An Approach to Energy Saving and Cost of Energy Reduction Using an Improved Efficient Technology ()
1. Introduction
The per capital electricity consumption of the developing countries has been considerably increased due to the increase in population and high demand for energy. Energy growth in Malaysia has been increasing in residential, commercial, industrial and transport [1] . An increase in energy consumption has a great implication on the environment and global warming, therefore the policy to use the energy efficiency should be taken into account [2] .
However, an efficient Management of Electrical energy Regulatory was introduced on 15 December, 2008 for the purpose of promoting energy efficiency in Malaysia. Thus, they make it compulsory for large commercial and industrial electrical consumers to manage their equipments so as to develop and implement EEMs to reduce energy losses, cost of energy and enforce efficient utilization of electrical energy [3] .
Due to the advancement of technology, researchers and engineers are always working to see that they produce an apparatus or equipments which are very efficient in terms of energy. Energy efficiency can be defined as using less energy to produce the same amount of services or useful output, for example, residential sector, commercial sector and industrial sector. Energy efficiency in terms of mathematical expression can be defined as the ratio of the useful output of a process and the energy input into a process, and it is expressed in percentage [4] .

The factors that contribute to high energy usage can be grouped into three.
Firstly, electricity consumption of the equipments itself. That is the purchase of fairly used equipment and non-energy efficient equipments.
Secondly, the number of equipments used for a particular place. As it is known that the number of equipments is directly proportion to the energy consumption. The used of many numbers of equipments such as fans, lights, air conditioner etc. than the design requirements.
Thirdly, the duration usage of the equipments. Long duration use of electrical equipment is directly proportion to the energy consumption [5] .
Buildings in the university are usually characterized by high amount of energy consumption. A large portion of energy is being channeled to lecture halls since learning and teaching are the main activities in the campus. As this building consumes a large portion of energy, the energy that being waste should be identified and also should find a way of achieving energy efficiency is very important, that is using less energy to provide the same amount [6] . Some of the advantages of efficient use of energy is shown in Figure 1 [7] .
![]()
Figure 1. Advantage of energy effifciency.
This paper aims at reducing the amount of energy consumption by replacing the existing electrical with high efficient electrical appliances; these also tend to reduce the cost of energy paid to the utility. It also presents the results and analysis of energy audit of five tutorial rooms, level 4 buildings in the Faculty of Electrical Engineering 19 A, University Teknologi Malaysia (UTM).
2. Methodology
In this section, the method and the steps carried out is briefly described based on the case study. In order to understand fully the concept, energy consumption, price of equipments, cost of energy saving, bill of saving and the payback period are clearly explained and analyzed.
2.1. Energy Management and Energy Auditing
Due to an increase in energy consumption worldwide, energy management and energy auditing are considered to be a global challenge [8] .
Energy management is termed as the strategy of adjusting and optimizing energy, using systems and procedures so as to reduce energy requirements per unit of output while holding constant or reducing total cost of producing the output of the systems while the users leave permanent access to the energy they need. The main objectives of energy managements are: resources conservation, climate protection and cost savings [9] .
An energy audit is a fundamental of energy management services which employs methods of energy analysis to evaluate the energy usage and develop energy efficiency measures EEMs in the building. The energy audit for this case study disclosed electrical energy usage for lighting, air conditioner and projector. However an improved energy efficient equipments or energy efficiency measures EEMs are used aimed at reducing the cost of energy [3] .
2.2. Electricity Consumption
The electricity consumption of the existing appliances and the proposed appliances was computed by multiplication of the number of equipments N, power rating W and the operating hours OH. The mathematical expression is given below:
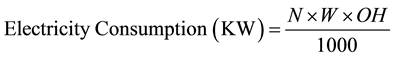
2.3. Cost of Electricity Consumption
Cost of electricity consumption is the multiplication of electricity consumption with the price of electricity per kW∙h [dsm5].
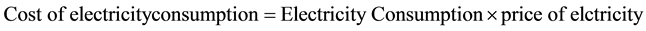
2.4. Energy Saving
Energy saving is the differences between the energy consumption of existing appliances and the proposed appliances.
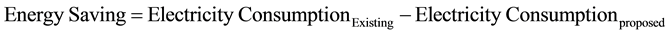
2.5. Bill Saving
Bill saving was computed by multiplying energy saving with the electricity tariff. The mathematical expression is given as:
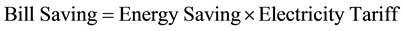
2.6. Payback Period
The payback period is defined as the time (usually expressed in years) required for the cumulative operational savings of an option (or equipment) to equal the investment cost of that option [2] .
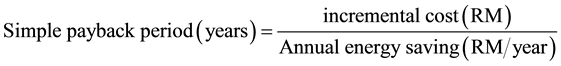
3. Study Area
Tutorial Room 1 to 5 located in block P19 at the Faculty of Electrical Engineering (FKE), UTM was selected as the case study area. The classrooms selected are used as a lecture theatre for graduate studies. Electrical wattage and quantity of each of the equipments were studied and recorded. We are able to count and record all the equipments from tutorial Room 1 to 5. Since the tutorial rooms have the same electrical equipments, therefore Table 1 shows the quantity of electrical equipments of one of the tutorial rooms, which is TR1.
