Research on the Forecast and Development of China’s Public Fiscal Revenue Based on ARIMA Model ()
1. Introduction
The current fiscal year pre-determine count deviation widens the urgent need to enhance scientific and budget management. Revenue and expenditure for the coming fiscal year to carry out an accurate forecast, budget and final accounts for the lower deviation is significant. In this paper, revenue and expenditure for the time series, and the use of long sequences of its own laws and trends are analyzed. Looking for the relationship between fiscal revenue and expenditure is to predict future changes in revenue, to help reduce the budget deviation and to solve the budget execution “pro-cyclical” problem for reasonable budget plan, and the revenue from the constraints of the budget into prospective, the gradual establishment of a multi-year budget balancing mechanism.
2. Literature Review
Relationship between income and expenditure of government finance is the core issue of the budget involved, not only the need to balance the current relationship between fiscal revenue and expenditure, but to predict future revenue and expenditure, the budget is also a matter of efficiency.
Scholars almost have the following view: “living within our means”, the idea that changes in revenue caused by the financial expenditure; “Expenditure and Revenues”, the idea that the revenue expenditure decisions; the idea “fiscal sync” is that the financial revenue and expenditure and reinforce each other interdependence; the idea “institutional separation” is that there is no causal relationship between revenue and expenditure [1] . Some scholars from different countries and regions studied relationship between revenue and expenditure have quite different conclusions.
The study of the relationship between the revenue and expenditure in China is mainly focus on the relationship between taxes and spending, fiscal revenues and GDP, local government fiscal revenue and expenditure relations. Chang and Ho [2] analyzed the relationship by multivariate Granger causality test and error correction model (MVECM) to China’s revenue and expenditure of time series data in 1977-1999, get China’s fiscal synchronized views; Liuse the Association whole model 1950-2007 fiscal year balance of payments data that China's fiscal revenue and expenditure in different relations in different periods, were in line with “Expenditure and Revenues” and “fiscal sync” assumed; [3] Kai Wu, Chuwei Min analysis 1979-2003 fiscal revenues and GDP data for the year, and result is that there exists cointegrating relationship, but the revenue and expenditure in line with “institutional separation” theory; [4] Zihui Ma analysis the relationship between provincial financial revenue and expenditure drawn from the between 1979-1993 to two-way causality [5] .
Study abroad prediction model focused on the selection and improvement of the model, including changes to the city budget, local government property taxes to predict personal income tax forecasting studies [6] . Some scholars have combined genetic algorithm and BP neural network to build revenue forecasting model of tax revenue analysis and forecasting, particularly the use of BP neural network, gray prediction and self-regression model (Auto regressive and Moving Average Model, referred to as ARMA) methods [7] , in which the wider application ARMA method, mainly in electricity, coal, machinery and other fields, this method introduces some scholars, including investment in education [8] , administrative costs [9] , the stock market [10] , the credit asset markets [11] , real estate price index [12] and other areas of predictive analysis, but in revenue forecasting finances, especially at the national level Fiscal revenue forecast is seldom used.
Paper is structured as follows: firstly, the paper analyzes the relationship between revenue and expenditure based on the financial data in 1950-2013 with the cointegration, error correction method and Granger test; secondly, with the fiscal budget revenue source for the data in 1950-2013, use the ARIMA revenue forecasting model to predict the fiscal revenue; in which we choose five-year fiscal revenue data for testing in order to verify the accuracy and reliability of the ARIMA forecasting model in 2009-2013, and the data of 2014 and 2015 revenue provide reference to growth trend static forecast for our revenues; preliminary findings indicate that the role of people’s livelihood and financial might occur; and finally establish a multi-year balanced budget for around advice.
3. Relationship between Revenue and Expenditure
3.1. Variable Selection and Research Methods
To facilitate quantitative analysis, set income for SR, expenditures for natural ZC, the logarithm of income and expenditure, respectively LNSR and LNZC. Research method used is the correlation analysis, cointegration, error correction model test and causality test to obtain relevant information between revenue and expenditure by correlation analysis, cointegration test method to verify the existence of long-term revenue and expenditure between balanced relationship, error correction model is mainly on short-term relationship between the revenue and expenditure inspection, causality test is carried out in sequence through causal analysis cointegration test and error correction on the basis of income and expenditure observe causality.
