Separation/Analysis Rhodamine B by Anion Surfactant/Ionic Liquid Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Coupled with Ultraviolet Spectrometry ()
1. Introduction
Rhodamine B is an triphenylmethane dye (Figure 1) used in industrial fields, such as textile and foodstuff industry [1] [2] , which is harmful if swallowed by human beings and animals, and causes irritation to the skin, eyes and respiratory tract [3] . In many countries, rhodamine B has been banned in food products due to the ha-
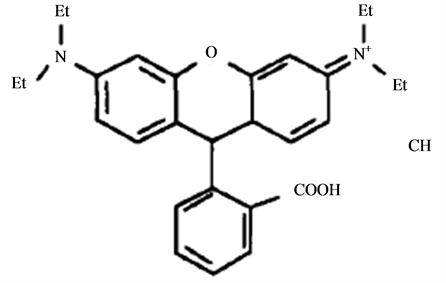
Figure 1. The chemical structure of rhodamine B.
zardous nature and harmful effects [2] . So it has been considered worthwhile to make efforts to develop a simple method for the determination of rhodamine B in real samples.
The direct determination of trace rhodamine B in real samples may not be possible because of low concentrations and matrix interferences, so the preliminary preconcentration and sample clean-up steps are necessary. The methods of preconcentration separation contain high performance liquid hromatography (HPLC) [1] -[4] , liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) [5] , cloud point extraction (CPE) [6] , solid phase extraction (SPE) [3] and so on. LLE is widely applied for the trace metals determination due to its inexpensive cost and easy operation. However, the extraction solvents of LLE are volatile, inflammable and toxic organic solvents which are easy to pollute the environment.
The aqueous two-phase systems (ATPSs) are a kind of LLE technique which is a simple and environmentally friendly separation system because traditional volatile solvents are not used in the whole process. ATPSs are usually composed of two polymers [7] , polymer/salt [8] , two surfactants [9] or RTILs/salt [10] , which have been used in separation and purification of various biological products [11] , metal ions [12] , dyes [13] , drug molecules [14] . However, 1) the high viscidity rich phase may make following determination difficult [14] in the most of polymers—ATPSs; 2) the phase equilibrium processes in surfactants—ATPSs are relatively time-consumming [9] ; 3) the RTILs-ATPSs were required a great quantity of ionic liquid and salt [10] . There are the synergistic effect between surfactants and ionic liquids (RTILs) due to their unique characteristics [15] [16] . RTILs and surfactants could form an ordered molecular assembly which not only own the inherent of surfactant but also possess many advantages of RTILs, and achieve the integration of their nature [16] . These features of ordered molecular offer numerous opportunities for the modification of existing extraction processes and for the development of new extraction processes. The ATPSs based on 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([Bmim] [BF4])/cationic surfactant (NPTABr) have been reported [17] . But, the ATPSs based on RTILs/anion surfactants seem to be lacking.
In this work, ATPSs based on RTILs (1-tetradecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide)/anionic surfactant (sodium dodecyl sulfate, SDS)/NaCl were established for separation/analysis trace rhodamine B in real samples coupled with ultraviolet spectrometry at 554 nm. The ATPSs showed a wide range of temperature, quick phase separation with low concentration of the RTILs/salt, which have been successfully applied to the determination of rhodamine B in real samples with satisfactory results.
2. Experimental
2.1. Instrumentation and Reagents
Ultraviolet spectrophotometer; pHS—25 pH meter (Shanghai, China); Fourier transform infrared spectrometer; High-speed centrifuge (feige); electronic balance (Beijing); magnetic stirring apparatus (Shanghai); conductivity meter (Shanghai).
A standard rhodamine B stock solution of 100.0 μg·mL−1 was prepared. The solution was diluted to 10.0 μg·mL−1. Series of HAc-NaAc buffer solutions, pH 3.0 to 8.0, 5% (w/v) solution of SDS and 3% solution of RTILs were prepared. All the chemicals were of analytical reagent grade and all solutions were prepared in deionized water.
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. Synthesis Method of RTILs
Briefly, 1-tetradecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide [C14mim][Br] was synthesized by adding equal amount (0.05 mol) of n-methylimidazole and 1-bromotetradecane to a 250.0 mL round bottom flask fitted with reflux condenser. The flask and its content were stirred and heated at 110˚C for 3 h. Subsequently, the outcome was washed three times with diethyl ether in a separation funnel. Finally, the collected ionic liquid was heated at 40 ◦C under vacuum last for 4h to remove the solvent.
2.2.2. Phase Diagrams [18]
The 0.3% (W/V) RTILs aqueous solution and 0.3% SDS solution were prepared with 2.0% NaCl solution. Samples were prepared by mixing stock-solutions of RTILs and SDS in test tubes at different ratios. The tubes were then immersed in a water bath at temperature T = 20˚C, 40˚C, 60˚C for about 5 min until phase equilibrium state was attained.
2.2.3. ATPS Extraction Procedure
1.0 mL standard solutions (10.0 μg·mL−1) of rhodamine B, 2.0 mL pH = 3.8 buffer solution, 1.0 mL 20% NaCl, 0.6 mL 3.0% RTILs and 1.0 mL 5.0% SDS were transferred into 10.0 mL centrifuge tube. The mixtures were diluted to the mark with water and shaken thoroughly. Separation of the phases was achieved by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 4 min. For the separation of two phases, the RTILs/SDS-rich phase was mixed with 1.0 mL acetate buffer (pH 3.8) and then diluted to 5.0 mL with distilled water. Then the absorbance was measured by ultraviolet spectrometry against a reagent blank.
2.2.4. Sample Preparation
According to literature [5] .
Determination of critical micell concentration (cmc).
According to literature [19] .
4. Conclusion
The ATPSs consisting of RTILs and SDS are an excellent strategy for extraction of rhodamine B from real samples. This novel extraction technique can be employed in combination with ultraviolet spectrometry as a viable for the quantitative determination of rhodamine B in real samples. The method is characterized with simplicity, rapidity, high selectivity and low cost.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20875082, 21155001) and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and the Foundation of the Excellence Science and Technology Invention Team in Yangzhou University.
Abbreviations
cmc: critical micell concentration SDS: sodium dodecyl sulfate RTILs: room temperature ionic liquids ATPSs: aqueous two-phase systems