Applied Mathematics
Vol. 4 No. 8 (2013) , Article ID: 35091 , 9 pages DOI:10.4236/am.2013.48148
Global analysis of Beddington-DeAngelis Type Chemostat Model with Nutrient Recycling and Impulsive Input
College of Mathematics and System Sciences, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, China
Email: *ahmadjanm@gmail.com
Copyright © 2013 Mehbuba Rehim et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received June 6, 2013; revised July 6, 2013; accepted July 13, 2013
Keywords: Beddington-DeAngelis Model; Chemostat Model; Nutrient Recycling; Global Attractivity
ABSTRACT
In this paper, a Beddington-DeAngelis type chemostat model with nutrient recycling and impulsive input is considered. Except using Floquet theorem, introducing a new method combining with comparison theorem of impulse differential equation and by using the Liapunov function method, the sufficient and necessary conditions on the permanence and extinction of the microorganism are obtained. Two examples are given in the last section to verify our mathematical results. The numerical analysis shows that if only the system is permanent, then it also is globally attractive.
1. Introduction
The chemostat is an important and basic laboratory apparatus for culturing microorganisms. It can be used to investigate microbial growth and has the advantage that parameters are easily measurable. The chemostat plays an important role in bioprocessing, hence the model has been studied by more and more people. Chemostats with periodic inputs were studied [1,2], those with periodic washout rate [3,4], and those with periodic input and washout [5]. In recent years, those with nutrient recycling [6-10] have been investigated and some investing results were obtained. Now many scholars pointed out that it was necessary to consider models with periodic perturbations, since those phenomena might be exposed in many real words. However, there are some other perturbations such as floods, fires and drainaye of sewage which are not suitable to be considered continually. Those perturbations bring sudden changes to the system. Systems with sudden changes are involving in impulsive differential equations which have been studied intensively and systematically [11-13]. Impulsive differential equations are found in almost every domain of applied sciences.
Recently, many papers studied chemostat model with impulsive effect the Lotka-Volterra type or Monod type functional response. But there are few papers which study a chemostat model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response, especially a Beddinton-DeAngelis type chemostat with nutrient recycling. The BeddingtonDeAngelis functional response is introduced by Beddington and DeAngelis [14,15]. It is similar to the wellknown Holling II functional response but has an extra term  in the denominator that models mutual interference in species. The model, we consider in this paper, takes the form:
in the denominator that models mutual interference in species. The model, we consider in this paper, takes the form:
 (1)
(1)
where S(t),  represent the concentration of limiting substrate and the microorganism respectively, D is the dilution rate, a is the uptake constant of the microorganism, k is the yield of the microorganism
represent the concentration of limiting substrate and the microorganism respectively, D is the dilution rate, a is the uptake constant of the microorganism, k is the yield of the microorganism  per unit mass of substrate, r is the death rate of microorganism, b is the fraction of the nutrient recycled by bacterial decomposition of the dead microorganism, p is the amount of limiting substrate pulsed each T, T is the period of pulsing. Obviously, we have
per unit mass of substrate, r is the death rate of microorganism, b is the fraction of the nutrient recycled by bacterial decomposition of the dead microorganism, p is the amount of limiting substrate pulsed each T, T is the period of pulsing. Obviously, we have  and
and . D, A, B, k, a, p are all positive constants.
. D, A, B, k, a, p are all positive constants.
The organization of this paper is as the following. In Section 2, we introduce some useful notations and lemmas. In Section 3, we will state and prove the main results on the global asymptotic stability and permanence. In Section 4, we give a brief discussion and the numerical analysis.
2. Preliminaries
In this section, we will give some notations and lemmas which will be used for our main results. Firstly, for convenience, we set 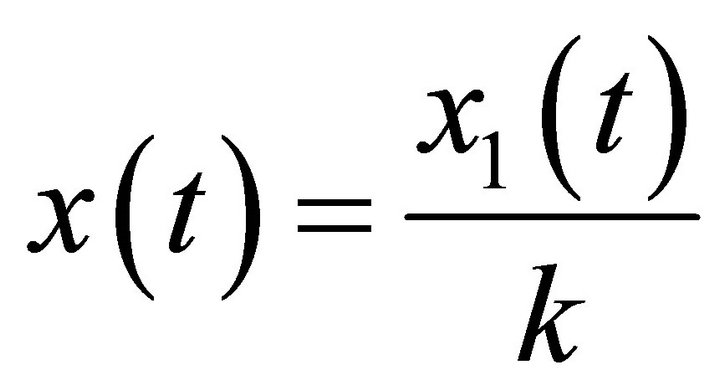 , then system (1) becomes
, then system (1) becomes
 (2)
(2)
Let .
.  ,
,  ,
, 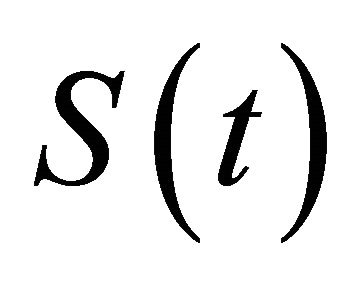 is left continuous at t = nT and x(t) is continuous at t = nT.
is left continuous at t = nT and x(t) is continuous at t = nT.
Lemma 1. Suppose 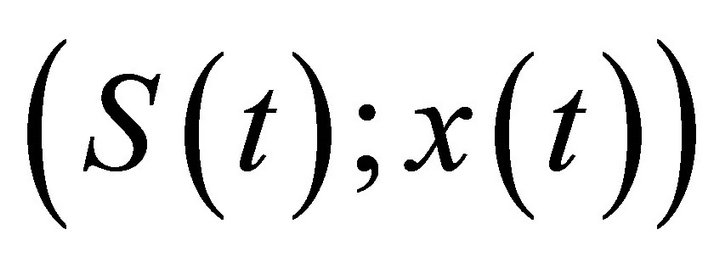 is any solution of system (2) with initial solution
is any solution of system (2) with initial solution . Then
. Then  for all
for all . Moreover, if
. Moreover, if  then
then  for all
for all .
.
The proof of Lemma 1 is simple, we omit it here.
In what follows, we give some basic properties about the following system.
 (3)
(3)
Clearly,