3.2. Johansen Cointegration Test and Error Correction Model
Cointegration common stochastic trend that exists, the regression equation for the detection of non-stationary sequence, as reflected in the establishment of a causal relationship between the existence of spurious regression problem, and test a set of linear combinations of non-stationary sequence is a stable equilibrium relationship. Johansen cointegration test is based on the VAR system, two-step stationary test it by cointegration regression residuals variance carried out, it is applied to facilitate and provide cointegrating vectors, this article will use the Johansen cointegration test.
The premise of non-cointegration stationary time series must have the same order integration of nature. Stationary test data sequence mainly unit root test methods, unit root test is whether there is a sequence of test unit root, if there is a unit root, compared with non-stationary time series. Test methods are mainly ADF unit root test, KPSS test, LLC test methods, this paper uses stationary ADF test methods. The null hypotheses H0 of ADF test for time series is containing a unit root. The results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
As can be seen from the test results, the sequence LNSR and sequence LNZC are non-stationary, therefore the significance level of 5% of the test can’t accept the null hypothesis of a unit root sequence contains. ADF test results of the first difference stationary series of LNSR and LNZC sequences are smooth, which both have a single order to meet the basic premise of cointegration.
Test with Eviews software tool, select the item containing the intercept and trend, select the entire range of co-lag test is (1, 1), cointegration test results of inspection test results are as Table 3.
From Table 3, there can be seen that at a significance level of 0.05, the Johansen maximum eigenvalue eigenvalues test results are refused without a stable income and expenditure sequence relationship null hypothesis and accept the existence of a stable relationship up the assumption that there is a long-term stable relationship between income and expenditure.
Although there are long-term equilibrium relationship between revenue and expenditure of two variables, but due to the impact of unexpected events, such as short-term imbalances may occur in the short term, and therefore on the basis of cointegration test to be amended on short-term imbalances. Using differential income sequence Ñ lnzc t} on differential expenditure sequence Ñ lnsr t} and the pre-error sequence {ECM t − 1} least squares regression ECM model was constructed as follows:
 (1)
(1)
Parameter estimation results are as Table 4.
![]()
Table 1. ADF test results of the original sequence.
![]()
Table 2. ADF test results after the first difference.
![]()
Table 3. Johansen maximum eigenvalue test results.
![]()
Table 4. Error correction test results.
Test results as measured by the estimated error correction model and Table 6 results show that the error correction term ECM (−1). The coefficient is −0.5178, less than zero and statistically significant, indicating that China’s fiscal expenditure affected by fluctuations in the phase error, and financial fluctuations in the current period income has a significant impact on the current volatility of financial expenditure; from the perspective of the absolute value of the regression coefficients, current fluctuations in revenue for fiscal spending big adjustment, each additional dollar of revenue will increase 0.9987 yuan fiscal spending on the expenditure of the error on the volatility of the current period adjustment to a lesser extent, the unit to adjust the ratio of −0.5178.
The above analysis found that the 1950-2013 fiscal revenues sequence of {lnsr t} and expenditures sequence {lnzc t} is not smooth, its first order difference stationary series, and are integrated of order one, make Johansen cointegration test shows the existence of two cointegration relations, and establish a short-term fluctuations in the error correction model, obtain short-term equilibrium relationship between revenue and expenditure striking conclusion, to meet the basic premise of Granger test, can cause between revenue and expenditure relationship using Granger causality test empirical analysis.
3.3. Granger Causality Test
By Spearman correlation coefficient and partial correlation coefficients, there can be seen a significant positive correlation between income and expenditure, by cointegration test further demonstrates the existence of a long- term stable relationship between income and expenditure can be causality. In this paper, income and expenditure variables granger causality test, which relies on the use of the best least-squares prediction of all the information on the variance of some point in the past. Under the conditions of the time series, economic variables X, Y between Granger causality in predictors of future process changes in Y, if Y is based on past information has been added in the past information of X, Y of the prediction of the effect of causing enhancement, namely the variable X is conducive to future changes in the interpretation of Y, then X is Y Granger causality of reason.
