Numerical Solution of Klein/Sine-Gordon Equations by Spectral Method Coupled with Chebyshev Wavelets ()
1. Introduction
Many physical phenomena encountered in science and engineering are governed by ordinary as well as partial differential equations. Some disciplines that use partial differential equations to describe the phenomena of interest are fluid mechanics, solid mechanics, quantum mechanic, propagation of acoustic and electromagnetic waves and problems in heat and mass transfer. Many linear and nonlinear phenomena appear in several areas of scientific fields like physics, chemistry and biology can be modeled by different type of partial differential equation such as evolution equation, reaction diffu- sion equation, Schrodinger type wave equations, Vander Poll’s equation, Telegraph equation, Lyapunov equation etc. A broad class of analytical methods and numerical methods available in the literature are used to handle these problems. In this present work we are dealing with two partial differential equation named as Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations. The Klein-Gordon equation is as follows:
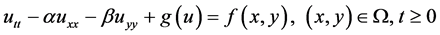 (1)
(1)
Wavelet analysis had made a lot of successes in different fields of science and engineering due to its beautiful properties such as orthogonality, multi-resolution analysis and computational efficiency. Wavelet permits the accurate representation of a variety of functions and operators. Wavelet analysis and wavelet transform are recently developed mathematical tool for solving the linear and non-linear ordinary differential equations, partial differential equations and integral equation. Wavelets also applied in numerous disciplines such as image compression, data compression and deionising data. Most commonly wavelets are Haar, Legendre, Chebyshev are used to find the numerical solution of partial differential equations. In addition wavelet approach can make a connection with some fast and reliable numerical methods. The spectral method has the advantage of exponential convergence property when orthogonal basis functions are involved. As a result, it plays a vital role in solving partial differential equation. It is important to choose the basis function for possible coupling with spectral method. The wavelet basis can combine the advantages of both infinitely differentiable and small compact support which is far better than the spectral and finite element basis.
In recent year, spectral method [19] [20] using Legendre polynomials and Legendre wavelets as basic functions are considered to solve the Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations. By inspiring the work done in [19] [20] , we use the Chebyshev wavelet as basis function coupled with spectral method for solving nonlinear Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations. Therefore, spectral collocation methods based on Chebyshev wavelet basis can obtain good spatial and spectral resolution while still keeping high efficiency.
The rest of the paper is as follows: In Section 2, Chebyshev wavelet and its properties are discussed. Operational matrix of derivative required for our subsequent development is presented in Section 3. Section 4 is devoted to present the Chebyshev wavelets spectral collocation method for solving Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations then approximate the unknown function. Section 5 deals with the illustrative examples and their solutions by the proposed approach compared with exact as well as with existing literature. Finally, concluding remarks are made in Section 6.
2. Wavelets and Chebyshev Wavelets
In the past decades, wavelets [21] [22] [23] shows their interest in different fields of science and technology due to its beautiful properties. Wavelets constitute the family of functions constructed from the dilation and translation of a single function known as the Mother wavelet. When the dilation parameter a and translation parameter b vary continuously we have the following family of continuous wavelets [23]
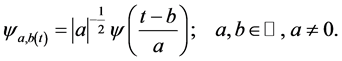 (2)
(2)
If we choose  and
and 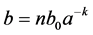 where
where  and
and 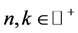 then we get the following family of discrete wavelets:
then we get the following family of discrete wavelets:
 (3)
(3)
These family of functions are a wavelet basis for  and makes an orthonormal basis for the special case
and makes an orthonormal basis for the special case 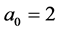 and
and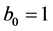 .
.
