A Generalized Tanh-Function Type Method and the(G'/G) -Expansion Method for Solving ()
1. Introduction
Direct searching for exact solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations (NLPDEs) plays an important role in the study of nonlinear physical phenomena and becomes one of the most exciting and extremely active areas of research investigation. In the past several decades, many effective methods for obtaining exact solutions of NLPDEs have been presented, such as inverse scattering method [1], Darboux and Bäcklund transformation [2,3], Hirota’s bilinear method [4], Lie group method [5], variational iteration method [6], Adomian decomposition method [7] and so on. Most recently, Prof. Ma and Lee [8] proposed a new direct method called the transformed rational function method to solve exact solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations. The transformed rational function method provides a more systematical and convenient handling of the solution process of nonlinear equations, unifying the tanh-function method, homogenous balance method, Jacobi elliptic function expansion method, F-expansion method, Exp-function method. The key point is to search for rational solutions to variablecoefficient ordinary differential equations transformed from given partial differential equations.
In this paper using the idea of the transformed rational function method, a generalized tanh-function type method is introduced to solve exact traveling solutions of NLPDEs. We also show that the 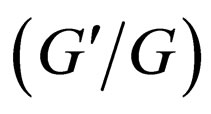 -expansion method [9-16] is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method, so the transformed rational function method includes the
-expansion method [9-16] is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method, so the transformed rational function method includes the  -expansion method. We demonstrate that all solutions obtained by the
-expansion method. We demonstrate that all solutions obtained by the 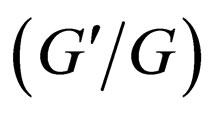 -expansion method were also found by the generalized tanhfunction type method. As applications, we consider mKdV equation. Compared with the
-expansion method were also found by the generalized tanhfunction type method. As applications, we consider mKdV equation. Compared with the  -expansion method, the generalized tanh-function type method gives new and more abundant solutions.
-expansion method, the generalized tanh-function type method gives new and more abundant solutions.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, using idea of the transformed rational function method, a generalized tanh-function type method for finding travelling wave solutions of NLPDEs was introduced. In Section 3, we show that the 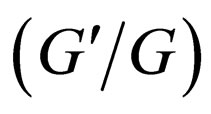 -expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method. In Section 4, we applied this method to mKdV equation and compared with the
-expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method. In Section 4, we applied this method to mKdV equation and compared with the 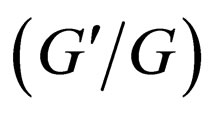 -expansion method, the generalized tanh-function type method gives new and more abundant solutions. In Section 5, some conclusions are given.
-expansion method, the generalized tanh-function type method gives new and more abundant solutions. In Section 5, some conclusions are given.
2. The Generalized Tanh-Function Type Method
A detailed describe of the transformed rational function method can be found in Ma and Lee’s paper [8]. Using the idea of the transformed rational function method, a new approach called the generalized tanh-function method is proposed. The key point of the new approach is based on the assumptions that the solutions can be expressed by Laurent polynomial (a special case of rational functions) and that solution variable satisfies Riccati equation. In the following we give the main steps of the generalized tanh-function type method for finding travelling wave solutions of NLPDEs.
For simplicity, let us consider the nonlinear partial differential equation with two independent variables  and
and , is given by
, is given by
 (2.1)
(2.1)
where  is an unknown function,
is an unknown function, 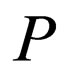 is a polynomial in
is a polynomial in 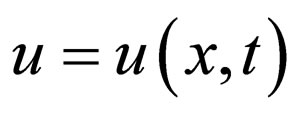 and its various partial derivatives, in which the highest order derivatives and nonlinear terms are involved.
and its various partial derivatives, in which the highest order derivatives and nonlinear terms are involved.
Step 1. Using the transformation
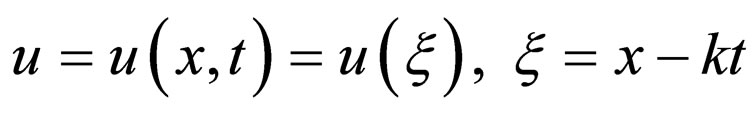 we reduce the Equation (2.1) to an ODE
we reduce the Equation (2.1) to an ODE
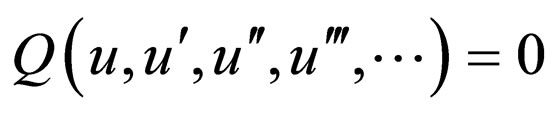 (2.2)
(2.2)
Step 2. Suppose that the solution of ODE (2.2) can be expressed by a finite series in  as follows:
as follows:
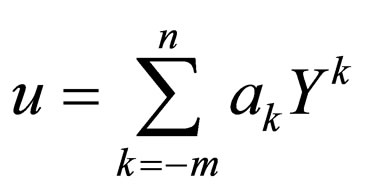 (2.3)
(2.3)
where 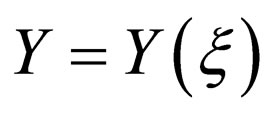 satisfied Riccati equation
satisfied Riccati equation
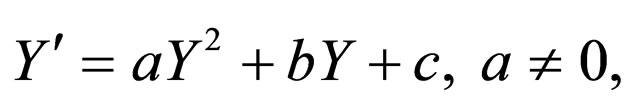 (2.4)
(2.4)
where .
. ,
,  ,
, 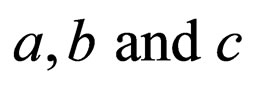 are constants to be determined later , and non-negative integers
are constants to be determined later , and non-negative integers  and
and 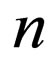 can be determined by considering the homogeneous balance between the highest order derivative and nonlinear terms appearing in ODE (2.2).
can be determined by considering the homogeneous balance between the highest order derivative and nonlinear terms appearing in ODE (2.2).
