Asymptotic Stability of Solutions of Lotka-Volterra Predator-Prey Model for Four Species ()
1. Introduction
The Lotka-Volterra model provides a nice mathematical device to study and understand complex systems of mutually interacting species or agent [1] . In the past decades, Lotka-Volterra type systems have been extensively investigated, especially in biology and ecology [2] -[8] . A basic issue addressed in the studies concerns stability property of the systems because of its relevance to the coexistence of different species in a community [9] . It turns out that the stability of a Lotka-Volterra system relies crucially on the interaction matrix of the system.
A Lotka-Volterra system of n-dimensions is expressed by the ordinary differential equations [4] [10] :
 (1.1)
(1.1)
where 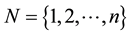 and n is the species number. In (1.1), the function
and n is the species number. In (1.1), the function 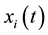 represents the density of species i at time t, the constant
represents the density of species i at time t, the constant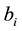 , is the carrying capacity of species i, and
, is the carrying capacity of species i, and  represents the effect of interspecific (if
represents the effect of interspecific (if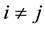 ) or intraspecific (if
) or intraspecific (if ) interaction. In vector form, System (1.1) is expressed as
) interaction. In vector form, System (1.1) is expressed as
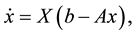
where  is an n-dimensional state vector,
is an n-dimensional state vector,  is an
is an 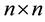 diagonal matrix,
diagonal matrix, 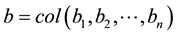 is an n-dimensional real vector, and
is an n-dimensional real vector, and 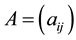 is an
is an 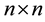 community matrix.
community matrix.
The existence and stability of a nonnegative equilibrium point of system (1.1) or subsystems of (1.1) has been investigated by many authors [9] [11] and [12] . The global stability of system (1.1) has been studied by many authors [9] [11] [13] -[16] .
In this paper, we shall concentrate on Lotka-Volterra systems of the fourth dimension. A Lotka-Volterra two preys-two predators system is studied by Takeuchi and Adachi [15] , and [16] . The first is Lotka-Volterra model of one prey-three predators and the second is Lotka-Volterra model of three prey-one predator.
This work is organized as follows: In Section 2, we describe our model. In Section 3, the existence conditions of nonnegative equilibrium points are established. The local stability analysis of the system is carried out in Section 4.
In Section 5, we present an example to clarify each case.
2. The Model
Lotka-Volterra Model
In this section we consider Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model between one and three species and assume that there is no interspicific competition between the three species x2, x3 and x4. This is represented by the following system of differential equations:
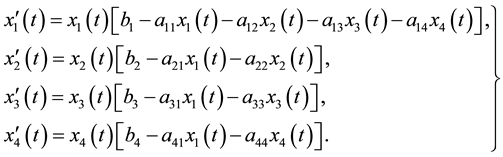 (2.1)
(2.1)
where  represents the density of species i at time t, the constant
represents the density of species i at time t, the constant ![]() is the carrying capacity of species i and
is the carrying capacity of species i and ![]() represents the effect of interspecific (if
represents the effect of interspecific (if![]() ) or intraspecific (if
) or intraspecific (if![]() ) interaction. In vector form, system (2.1) is expressed as:
) interaction. In vector form, system (2.1) is expressed as:
![]()
where ![]() is a 4-dimensional state vector,
is a 4-dimensional state vector, ![]() is a 4 × 4 diagonal matrix,
is a 4 × 4 diagonal matrix, ![]() is a 4-dimnsional real vector, and
is a 4-dimnsional real vector, and
![]() (2.2)
(2.2)
is a 4 × 4 community matrix.
The system (2.1) is a prey-predator system if the following assumption is satisfied.
(H1) ![]()
Two cases of system (2.1) can be distinguished:
The first case describes a one prey-three predators system where x1 represents the prey and x2, x3, x4 represent the predators. In this case we assume that the following conditions are satisfied in addition to (H1):
(H2) ![]()
(H3) ![]()
The second case describes a one predator-three preys system where x1 represents the predator and x2, x3, x4 represent the preys. In this case we assume that the following conditions are satisfied in addition to (H1).
(H2)' ![]()
(H3)' ![]()
3. Equilibrium Analysis
3.1. Existence of the Quilibrium Points
In this section, the existence of the equilibrium points of system (2.1) in each case is investigated. At most there are nine possible non-negative equilibrium points for system (2.1) in the first case, the existence conditions of them are given as the following:
1) The equilibrium points ![]() and
and ![]() are always exist where E1 is the equilibrium point in the absence of predation and
are always exist where E1 is the equilibrium point in the absence of predation and ![]() according to conditions (H1) and (H3).
according to conditions (H1) and (H3).
2) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in the first quadrant of the
exists in the first quadrant of the ![]() plane if and only if the following condition is satisfied
plane if and only if the following condition is satisfied
(H4): ![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are given by
are given by
![]() (3.1)
(3.1)
3) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in the first octant of
exists in the first octant of ![]() space if and only if the following conditions are satisfied:
space if and only if the following conditions are satisfied:
(H5): ![]()
![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are given by
are given by
![]() (3.2)
(3.2)
4) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in the positive cone (nonnegative octant)
exists in the positive cone (nonnegative octant)
![]() if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
(H6) ![]()
![]()
where ![]() are given by
are given by
![]() (3.3)
(3.3)
where
![]()
A is the interaction matrix defined in (2.2).
For the second case of system (2.1), at most there are fifteen possible nonnegative equilibrium points. The existence conditions of them are given as the following:
1) The equilibrium points
![]() , , and
, , and
are always exist where E2, E3, E4 are the equilibrium points in the absence of predation and ![]() according to conditions (H1) and (H3)'.
according to conditions (H1) and (H3)'.
2) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in the first quadrant of
exists in the first quadrant of ![]() plane if and only if the following condition is satisfied
plane if and only if the following condition is satisfied
(H4)': ![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are given by (3.1).
are given by (3.1).
3) In the absence of predator and one prey species, both the other two prey species grow. Thus, the equilibrium point ![]() always exists in the interior of
always exists in the interior of ![]() plane where
plane where![]() ,
, ![]() according to conditions (H1) and (H3)'.
according to conditions (H1) and (H3)'.
4) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in the first octant of
exists in the first octant of ![]() space if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
space if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
(H5)' ![]()
![]()
where![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are given by (3.2).
are given by (3.2).
5) In the absence of predator, all three prey species grow. Thus, the positive equilibrium point
![]() always exists in the interior of
always exists in the interior of ![]() space.
space.
6) The positive equilibrium point ![]() exists in
exists in ![]() if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
if and only if the following conditions are satisfied
(H6)': ![]()
![]()
where ![]() are given by (3.3).
are given by (3.3).
3.2. Remark
We will use the symbols![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points
to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, where
respectively, where ![]() and
and ![]() are given by (3.1), the symbols
are given by (3.1), the symbols![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points
to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, where
respectively, where ![]() are given by (3.2) and use the symbols
are given by (3.2) and use the symbols
![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points
to denote the nonnegative equilibrium points![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() respectively.
respectively.
4. Stability Analysis
4.1. Stability of Equilibrium Points
In this section, the local stability analysis of equilibrium points is investigated. Assuming that all previous equilibrium points existing.
The Jacobian matrix J of system (2.1) is given by:
![]() (4.1)
(4.1)
Computing the variation matrixes corresponding to each equilibrium point and then using Routh-Hurwitz criteria [17] , the following results can be observed:
1) Substituting by E0 in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the eigenvalues ![]()
So for the first case, E0 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2x3x4 space and with unstable manifold in the x1 direction. Near E0 the prey’s population x1 grows while the predators’ populations x2, x3 and x4 decline.
For the second case, E0 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1 direction and with unstable manifold in the x2x3x4 space. Near E0 the predator population x1 decline while the preys’ populations x2, x3 and x4 grow.
2) Substituting by E1 in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the eigenvalues![]() ,
, ![]() ,
,
![]() .
.
(By using (H3) and (H4)).
So E1 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1 direction and with unstable manifold in the x2x3x4 space. Near E1 the prey species x1 remains close to![]() .
.
Similarly, E2 has three positive eigenvalues
![]()
(By using (H3)' and (H4)')
So E2 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2 direction and with unstable manifold in the x1x3x4 space. Near E2 the prey species x2 remains close to![]() .
.
E3 and E4 have the same stability behavior of E2.
We now state the local stability behavior of other equilibrium points in the form of Theorems. The proofs of these theorems follow directly from the Routh-Hurwitz criteria [12] .
Theorem 4.1
1) E12 is locally asymptotically stable in the x1x2 plane.
2) If E1230 and E1204 exist, then E1200 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1x2 plane and with unstable manifold in the x3x4 plane.
Proof
Consider the following subsystem from (2.1)
![]() (4.2)
(4.2)
Evaluating the variation matrix of system (4.2) at E12, we have
![]()
The characteristic polynomial is
![]() (4.3)
(4.3)
Since
![]()
Then, ![]() and
and ![]() have negative real parts. Thus, E12 is locally asymptotically stable in the x1x2 plane.
have negative real parts. Thus, E12 is locally asymptotically stable in the x1x2 plane.
