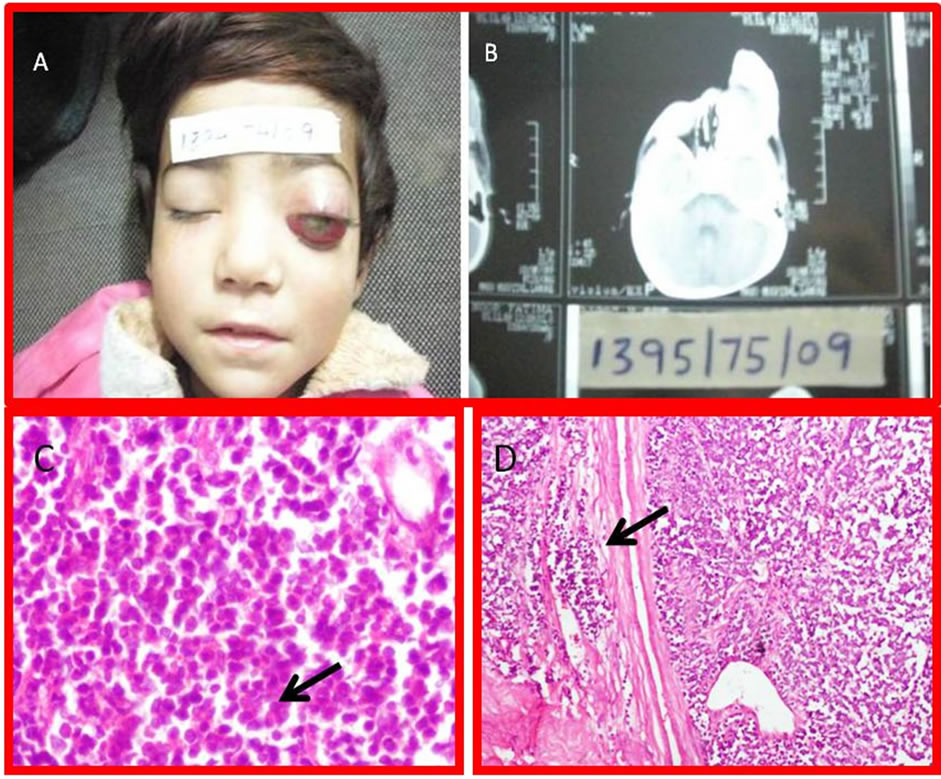
Figure 3. (A) Gross picture of retinoblastoma with proptosis of Rt eye (unilateral retinoblastoma) with (B) B Scan of the bilateral tumor; (C) Photomicrograph of classical histological picture with rosette (arrow) formation (H & E stain 40×); (D) Classical histological picture with rosette formation and vascular invasion (H & E stain 10×).
plasms. The age range of bilateral tumors was 2 - 6 years while the range in unilateral tumor was 1 - 10 years. Our findings about the ages of our patients are not consistent with data of UK presented by Yun et al. (2011) and age range of retinoblastoma in Iran presented by Nabie et al. (2012) [11].
In our study the age range is wider in unilateral cases as compared to bilateral retinoblastomas. These findings are consistent with Yun et al. and Lohmann [1,12]. Our findings are consistent with published data about Pakistan by Arif and Islam (2012) [13]. In our study there were 32 (61.5%) female and 20 (males suffering from 38%) of retinoblastoma with male to female ratio of 1:1.5. The data is not consistent with study by Arif and Islam where there were males, were 97 (55%) and females were 79 (45%) Bhurgri et al. also presented data with different frequency as compared to our findings [14].
This frequency is also different from the results of Munier et al. (1996) and Saiju et al. (2006). In both of these studies, the males showed predominance tumor burden as compared to females [15].
Our findings are consistent with Nabie et al that retinoblastoma was more common in females as compared to males and their male to female ration was 1:1.4 [11]. In our study amongst 52 cases, 37 (71.2%) had unilateral retinoblastoma and 15 (28.28%) patients were with bilateral disease.
In Unilateral cases, 20 (38.5%) patients had disease in the right eye and 17 (32.7%) cases in left eye. In one study in United State of America, the proportion of bilateral cases (26.7%) versus unilateral cases (71.9%) is stable over the 30-year period [3], which is consistent with our study. In a study in China, the frequency of bilateral retinoblastoma were greater than our study, it was found that bilateral retinoblastoma was present in 150 (32%) of the patients. Bilateral retinoblastoma as compared with unilateral retinoblastoma was diagnosed at a significantly (p < 0.001) younger mean age (1.25 years versus 2.5 years) [16]. The findings are not consistent with our results both in laterality and incidence of age. The findings are consistent with Arif and Islam (2010), who found 64.51% had unilateral tumours and 35.4% presented with bilateral disease. On clinical examinations, 28 (53.8%) patients presented with proptosis of, 20 (38.5%) cases presented with leukocoria eye (white pupillary reflex or cat’s eye reflex, 3 cases (5.8%) with strabismus and 1 (1.9%) case presented with painful red eye due to secondary glaucoma. The clinical findings in all the stages of retinoblastoma were numerous and varied. In a study by Balasubramanya et al. (2004), the clinical presentation of their patients were different from our patients, it was found that out of a total of 392 cases of retinoblastoma were reviewed; 72.2% of the patients had leukocoria, 13% had proptosis, 10% had strabismus, 1.5% were asymptomatic (detected on screening), 3.3% had atypical presentations and (0.76%), secondary glaucoma (0.76%) [17]. These clinical findings are not consistent from our data. In our patients proptosis (53.8% vs 13%) was more common presenatation as compared to leukocoria (38.5% vs 72.2%). Our findings are consistent with Arif and Islam (2010), a Pakistani study, who found that 83/176 (47.3%) presented with proptosis and fungating mass and 41 (30.14%) presented with leukocoria [13]. In another study of 360 eye RB with median age of two years, glaucoma was the most common clinical finding at presentation apart from leucocoria [18].