Step 3. By substituting (2.3) along with (2.4) into ODE (2.2) and collecting all terms with the same order of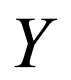 , ODE (2.2) will yield a system of algebraic equation with respect to
, ODE (2.2) will yield a system of algebraic equation with respect to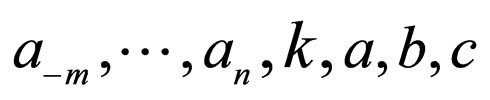 , because all the coefficient of
, because all the coefficient of 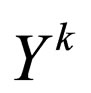 have to vanish.
have to vanish.
Step 4. With the aid of Mathematica or Maple, one can determine,  and
and 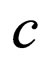 by solving the system of algebraic equation of Step 3.
by solving the system of algebraic equation of Step 3.
Step 5. Substituting  and the solutions of Riccati Equation (2.4) into (2.3) we can obtain the solutions of the nonlinear partial differential Equation (2.1)
and the solutions of Riccati Equation (2.4) into (2.3) we can obtain the solutions of the nonlinear partial differential Equation (2.1)
Using the following formula of indefinite integrals, we can obtain general solution of Riccati Equation (2.4).
The formula of indefinite integrals
Let , then we have the following results:
, then we have the following results:
Case 1. when ,
,

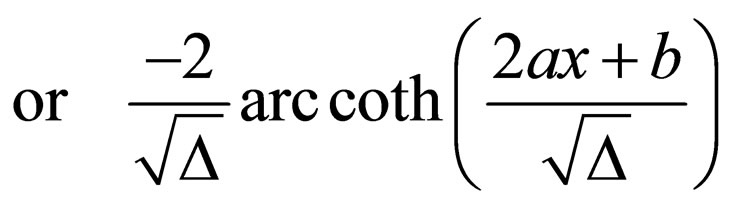
Case 2. when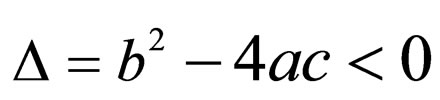 ,
,

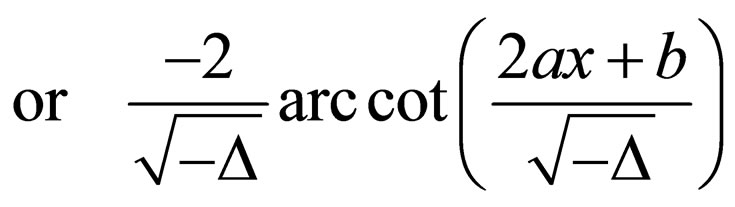
Case 3. when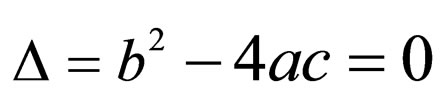 ,
,
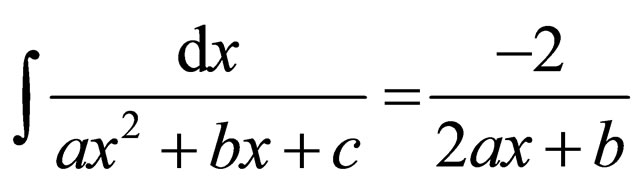
Using above the formula of indefinite integrals, the Riccati Equation (2.4) has the following general solutions:
1) If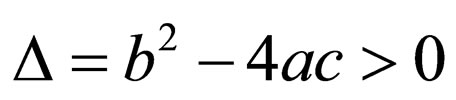 ,
,
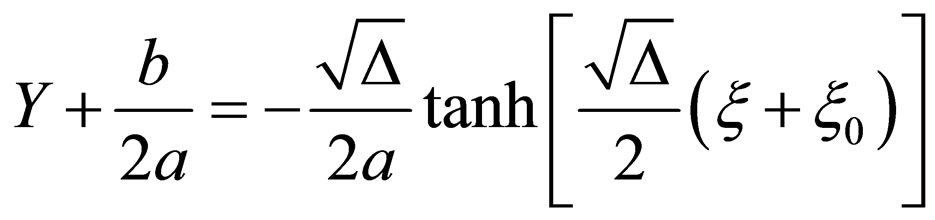
 (2.5a)
(2.5a)
2) If ,
,
 (2.5b)
(2.5b)
3) If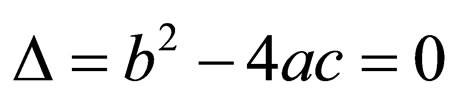 ,
,
 (2.5c)
(2.5c)
where  are constants.
are constants.
By using formula
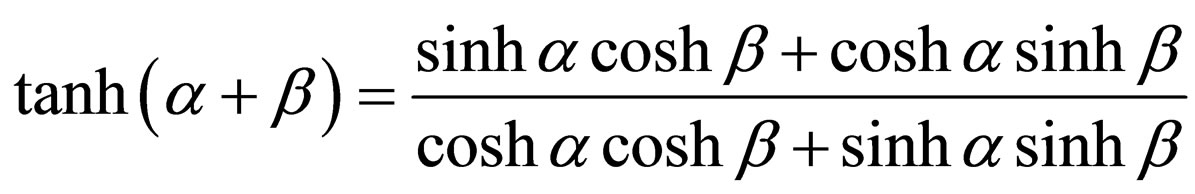 ,
,
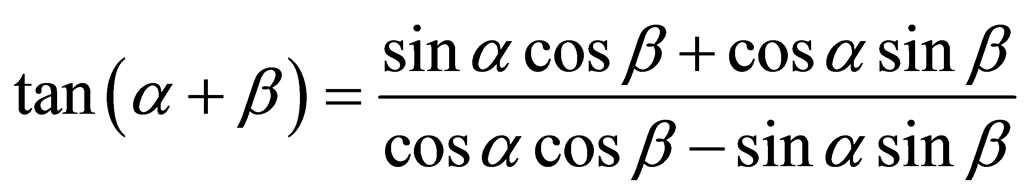 .
.
