Linear Dimension Reduction for Multiple Heteroscedastic Multivariate Normal Populations ()
1. Introduction
The fact that the Bayes probability of misclassification (BPMC) of a statistical classification rule does not increase as the dimension or feature space increases, provided the class-conditional probability densities are known, is well-known. However, in practice when parameters are estimated and the feature-space dimension is large relative to the training-sample sizes, the performance or efficacy of a sample discriminant rule may be considerably degraded. This phenomenon gives rise to a paradoxical behavior that [1] has called the curse of dimensionality.
An exact relationship between the expected probability of misclassification (EPMC), training-sample sizes, feature-space dimension, and actual parameters of the class-conditional densities is challenging to obtain. In general, as the classifier becomes more complex, the ratio of sample size to dimensionality must increase at an exponential rate to avoid the curse of dimensionality. The authors [2] have suggested a ratio of at least ten times as many training samples per class as the feature dimension increases. Hence, as the number of feature variables p becomes large relative to the training-sample sizes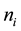 ,
, 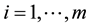 , where m is the number of classes, one might wish to use a smaller number of the feature variables to improve the classifier performance or computational efficiency. This approach is called feature subset selection.
, where m is the number of classes, one might wish to use a smaller number of the feature variables to improve the classifier performance or computational efficiency. This approach is called feature subset selection.
Another effective approach to obtain a reduced dimension to avoid the curse of dimensionality is linear dimension reduction (LDR). Perhaps the most well-known LDR procedure for the m-class problem is linear discriminant analysis (LDA) from [3] , which is a generalization of the linear discriminant function (LDF) derived in [4] for the case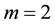 . The LDA LDR method determines a vector
. The LDA LDR method determines a vector 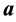 that maximizes the ratio of between- class scatter to average within-class scatter in the lower-dimensional space. The sample within-class scatter matrix is
that maximizes the ratio of between- class scatter to average within-class scatter in the lower-dimensional space. The sample within-class scatter matrix is
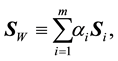 (1)
(1)
where 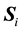 is the estimated sample covariance matrix for the ith class, and the sample between-class scatter matrix is
is the estimated sample covariance matrix for the ith class, and the sample between-class scatter matrix is
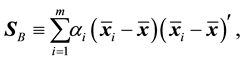 (2)
(2)
where 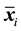 is the sample mean vector for class
is the sample mean vector for class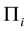 ,
, 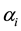 is its a priori probability of class membership,
is its a priori probability of class membership, 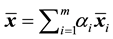 is the estimated overall mean, and
is the estimated overall mean, and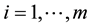 . For
. For 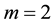 with
with , [4] determined the vector
, [4] determined the vector 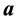 that maximizes the criterion function
that maximizes the criterion function
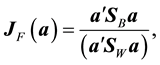
which is achieved by an eigenvalue decomposition of![]() . An attractive feature of LDA as a LDR method is that it is computationally appealing; however, it attempts to maximally separate class means and does not incorporate the discriminatory information contained in the differences of the class covariance matrices. Many alternative approaches to the LDA LDR method have been proposed. For example, canonical variables can be viewed as an extension to the LDF when
. An attractive feature of LDA as a LDR method is that it is computationally appealing; however, it attempts to maximally separate class means and does not incorporate the discriminatory information contained in the differences of the class covariance matrices. Many alternative approaches to the LDA LDR method have been proposed. For example, canonical variables can be viewed as an extension to the LDF when ![]() and
and ![]() (see [5] ). Other straightforward extensions of the LDF include those in [6] [7] .
(see [5] ). Other straightforward extensions of the LDF include those in [6] [7] .
Extensions of LDA that incorporate information on the differences in covariance matrices are known as heteroscedastic linear dimension reduction (HLDR) methods. The authors [8] have proposed an eigenvalue-based HLDR approach for![]() , utilizing the so-called Chernoff criterion, and have extended the well-known LDA method using directed distance matrices that can be considered a generalization of (2). Additional HLDR methods have been proposed by authors such as [9] - [10] .
, utilizing the so-called Chernoff criterion, and have extended the well-known LDA method using directed distance matrices that can be considered a generalization of (2). Additional HLDR methods have been proposed by authors such as [9] - [10] .
Using results by [13] that characterize linear sufficient statistics for multivariate normal distributions, we develop an explicit LDR matrix ![]() such that
such that
![]()
where![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() denotes the space of all
denotes the space of all ![]() real matrices. Using the Bayes classification procedure in which we assume equal costs of misclassification and that all class parameters are known, we determine the reduced dimension
real matrices. Using the Bayes classification procedure in which we assume equal costs of misclassification and that all class parameters are known, we determine the reduced dimension ![]() that is the smallest reduced dimension for which there exists a LDR matrix
that is the smallest reduced dimension for which there exists a LDR matrix ![]() that preserves all of the classification information originally contained in the p-dimen- sional feature space. We then derive a linear transformation that assigns
that preserves all of the classification information originally contained in the p-dimen- sional feature space. We then derive a linear transformation that assigns ![]() to
to ![]() if and only if the corresponding Bayes classification rule assigns
if and only if the corresponding Bayes classification rule assigns ![]() to
to![]() , where
, where![]() . We refer to this method as the SY LDR procedure.
