Received 11 November 2015; accepted 4 December 2015; published 7 December 2015


1. Introduction: Potential Problems with Relevance Theory in Real-Time Interpretation of Utterances
Relevance theory (RT) has made substantial contributions not only to linguistics but also to both the communication and cognitive sciences. As a theory of verbal communication and/or communication in general, RT defines relevance using two concepts that are cognitively well motivated: cognitive effects and processing costs. However, there are few studies that examine the plausibility of RT in the real-time interpretation of utterances or that utilize RT as an experimental framework to investigate the understanding of implicature1. One reason for the scarcity of studies in this area is the difficulty of experimentally manipulating cognitive effects and processing costs independently. However, an even more important reason from a theoretical perspective involves the evaluation of relevance. This article will discuss relevance from the perspective of real-time language processing and will propose a new evaluation of relevance that is appropriate to real-time communication. Specifically, I claim that relevance can be evaluated as the ratio of cognitive effects to the processing costs required for these effects. In this study, I demonstrate that my proposal produces favorable theoretical consequences regarding both the convergence of the computation of the interpretation of utterances and the disambiguation of potentially ambiguous utterances.
I begin my argument by identifying a theoretical and empirical problem in the evaluation of relevance by Sperber & Wilson (1995) . Next, I propose cognitive effects as the sigmoid function of processing costs based on various neural and cognitive findings that involve language processing, and relevance is thus defined at this juncture as the ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs. Finally, I demonstrate that the function of relevance has an extremal value and that this property of the function produces favorable theoretical consequences for understanding the intentions of a speaker.
2. Mutual Dependence between Cognitive Effects and Processing Costs
In this section, I identify a theoretical problem in the evaluation of relevance in RT from the perspective of real- time language processing. RT proposes (1) as the fundamental property of human cognition.
1) Cognitive principle of relevance
Human cognition tends to be geared toward the maximization of relevance (Sperber & Wilson, 1995, 2002) .
Relevance is defined by cognitive effects and processing costs in (2) and (3), respectively.
2) Cognitive effects
Enrichments, revisions and reorganizations of existing beliefs and plans that improve an organism’s knowledge and capacity for successful action.
3) Degree of relevance
a) An assumption is relevant in a context to the extent that its contextual effects in this context are large.
b) An assumption is relevant in a context to the extent that the effort required to process it in this context is small.
One of the first theoretical problems to be noted when interpreting an utterance is the problem of ambiguity. In other words, when two interpretations are possible―the first with small cognitive effects and low processing costs and the second with large cognitive effects and high processing costs―the evaluation criteria in (3) do not specify which interpretation is more relevant or how the more relevant interpretation should be chosen in real time. Although a speaker’s communicative intention is not always understood as intended and misunderstandings may occur when the speaker’s intention is not communicated well or is over-interpreted, we also know that the communicative intention of a speaker is understood correctly and instantaneously most of the time. We can thus assume that our cognitive system employs a mechanism to avoid or disambiguate the potential ambiguity in interpreting an utterance.
Another more important problem is the mutual dependence between cognitive effects and processing costs. Because the retrieval of context is not constrained in principle, there are an infinite number of contextual implications that can be derived. The cognitive effects thus monotonically increase as more processing resources are devoted to interpret an utterance. Hence, cognitive effects and processing costs are positively correlated in the real-time interpretation of utterances. Therefore, cognitive effects and processing costs can be understood as two separate manifestations of one processing entity, although the two are conceptually distinct. The mutual dependence between cognitive effects and processing costs is one of the primary reasons why it is difficult to apply RT to the real-time interpretation of utterances. For RT to be more effective in interpreting utterances, the evaluation of relevance by cognitive effects and processing costs should be more detailed than in (3).
3. Relevance in Real-Time Interpretation of Utterances: Relationship between Cognitive Effects and Processing Costs
In this section, I propose a new evaluation of relevance that is appropriate to the real-time interpretation of utterances. First, let us assume that cognitive effects increase on a linear basis as more cognitive efforts are expended, as shown in Figure 1.
At this juncture, we can assume that the retrieval of context proceeds from a more accessible context to a less accessible context. It is thus reasonable to assume that cognitive effects do not continue to increase on a linear basis with processing costs because it should require greater processing costs to retrieve less accessible contexts. The transition of cognitive effects will thus be saturated in the time course of processing, as shown in Figure 2.