Income (LNSR) and expenditure (LNZC) with two non-stationary-order single whole sequence cointegration tests, we found that the presence of long-term and stable relationship between the two, which can be Granger causality test, the following will build regression model estimation. Granger causality test hypotheses about x and y, the forecast information is reflected in the corresponding time series, based on the estimated regression testing following requirements:
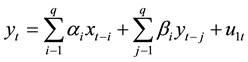 (2)
(2)
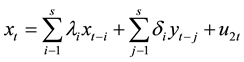 (3)
(3)
In actual operation, the use of Eviews 8.0 software revenue (LNSR) and expenditure (LNZC) conduct Granger causality test, and using Eveiws software under VAR model has been established for LNSR, LNZC Granger test, they observed the existence of a significant Granger causality. Lag choices have a greater impact on the test results, as to avoid causing lag selection error invalid test results, based on both the issue of our study, in Granger inspection has lagged its one, two, three tested, the results of both income and expenditure related to the inclusion in Table 5.
From the above table test, concluded that in the case of second-order lag, income is the Granger cause of expenditures. This is our principle to prepare the budget fixed income support adapt to the relationship between income and expenditure budget and final accounts as the basis, during the fiscal year forecast, the revenue forecast for the key points. China’s fiscal budget the main reference for the future year revenue forecast, forecasting accuracy will directly affect the rationality of budgeting, thus affecting the financial budget and final accounts to perform and lead to deviation. In this paper, a non-steady-order single whole sequence income variable constructed ARIMA model for forecasting revenue analysis.
![]()
Table 5. Granger causality test results.
Note: *indicates a probability value P value of less than 5% significance level, reject the null hypothesis.
4. Arima Model Estimation, Testing and Forecasting
4.1. Study Design
ARIMA (p, d, q) model is autoregression for the non-stationary sequence quadrature moving average process. Which refers to the autoregressive AR, p refers to the number of autoregressive model; MA moving average, q is the number of items moving average model; I mean is integral, d is the sequence must become stable before whichever difference times.
General expression ARIMA (p, d, q) model is:
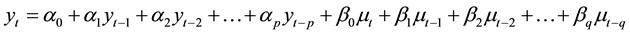 (1)
(1)
ARIMA model established steps include: first, the time series and zero mean stationary process, ARIMA time series model building premise is to meet zero mean and stability, this paper conversion and zero mean difference of test processing; second, model identification, determined in accordance with stationary test d value, using time series correlation diagram (ACF) and partial correlation chart (PACF) to select the appropriate p, q value; third, choose the model parameter estimation, testing whether statistical significance; fourth, the diagnostic model adaptability, white noise tests conducted residual sequence; fifth, in the choice of the optimal ARIMA model on the basis of income projections.
This paper obtain 64 years of data from 1950 to 2013 years, of which 1950-2008 year data as a sample, using 2009-2013 five-year revenue data as the test value, designed to test the predictive value and the real value error between.
4.2. Variables and Data
To ensure consistent caliber, 1950-2013 years of research based on data gathered from public financial revenue, “China Financial Yearbook” balance of payments data released by the Finance Budget and Finance disclosure.
Figure 1 is a revenue (LNSR) sequence timing diagram, Figure 2 is a timing diagram showing the sequence LNSR differential post, can be seen in the income (LNSR) differential processing sequence after a reduced tendency to fluctuation of time, observing values fluctuate around the mean, and the mean time t is independent stabilized. To test the difference after stationary sequence, the first difference of the series after the ADF test, ADF test of the null hypothesis H0 for time series contain a unit root. The results are shown in Table 6.
Mean difference transformation of the test and zero. From Table 6 ADF stationary test results, revenue (LNSR) non-stationary series, but after the first difference stationary, the sequences were obtained first-order differential processing income (DLNSR) sequences.