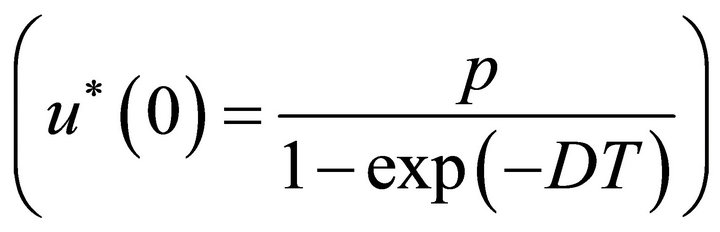
is a positive periodic solution of system (3). Any solution of system (3) is

Hence, we have the following result.
Lemma 2. System (3) has a positive periodic solution  and
and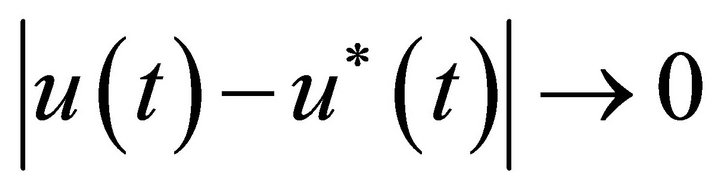 , as
, as  for any solution u(t) of system (3). Moreover,
for any solution u(t) of system (3). Moreover,  if
if  and
and  and
and  .
.
The proof of Lemma 2 can be found in [16].
Lemma 3. There exists a constant M > 0 such that S(t) < M, x(t) < M for each solution of (S(t); x(t)) system (2), for t large enough.
Proof Let (S(t); x(t)) be any solution of system (2) with initial value . Define a function
. Define a function .
.
Then

From the comparison theorem of impulsive differential equations, we have  for all t¸ 0, where u(t) is the solution of system (3). From Lemma 2, we have
for all t¸ 0, where u(t) is the solution of system (3). From Lemma 2, we have 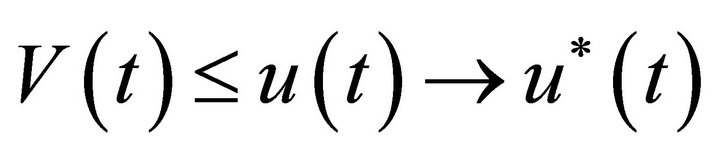 as
as , where
, where