Computing the variation matrix (4.1) at E1200, we have
![]()
The characteristic equation of matrix V12 is
![]()
Comparing with (4.3) we get that ![]() and
and ![]() have negative real parts and
have negative real parts and
![]()
If E1230 and E1204 exist, then ![]() and
and ![]() (by using (H5) and (H5)').
(by using (H5) and (H5)').
Therefore, E1200 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1x2 plane and with unstable manifold in the x3x4 plane.
4.2. Remark
1) Behavior of solutions near the equilibrium points E13 and E14 are the same behavior of solutions near the equilibrium point E12.
2) Behavior of solutions near E1030 and E1004 are the same behavior of solutions near E1200.
Theorem 4.1
a) E23 is locally asymptotically stable in the x2x3 plane.
b) If E1230 exists, then E0230 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2x3 plane and with unstable manifold in the x1x4 plane.
Proof
Consider the following subsystem from (2.1)
![]() (4.4)
(4.4)
Evaluating the variation matrix of system (4.4) at E23, we have
![]()
which have the eigenvalues ![]() and
and ![]() (by using (H3)').
(by using (H3)').
Therefore, E23 is locally asymptotically stable in the x2x3 plane.
Substituting by E0230 in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the eigenvalues
![]()
If E1230 exists, then
![]()
(By using (H3)' and (H5)').
Hence E0230 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2x3 plane and with unstable manifold in the x1x4 plane.
Theorem 4.2
a) E123 is locally asymptotically stable in the x1x2x3 space.
b) If ![]() exists, then E1230 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1x2x3 space and with unstable manifold in the x4 direction.
exists, then E1230 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1x2x3 space and with unstable manifold in the x4 direction.
Proof
Consider the following subsystem from (2.1)
![]() (4.5)
(4.5)
Evaluating the variation matrix of system (4.5) at E123, we have
![]()
which has the characteristic polynomial
![]() (4.6)
(4.6)
where
![]()
From Routh-Hurwitz criterion, E123 is locally asymptotically stable if and only if![]() ,
, ![]() and
and![]() .
.
It is clear that all the coefficients c1, c2 and c3 are positive and
![]()
Therefore E123 is locally asymptotically stable in the x1x2x3 space.
Substituting by E1230 in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the characteristic equation
![]()
Comparing with (4.6), we obtain that![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() have negative real parts while
have negative real parts while ![]() (by using (H6) and (H6)')
(by using (H6) and (H6)')
Therefore, E1230 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x1x2x3 space and with unstable manifold in the x4 direction.
Remark 4.1
1) Behavior of solutions near E124 and E134 are the same behavior of solutions near the equilibrium point E123.
2) Behavior of solutions near E1204 and E1034 are the same behavior of solutions near E1230.
Theorem 4.3
a) E234 is locally asymptotically stable in the x2x3x4 space.
b) If ![]() exists, then E0234 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2x3x4 space and with unstable manifold in the x4 direction.
exists, then E0234 is a saddle point with locally stable manifold in the x2x3x4 space and with unstable manifold in the x4 direction.
Proof
Proof of this theorem follows directly as proof of Theorem 4.2
Now, we study asymptotic stability of the positive equilibrium![]() .
.
Substituting by ![]() in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the characteristic equation
in the variation matrix (4.1), we get the characteristic equation
![]()
where
![]()
From Routh-Hurwitz criterion [12] , ![]() is locally asymptotically stable if and only if
is locally asymptotically stable if and only if ![]() and
and![]() .
.
It is clear that all the coefficients c1, c2, c3 and c3 are positive and if
![]()
Then ![]() is locally asymptotically stable in
is locally asymptotically stable in![]() .
.
Theorem 4.4
![]() is globally asymptotically stable in
is globally asymptotically stable in ![]() for every carrying capacity
for every carrying capacity![]() .
.
Proof.
We define the Liapunov function ![]() by
by
![]()
where![]() ,
, ![]()
In the region
![]()
It is clear that
![]()
Then calculating the time derivative of V along the positive solutions of system (2.1), we have
![]()
Then, we can choose
![]()
Hence, we obtain
![]()
Therefore, it follows from well-known Liapunov-LaSalle theorem that the positive equilibrium ![]() is globally asymptotically stable in
is globally asymptotically stable in![]() .
.
5. Numerical Simulations
The reader can be check local asymptotic stability of the system 2.1 for:
Example 5.1
![]()
Example 5.2
![]()
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all staff members who help me in this article.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.