As our first approximation, let us assume that the cognitive effects are a sigmoid function of processing costs in formula (1) in (4). A sigmoid function is the most common psychometric function in human neural and cognitive behaviors. Many recent studies report and examine sigmoid functions in experimental settings of human cognition, including those involving episodic memory (Kumaran & McClelland, 2012) , event-related potentials elicited by sentences (Sassenhagen, Schlesewsky, & Bornkessel-Schlesewsky, 2014) , the interaction between sound and vision in perception (Sutherland, Thut, & Romei, 2014) , visual awareness (Cox, Lowe, Blake, & Maier, 2014) , task accuracy and awareness (Sandberg, Bibby, Timmermans, Cleeremans, & Overgaard, 2011) ,
![]()
Figure 1. Linear relationship between cognitive effects and processing costs.
![]()
Figure 2. Linear relationship between cognitive effects with saturation and processing costs.
numerosity discrimination (Cappelletti, Didino, Stoianov, & Zorzi, 2014) , sense of agency (Farrer, Valentin, & Hupé, 2013) , and the judgment of borderline cases and contradictions, (Blutner, Pothos, & Bruza, 2013) . The constant C in the formula (1) indicates the value of the inflection point on the x-axis in Figure 3 and is understood to represent the accessibility of contexts and information retrieved in an utterance interpretation. In other words, C will be greater when the contexts to be retrieved regarding an utterance interpretation are less accessible.
4) Cognitive effects as a sigmoid function of processing costs, where C is the constant corresponding to the accessibility of contexts and the information to be retrieved.
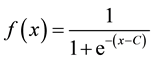 (1)
(1)
I can identify certain theoretically favorable properties of the sigmoid function between cognitive effects and processing costs. First, the increase in cognitive effects saturates shortly after the inflection point in the time course of the interpretation of an utterance. This saturation is a good manifestation of real-time utterance interpretation because more accessible contexts should be retrieved before less accessible contexts and because the cognitive effects achieved by contexts that are difficult to access should be small. Second, the value of the first derivative (f’(x)) increases until the inflection point is reached. Therefore, the cognitive effects gained per unit of processing costs increase as far as the inflection point, which should serve as strong motivation for processing because if a certain amount of cognitive effects is constantly gained from the very beginning of processing, then the comprehender will not be motivated to continue processing.
In the previous section, I noted the mutual dependence between cognitive effects and processing costs, and I claimed that relevance in such terms should be evaluated in greater detail. Now, as the simplest approximation of relevance in real-time utterance interpretation, I propose the ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs in formula (2) and Figure 4.
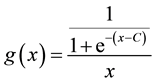 (2)
(2)
We should note here that the transition of relevance represented by formula (2) and Figure 4 reaches its maxi- mum point shortly after the processing cost reaches the inflection point. Next, I discuss the theoretical consequences of the maximum point.
4. Discussion: Theoretical Consequences
In this section, I discuss the theoretical consequences of my proposals: cognitive effects as the sigmoid function
![]()
Figure 3. Cognitive effects as a sigmoid function of processing costs.
![]()
Figure 4. Relevance as a ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs.
of processing costs and relevance as the ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs.
4.1. Convergence of Computation
The greatest difference between syntactic processing and interpreting an utterance―and the interpretation of implicature, in particular―is that there is no marker available to indicate the end of processing for the latter. Syntactic processing proceeds incrementally (to some extent) and ends by assigning a syntactic structure to the sentence input. By contrast, an utterance interpretation involves computing explicatures and inferences to derive implicatures, in addition to understanding the literal meaning of an utterance. Inferences deriving implicature are not necessarily deductive, and the logical consequences of these inferences are therefore not specified. The problem of the convergence of computation emerges here regarding when the retrieval of contexts and the inferences should be stopped. We know that the communicative intention of a speaker is instantaneously understood in general and that misunderstanding rarely arises. Therefore, it must be true that an utterance processor employs a mechanism to converge computation in interpreting an utterance. According to Sperber & Wilson (2002) , the comprehension process proceeds as in (5).
5) Relevance-theoretic comprehension procedure
a) Follow the path of least effort in computing cognitive effects. In particular, test interpretive hypotheses (e.g., disambiguations, reference resolutions, implicatures) in the order of accessibility.
b) Stop when your expectations of relevance are satisfied.