Hence,

Thus, V(t) is ultimately bounded. From the definition of V(t), there exists a constant
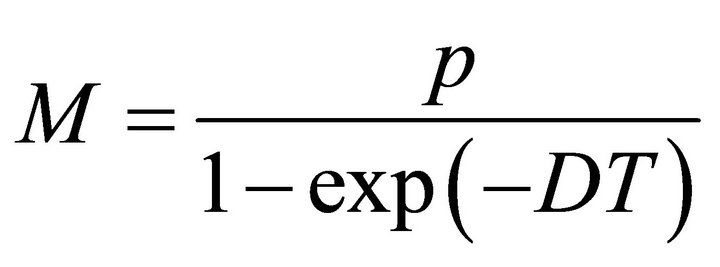
such that S(t) < M, x(t) < M for any solution (S(t), x(t)) of system (2), for t large enough. This completes the proof.
The solution of system (2) corresponding to x(t) = 0 is called microorganism-free periodic solution. For system (2), if we choose , then system (2) becomes to the following system
, then system (2) becomes to the following system
 (4)
(4)
System (4) has a unique global uniformly attractive positive solution

Hence, system (2) has a positive periodic solution  at which microorganism culture fails. In the next section, we will study the global asymptotical stability of the microorganism-free periodic solution
at which microorganism culture fails. In the next section, we will study the global asymptotical stability of the microorganism-free periodic solution  as a solution of system (2).
as a solution of system (2).
3. Main Results
Theorem 1. Suppose
 (5)
(5)
Then periodic solution  of system (2) is globally attractive.
of system (2) is globally attractive.
Proof Let ( ,
, ) be any positive solution of system (2). Define a function as follows
) be any positive solution of system (2). Define a function as follows

Then similar to the proof of Lemma 3, we obtain  for all
for all  where u(t) is the solution of system (3) and
where u(t) is the solution of system (3) and  as
as . Hence, there exists a function
. Hence, there exists a function  satisfying
satisfying 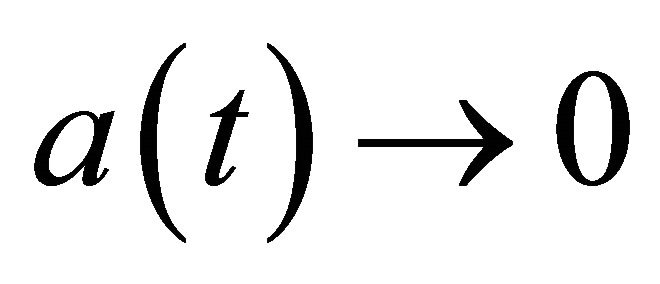 as
as  such that
such that

By the definition of , we have
, we have

It follows from the second equation of system (2) that
 (6)
(6)
From condition (5), for any enough small  we have
we have

Since ![]() which gives
which gives

Hence, there exist constants  and
and , such that
, such that
 (7)
(7)
If  for all
for all , then from (6) we have
, then from (6) we have
 (8)
(8)
For any , we choose an integer
, we choose an integer  such that
such that  then integrating (8) from
then integrating (8) from  to t, from (7) we have
to t, from (7) we have
 (9)
(9)
where 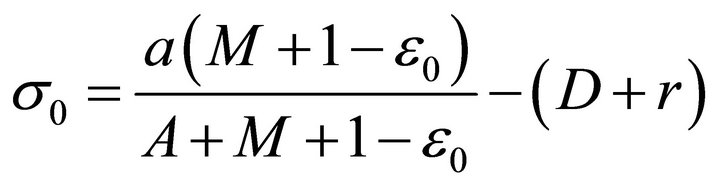 and M is given in Lemma 3. Since
and M is given in Lemma 3. Since  as
as , from (9) we have
, from (9) we have  as
as , which is a contradiction. Hencethere is a
, which is a contradiction. Hencethere is a , T0, such that
, T0, such that .
.
Now, we claim that there exists a constant  such that
such that
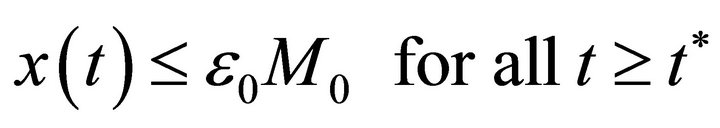
In fact, if there exists a  such that
such that , then there exists a
, then there exists a  such that
such that 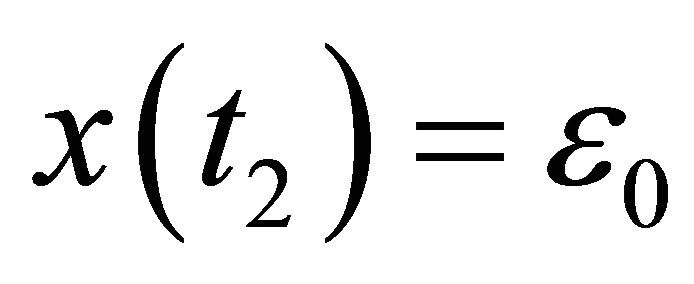 and
and  for
for . Choose an integer
. Choose an integer  such that
such that 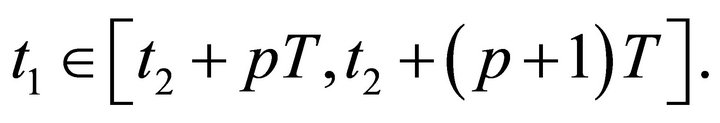 Since for any
Since for any 