We can change (2.5a) and (2.5b) into the following result respectively
4) If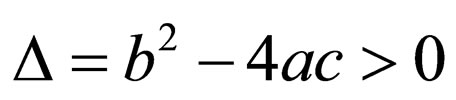 ,
,
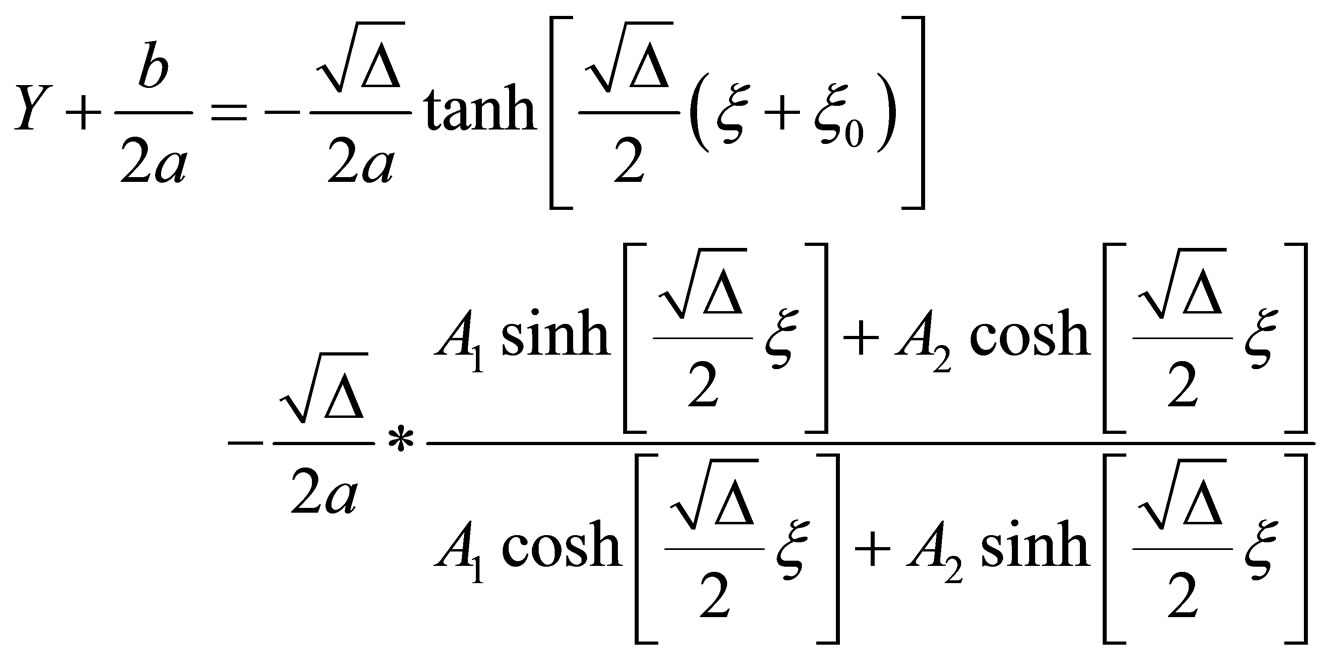 (2.6a)
(2.6a)
where  be constants.
be constants.
5) If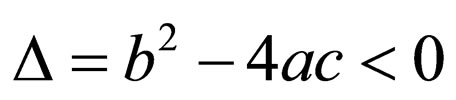 ,
,
 (2.6b)
(2.6b)
where 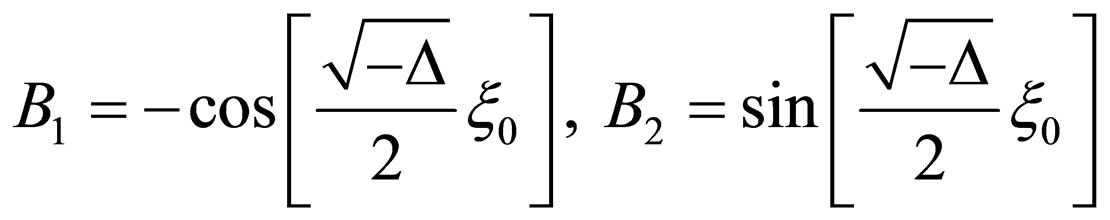 be constants.
be constants.
We notice that the expressions (2.6a) and (2,6b) are more cumbersome than (2.5a) and (2.5b), and solutions expression of the 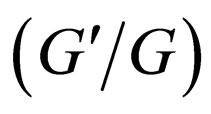 -expansion method are just from (2.6a) and (2.6b).
-expansion method are just from (2.6a) and (2.6b).
3. The 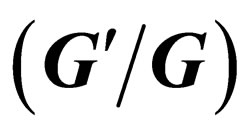 -Expansion Method: A Special Case of the Generalized Tanh Function Type Method
-Expansion Method: A Special Case of the Generalized Tanh Function Type Method
Recently, Wang et al. [9] introduced a new method called the 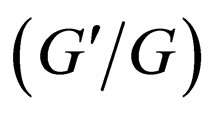 -expansion method to look for travelling wave solutions of NLPDEs. Later, the
-expansion method to look for travelling wave solutions of NLPDEs. Later, the 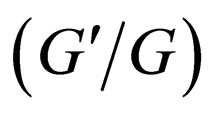 -expansion method is used by some authors, such as in [10-15]. The
-expansion method is used by some authors, such as in [10-15]. The  -expansion method is based on the assumptions that the travelling wave solutions can be expressed by a polynomial in
-expansion method is based on the assumptions that the travelling wave solutions can be expressed by a polynomial in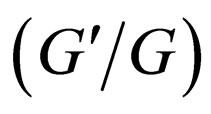 , that is
, that is 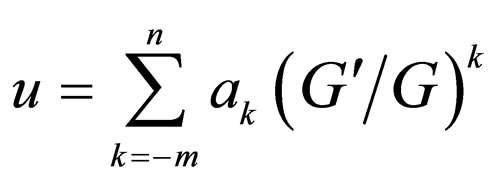 and
and  satisfies a second order linear ordinary differential equation (LODE):
satisfies a second order linear ordinary differential equation (LODE):
 (3.1)
(3.1)
Where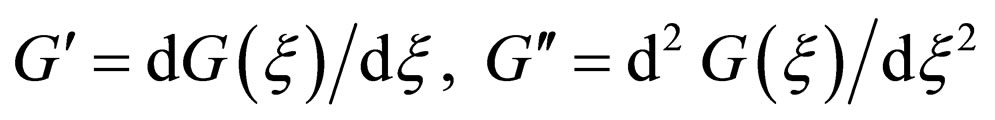 . The degree of the polynomial can be determined by the homogeneous balance method. The coefficients of the polynomial can be obtained by solving a set of algebraic equations resulted from the process of using the method.