For the zero mean test of stationary sequence DLNSR, the null hypothesis is that DLNSR’s mean being set to zero. As is shown that, the distribution of the sample mean m = 0.118865, sample standard deviation s = 0.15 6854, the sample mean to fall between (0 ± 2)s, which can not reject the hypothesis sequence DLNSR mean zero. Accept the null hypothesis of zero mean that the overall sequence DLNSR is zero mean sequence.
4.3. Model Estimation and Testing
Observed autocorrelation and partial autocorrelation function stationary sequence, if the partial correlation function for censored nature, and the autocorrelation function is trailing, you can conclude that this sequence applies to AR model; if the partial correlation function is trailing, autocorrelation function is truncated, the sequence for MA model; partial correlation function and the autocorrelation function if the stationary time series are trailing, and is suitable for ARMA models. This paper mainly from stationary series DLNSR correlation analysis and
![]()
Figure 2. DLNSR sequence timing diagram.
partial correlation diagram drawn DLNSR related sequences and partial correlation diagram below to identify the appropriate p, q value.
Figure 3 is the serial correlation and partial correlation graph, which is trailing, applicable ARMA model. Setting p, q value late model estimation and testing, to AIC Akaike information criterion for the selection of the basis, after repeated screening, and ultimately determine p = 2, q = 6. And because the sample sequence for a first-order differential DLNSR smooth sequence, so d = 1, and therefore to determine the optimal model for the ARIMA (2, 1, 6).
Based on the above analysis of the sample sequence DLNSR the ARIMA (2, 1, 6) model, least squares regression, the first model:
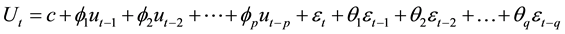 (4)
(4)
where p = 2, q = 6, Ut is DLNSR.
The above model was fitted using least squares regression to obtain the estimated coefficients and significance levels are as follows (Table 7).
![]()
Figure 3. Serial correlation and partial correlation.
![]()
Table 7. Regression results of ARIMA (2, 1, 6) model.
The results of model fitting P value significance level of 0.05 T statistic compares to reject the null hypothesis, by t test that model fit remarkably effective. R2 was 0.51 higher goodness fitting description, model fit well. AR and MA root observed values are within the unit circle, considered the model is valid.
After the parameter estimation, adaptive response model fit tested, mainly on the model residuals white noise test sequence. If the residuals are not white noise, indicating that there is some important information has not been extracted, should be re-set model. You can test for residuals pure randomness, can also be used for residuals test, get a white noise sequence, it shows the time series of useful information has been extracted is completed, the rest is random disturbance, unpredictable and used in the modeling can be terminated. If the residuals are not white noise, it shows that there is residual useful information; you need to modify the model or further extraction. Figure 4 is the fitting chart of residuals and Figure 5 is the timing chart of residuals.
First, the observation residuals fitting diagram and timing chart, we can see a steady residual fundamental volatility model fits better. Then we do the residual white noise test. The main basis to determine whether the residual white noise sequence is to observe whether the autocorrelation coefficients are all within the sample sequence random intervals. Residual white noise test sequence, if it is white noise sequence, through testing. Therefore, the residual sequence autocorrelation and partial correlation test, the null hypothesis that the residual sequence is white noise sequence.
As can be seen from Figure 6 residual autocorrelations and partial correlation diagram, autocorrelation coefficient (AC) random values fall within the range. Q statistic p value from the point of view, each probability value is greater than the significance level of 0.05, indicating that there are less than the Q value of the test level of 0.05 chi-square distribution critical value, random error model is established after a white noise sequence, you can accept the null hypothesis, the residual sequence is white noise sequence, establish a reasonable model.
We should also observe whether there exist ARCH effects. ARCH (2) effect test results are shown in Table 8.
LM test statistic and its use being accompanied by a significant level of probability and comparison to determine whether the presence of ARCH effects residuals, the null hypothesis of LM test is: LM test regression coefficient is zero, that does not have the ARCH effects. As can be seen from Table 8, LM statistical value of 0.18, with the probability of 0.92, was significantly greater than the significance level α = 0.05, the null hypothesis can be accepted that the ARIMA (2, 1, 6) models ARCH effect does not exist, model is valid.
