Oxone-Mediated Oxidative Esterification of Heterocyclic Aldehydes Using Indium(III) Triflate ()
In a recent trend, the direct oxidative methyl esterification of aldehydes has received a great deal of interest in the field of organic synthesis. A couple of the esterifying transformations of aldehydes using metal-based reagents have been reported, including iridium [1-3], rhenium [4], ruthenium [5], rhodium [6], palladium [7,8], manganese [9], iron [10], copper [11], tin [12], and PDC [13,14]. However, the use of these heavy/transition metal oxidants could cause environmental concerns. As a consequence, esterification methodologies that combine catalytic amounts of fourth-row transition metal-based reagents, such as titanosilicate [15], vanadium pentoxide [16,17], iron salt, and zinc salt [18,19], have been introduced, although the oxidizing reagents are limited to the utilization of H2O2 in many cases.
Our previous report included an efficient method for high-yielding methyl esterification that is catalyzed by a trivalent indium reagent under mild reaction conditions [20]. The practical preparation of methyl esters can be carried out by treating carboxylic acids in methanol that contains a catalytic amount of trimethylsilyl chloride [21]. Our group has conducted research on trivalent indium reagents, and we have reported several methodologies for In(OTf)3 [22,23]. As part of our ongoing study, we have developed the oxone-mediated oxidative methyl esterification of benzaldehyde derivatives. The reactions were accelerated in the presence of In(OTf)3 in many cases, via the use of an effective oxidant, Oxone® monopersulfate compound (oxone), which is a triple salt of potassium composed of potassium peroxymonosulfate [24]. Based on this established methyl esterification of benzaldehyde derivatives [24,25], we further explored an application to heterocyclic aldehydes. The reactions were examined using methanol as well as other alcohols in order to elucidate a suitable range. Herein, we report the details of our study.
2. Results and Discussion
First, the three isomers of pyridinecarboxaldehydes were subjected to oxidative transformation (Table 1). The position of the aldehyde substituents was decisive for the formation of the corresponding methyl esters. Only 4- pyridinecarboxaldehyde yielded the expected ester product sufficiently (Table 1, entry 3). In contrast, 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde seemed to be decomposed just after 1.5 h (Table 1, entry 1).
Given the above results, we then focused on determining the limitations of alcohols, employing 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde as the starting material. Thus, the reactions were attempted not only in methanol but also in other alcohols with elongated carbon chains, actually extending them one by one. Table 2 shows the results of the oxidative esterification using alcohols with longer carbon chains. Under the reaction conditions, the expected ethyl ester and propyl ester were prepared in a similar manner with no experimental differences (Table 2, entries 2 and 3). Moreover, the reactions using butanol and pentanol furnished the corresponding esters in high yields, despite requiring 65 h for completion (Table 2, entries 4 and 5). The reactions using heavier alcohols such as hexanol and heptanol, which are viscous liquids with boiling points of 156 and 176˚C, respectively, required high temperatures for reflux. However, neither produced any of the expected ester products, leaving blackened reaction mixtures (Table 2, entries 6 and 7).
The study was then resumed using 5-membered heterocyclic aldehydes under the same reaction processes. In the events shown in Table 3, the oxone-mediated oxidative methyl esterification of thiophenecarbaldehydes and furaldehydes resulted in moderate yields through the appropriate reaction temperatures.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, heterocyclic aldehydes were subjected to oxone-mediated esterifying reactions. Reactions using methanol as well as other alcohols with longer carbon chains were attempted in order to elucidate a suitable range. In the case of 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, pentanol gave a good yield while hexanol and heptanol did not. Esterification was also conducted on 5-membered heterocyclic aldehydes, and methyl esters were formed in moderate yields. Further analysis of the method is now being conducted.

Table 1. Reactions of the three isomers of pyridinecarboxaldehydes.