. The degree of the polynomial can be determined by the homogeneous balance method. The coefficients of the polynomial can be obtained by solving a set of algebraic equations resulted from the process of using the method.
In here we show that the 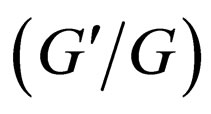 -expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method. It is not difficult to find if we make the transformation
-expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method. It is not difficult to find if we make the transformation  then Equation (3.1) is equivalent to the following special Riccati equation
then Equation (3.1) is equivalent to the following special Riccati equation
 (3.2)
(3.2)
where  are constants. In the
are constants. In the 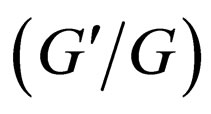 -expansion method,
-expansion method, 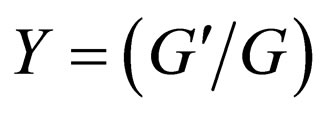 uses the result from (2.6a) and (2.6b), so the
uses the result from (2.6a) and (2.6b), so the 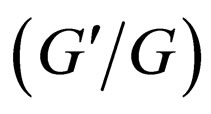 -expansion method is equivalent to the generalized tanh-function type method.
-expansion method is equivalent to the generalized tanh-function type method.
Remark 1. In Equation (2.3) and Riccati Equation (2.4), if 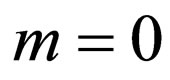 and
and 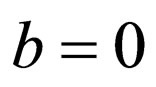 respectively, then the generalized tanh-function type method degenerate the tanh method. The idea of the tanh-function type method can go back to [17].
respectively, then the generalized tanh-function type method degenerate the tanh method. The idea of the tanh-function type method can go back to [17].
Remark 2. If we take  in Equation (2.3) and take
in Equation (2.3) and take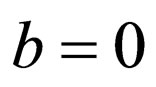 ,
,  in Equation (2.4), then the generalized tanh-function type method degenerate modified extended tanh method which can be obtained more exact solutions than tanh-function method, hyperbolic function method and other more sophisticated methods [18].
in Equation (2.4), then the generalized tanh-function type method degenerate modified extended tanh method which can be obtained more exact solutions than tanh-function method, hyperbolic function method and other more sophisticated methods [18].
Remark 3. In Riccati Equation (2.4), if 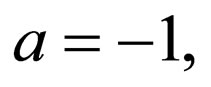

 , the generalized tanh-function type method is equivalent to
, the generalized tanh-function type method is equivalent to  -expansion method.
-expansion method.
4. Application to mKdV Equation
In the section we will illustrate the generalized tanhfunction method with mKdV equation.
Let us consider mKdV equation in the form [9].
 (4.1)
(4.1)
Using the wave variable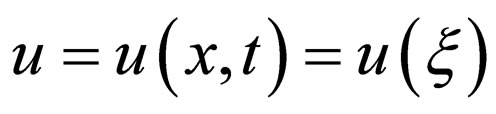 ,
,  converts Equation (4.1) to an ODE
converts Equation (4.1) to an ODE
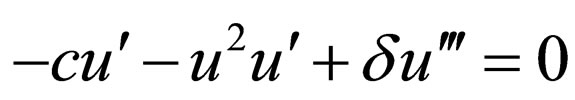 (4.2)
(4.2)
where . Suppose that the solution of Equation (4.2) can be expressed by a finite series in
. Suppose that the solution of Equation (4.2) can be expressed by a finite series in 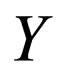 as follows:
as follows:
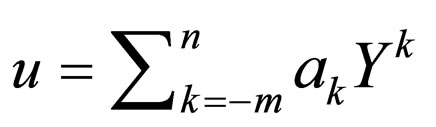 (4.3)
(4.3)
where 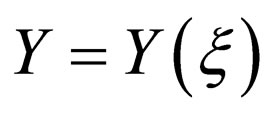 satisfied a first order ordinary differential equation
satisfied a first order ordinary differential equation
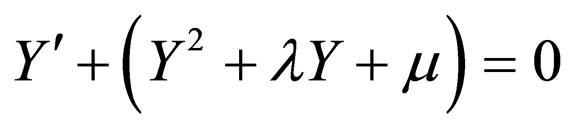 (4.4)
(4.4)
where  are constants to be determined later,
are constants to be determined later,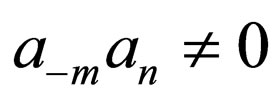 .
.