Chebyshev wavelets  have four arguments,
have four arguments, 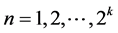
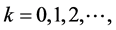 , m is the degree of Chebyshev polynomial of first kind and t denotes the normalized time. They are defined on the interval
, m is the degree of Chebyshev polynomial of first kind and t denotes the normalized time. They are defined on the interval ![]() by
by
![]() (4)
(4)
where
![]()
![]() in (4) are well known Chebyshev polynomial of order m, which is orthogonal
in (4) are well known Chebyshev polynomial of order m, which is orthogonal
with respect to the weight function ![]() and satisfy the following recursive formula:
and satisfy the following recursive formula:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Moreover, the set of Chebyshev wavelet are an orthogonal set with respect to the weight function![]() .
.
Any function ![]() may be expanded in terms of Chebyshev wavelet as
may be expanded in terms of Chebyshev wavelet as
![]() (5)
(5)
where the wavelet coefficients of the series representation in (5) become
![]() (6)
(6)
If the infinite series in (5) is truncated then Equation (5) can be written as
![]() (7)
(7)
where C and ![]() are
are ![]() matrices given by:
matrices given by:
![]() (8)
(8)
![]() (9)
(9)
3. Chebyshev Wavelets Operational Matrix of Derivative
In this section, we first derive the operational matrix D of derivative which plays a great role in order to reducing the given problem into solving the system of algebraic equation. For this, we concern with some Theorem and Corollary as follows.
Theorem 1 [24] . Let ![]() be the Chebyshev wavelets vector defined in (9), then we have
be the Chebyshev wavelets vector defined in (9), then we have
![]() (10)
(10)
where D is ![]() operational matrix of derivative as follows:
operational matrix of derivative as follows:
![]() (11)
(11)
in which O is an ![]() zero matrix, F is an
zero matrix, F is an ![]() matrix and its
matrix and its ![]() element is defined as follows:
element is defined as follows:
![]() (12)
(12)
Corollary 1. By using Equation (10), the operational matrix for nth derivative can be derived as
![]()
where ![]() is the nth power of matrix D.
is the nth power of matrix D.
4. Chebyshev Wavelets Spectral Collocation Method
In different type of numerical methods, spectral methods are one of the most popular methods of discretization for the numerical solution of partial differential equations and integral equations. The main advantage of this method lies in their accuracy for a given number of unknowns. For smooth problems in simple geometries, they offer exponential rates of convergence or spectral accuracy. In the recent literature, Galerkin, collocation, and Tau methods are the three most widely used spectral versions, in which collocation methods have become increasingly popular for solving differential equations, also they are very useful in providing highly accurate solutions to nonlinear differential equations. Now, we focus on the solution nature of this method as follows:
Let us consider the equation in the form:
![]() (13)
(13)
with the initial conditions
![]() (14)
(14)
or boundary conditions
![]() (15)
(15)
In order to transform the arbitrary domain ![]() into the domain defined for Chebyshev wavelet basis
into the domain defined for Chebyshev wavelet basis![]() , on can use the translation
, on can use the translation
![]()
By employing q-weight scheme [20] , discreting the Equation (13), we can get
![]() (16)
(16)
where ![]() is the time step size with the expression
is the time step size with the expression ![]()
Now Equation (16) becomes
![]() (17)
(17)
In the light of Equation (7),the term ![]() can be expanded by Chebyshev wavelet as
can be expanded by Chebyshev wavelet as
![]() (18)
(18)
Submitting Equation (18) into Equation (17), we have
![]() (19)
(19)
in which ![]() and
and![]() , where D is the deri- vative matrix taken from Equation (10)
, where D is the deri- vative matrix taken from Equation (10)
Also, by using the boundary conditions given in Equation (15), one can get
![]() (20)
(20)
Collocating Equation (19) in ![]() Gauss-Chebyshev points
Gauss-Chebyshev points![]() , we have
, we have
![]() (21)
(21)
Equation (20) and (21) can be written as matrix form
![]() (22)
(22)
where A and B are ![]() and
and ![]() matrices, respectively.
matrices, respectively.