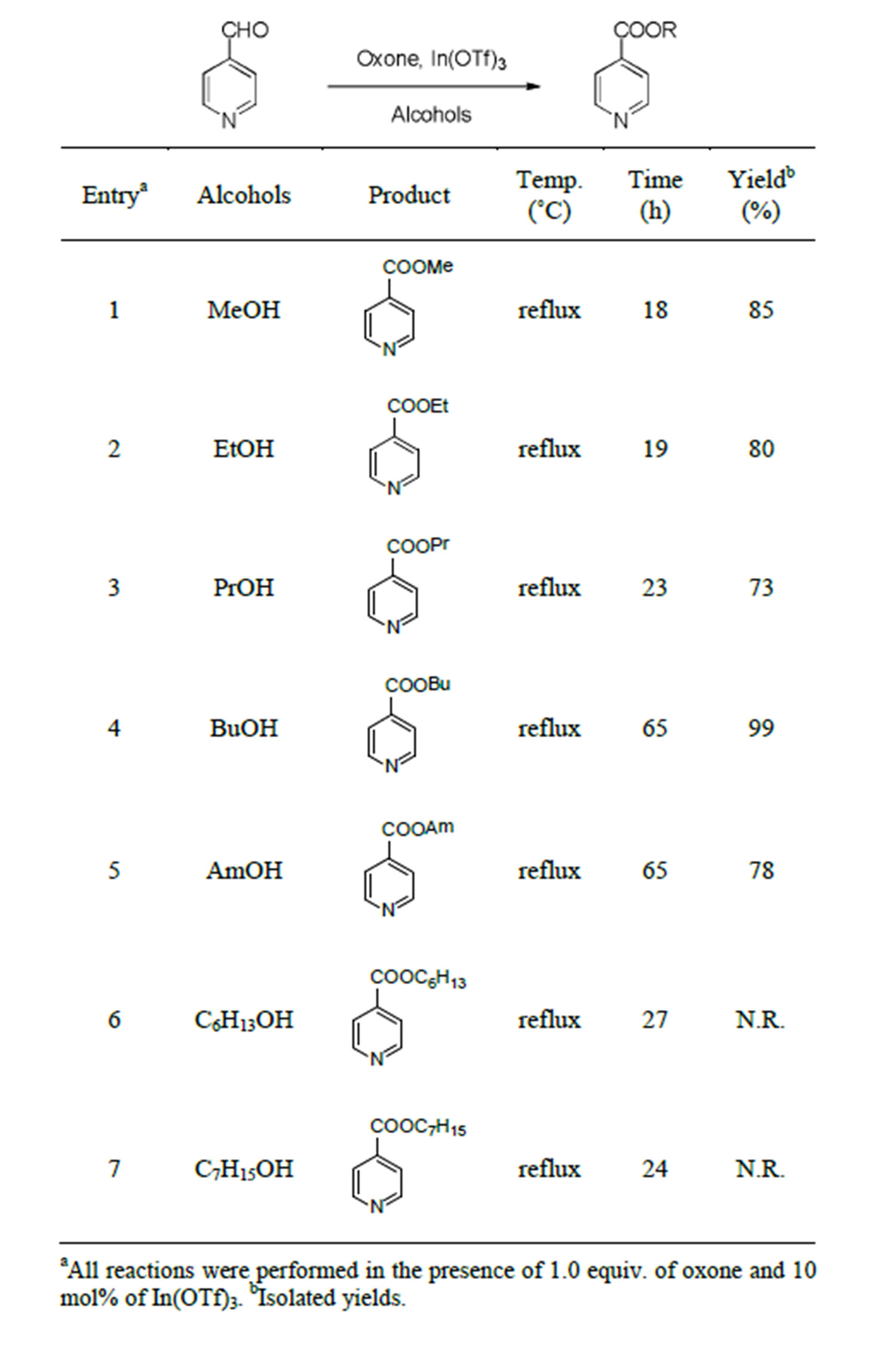
Table 2. Reactions of 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde in alcohols with elongated carbon chains.

Table 3. Reaction of the 5-membered heterocyclic aldehydes.
4. Experimental
4.1. Materials and Instruments
All reagents were of analytical grade purchased commercially and used without further purification. All reactions were carried out under argon using magnetic stirring unless otherwise noted. 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectral data were recorded on a JEOL JMTC-500 spectrometer using TMS as the internal standard.
4.2. General Experimental Procedure
4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde (1 mmol) was dissolved in methanol (5 mL), then oxone (1 mmol) and In(OTf)3 (10 mol%) were added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was heated at reflux, and was monitored for completion by TLC. Upon cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was filtered. The filtrate was condensed using a rotary evaporator. Flush column chromatography on silica gel furnished the corresponding products, which were confirmed by spectroscopy.
4-Pyridinecarboxylic acid propyl ester: 1H NMR (500 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ = 8.73 (2H, dd, J = 4.5, 1.5 Hz), 7.93 (2H, dd, J = 4.5, 1.5 Hz), 4.32 (2H, t, J = 6.5 Hz), 1.81 (2H, sextet, J = 7.5 Hz), 1.04 (3H, t, J = 7.5 Hz); 13C NMR (125 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ = 166.1, 151.3, 139.8, 124.4, 68.5, 23.0, 10.7.
4-Pyridinecarboxylic acid pentyl ester: 1H NMR (500 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ = 8.73 (2H, dd, J = 5.0 and 2.0 Hz), 7.92 (2H, dd, J = 5.0 and 2.0 Hz), 4.36 (2H, t, J = 7.0 Hz), 1.79 (2H, quintet, J = 7.0 Hz), 1.47-1.38 (4H, m), 0.94 (3H, t, J = 7.0 Hz); 13C NMR (125 MHz, MeOH-d4) δ = 166.1, 151.3, 139.8, 124.4, 67.1, 29.4, 29.3, 23.4, 14.3.
NOTES