. We refer to this method as the SY LDR procedure.
Moreover, we use Monte Carlo simulations to compare the classification efficacy of the BE method, sliced inverse regression (SIR), and sliced average variance estimation (SAVE) found in [14] -[16] , respectively, with the SY method.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. We begin with a brief introduction to the Bayes quadratic classifier in Section 2 and introduce some preliminary results that we use to prove our new LDR method in Section 3. In Section 4, we provide conditions under which the Bayes quadratic classification rule is preserved in the low-dimensional space and derive a new LDR matrix. We establish a SVD-based approximation to our LDR procedure along with an example of low-dimensional graphical representations in Section 5. We describe the four LDR methods that we compare using Monte Carlo simulations in Section 6. We present five Monte Carlo simulations in which we compare the competing LDR procedures for various population parameter configurations in Section 7. In Section 8, we compare the four methods using bootstrap simulations for a real data example, and, finally, we offer a few concluding remarks in Section 9.
2. The Bayes Quadratic Classifier
The Bayesian statistical classifier discriminates based on the probability density functions![]() ,
, ![]() , of each class. The Bayes classifier is optimal in the sense that it maximizes the class a posteriori probability provided all class distributions and corresponding parameters are known. That is, suppose we have m classes,
, of each class. The Bayes classifier is optimal in the sense that it maximizes the class a posteriori probability provided all class distributions and corresponding parameters are known. That is, suppose we have m classes, ![]() , with assumed known a priori probabilities
, with assumed known a priori probabilities![]() , respectively. Also, let
, respectively. Also, let ![]() denote the p-dimensional multivariate normal density corresponding to population
denote the p-dimensional multivariate normal density corresponding to population![]() ,
,![]() . The goal of statistical decision theory is to obtain a decision rule that assigns an unlabeled observation
. The goal of statistical decision theory is to obtain a decision rule that assigns an unlabeled observation ![]() to
to ![]() if
if ![]() is the maximum overall a posteriori
is the maximum overall a posteriori![]() ,
,![]() . Then,
. Then,
![]()
the Bayes classifier assigns ![]() to class
to class ![]() if
if
![]()
This decision rule partitions the measurement or feature space into m disjoint regions![]() , where
, where![]() , such that
, such that ![]() is assigned to class
is assigned to class ![]() if
if![]() . Using Bayes’ rule, the a posteriori probabilities of class membership
. Using Bayes’ rule, the a posteriori probabilities of class membership ![]() can be defined as
can be defined as
![]()
One can re-express the Bayes classification as the following:
Assign ![]() to
to ![]() if
if
![]() (3)
(3)
This decision rule is known as the Bayes’ classification rule. Let ![]() be modeled as a p-dimensional multivariate normal distribution, and let
be modeled as a p-dimensional multivariate normal distribution, and let
![]() (4)
(4)
The Bayes decision rule (4) is to classify the unlabeled observation ![]() into the class
into the class ![]() such that
such that![]() . The classification rule defined by (4) is known as the quadratic discriminant function (QDF), or the quadratic classifier.
. The classification rule defined by (4) is known as the quadratic discriminant function (QDF), or the quadratic classifier.
3. Preliminary Results
The following notation will be used throughout the remainder of the paper. We let ![]() denote the set of
denote the set of ![]() positive definite matrices and
positive definite matrices and ![]() denote the set of
denote the set of ![]() symmetric matrices. Also, we let
symmetric matrices. Also, we let ![]() represent the Moore-Penrose pseudo-inverse of
represent the Moore-Penrose pseudo-inverse of![]() .
.
The proof of the main result for the derivation of our new LDR method requires the following notation and lemmas. Let ![]() be
be
![]() (5)
(5)
where![]() ,
, ![]() such that
such that![]() , and
, and ![]() and
and ![]() for at least one value of k, where
for at least one value of k, where ![]() and
and![]() . Also, let
. Also, let![]() , and let
, and let ![]() and
and ![]() be matrix components of a full-rank decomposition of
be matrix components of a full-rank decomposition of ![]() so that
so that ![]() with
with![]() . Then, the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse of
. Then, the Moore-Penrose pseudoinverse of ![]() is
is![]() , and, also,
, and, also, ![]() and
and![]() . This result implies that for
. This result implies that for![]() ,
,
(i) ![]() and
and
(ii)![]() .
.
We now state and prove three lemmas that we use in the proof of our main result.
Lemma 1 For ![]() in (5), where
in (5), where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() such that
such that![]() , and
, and![]() , we have that
, we have that
(a)![]() ,
,
(b)![]() , and
, and
(c)![]() .
.
Proof. Part (a) follows from the fact that![]() ,
, ![]() , and from (ii) above. Parts (b) and (c) follow directly from (a).
, and from (ii) above. Parts (b) and (c) follow directly from (a).
Lemma 2 For ![]() in (5), where
in (5), where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() such that
such that
![]() , and
, and![]() , we have that
, we have that![]() .
.