 (10)
(10)
integrating the above inequality from t2 to t1, from (7) we obtain (10).
Obviously, let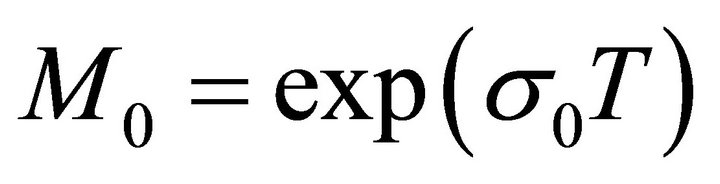 , then from (10) we obtain a contradiction. Hence,
, then from (10) we obtain a contradiction. Hence, 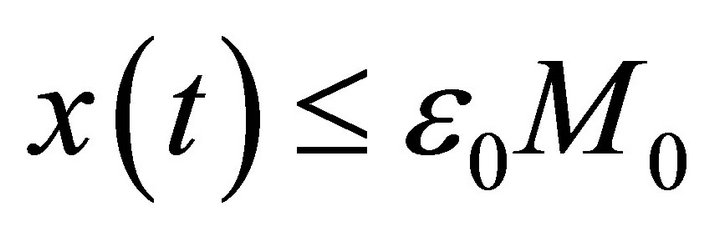 for all
for all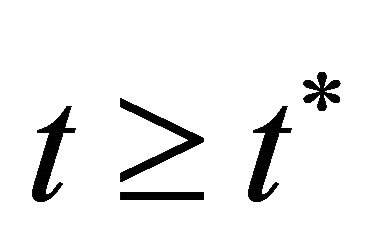 . Since
. Since  is arbitrary, we finally have
is arbitrary, we finally have
![]() .
.
This completes the proof.
Theorem 2. Suppose
 (11)
(11)
Then system (2) is permanent.
Proof Let (S(t); x(t)) be any solution of system (2) with initial value . By Lemma 3, the first equation of system (2) becomes
. By Lemma 3, the first equation of system (2) becomes

Using Lemma 2 and the comparison theorem of impulsive differential equation, we obtain 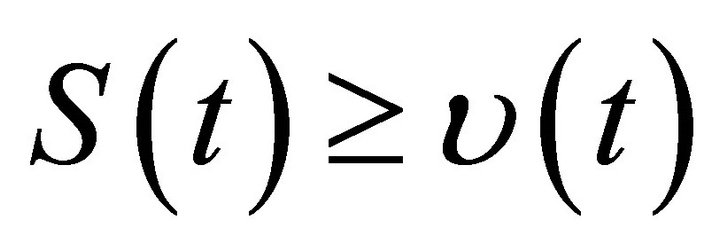 for all,
for all,  where
where 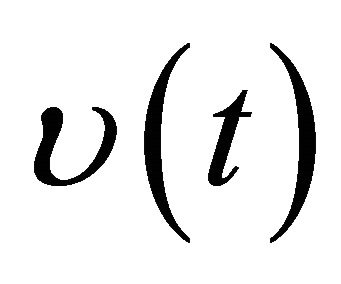 is the solution of the following impulsive system
is the solution of the following impulsive system
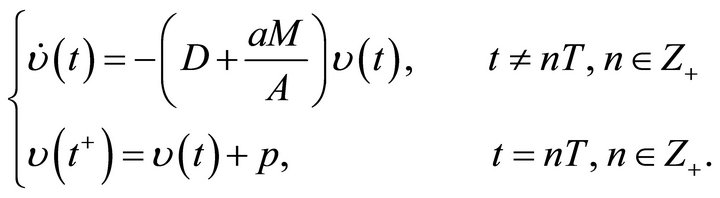
with initial condition . Further from Lemma 2, we have
. Further from Lemma 2, we have

where

Therefore, we finally obtain

This shows that S(t) in system (2) is permanent.
In the following, we want to find a constant , such that
, such that  for t large enough.
for t large enough.
Since

we can chose a constant  small enough such that
small enough such that

Consider the following auxiliary impulsive system
 (12)
(12)
from Lemma 2, system (12) has a globally uniformly attractive positive periodic solution