Our treatment options were different from Gunalp et al. (199) where enucleation was more as compared to exentration [19]. While similar procedures option was found in a study by Addu et al. (2011). They performed thirtyone patients (74%) had exenteration and enucleation was performed in 11 patients (26%) [20].
Shah has described chemoreduction followed by laser or cryotherapy is the treatment of choice. Subtenon carboplatin injection is also an accepted treatment modality for vitreous seeds, along with systemic chemotherapy. Transient periocular edema, optic neuropathy and fibrosis of orbital tissues are the known side effects of subteneon carboplatin injection [21]. In our study Cryotherapy was performen in 6/52 (11.5%) cases in that eye of a bilateral cases where a small sized tumour was located, remote from the disc and macula. Cryotherapy was also used for recurrence after radiation therapy. This treatment was in 5 (9.6%) cases on right side and one case (1.9%) on left side.
Regarding Optic Nerve Invasion (ONI) prognostic factors of the lesion, 29/52 (55.7%) patients showed involvement of ONI, 17/52 (32.7%) were from 1 - 3 years age and 12/52 (23%) were from 4 - 6 years. Therefore age is not related to ONI. Statistically there was no difference in the involvement of ONI with the age of patients (p = 0.217). In a study, Fifty-five of 297 RB (18.5%) had high-risk features with optic nerve invasion in 31 (10.4%), [22].
Our study is also consistent with Shields et al. who found no association of age with ONI [23]. Our findings are also consistent with Arif and Islam (2010), who found no correlation age and laterality as potential factors in metastasis. There was also no statistical difference seen in gender for ONI (p = 0.578). in our study, as 11 males and 18 females showed ONI. Statistically no significance was determined for ONI with respect to side of origin as 11 patients with right eye involvement 9 with involvement of the left side and 9 bilateral cases showed optic nerve involvement. However 9/15, bilateral lesions showed ONI as compared to 20/37 unilateral lesions showed ONI. Our study is consistent with Shields et al who found no association of sex with ONI and concludes that “factors not predictive for invasion included the age, race, and sex of the patient and the tumor laterality, inheritance, size, and growth pattern” which is consistent to our study [23].
In our study, proptosis and fungating mass were considered factors that can result in ONI. 21/52 patients with proptosis, 5/52 patients with Leucocoria, 2 cases with strabismus and one with secondary glaucoma, showed association of ONI (p = 0.001). Study by Essuman et al. (2010) also found positive association between ONI and presentation of the patients. Patients with proptosis showed more ONI in their patients [24]. Greater the size of tumor, more the ONI (p = 0.005). Our study is consistent with an Indian study of Chawla et al. (2012) who found tumor volume showed a significant association with optic nerve invasion (p = 0.023) [25].
Regarding Optic Disc invasion (ODI) with the lesion, 28/52 (53.8%) patients showed ODI, 19/52(36.5%) were from 1 - 3 years age and 9/52 (17.3%) were from 4 - 6 years. Statistically there was no difference in the involvement of ODI with the age of patients (p = 0217). but statistically significant inverse relationship between age and ODI was seen in this study [22]. In another study, ODI was significantly associated with time rather than age [26]. Shields et al. (1993-1994) findings are consistent with our studies who found no association of age with ODI [23,27].
Gender and laterality was not correlated with ODI as 12/52 (23%) males and 16/52 (30.7%) females showed ODI. There was also no statistical difference seen in gender for ODI (p = 0.578). 11/52 retinoblastoma on right side, 7/52 (13.5%) on left side and 10/52 (19.23%) bilateral lesions showed optic disc involvement, again statistically no significance was determined for ODI with respect to side of origin (0.376).
Our study also shows no association (0.192) with unilateral or bilateral retinoblastoma and ODI as only 10/15, bilateral lesions showed ODI as compared to 18/37 unilateral lesions showed ODI. Findings are also consistent with literature [1,16,28,29]. A strong to strongest association was seen with patient’s presentation, symptoms and size of the tumors and ODI. 21/52 endophytic and 6/52 exophytic lesions showed association of ODI (p = 0.043), 20/52 patients with proptosis, 5/52 patients with Leucocoria and 3/52 cases with strabismus showed association of ODI (p = 0.001). Greater the size of tumor, more the ODI (p = 0.001). Patients with proptosis showed more ODI [24]. Greater the size of tumor, more the ODI (p = 0.005). Our study is consistent with an Indian study of Chawla et al. (2012) who found tumor volume showing a significant association with invasion [25].
We concluded that a positive association was seen with tumor size and tumor extension (optic nerve, and extraocular extension). No Association was see age, gender and laterality of the tumors.
5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful for Dr. Samina Qamar, Dr. Shamia Zeeshan and Dr. Saqib Hussain for helping us is preparing slides, photography and H & E staining. We are also thankful for Mr. Waheed for his support in tissue processing and microtomy.
6. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Khan, A.A., conceived of the study, analyzed the data and participated in the redaction of the manuscript, conducted pathological analyses. Bukhari, M.H., Supervised the research project, read the article, gave analytical support for all the analysis and made possible language changes. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript. RM worked as co-supervisor.
NOTES