Proof. Because ![]() and
and![]() , the result follows because
, the result follows because
![]()
Lemma 3 Let ![]() in (5), where
in (5), where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() such that
such that![]() , and
, and![]() . Also, let
. Also, let![]() , where
, where ![]() such that
such that![]() . Then,
. Then,
(a) ![]()
(b)![]() , where
, where![]() , and
, and
(c)![]() .
.
Proof. The proof of part (a) of Lemma 3 follows from (i), and we have that
![]() (6)
(6)
for each![]() . Hence, (b) and (c) follow from (6).
. Hence, (b) and (c) follow from (6).
4. Linear Dimension Reduction for Multiple Heteroscedastic Nonsingular Normal Populations
We now derive a new LDR method that is motivated by results on linear sufficient statistics derived by [13] and by a linear feature selection theorem given in [17] . The theorem provides necessary and sufficient conditions for which a low-dimensional linear transformation of the original data will preserve the BPMC in the original feature space. Also, the theorem provides a representation of the LDR matrix.
Theorem 1 Let ![]() be a p-dimensional multivariate normal population with a priori probability
be a p-dimensional multivariate normal population with a priori probability![]() , mean
, mean![]() , and covariance matrix
, and covariance matrix![]() ,
, ![]() , such that
, such that ![]() and
and ![]() for some
for some![]() . Next, let
. Next, let
![]() (7)
(7)
Finally, let ![]() be a full-rank decomposition of
be a full-rank decomposition of![]() , where
, where![]() . Then, the p- dimensional Bayes procedure assigns
. Then, the p- dimensional Bayes procedure assigns ![]() to
to ![]() if and only if the q-dimensional Bayes procedure assigns
if and only if the q-dimensional Bayes procedure assigns ![]() to
to ![]() for
for![]() .
.
Proof. Let
![]()
where![]() ,
,![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be full-rank with
be full-rank with![]() , where
, where
![]() such that
such that![]() . Then
. Then![]() , where
, where
![]()
![]() . By Lemma 3, we conclude that
. By Lemma 3, we conclude that ![]() and
and ![]() for
for![]() . Thus,
. Thus,
![]() . That is,
. That is, ![]() does not depend on class
does not depend on class![]() .
.
Recall that for![]() ,
, ![]() , the p-variate Bayes procedure defined by (3) assigns
, the p-variate Bayes procedure defined by (3) assigns ![]() to
to ![]() if and only if
if and only if
![]()
Therefore, the original p-variate Bayes classification assignment is preserved by the linear transformation![]() .
.
Theorem 1 is important in that if its conditions hold, we obtain a LDR matrix for the reduced q-dimensional subspace such that the BPMC in the q-dimensional space is equal to the BPMC for the original p-dimensional feature space. In other words, provided the conditions in Theorem 1 hold, we have that the LDR matrix ![]() exists and that
exists and that![]() , where
, where![]() .
.
With the following corollary, we demonstrate that for two multivariate normal populations such that ![]() and
and![]() , our LDR matrix derived in Theorem 1 reduces to the LDF of [4] .
, our LDR matrix derived in Theorem 1 reduces to the LDF of [4] .
Corollary 1 Assuming we have two multivariate normal populations ![]() and
and![]() , the pro- posed LDR matrix in Theorem 1 reduces to
, the pro- posed LDR matrix in Theorem 1 reduces to![]() , which is the well-known Fisher’s LDF.
, which is the well-known Fisher’s LDF.
Proof. The proof is immediate from (7).
5. Low-Dimensional Graphical Representations for Heteroscedastic Multivariate Normal Populations
5.1. Low-Dimensional LDR Using the SVD
If![]() , one cannot use Theorem 1 to directly obtain a
, one cannot use Theorem 1 to directly obtain a ![]() LDR matrix that preserves the full- feature BPMC. Also, in some situations when Theorem 1 holds, we may desire to determine a low-dimensional representation with dimension less than q, say r, where
LDR matrix that preserves the full- feature BPMC. Also, in some situations when Theorem 1 holds, we may desire to determine a low-dimensional representation with dimension less than q, say r, where![]() . Even if the required conditions of Theorem 1 hold, we may desire to determine a low-dimensional representation with dimension less than q, say r, where
. Even if the required conditions of Theorem 1 hold, we may desire to determine a low-dimensional representation with dimension less than q, say r, where![]() . Thus, we seek to construct an r-dimensional representation which preserves as much of the original p-dimensional BPMC as possible.
. Thus, we seek to construct an r-dimensional representation which preserves as much of the original p-dimensional BPMC as possible.
One method of obtaining an r-dimensional LDR matrix, ![]() , is the SVD approximation to
, is the SVD approximation to ![]() in (7). We use the following theorem from [17] to determine such an r-dimensional LDR matrix.
in (7). We use the following theorem from [17] to determine such an r-dimensional LDR matrix.
Theorem 2 Let ![]() denote the class of all
denote the class of all ![]() real matrices of rank p, and let
real matrices of rank p, and let ![]() denote the class of all
denote the class of all ![]() real matrices of rank r, where
real matrices of rank r, where![]() . If
. If ![]() and
and![]() , given by
, given by![]() , then
, then
![]()
where![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the usual Euclidean or Frobenius norm of a matrix
is the usual Euclidean or Frobenius norm of a matrix![]() , given by
, given by
![]()
Furthermore,![]() .