Since , for above
, for above , there is a
, there is a  and
and  such that
such that
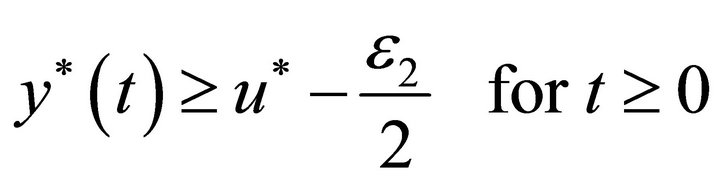 (13)
(13)
Further, for above  and M > 0, where M is given in Lemma 3, there is a
and M > 0, where M is given in Lemma 3, there is a  such that for any
such that for any  and
and  we have
we have
 (14)
(14)
where  is the solution of system (12) with initial condition
is the solution of system (12) with initial condition .
.
For any  ¸ if
¸ if  for all
for all , then from system (2) we have
, then from system (2) we have

By the comparison theorem of impulsive differential equations, we have 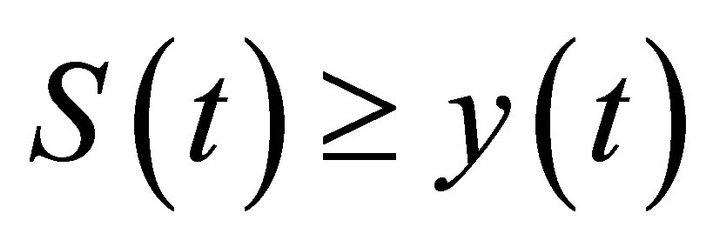 for
for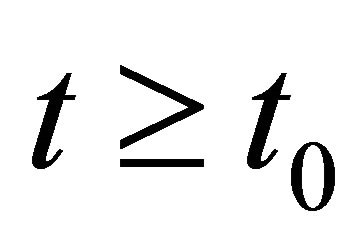 , where y(t) is the solution of system (12) with initial condition
, where y(t) is the solution of system (12) with initial condition . From (14) we have
. From (14) we have

Hence, from (13) we further have

From the second equation of system (2) we have
 (15)
(15)
Let  such that
such that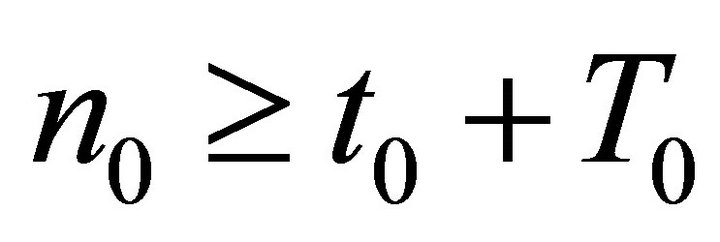 . Integrating (15) on
. Integrating (15) on  for all
for all , we have
, we have

Hence,  for all
for all . Then we have
. Then we have , which is a contradiction. Hence, there exists a
, which is a contradiction. Hence, there exists a  such that
such that .
.
If  for all
for all , then our goal is obtained. Hence, we need only to consider these solutions which are oscillatory about
, then our goal is obtained. Hence, we need only to consider these solutions which are oscillatory about . Let
. Let  and
and ![]() be two large enough times such that
be two large enough times such that  and
and  for all
for all . When
. When , since
, since

integrating this inequality for any , we have
, we have
 (16)
(16)
Let . For any
. For any , if
, if , then according to the above discussing on the case of
, then according to the above discussing on the case of , we also have inequality (16). Particularly, we obtain
, we also have inequality (16). Particularly, we obtain , since
, since  for all
for all , from system (2) we have
, from system (2) we have

