Periungual Capillaroscopy Findings in a Series of Patients with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener): An Observational Study ()
1. Introduction
Periungual capillaroscopy dates from 1911 [1], it is a simple and non-invasive technique for studying cutaneous microcirculation. It is performed on the periungual bed as this area is where the capillaries are arranged parallel to the skin surface, thus enabling the study of their entire length.
It is useful in both the diagnosis and prognosis of certain rheumatic diseases that present with microcirculation damage. Nowadays the main indication of this technique is in the differential diagnosis of Raynaud’s phenomenon [2,3] and prognosis of scleroderma.
Currently we only have one specific pattern of involvement of cutaneous microcirculation: sclerodermiform pattern, typical of scleroderma. This pattern was first defined by Maricq in 1973 [4], and then redefined in 2000 by Cutolo [5].
In other rheumatic diseases such as dermatomyositis/ polymyositis [6], mixed connective tissue disease, systemic lupus erythematosus—antiphospholipid syndrome [7,8], Sjögren’s syndrome [9], rheumatoid arthritis [7] and psoriatic arthritis [10, we find capillaroscopic alterations suggestive of each of these rheumatic diseases, but specific capillaroscopic patterns have not yet been described for each of them. Further research studies are warranted in order to define specific patterns.
Currently there are limited publications on possible capillaroscopic alterations in patients with vasculitis, and to date there is no known specific capillaroscopic pattern as is the case in other rheumatic diseases [11-13].
As with other types of vasculitis, in granulomatosis with polyangiitis in (GPA) (Wegener) there have been
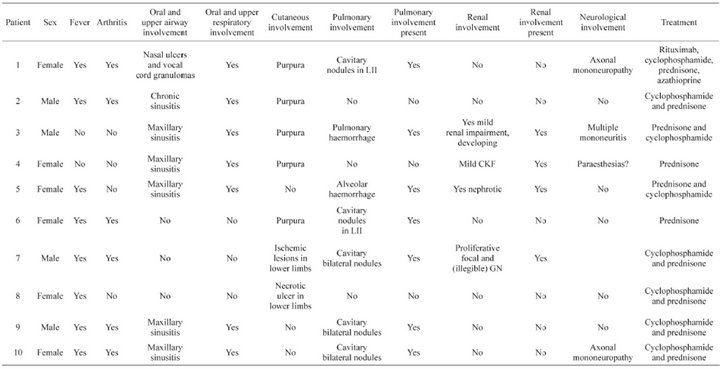
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the patient.
few studies on the possible capillaroscopic alterations that these patients may present. Anders et al., studied 12 patients with GPA and found capillaroscopic alterations in 92%, with avascular areas being the characteristic finding in these patients. Capillary dilatations were not observed [14].
With further studies on the findings of periungual capillaroscopy and comparison with what is described in the literature to date, we might obtain capillaroscopic alterations specific to this type of vasculitis as we have in other rheumatic diseases, and therefore use this technique as another tool for a given diagnosis and prognosis of this pathology.
The aim of the study is to describe the findings in periungueal capillaroscopy in our series of patients with GPA and compare them with those in the literature today.
2. Methods
A descriptive cross-sectional study on alterations detected in periungual capillaroscopy in patients with GPA was carried out.
2.1. Subjects/Patients
The study was carried out at the Rheumatology Unit of the Virgen de Valme Hospital, Seville, Spain.
We reviewed all patients diagnosed with GPA under the ACR criteria [15], which are currently seen in our unit. Demographic and clinical variables were recorded.
2.2. Measurements and Data Collection
The capillaroscope employed was a stereomicroscope (stereoscope) with trinocular head, zoom range from 1x to 4x magnification, with cold light illuminator and high resolution camcorder eyepiece.
Periungual capillaroscopy was performed on the 3rd, 4th and 5th fingers of the right and left hands in each patient and always by the same rheumatologist. In each capillaroscopy the following were assessed:
1) The morphology of the loops: predominant type and presence of neovessels;
2) Dilatation of the loops: size, frequency of dilated loops and location of the dilatation;
3) Capillary density and presence of avascular areas;
4) Haemorrhages: number and form;
5) Visibility of venular plexus;
6) General appearance.
2.3. Analysis
The sample is described in terms of the distribution of variables using central tendency measures. The capillaroscopic findings in each patient are described and correlated with the organ system involvement of the patients.
3. Results
We reviewed 10 patients with GPA. The current average age was 55.7 ± 16.5 years. They were predominantly women (60%). The average age at diagnosis was 49.4 ± 15.86 years. Seventy percent of patients presented involvement of the upper respiratory tract (sinusitis, nasal ulcers); the same percentage presented pulmonary involvement (cavitary nodules or alveolar haemorrhage); skin symptoms such as purpura or necrotic ulcers were present in 70%. Forty percent had renal involvement (kidney failure, proliferative glomerulonephritis), and 40% had peripheral neurological involvement (Table 1).
All patients were able to undergo the capillaroscopic study. Capillaroscopic alterations were found in 8 of the 10 patients. Among patients with pathological capillaroscopy 62.5% had alterations in capillary morphology (tortuous capillaries), 50% haemorrhage (single or multiple), 37.5% avascular areas and 75% lower capillary density. There was no capillary dilatation, megacapillaries, and formation of new vessels (Table 2).
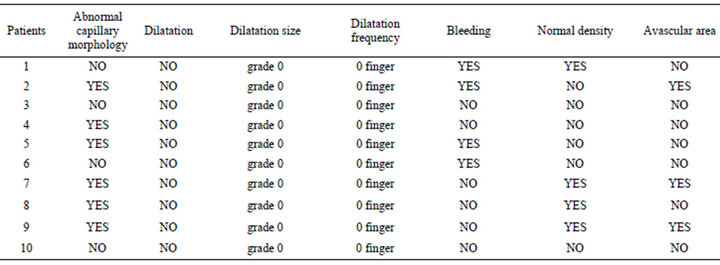
Table 2. Capillaroscopic characteristics.
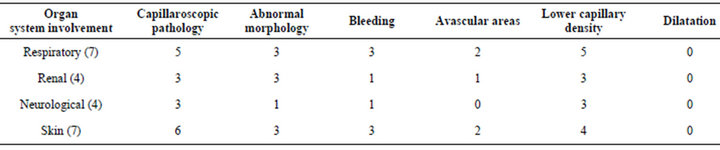
Table 3. Capillaroscopic alterations according to organ system involvement.
When the data were analysed in terms of organ system involvement, the following were found (Table 3).
4. Discussion
Periungual capillaroscopy is most useful for the study of Raynaud’s phenomenon, especially in SS, because of its prognostic value and correlation with disease severity, as there are clearly defined patterns.
In our series, we observed a higher frequency of twisting capillaries than in the healthy population, and an increase in the presence of bleeding in the periungual bed. In the patients studied, we found less capillary density and presence of avascular areas. None of these findings in periungual capillaroscopy could be related to specific organ system involvement. Our results contrast with Anders et al., published in 2000. They studied 12 patients with GPA and found capillaroscopic alterations in 92%, with avascular areas being the characteristic finding in these patients. No capillary dilatations were observed [14]. Both studies are on a small number of patients.
In summary, the data obtained in our study and in other previous series, leads us to believe that patients with GPA present alterations in skin microcirculation. These are preliminary results and could not be used to draw conclusions. Further studies are warranted with larger numbers of patients to compare the alterations detected.