.
Using Theorems 1 and 2, we now construct a linear transformation for projecting high-dimensional data onto a low-dimensional subspace when all class distribution parameters are known. Let ![]() be the SVD of the matrix
be the SVD of the matrix![]() , where
, where ![]() for
for![]() ,
, ![]() , which are the singular values of
, which are the singular values of ![]() with
with ![]() for
for![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() for
for![]() . Let
. Let ![]() and define
and define
![]() with
with ![]() for
for![]() . From Theorem 2, we have that
. From Theorem 2, we have that ![]()
is a rank-r approximation of![]() , and, therefore, a rank-r approximation to
, and, therefore, a rank-r approximation to ![]() is
is![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() is an
is an ![]() LDR matrix that yields an r-dimensional representation of the original p-dimensional class models. One can also use
LDR matrix that yields an r-dimensional representation of the original p-dimensional class models. One can also use ![]() to construct low-dimensional representations of high-dimensional class densities.
to construct low-dimensional representations of high-dimensional class densities.
We next provide an example to demonstrate the efficacy of Theorems 1 and 2 to determine low-dimensional representations for multiple multivariate normal populations with known mean vectors and covariance matrices. In the example, we display the simplicity of Theorem 1 to formulate a low-dimensional representation for three populations ![]() with unequal covariance matrices and original dimension
with unequal covariance matrices and original dimension![]() . Note that unlike the low-dimensional representation of [18] , our Theorem 1 does not restrict the reduced dimension to be
. Note that unlike the low-dimensional representation of [18] , our Theorem 1 does not restrict the reduced dimension to be![]() .
.
5.2. Example
Consider the configuration![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() , where
, where
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
We have![]() , and, thus, by Theorem 1, the six-dimensional multivariate normal densities can be compressed to the dimension
, and, thus, by Theorem 1, the six-dimensional multivariate normal densities can be compressed to the dimension ![]() without increasing the BPMC.
without increasing the BPMC.
Using Theorem 1, we have that an optimal two-dimensional representation space is![]() , where
, where
![]() (8)
(8)
The optimal two-dimensional ellipsoidal representation is shown in Figure 1.
We can also determine a one-dimensional representation of the three multivariate normal populations through application of the SVD described in Theorem 2 applied to the matrix M given in (7). A one-dimensional representation space is column one of the matrix F in (8), and the graphical representation of this configuration of univariate normal densities is depicted in Figure 2.
6. Four LDR Methods for Statistical Discrimination
In this section, we present and describe the four LDR methods that we wish to compare and contrast in Sections 7 and 8.
![]()
Figure 1. The optimal two-dimensional representation for normal densities from the example in Section 5.2.
![]()
Figure 2. The optimal one-dimensional representation for normal densities from the example in Section 5.2.
6.1. The SY Method
In Theorem 1, we assume the parameters ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() , are known, but in reality this assumption is rarely the case. In a sampling situation, we can replace the columns of the
, are known, but in reality this assumption is rarely the case. In a sampling situation, we can replace the columns of the ![]() matrix in (7) by their sample estimators yielding
matrix in (7) by their sample estimators yielding
![]()
provided![]() ,
,![]() . Our estimator
. Our estimator![]() , along with Theorems 1 and 2, yields a LDR technique based on the selection of an r-dimensional hyperplane determined from a rank-r approximation to the full-rank matrix
, along with Theorems 1 and 2, yields a LDR technique based on the selection of an r-dimensional hyperplane determined from a rank-r approximation to the full-rank matrix![]() .
.
Thus, using the SVD, we let![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() are the singular values of
are the singular values of ![]() for
for![]() , and let
, and let![]() . Also, let
. Also, let
![]() (9)
(9)
with ![]() for
for ![]() and
and![]() . From Theorem 2, we have that
. From Theorem 2, we have that ![]() is a rank-r approximation of
is a rank-r approximation of![]() , and a rank-r approximation to F is
, and a rank-r approximation to F is![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() is our new
is our new ![]() LDR matrix.
LDR matrix.
Provided ![]() is relatively small,
is relatively small, ![]() will yield an
will yield an ![]() such that
such that
![]() , and in certain population parameter configurations, we may have that
, and in certain population parameter configurations, we may have that ![]() . We refer to our new LDR matrix as the SY LDR method.
. We refer to our new LDR matrix as the SY LDR method.
6.2. The BE Method
A second LDR method presented by [14] is
![]()
for![]() , provided all multivariate normal population parameters are known. For the unknown parameter case, an estimator of
, provided all multivariate normal population parameters are known. For the unknown parameter case, an estimator of ![]() is then
is then
![]() (10)
(10)
The LDR matrix derived in [14] , which we refer to as the BE matrix, was also obtained when we determined low-rank approximation to ![]() by using the SVD. That is, let
by using the SVD. That is, let ![]() be the SVD of
be the SVD of![]() , where
, where
![]() (11)
(11)
with ![]() for
for![]() , and let
, and let![]() . Define
. Define ![]() as in (9) with
as in (9) with ![]() for
for![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() is a rank-r approximation of
is a rank-r approximation of![]() , and
, and ![]() is a rank-r approximation of
is a rank-r approximation of![]() . Thus, the BE LDR matrix is
. Thus, the BE LDR matrix is![]() , or, equivalently,
, or, equivalently, ![]() , where the
, where the ![]() eigenvector corresponds to the
eigenvector corresponds to the ![]() largest singular value and
largest singular value and![]() .