Hence, from the comparison theorem of impulsive differential equations, we have  for all
for all , where y(t) is the solution of system (12) with initial condition
, where y(t) is the solution of system (12) with initial condition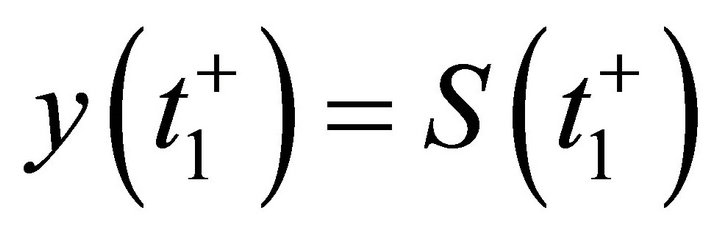 . From (14), we have
. From (14), we have

Further from (13), we also have

Thus, from system (2), we have
 (17)
(17)
For any , we choose an integer
, we choose an integer 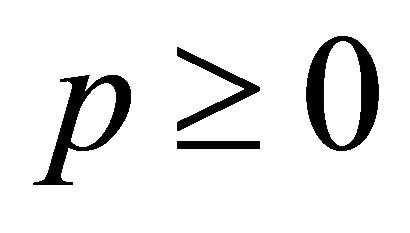 such that
such that
 .
.
Integrating (17) from  to t, we have
to t, we have

where
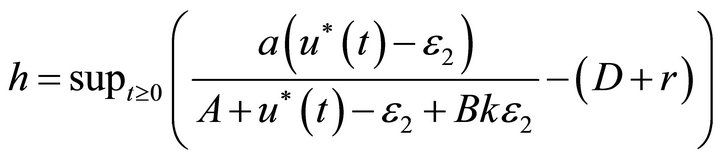
From the above discussion, we have , and
, and  is independent of any solution (S(t); x(t)) of system (2). This completes the proof.
is independent of any solution (S(t); x(t)) of system (2). This completes the proof.
As a consequence of Theorem 1 and Theorem 2, we have the following corollary.
Corollary 1 For system (2), the following conclusions hold.
a) The microorganism-extinction solution  is globally attractive if and only if
is globally attractive if and only if

b) The microorganism x(t) of System (2) is permanent if and only if

4. Discussion and Numerical Analysis
In this paper, we investigate Beddington-DeAngelis type chemostat with nutrient recycling and impulsive input. We prove that the microorganism-free periodic solution of the system (2) is globally attractive. The necessary and sufficient condition for permanence of system (2) are obtained in this paper.
According to Theorem 1, the microorganism-free periodic solution  is globally attractive if (5) hold. That is, this kind of microorganisms can not be cultivated under this condition. Suppose that
is globally attractive if (5) hold. That is, this kind of microorganisms can not be cultivated under this condition. Suppose that  and set
and set

Then Theorem 1-2 can be state as: If  and
and , then the microorganism will eventually disappear; If
, then the microorganism will eventually disappear; If  and
and , then system (2) is permanent. This implies that if we choose a smaller impulsive input of nutrient when the death rate of microorganism is larger than some certain value, then the microorganism x(t) will tend to extinct; If we choose a lager impulsive input of nutrient, then system can coexist. By the above analysis, we know that conditions for the system coexist or non-coexist are due to the influences of the impulsive perturbations.
, then system (2) is permanent. This implies that if we choose a smaller impulsive input of nutrient when the death rate of microorganism is larger than some certain value, then the microorganism x(t) will tend to extinct; If we choose a lager impulsive input of nutrient, then system can coexist. By the above analysis, we know that conditions for the system coexist or non-coexist are due to the influences of the impulsive perturbations.
In order to illustrate our mathematical results and investigate the effect of impulsive input nutrient we present the following results of a numerical simulation.
From Theorem 1, we consider dynamical behavior of the system (2) with D =2, a = 5, A = 20, B = 2, b = 1, k = 0.5, r = 0.5, p = 10, T = 2, then system (2) becomes
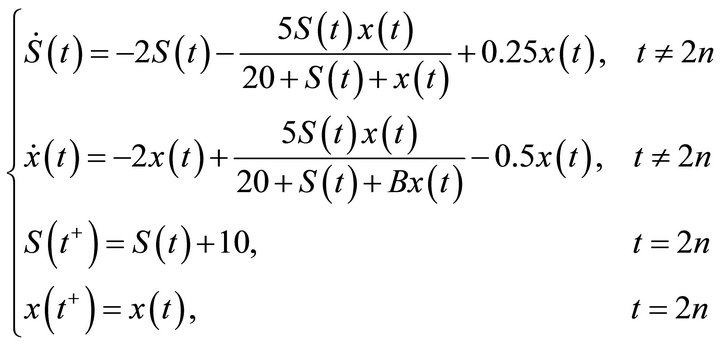 (18)
(18)
By calculating, we obtain