Balancing the order of 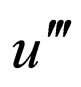 with the order
with the order  in Equation (4.2) gives
in Equation (4.2) gives
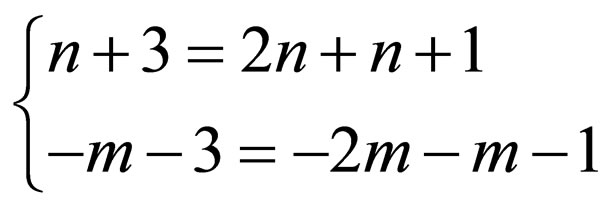 (4.5)
(4.5)
We find
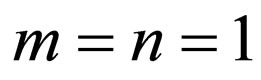
So we can suppose that the solution of Equation (4.2) is of the form
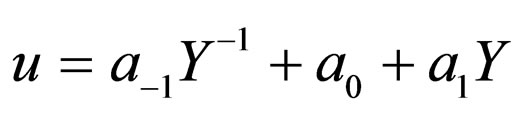 (4.6)
(4.6)
Substituting Equation (4.6) into Equation (4.2) and making using of Equation (4.4), with the aid of Mathematica we obtain a system of algebraic equations for 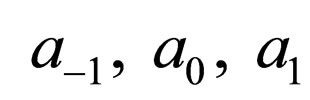 and
and  as follows:
as follows:
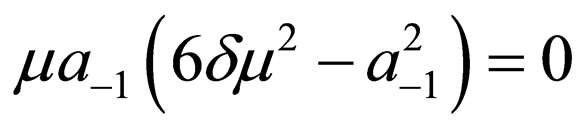 ,
,
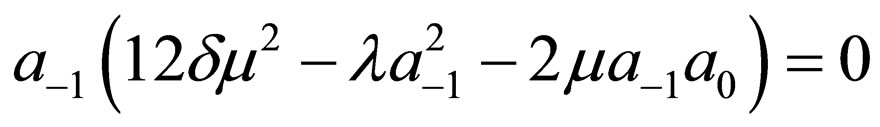 ,
,

 ,
,
 ,
,
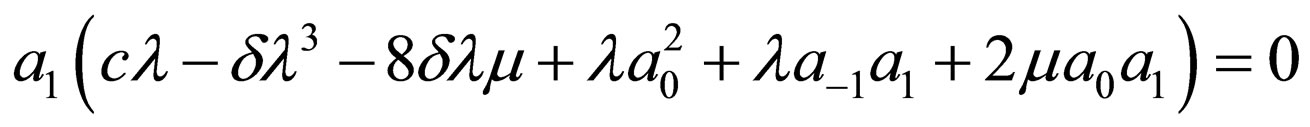 ,
,
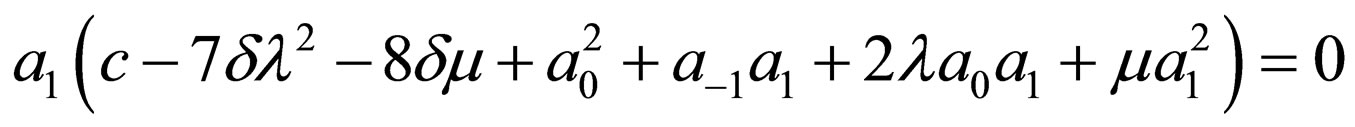 ,
,
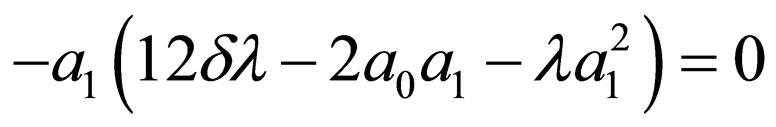 ,
,
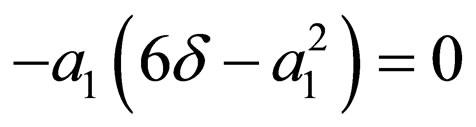 .
.
Solving the algebraic equations above by Mathematica gives three cases, namely:
Case 1:
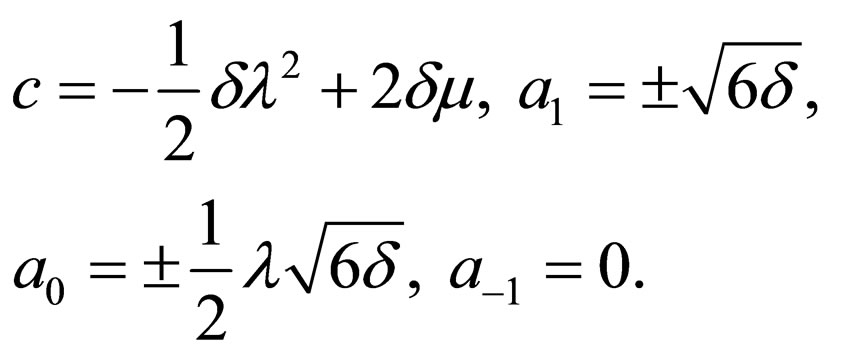 (4.7a)
(4.7a)
Case 2:
 (4.7b)
(4.7b)
Case 3:
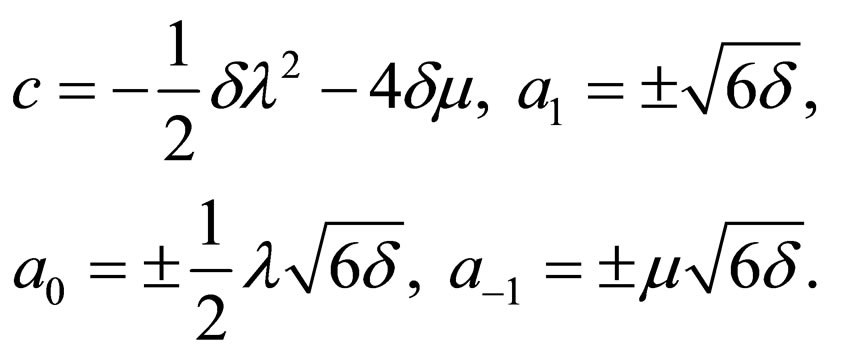 (4.7c)
(4.7c)
By using Equations (4.7a)-(4.7c), express (4.6) can be written as
 (4.8a)
(4.8a)
where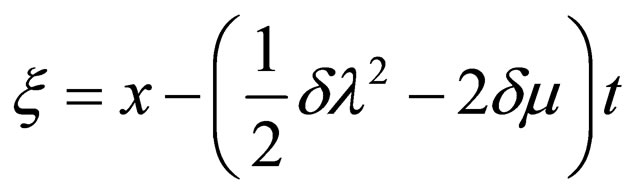 .
.
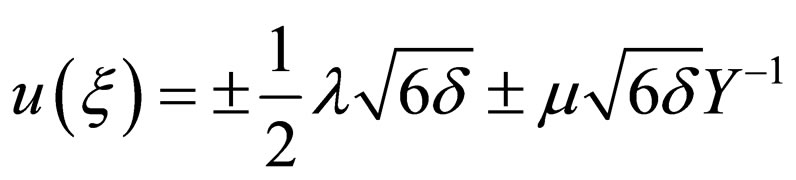 (4.8b)
(4.8b)
where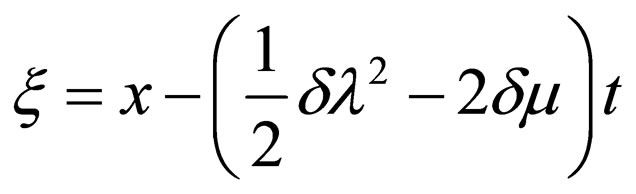 .