.
The BE LDR approach is based on the rotated differences in the means. The LDR matrix (10) uses a type of pooled covariance matrix estimator for the precision matrices. However, the BE method does not incorporate all of the information contained in the different individual covariance matrices. Another disadvantage of the BE LDR approach is that it is limited to a reduced dimension that depends on the number of classes, m. For![]() , BE allows one to reduce the data to only one dimension, regardless of the full-feature vector dimension. Therefore, one may lose some discriminatory information with the application of the BE LDR method when the covariance matrices are considerably different.
, BE allows one to reduce the data to only one dimension, regardless of the full-feature vector dimension. Therefore, one may lose some discriminatory information with the application of the BE LDR method when the covariance matrices are considerably different.
6.3. Sliced Inverse Regression (SIR)
The next LDR method we consider is sliced inverse regression (SIR), which was proposed in [16] . Assuming all population parameters are known, we first define ![]() as the within-group covariance matrix and
as the within-group covariance matrix and ![]() as the between-group covariance matrix, where
as the between-group covariance matrix, where ![]() is the overall population mean. As its criterion matrix, the SIR LDR method uses
is the overall population mean. As its criterion matrix, the SIR LDR method uses
![]() (12)
(12)
where ![]() is the marginal covariance matrix of
is the marginal covariance matrix of![]() . When population parameters must be estimated, an estimator of (12) is
. When population parameters must be estimated, an estimator of (12) is
![]() (13)
(13)
where ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() given in (1) and (2), respectively. Let
given in (1) and (2), respectively. Let ![]() be the SVD of (13), and let
be the SVD of (13), and let![]() , where
, where ![]() is composed of eigenvectors of (13) such that the
is composed of eigenvectors of (13) such that the ![]() eigenvector of (13) corresponds to the
eigenvector of (13) corresponds to the ![]() largest singular value of (13),
largest singular value of (13),![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() is a rank-r approximation of
is a rank-r approximation of![]() , and the
, and the ![]() SIR LDR matrix is
SIR LDR matrix is![]() , which is composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the r largest singular values of
, which is composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the r largest singular values of![]() .
.
6.4. Sliced Average Variance Estimation (SAVE)
The last LDR method we consider is sliced average variance estimation (SAVE), which has been proposed in
[19] -[20] . The SAVE method uses the ![]() criterion matrix
criterion matrix![]() , where
, where
![]() . We use a form of SAVE given in [21] , which is
. We use a form of SAVE given in [21] , which is
![]() (14)
(14)
where![]() . An estimator of
. An estimator of ![]() is
is
![]() (15)
(15)
where, ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() given in (1) and (2), respectively. Next, let
given in (1) and (2), respectively. Next, let
![]() be the SVD of (15), and let
be the SVD of (15), and let![]() , where
, where ![]() is composed of the eigenvectors of (15) such that the
is composed of the eigenvectors of (15) such that the ![]() column of
column of ![]() corresponds to the
corresponds to the ![]() of (15) with the
of (15) with the ![]() largest singular value,
largest singular value,![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() is a rank-
is a rank-![]() approximation of
approximation of![]() , and, thus, the
, and, thus, the ![]() SAVE LDR matrix is
SAVE LDR matrix is![]() . An alternative representation of the r-dimensional SAVE LDR matrix is
. An alternative representation of the r-dimensional SAVE LDR matrix is![]() , which is composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the r largest singular values of
, which is composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the r largest singular values of![]() .
.
7. A Monte Carlo Comparison of Four LDR Methods for Statistical Classification
Here, we compare our new SY LDR method derived above to the BE, SIR, and SAVE LDR methods. Specifically, we evaluate the classification efficacy in terms of the EPMC for the SY, BE, SIR, and SAVE LDR methods using Monte Carlo simulations for five different configurations of multivariate normal populations with![]() . We have generated 10,000 training-sample and test datasets from the appropriate multivariate normal distributions for each parameter configuration. The test data were assigned to either population class
. We have generated 10,000 training-sample and test datasets from the appropriate multivariate normal distributions for each parameter configuration. The test data were assigned to either population class ![]() or
or ![]() when
when ![]() or
or![]() ,
, ![]() , or
, or ![]() when
when ![]() using the sample QDF corresponding to (4). We have applied the four competing LDR matrices
using the sample QDF corresponding to (4). We have applied the four competing LDR matrices![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() and calculated the EPMCs for the full-dimensional QDF and for the four reduced-dimensional QDFs by averaging the estimated conditional error rate over all training samples. We examined the effect of the training-sample sizes on the four LDR methods using sample sizes
and calculated the EPMCs for the full-dimensional QDF and for the four reduced-dimensional QDFs by averaging the estimated conditional error rate over all training samples. We examined the effect of the training-sample sizes on the four LDR methods using sample sizes ![]() and
and![]() ,
, ![]() or
or![]() .