3.1. Energy Audit of the Existing Equipments.
All the tutorial rooms have three things in common; which are; the air conditioning system, the projector and the lightning. The air conditioning system has the highest power consumption of 91.82%, followed by the projector system 7.39% and then the lightening bulbs 0.79%. The power consumption for each load is summarized in Table 2.
It should be noted that the level of energy consumption by each of the tutorial rooms differs, as each tutorial room has its own lecture time table. In Table 3, analysis of energy consumption characteristics for each of the selected tutorial rooms is carried out.
Although beside the used of lightning, projector and air conditioning, which are mainly provided for the purpose of lectures, sometime student comes with their handset chargers, laptop chargers and variety of electrical loads. These miscellaneous electrical loads are not included in this case study. Figure 2 shows the percentage of power consumption of the existing equipments. Air conditioner has the highest power consumption having 98.2% followed by projector with 7.39% and lighting with 0.79%.
![]()
Table 1. Quantity of electrical equipments in tutorial Room 1.
*For the five tutorial rooms × 5.
![]()
Table 2. Power consumption of existing equipments.
*For the five tutorial rooms × 5.
![]()
Table 3. Analysis of energy consumption characteristics of existing equipments.
*Energy consumption per year × 52.
![]()
Figure 2. Piechart of power consumption of the proposed equipments.
3.2. Proposed Efficient Energy Equipments and the Analysis of Energy Consumption
In this section, the energy efficient equipments are proposed to replace the existing equipments. Table 4 shows the less power consumption equipments that have high energy efficient than the existent ones.
In selecting the lightning bulb, A T5 lightning bulb with high lumens of about 3200 Lumens and with a power consumption of 21 W was selected to replace the existing one. The existing T8 lamps have lumens of about 2800 lumens. Therefore, using this T5 lamp reduces the number of lamps in each tutorial room from 40 lamps to 35 lamps. A projector with an 80 W energy consumption was also selected to replace the existing one of 300 W and air conditioner of 3 hp was selected to replace the existing one of 3730 W. Table 5 shows the of energy consumption for the proposed equipments. Figure 3 shows the percentage of power consumption of the proposed equipments, air conditioner has the highest wattage consumption with 95.7% followed by projector with 3.4% then the lighting lamp with 0.9%.
3.3. Analysis for Energy Saving, Cost of Energy and Payback Period
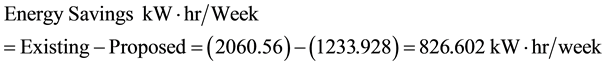
Therefore, energy saving per year = 42,983.304 kW∙hr/year
Using the data tariff obtained from the TNB website and as shown in Table 6, the cost energy consumption per kW∙hr is 36.5 sen/kW∙hr.
1) Total energy consumption of the existing equipments per week and per year is 2060.56 kW∙hr/week, and 107,149.12 kW∙hr/year respectively.
Therefore;
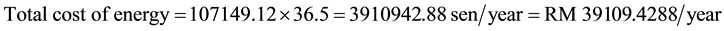
2) Total energy consumption of the proposed equipments per week and per year is 1233.928 kW∙hr/week, and 64,164.256 kWhr/year respectively.
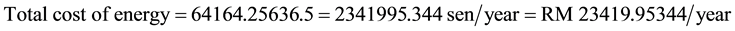
Total cost of energy saving RM 15,688.91/year.
3) The Payback period for the Air conditioner can be calculated as follows:
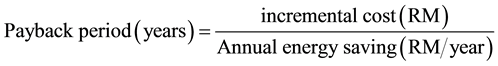
![]()
![]()
Figure 3. Piechart of power consumption of the existing equipment
![]()
Table 4. Proposed equipments to be replaced.
*For the five tutorial rooms × 5.
![]()
Table 5. Analysis of energy consumption characteristics for the proposed equipments.
*Energy consumption per year × 52.
Therefore the payback period of air conditioner is one (1) year. The same procedure applies to lighting and projector.
Table 7 shows the quantity numbers, incremental price (RM) which is the price difference between the pro- posed and existing equipment, annual energy saving (kWh), Energy bill saving (RM/years) and the payback period (years) of each equipments.
4. Conclusion
The analysis demonstrates how a meaningful amount of energy can be saved and minimized cost of energy in Tutorial Room 1 to 5 of block 19 in FKE. Although in the previous years, the university has tried tirelessly to reduce its energy consumption and cost of energy paid. Based on this case study, in order to achieve an optimal energy performance, energy audit is a good method to reduce the energy wastes and to improve the energy effi-
![]()
Table 6. TNB pricing and tariff of electricity consumption [10] .
![]()
Table 7. Energy efficiency measures for air conditioner, projector and lighting lamps.
ciency of the equipments considered for the case study, which are: lighting lamps, air conditioner and projector. Energy management and energy audit help in identifying several energy saving measures so as to improve the energy efficiency and reduce the cost of energy. From the analysis, it is calculated that if the proposed equipments are replaced, then the energy saved per year is 42,983.304 kW/hr and the cost of energy saving will be RM 15,688.91/year. If the university management can implement the proposed equipments, the energy consumption and the cost of energy will definitely reduce as seen in the analysis. The analysis in this paper is based on five tutorial rooms if compared to the university energy consumption is not up to 1%. Although the proposed equipments have high efficiency and less power consumption, their price is very expensive compared to the existing one. A payback period is calculated to show the time taken to recover its initial outlay from the saving of the cost of energy paid to the TNB.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.