and
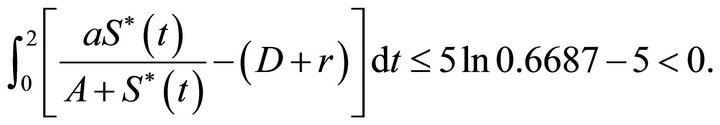
That is condition (5) holds. We choose initial value 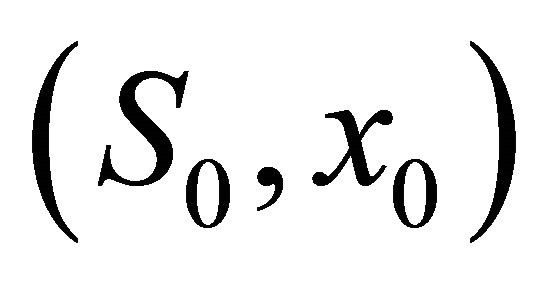 = (1,1.3), (1,2.5), (3,3.4), (4,4.7), (5,6), (6,7.3), (7,7.9), (8,9.5), (9,10.7), (10,12.5) respectively, then from the numerical simulation (Figure 1) we see that there exists a positive periodic solution
= (1,1.3), (1,2.5), (3,3.4), (4,4.7), (5,6), (6,7.3), (7,7.9), (8,9.5), (9,10.7), (10,12.5) respectively, then from the numerical simulation (Figure 1) we see that there exists a positive periodic solution  of system (18) such that any solution (S(t), x(t)) of system (20) with initial value
of system (18) such that any solution (S(t), x(t)) of system (20) with initial value 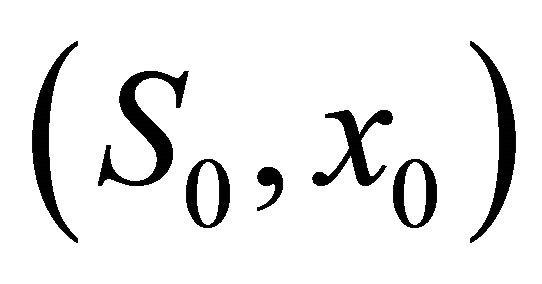 tends to
tends to  as
as . Therefore, if condition (5) holds, then system (18) has a positive periodic solution which is globally attracttive.
. Therefore, if condition (5) holds, then system (18) has a positive periodic solution which is globally attracttive.
From Theorem 1, we consider dynamical behavior of the system (2) with D =1, a = 10, A = 10, B = 2, b = 1, k = 0.5, r = 0.2, p = 12, T = 2, then system (2) becomes
 (19)
(19)
By calculating, we obtain
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 1. (a) Time-series of the nutrient S for periodic oscillation; (b) Time-series of the microorganism population x for extinction.
and