.
For the SY and SAVE LDR approaches, we reduce the dimension to![]() . In general, for m populations, we remark that the BE LDR method can reduce the feature vector to at most the dimension
. In general, for m populations, we remark that the BE LDR method can reduce the feature vector to at most the dimension ![]() because that is the column dimension of the matrix
because that is the column dimension of the matrix![]() . This limitation is potentially a major drawback when the ratio
. This limitation is potentially a major drawback when the ratio ![]() is small and especially when
is small and especially when![]() . In particular, for the BE and SIR LDR approaches, we can reduce only to the dimension
. In particular, for the BE and SIR LDR approaches, we can reduce only to the dimension ![]() when
when![]() . When
. When![]() , the BE LDR method can be applied to reduce the dimensions to at most
, the BE LDR method can be applied to reduce the dimensions to at most![]() , and for the SIR LDR method, we can reduce the number of original features to at most
, and for the SIR LDR method, we can reduce the number of original features to at most![]() . However, the SY LDR method avoids this shortcoming and allows one to reduce the original feature vector to our choice of reduced dimension r, where
. However, the SY LDR method avoids this shortcoming and allows one to reduce the original feature vector to our choice of reduced dimension r, where![]() , for any finite number of populations m.
, for any finite number of populations m.
The five Monte Carlo simulations were generated using the programming language R. Table 1 gives a description of the number of populations and the theoretically optimal rank of the four LDR indices for each configuration. In Figures 3-7, we display the corresponding EPMCs of the four competing LDR methods for the various population configurations and values of ![]() and r, where
and r, where![]() . The estimated standard error of all EPMCs in the following tables was less than 0.001. For each configuration, we also calculated
. The estimated standard error of all EPMCs in the following tables was less than 0.001. For each configuration, we also calculated![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() along with their respective singular values using the SVD. These singular values contain information concerning the amount of discriminatory information available in each reduced dimension. In the subsequent subsections, we use the following notation:
along with their respective singular values using the SVD. These singular values contain information concerning the amount of discriminatory information available in each reduced dimension. In the subsequent subsections, we use the following notation:![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() denote the estimated EPMCs for the SY, BE, SIR, and SAVE LDR methods, respectively, for each of the appropriate reduced dimensions.
denote the estimated EPMCs for the SY, BE, SIR, and SAVE LDR methods, respectively, for each of the appropriate reduced dimensions.
7.1. Configuration 1: m = 2 with Moderately Different Covariance Matrices
The first population configuration we examined was composed of two multivariate normal populations ![]() and
and![]() , where
, where![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 1. A description of Monte Carlo simulation parametric configurations and singular values in Section 2 with unequal covariance matrices and![]() .
.
![]()
and
![]()
Here, ![]() , which implies
, which implies ![]() because
because![]() . The
. The
singular values of ![]() in Table 2 indicate that most of the classificatory information can be captured when
in Table 2 indicate that most of the classificatory information can be captured when![]() , because the subsequent singular values are small relative to the first. Also, the BE LDR technique loses classificatory information from pooling the acutely dissimilar pair of covariance matrices.
, because the subsequent singular values are small relative to the first. Also, the BE LDR technique loses classificatory information from pooling the acutely dissimilar pair of covariance matrices.
When![]() , the EPMC was reduced by the SY, BE, and SIR LDR methods but not for the SAVE LDR method. This effect occurred because the training-sample size
, the EPMC was reduced by the SY, BE, and SIR LDR methods but not for the SAVE LDR method. This effect occurred because the training-sample size![]() ,
, ![]() , are small relative to the full- feature dimensionality
, are small relative to the full- feature dimensionality![]() , and, therefore, insufficient data were available to accurately estimate the
, and, therefore, insufficient data were available to accurately estimate the ![]() total population parameters. Thus, by reducing the full-feature dimension
total population parameters. Thus, by reducing the full-feature dimension ![]() to dimension
to dimension![]() , we considerably increased the ratio of the training-sample size relative to the original new dimension so that
, we considerably increased the ratio of the training-sample size relative to the original new dimension so that ![]() to
to![]() , where
, where![]() . Thus, we achieved improved parameter estimates in the r-
. Thus, we achieved improved parameter estimates in the r-
dimensional subspaces. Not surprisingly, for![]() ,
, ![]() , we found that
, we found that ![]()
and for![]() ,
, ![]() , which demonstrated the advantage of employing LDR in the classification process, and, more specifically, demonstrated the value of the SY LDR method. Additionally, as
, which demonstrated the advantage of employing LDR in the classification process, and, more specifically, demonstrated the value of the SY LDR method. Additionally, as ![]() increased, the
increased, the ![]() approached
approached ![]() for all four LDR methods as r increased.
for all four LDR methods as r increased.
In addition, the SIR LDR method did not utilize discriminatory information contained in the differences of the covariance matrices when![]() ,
,![]() . However, for
. However, for![]() ,
, ![]() , all four LDR methods yielded essentially the same EPMC, except for SAVE when
, all four LDR methods yielded essentially the same EPMC, except for SAVE when![]() .
.