Again using the first and second initial conditions given in Equation (14), we have
![]() (23)
(23)
and
![]() (24)
(24)
Equation (24) can be written as
![]()
Equation (22) using Equation (23) gives a linear system of equations with ![]() unknown and equations, which can be solved to find
unknown and equations, which can be solved to find ![]() in each step
in each step ![]() so the unknown function
so the unknown function ![]() in any time
in any time ![]() can be found. Moreover, we defined the error bound for
can be found. Moreover, we defined the error bound for ![]() and
and ![]() as
as
![]()
where ![]() and
and![]() .
.
5. Numerical Results and Discussions
In this section, we use Chebyshev wavelets spectral collocation method described in section 4 to solve nonlinear type of Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations. The proposed method provides a reliable technique which is computer oriented if compared with traditional techniques. To give the clear overview of this method we consider three examples of Klein-Gordon equation and Sine-Gordon equation. All the results are calculated by using the symbolic calculus software MATLAB 2013a and Mathematica.
Example 1 [25] We consider the nonlinear Klein-Gordon Equation (13) with![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() with the initial conditions
with the initial conditions
![]()
and the Dirichlet boundary condition
![]()
The analytical solution is given by
![]()
The obtained ![]() and
and ![]() errors of Example 1 at step size 0.0001 is presented in comparison with the existing method in Table 1 and Table 2 for
errors of Example 1 at step size 0.0001 is presented in comparison with the existing method in Table 1 and Table 2 for ![]() and
and ![]() and graphically shown in Figure 1 for
and graphically shown in Figure 1 for![]() . It is evident from Table 1, Table 2 and Figure 1 that the solutions obtain by using CWSCM are in good agreement and are better than the results obtained by existing method presented in [25] . However, the errors may be reduced significantly if we increase level of resolution.
. It is evident from Table 1, Table 2 and Figure 1 that the solutions obtain by using CWSCM are in good agreement and are better than the results obtained by existing method presented in [25] . However, the errors may be reduced significantly if we increase level of resolution.
![]()
Figure 1. Comparison of exact solution with approximate solution for Example 1 at![]() .
.
Example 2 [25] We consider the nonlinear Klein-Gordon Equation (13) with![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() in the interval
in the interval ![]() with the initial con- ditions
with the initial con- ditions
![]()
and the Dirichlet boundary condition
![]()
The analytical solution is given by
![]()
The ![]() and
and ![]() errors of Example 2 at step size 0.0001 are presented in com- parison with the existing method in Table 3 and Table 4 for
errors of Example 2 at step size 0.0001 are presented in com- parison with the existing method in Table 3 and Table 4 for ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() . From Table 3, Table 4 and Figure 2, it is clear that CWSCM performs much better than existing methods [25] and with the increase in number of collocation points the errors decrease for the solution.
. From Table 3, Table 4 and Figure 2, it is clear that CWSCM performs much better than existing methods [25] and with the increase in number of collocation points the errors decrease for the solution.
Example 3 [20] Consider the following nonlinear Sine-Gordon equation
![]()
where![]() , and the initial conditions
, and the initial conditions
![]()
and the Dirchlet boundary conditions
![]()
The exact solution is given by
![]()
![]()
Figure 2. Comparison of exact solution with approximate solution for Example 2 at![]() .
.
The numerical solution of Sine-Gordon equation has presented in Table 5 which shows the comparison of the errors of the present method with the exact solution. It is obvious from the table that the present method is more accurate, simple and fast. Comparison between an exact and approximate solution is shown in Figure 3.
6. Concluding Remarks
In this article, we have proposed an efficient and accurate method based on Chebyshev wavelets to solve both Klein-Gordon and Sine-Gordon equations arising in different field of sciences, engineering and technology. The main advantage of this method is that it transforms the problem into algebraic equation so that the computation is effective and simple. To appraise the performance and efficiency of the method, three benchmark problems are included and discussed. The numerical results are compared with a few existing methods reported recently in the literature. The numerical experi- ments confirm that the spectral method coupled with Chebyshev wavelets is superior to other existing ones.
![]()
Figure 3. Comparison of exact solution with approximate solution for Example 3 at![]() .
.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Editor and the referee for their comments.