4.4. Forecasting and Analysis
In order to test the effect of the forecast on China 2009-2013 five-year revenue with model ARIMA (2, 1, 6), we forecast the dynamic and static prediction forecast chart as follows.
Figure 7 and Figure 8 for the dynamic prediction chart can be seen from the timing diagram in Figure 7 predicted values, the data obtained in the basic dynamic prediction presents a linear trend in Figure 8 comparison of actual and predicted values found in the results of dynamic prediction error large, dynamic prediction method should not be used to predict revenue.
![]()
Figure 6. Residuals autocorrelation and partial correlation chart.
![]()
Figure 7. Dynamic predictive value (SRF).
Static analysis and found that the prediction error between the predicted value and the actual value is smaller predictive value was observed from Figure 9 presents a timing diagram of the basic exponential growth, which is consistent with the actual revenue growth trend. Figure 10 predictive value compared with the original sequence SR found good fitting results, the paper selection static prediction method to predict revenue.
By static prediction respectively 2009-2013 year data to predict the predicted value and the actual comparison of the data as Table 9.
Table 9 predictions observed, 2009-2013 year forecast error rate is small, good prediction results. Using the same static prediction method, in 2014 and 2015 revenue forecast to do, the results are shown in Figure 11, the result is forecast revenue of 14.2 trillion Yuan in 2014, forecast revenue of 15.61 trillion Yuan in 2015, the actual prediction results will be verified in the actual implementation of the results of these two years.
Figure 11 is 1994-2013 fiscal year revenue growth and GDP growth line graph, the connection can be seen from a low point in 1994-2013, far higher than the overall GDP growth in revenue, this 20-year period growth
![]()
Figure 9. Static predictive value (SRF).
![]()
Table 8. ARCH (2) effects of lm test results.
![]()
Figure 11. Revenue growth in comparison with the GDP growth rate (%).
![]()
Table 9. Static prediction (unit: one trillion yuan).
has become the norm and frequent fluctuations, fluctuations in the difference between 3.72% - 19.41%; from the smooth growth of view, GDP growth tends to stable, while revenue growth rate fluctuations, the lowest in 10.14%. The highest growth rate is 32.41%. From 2012 to 2013, revenue growth rate dropped from 25% to 10.14%.
Forecast the revenue of 2014 and 2015, forecast future revenues derived growth rate is 9.93% and 9.97%, from the predicted results, 2013-2015 annual revenue growth rate fluctuations basically a steady trend, slowing revenue growth, which may be associated with the Chinese government in recent years to implement the people’s livelihood fiscal and other policies, fiscal revenue slowed development will contribute to improving the livelihood of public finance policy and goal-oriented.
5. Conclusions
Through revenue and expenditure respectively causality and revenue forecasts empirical research use ARIMA China’s fiscal revenue model to predict and fit the sample data and the real value is a relatively low error rate, and the actual prediction model construction with high reliability, you can predict the future annual revenue.
Forecast budgeting have an important role in the fiscal year, forecasting revenue and expenditure from the budget to improve the ability to execute the process of resolving the revenue and expenditure of the “pro-cyc- lical” that is to break even when the recession is caused by the economy “worse” and achieve economic prosperity when the balance of payments and lead to “hot on the heating” problem, to achieve budget revenue from binding into a prospective, multi-year budget balancing mechanism to establish the angle of departure, such as the need to establish the revenue and expenditure forecasting system to improve revenue forecasting accuracy, and to prompt fiscal year forecast a more systematic and facilitation. This study provides a reference of budget revenue forecasting methods and models.
Public finance policy effects from future financial expenditure forecasts deviate gradually narrowing trend in order to improve people’s livelihood and development-oriented emerging. Our revenue growth rate is higher than the GDP growth rate and frequent fluctuations, but revenue growth rate is declined significantly in recent years, and the forecast growth in the next two years is basically in a steady revenue volatility trend. And strengthening the people’s livelihood spending slows revenue growth rate, and may be associated with the Chinese government in recent years to finance the implementation of livelihood. At the insistence of the people’s livelihood improvement and development oriented public finances continuing role, it may achieve more significant results in improving people’s livelihood and future development.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.