.
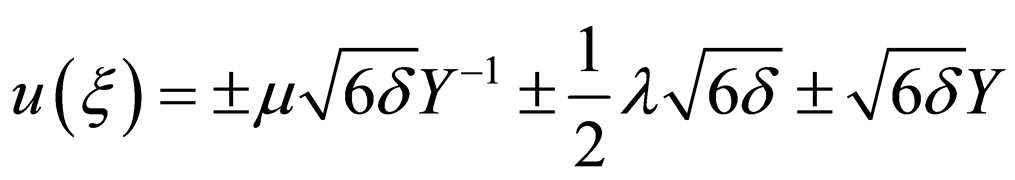 (4.8c)
(4.8c)
where .
.
Substituting (2.6a)-(2.6b) into (4.8a)-(4.8c) we have three types of travelling wave solutions of the mKdV equation as follows:
Case 1. 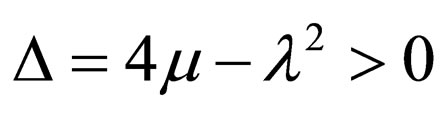
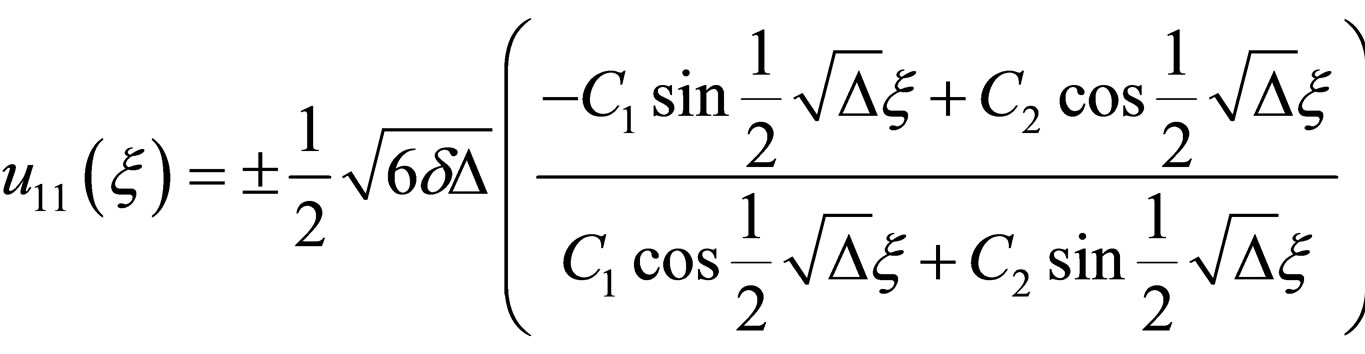 (4.9a)
(4.9a)
where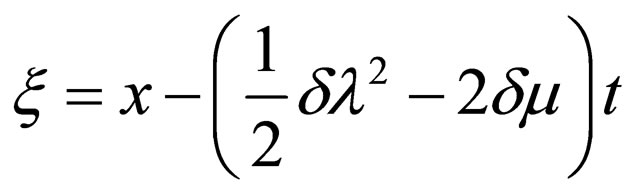 .
.
 (4.9b)
(4.9b)
Where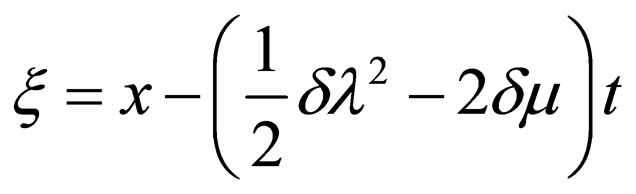 ,
,
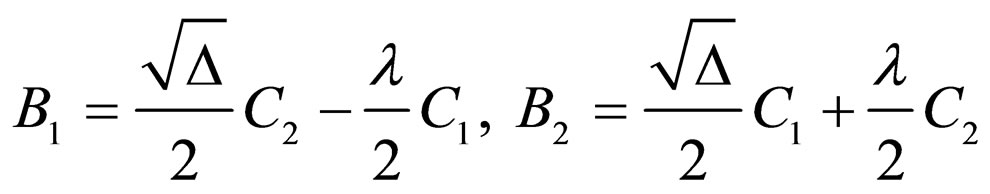 .
.