That is condition (11) holds. We choose initial value  then from the numerical simulation (Figure 2) we see that system (19) is permanent.
then from the numerical simulation (Figure 2) we see that system (19) is permanent.
It is difficult to study the global attractivity of system (2) analytically. We present here two examples to show that system (2) is global attractive under the condition (11). Setting D = 1, a = 6, A = 8, r = 0:4, p = 18, T = 2, b = 1, so that condition (11) holds. Choosing initial value  (2.5,1.6), (4.7,2.6), (7.1,6.3), (9.4,5.8), (12.2,7.3), (14.4), (16.5,9.7), (19.3,11.4), (21.4,12.5), (23,12), respectively, then from the numerical simulation (Figure 3) we see that there exist a unique T-period solution
(2.5,1.6), (4.7,2.6), (7.1,6.3), (9.4,5.8), (12.2,7.3), (14.4), (16.5,9.7), (19.3,11.4), (21.4,12.5), (23,12), respectively, then from the numerical simulation (Figure 3) we see that there exist a unique T-period solution  of system (2) which is globally attractive. Let D = 1, a = 6, A = 8, r = 0:2, p = 20, T = 2, b = 1. Then the condition (3.9) holds for those parameters. Choosing initial values
of system (2) which is globally attractive. Let D = 1, a = 6, A = 8, r = 0:2, p = 20, T = 2, b = 1. Then the condition (3.9) holds for those parameters. Choosing initial values  = (0.5,0.4), (1,0.8), (1.5,1.2), (2,1.6), (2.5,2), (3,2.4), (3.5,2.8), (4,3.2), (4.5,3.6), (5,4), respectively, the numerical simulation (Figure 3) also show that system (2) is globally attractive. Therefore, we can guess if only condition (11) holds then
= (0.5,0.4), (1,0.8), (1.5,1.2), (2,1.6), (2.5,2), (3,2.4), (3.5,2.8), (4,3.2), (4.5,3.6), (5,4), respectively, the numerical simulation (Figure 3) also show that system (2) is globally attractive. Therefore, we can guess if only condition (11) holds then
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 2. (a) Time-series of the nutrient S for permanence and periodic oscillation; (b) Time-series of the microorganism population x for permanence.
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 3. (a) Time-series of the nutrient S for global attractivity; (b) Time-series of the microorganism population x for global attractivity.
the system (2) has a unique T-period solution which is globally attractive
5. Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11261056, 11261058).
REFERENCES
- H. L. Smith, “Competitive Coexistence in an Oscillating Chemostat,” SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 40, No. 3, 1981, pp. 498-522. doi:10.1137/0140042
- S. B. Hsu, “A Competition Model for a Seasonally Fluctuation Nutrient,” Journal of Mathematical Biology, Vol. 9, No. 2, 1980, pp. 115-132.
- G. J. Butler, S. B. Hsu and P. Waltman, “A Mathematical Model of the Chemostat with Periodic Washout Rate,” SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 45, No. 3, 1985, pp. 435-449. doi:10.1137/0145025
- P. Lemas, “Coexistence of Three Competing Microbial Populations in a Chemostat with Periodic Input and Dilution Rate,” Mathematical Bioscience, Vol. 129, No. 2, 1995, pp. 111-142. doi:10.1016/0025-5564(94)00056-6
- S. S. Pilyugin and P. Waltman, “Competition in Unstirred Chemostat with Periodic Input and Washout,” SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 59, No. 2, 1999, pp. 1157-1177.
- X. He and S. Ruan, “Global Stability in Chemostat-Type Plankton Models with Delayed Nutrient Recycling,” Research Report, The School of Mathematical and Statistics, University of Sydney, 1996, pp. 96-98.
- S. Ruan, “The Effect of Delays on Stability and Persistence in Plankton Models,” Nonlinear Analysis: Real Word Applications, Vol. 24, No. 4, 1995, pp. 575-585.
- S. Ruan and X. He, “Global Stability in Chemostat-Type Competition Models with Nutrient Recycling,” SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, Vol. 58, No. 1, 1998, pp. 170-192. doi:10.1137/S0036139996299248
- V. S. H. Rao and P. R. S. Rao, “Global Stability in Chemostat Models Involving Time Delays and Wall Growth,” Nonlinear Analysis: Real Word Applications, Vol. 5, No. 1, 2005, pp. 141-158.
- S. R. J. Jang, “Dynamics of Variable-Yield NutrientPhytoplankton-Zooplankton Models with Nutrient Recycling and Self-Shading,” Journal of Mathematical Biology, Vol. 40, No. 3, 2000, pp. 229-250. doi:10.1007/s002850050179
- S. Sun and L. Chen, “Complex Dynamics of a Chemotat with Variable Yield and Periodically Impulsive Perturbation on the Substrate,” Journal of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 43, No. 1, 2008, pp. 338-348. doi:10.1007/s10910-006-9200-z
- V. Lakshmikantham, D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeoonov, “Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations,” World Science, Singapore City, 1989. doi:10.1142/0906
- D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeoonov, “Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications,” Longman Scientific and Thechnical, London, 1993.
- D. L. DeAngelis, R. A. Goldstein and R. V. Oneill, “A Model for Trophic Interaction,” Ecology, Vol. 56, No. 4, 1975, pp. 661-692. doi:10.2307/1936298
- J. R. Beddington, “Mutual Interference between Parasites and Its Effect on Searching Efficiency,” Journal of Animal Ecology, Vol. 44, No. 1, 1975, pp. 331-340. doi:10.2307/3866
- Z. D. Teng, R. Gao, R. Mehbuba and K. Wang, “Global Behaviors of Monod type Chemostat Model with Nutrient Recycling and Impusive Onput,” Journal of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol. 47, No. 1, 2010, pp. 276-294. doi:10.1007/s10910-009-9567-8
NOTES
*Corresponding author.