However, the convergence of processing proposed in (5b) is cognitively implausible; because cognitive effects are evaluated in comparison with a comprehender’s set of assumptions, it is impossible to predict the degree of relevance before the beginning of the interpretation. Moreover, the relevance function g(x) has certain favorable properties for the convergence of computation; thus, relevance increases following the beginning of interpretation but begins to decrease monotonically following the maximum point.
The comprehender can therefore decide to stop the computation at the maximum point, which can be recognized following the development of relevance and the efforts required for it. Thus, the comprehender does not have to predict the degree of relevance before beginning the interpretation. Furthermore, I believe that one of the greatest contributions of RT to pragmatics is the evaluation of relevance based on cognitive effects and processing costs that are conceptually independent from one another. This dichotomic evaluation enabled the scientific investigation of “relation” in Grice (1975) , but the relevance in (5b) seems primitive, which presupposes an independent mechanism to evaluate relevance. This presupposition may impair the original significance of RT. Nonetheless, we can maintain the significance of RT with the assumption of relevance as the ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs.
4.2. Ambiguity of Interpretation
Relevance is evaluated based on cognitive effects and processing costs in the original RT as in (6).
6) a) An assumption is relevant in a context to the extent that its contextual effects in this context are large.
b) An assumption is relevant in a context to the extent that the effort required to process it in this context is small.
One of the potential problems with RT that has been frequently identified since its early development is the possibility of ambiguity between an interpretation with small cognitive effects and small processing costs and one with large effects and high costs. Following (6), it seems difficult to choose one of the two possible interpretations. When we evaluate relevance by g(x) in formula (2), the interpretation is uniquely determined because the processing terminates at the maximum point. This finding is consistent with the observation that the communicative intention of a speaker is understood as intended by the comprehender most of the time.
4.3. Experimental Examination
The accessibility of the contexts to be retrieved in interpreting an utterance varies depending on the utterance context and on the comprehender’s assumptions. It is therefore assumed that C in the sigmoid function of relevance will change based on the situation and the assumptions. The maximum value of g(x) is given as the solution to the differential equation for the first derivative of g(x), as in formula (3)
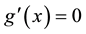 (3)
(3)
We can predict the relationship between C and processing costs (x) in the convergence of utterance interpretation by the Equation (3), as in formula (4) or (5).
 (4)
(4)
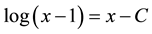 (5)
(5)
Processing costs can be experimentally observed as reading or reaction times and can also be observed in the strength of neural activity (e.g., in the amplitude of an event-related brain potential). Individual variation is expected regarding the accessibility of contexts for each utterance situation, and accessibility can be manipulated experimentally by presenting certain contexts. We can thus experimentally examine utterance interpretation in terms of relevance in the task of understanding communicative intention.
5. Conclusion
This article has proposed a new evaluation of relevance in real-time interpretation of utterances interpretation. I have demonstrated that the retrieval of context that is unlimited in principle will converge and that the potential ambiguity of an utterance interpretation can be resolved by assuming that relevance is the ratio of cognitive effects to processing costs. Moreover, this evaluation of relevance is theoretically favorable in that we can maintain the architecture of RT by evaluating relevance dichotomically based on cognitive effects and processing costs. Furthermore, experimental examination of the understanding of implicature is possible using RT as the experimental framework based on the assumption that the interpretation will converge at the maximum point of relevance.
NOTES
![]()
1We have found some experimental studies that examine the processes involved in interpreting utterances, including the recognition probe task for indirect speech acts by Holgraves (2008) , eye movements for scalar implicature by Huang & Snedeker (2009) and Grodner, Klein, Carbary, & Tanenhaus (2010) , and event-related potentials and magnetoencephalography for the perception of indirect speech acts by Egorova, Shtyrov, & Pulvermüller (2013) and Egorova, Pulvermüller, & Shtyrov (2014) . However, in these studies, we cannot determine that RT has been utilized to help design the experiments and/or to predict the results, although RT is sometimes referred to as the theoretical background for such studies. Gibbs Jr. & Bryant (2008) is one of the few studies that do examine RT in an experimental setting, although that study actually uses RT to interpret―rather than predict―experimental results.