7.2. Configuration 2: m = 3 with Two Similar Covariance Matrices and One Spherical Covariance Matrix
The second Monte Carlo simulation used a configuration with the three multivariate normal populations![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() where
where![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods for Configuration 1.
![]()
![]()
and
![]()
In this configuration, the population means are unequal but relatively close. Moreover, ![]() and
and ![]() are unequal but notably more similar to one another than to
are unequal but notably more similar to one another than to![]() . However, the variance of the third feature in
. However, the variance of the third feature in ![]() is significantly greater than the population variances of the third feature for either
is significantly greater than the population variances of the third feature for either ![]() or
or![]() .
.
As a result of markedly different covariance matrices, the BE and SIR LDR methods are not ideal because both methods aggregated the sample covariance matrices. The SY LDR method, however, attempts to estimate each individual covariance matrix for all three populations, and uses this information that yielded SY as the superior LDR procedure. Table 3 gives the singular values of each of the LDR methords considered here.
For the larger sample-size scenario, ![]() ,
, ![]() , the SAVE LDR was more competitive with SY than either BE or SIR when
, the SAVE LDR was more competitive with SY than either BE or SIR when![]() . However, the SY LDR remained the preferred LDR method. In Figure 4, we added noise to the SY method when we used
. However, the SY LDR remained the preferred LDR method. In Figure 4, we added noise to the SY method when we used![]() , and, we eliminated essential discriminatory information for the SY procedure when we chose
, and, we eliminated essential discriminatory information for the SY procedure when we chose![]() . Thus, the optimal choice for the reduced dimension for the SY LDR method was
. Thus, the optimal choice for the reduced dimension for the SY LDR method was![]() , regardless of the training-sample size of
, regardless of the training-sample size of![]() ,
,![]() . Furthermore, in our simulation we determined
. Furthermore, in our simulation we determined
![]()
Table 3. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods applied to Configuration 2.
that ![]() for ni = 50 and
for ni = 50 and ![]() for ni = 25,
for ni = 25,
![]() . This significant reduction from
. This significant reduction from ![]() demonstrated a significant benefit of dimension reduction in general and the SY LDR in particular.
demonstrated a significant benefit of dimension reduction in general and the SY LDR in particular.
7.3. Configuration 3: m = 2 with Relatively Close Means and Different But Similar Covariance Matrices
In this configuration, we have ![]() and
and ![]() with
with![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]()
and
![]()
As in Configuration 1, we have that![]() , and, hence,
, and, hence,![]() . In Configuration 3, the BE and SIR LDR methods outperformed the SY and SAVE LDR methods because of the similarity in the covariance matrices. This phenomenon occurred because both LDR methods aggregated the sample covariance matrices, which resulted in less-variable covariance matrix estimators and, therefore, smaller values of
. In Configuration 3, the BE and SIR LDR methods outperformed the SY and SAVE LDR methods because of the similarity in the covariance matrices. This phenomenon occurred because both LDR methods aggregated the sample covariance matrices, which resulted in less-variable covariance matrix estimators and, therefore, smaller values of ![]() and
and![]() . From Table 4, we see that the first singular value for
. From Table 4, we see that the first singular value for ![]() was considerably less predominant than the first singular value for
was considerably less predominant than the first singular value for ![]() in Configuration 1. This result explained the inferiority of the SY method for this configuration, regardless of the chosen
in Configuration 1. This result explained the inferiority of the SY method for this configuration, regardless of the chosen![]() ,
,![]() .
.
For![]() , we have that
, we have that ![]() for
for ![]() and
and ![]() for
for![]() . Again, we exemplify the value of LDR as a classification tool. In this configuration, not only was
. Again, we exemplify the value of LDR as a classification tool. In this configuration, not only was ![]() considerably reduced as
considerably reduced as ![]() increased, but the difference between
increased, but the difference between ![]() and
and ![]() decreased as well. This example demonstrated the fact that the SY method is not a uniformly superior LDR approach even when covariance matrices are unequal. However,
decreased as well. This example demonstrated the fact that the SY method is not a uniformly superior LDR approach even when covariance matrices are unequal. However, ![]() was not much greater than either
was not much greater than either ![]() or
or![]() . Here, SAVE is not as competitive as the three other LDR methods because it does not use all the information in the difference of the covariance matrices and means to obtain a better information-preserving subspace.
. Here, SAVE is not as competitive as the three other LDR methods because it does not use all the information in the difference of the covariance matrices and means to obtain a better information-preserving subspace.