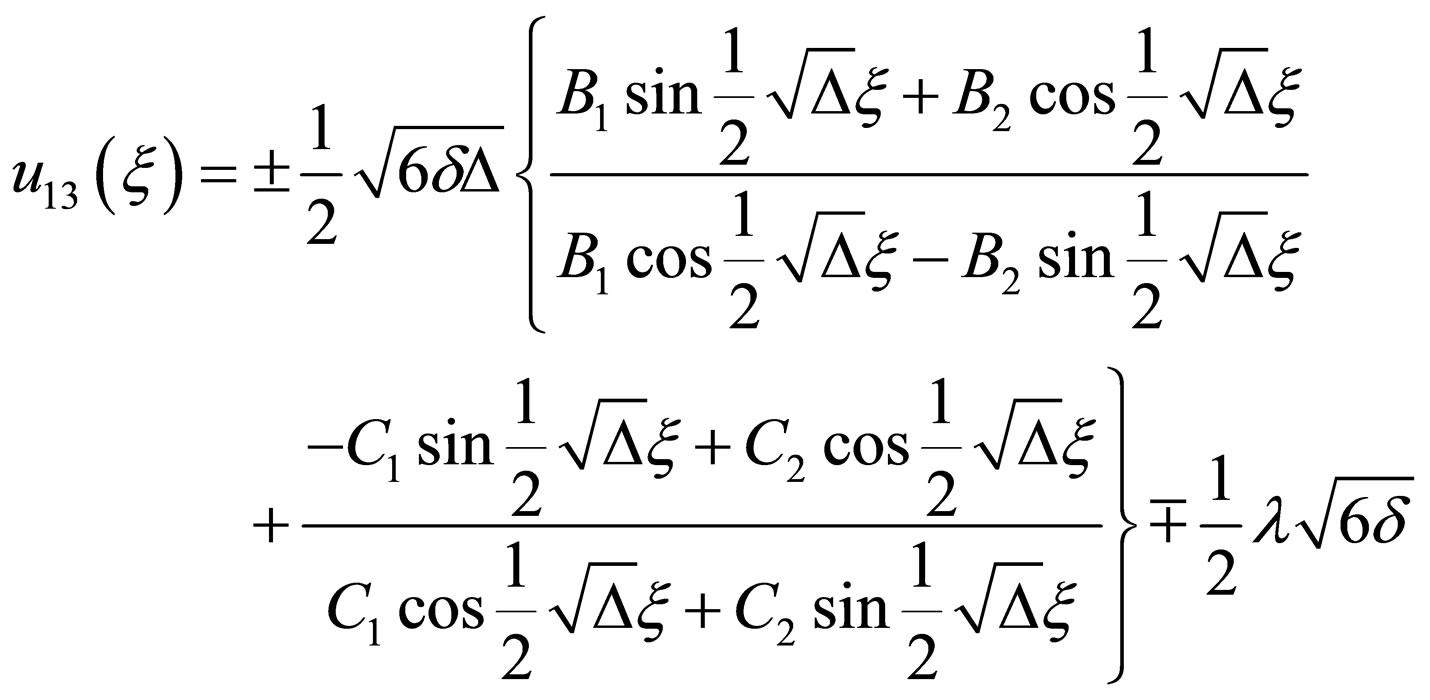 (4.9b)
(4.9b)
where ,
,
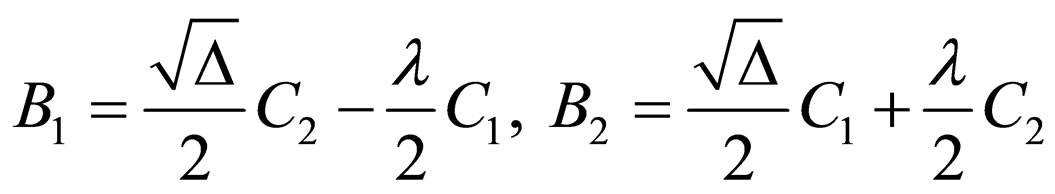 .
.
Case 2. 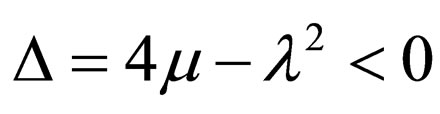 ,
,
 (4.10a)
(4.10a)
where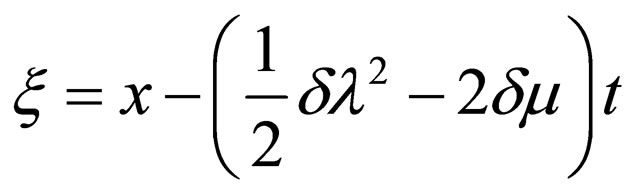 .
.
 (4.10b)
(4.10b)
where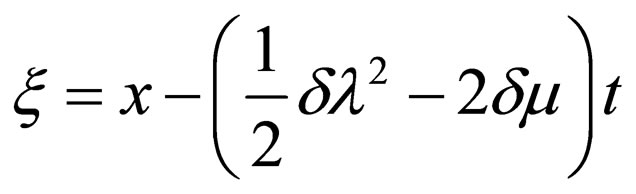 ,
,
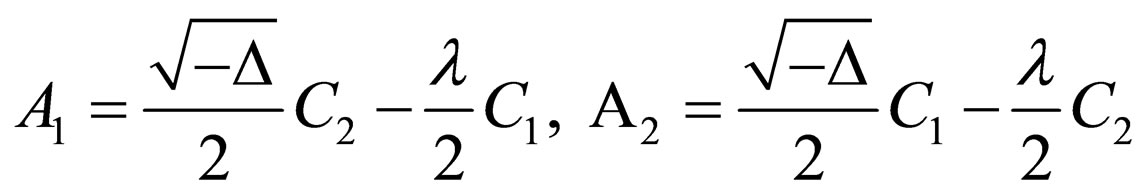
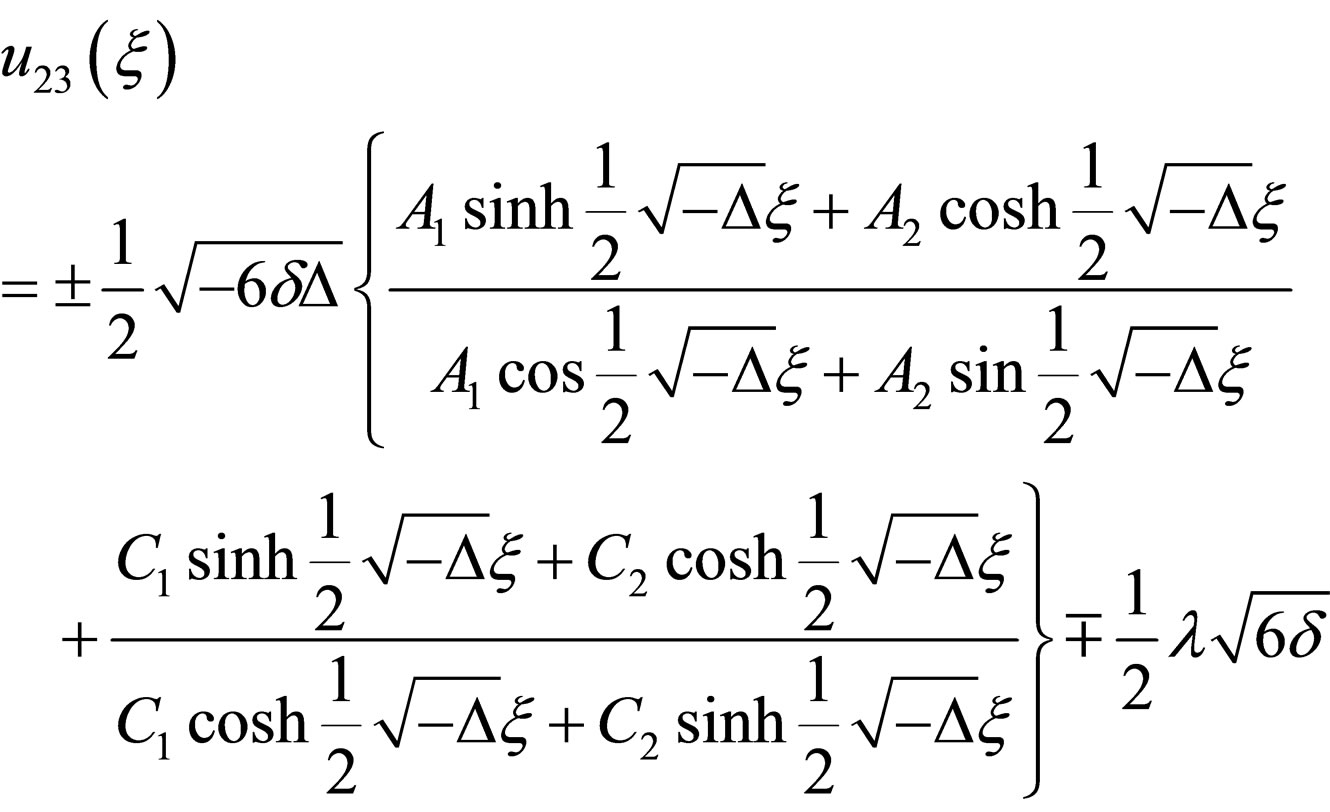 (4.10c)
(4.10c)
where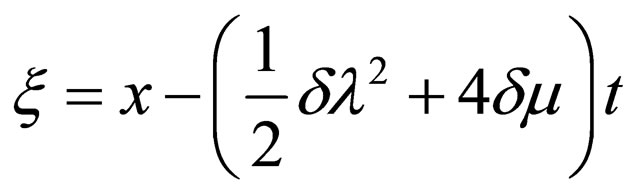 ,
,
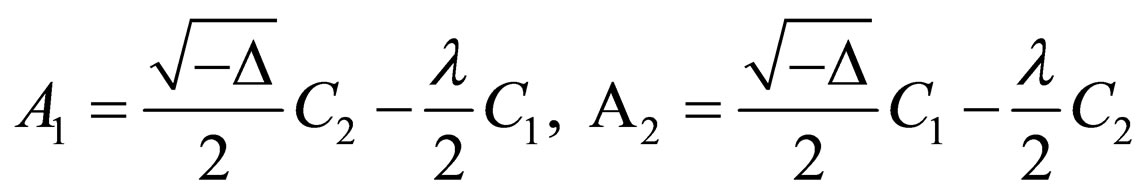
Case 3.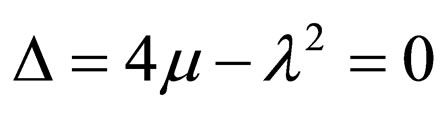 ,
,
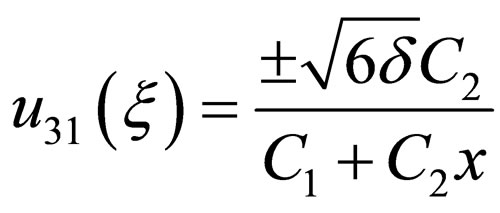 (4.11a)
(4.11a)
 (4.11b)
(4.11b)
where 
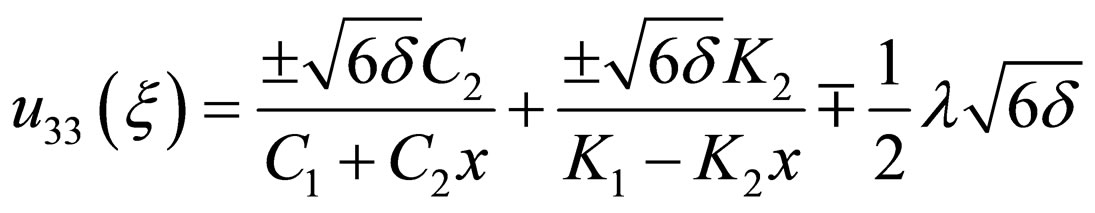 (4.11c)
(4.11c)
Where .
.
The example comes from Wange’s Letter [9], but it is worth noticing that the solutions (4.9c), (4.10c), (4.11c) are not obtained by Wang [9] by using the 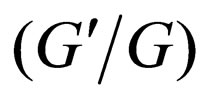 -expansion method. The example shows that the more abundant travelling solutions can be obtained by using the generalized tanh-function method.
-expansion method. The example shows that the more abundant travelling solutions can be obtained by using the generalized tanh-function method.
5. Conclusion
The generalized tanh-function type method can be viewed as an application of the transformed rational function method. In fact, using the idea of the transformed rational function method, many methods to solve NLPDEs can be obtained. In this letter we show that the 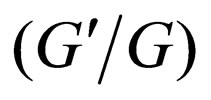 - expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method, so the
- expansion method is a special case of the generalized tanh-function type method, so the  -expansion method is considered as a special deformation application of the transformed rational function method. It is worthy noticing that the generalized tanh-function type method is more concise and straightforward to seek exact solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations (NLPDEs) and can be applied to many other NLPDEs in mathematical physics.
-expansion method is considered as a special deformation application of the transformed rational function method. It is worthy noticing that the generalized tanh-function type method is more concise and straightforward to seek exact solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations (NLPDEs) and can be applied to many other NLPDEs in mathematical physics.
6. Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Referees for valuable suggestions. This paper is supported by Jiaying University 2011KJZ01.