7.4. Configuration 4: m = 3 with Two Similar Covariance Matrices Except for the First Two Dimensions
In this situation, we have three multivariate normal populations:![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() ,
,
![]()
Table 4. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods for Configuration 3.
where![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
and
![]()
For the fourth configuration, the covariance matrices are considerably different from one another, which benefits both the SY and SAVE LDR methods. Specifically, the SY LDR procedure uses information contained in the unequal covariance matrices to determine classificatory information contained in ![]() and in
and in![]() ,
,![]() . The largest
. The largest ![]() for all four LDR methods occurred when
for all four LDR methods occurred when![]() . Generally, the
. Generally, the ![]() decreased as r increased. For the SY method, we have
decreased as r increased. For the SY method, we have![]() , which clarifies the reason that
, which clarifies the reason that ![]() and r were inversely related. As one can see in Table 5, the first three singular values of
and r were inversely related. As one can see in Table 5, the first three singular values of ![]() were relatively large. However, the pooling of the sample covariance matrices used in BE and SIR tended to obscure classificatory information in the sample covariance matrices. The only improvement from the full dimension we found for the values of r and
were relatively large. However, the pooling of the sample covariance matrices used in BE and SIR tended to obscure classificatory information in the sample covariance matrices. The only improvement from the full dimension we found for the values of r and ![]() considered here was the SY method when
considered here was the SY method when ![]() for
for![]() ,
,![]() . Specifically, we have that
. Specifically, we have that ![]() when
when![]() , although
, although ![]() when
when![]() ,
,![]() .
.
This population configuration illustrated the fact that we cannot always choose ![]() and expect to see a reduction in
and expect to see a reduction in![]() . However, we can often reduce the
. However, we can often reduce the ![]() if we use both a judicious choice of r and an appropriate LDR method.
if we use both a judicious choice of r and an appropriate LDR method.
7.5. Configuration 5: m = 3 with Diverse Population Covariance Matrices
In Configuration 5, we have three multivariate normal populations:![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() , where
, where![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
![]()
with
![]()
![]()
Table 5. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods for Configuration 4.
![]()
and
![]()
Here, we have three considerably different covariance matrices. For this population configuration, the SY method outperformed the three other LDR methods for the reduced dimensions![]() . Examining the singular values of
. Examining the singular values of![]() , we see that most of the discriminatory information was contained in the first transformed dimension. This fact was illustrated with how
, we see that most of the discriminatory information was contained in the first transformed dimension. This fact was illustrated with how ![]() and r were directly related, regardless of the training-sample size
and r were directly related, regardless of the training-sample size![]() ,
,![]() .
.
The BE and SIR LDR methods did not perform as well here because of the pooling of highly diverse estimated covariance matrices. While the SAVE LDR procedure was the least effective LDR method for![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() were inversely related. While each of the four LDR methods decreased from
were inversely related. While each of the four LDR methods decreased from ![]() for some combination of
for some combination of ![]() and r, the largest reduction in EMPC was for the SY LDR method where
and r, the largest reduction in EMPC was for the SY LDR method where ![]() for
for ![]() and
and ![]() for
for![]() ,
,![]() . This result implied that the SY LDR method was especially useful when
. This result implied that the SY LDR method was especially useful when ![]() was relatively small and the covariance matrices were considerably different.
was relatively small and the covariance matrices were considerably different.
8. A Parametric Bootstrap Simulation
In the following parametric bootstrap simulation, we use a real dataset to obtain the population means and covariance matrices for three multivariate normal populations. The chosen dataset comes from the University of Califorina at Irvine Machine Learning Repository, which describes the diagnoses of cardiac Single Proton Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) images. Each patient in the study is classified into two categories: normal or abnormal. The dataset contains 267 SPECT image sets of patients. Each observation consists of 44 continuous features for each patient. However, for our simulation, we chose only ten of the 44 features. The ten selected features were F2R, F6R, F7S, F9S, F11R, F11S, F14S, F16R, F17R, and F19S. Hence, we performed the parametric bootstrap Monte Carlo simulation with two populations: ![]() and
and![]() , where
, where
![]()
![]()
Table 6. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods for Configuration 6.
![]()
![]()
and
![]()
For this dataset, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and![]() . Table 6 gives the singular values for each of the LDR methods considered here.
. Table 6 gives the singular values for each of the LDR methods considered here.
Figure 8 gives the EPMCs for the reduced dimensions 1, 2, and 3 for each of the LDR methods. In this exam- ple, a considerable amount of discriminatory information is contained in the covariance matrices, which are ex- tremely different. Hence, not surprisingly, neither the BE nor the SIR LDR methods performed well for![]() . Furthermore,
. Furthermore, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() were inversely related to r, regardless of the training-sample size
were inversely related to r, regardless of the training-sample size![]() ,
,![]() . From Table 7, we see that one reason that
. From Table 7, we see that one reason that ![]() increased as r decreased is that the singular values are relatively large up to
increased as r decreased is that the singular values are relatively large up to![]() . Thus, when we chose
. Thus, when we chose![]() , we discarded some necessary discriminatory information.
, we discarded some necessary discriminatory information.
For![]() ,
, ![]() , SAVE slightly outperformed the other three LDR methods, though the SY LDR approach was very competitive. For
, SAVE slightly outperformed the other three LDR methods, though the SY LDR approach was very competitive. For![]() ,
, ![]() , we found that SY
, we found that SY ![]() was the smallest error rate and that
was the smallest error rate and that![]() . This particular example verified that one can implement the SY method and obtain excellent results even though the conditions of Theorem 1 do not essentially hold. This example also illustrated the prospect that, with a judicious choice of r combined with the appropriate LDR method, we can significantly reduce the feature dimension while still preserving the EMPC.
. This particular example verified that one can implement the SY method and obtain excellent results even though the conditions of Theorem 1 do not essentially hold. This example also illustrated the prospect that, with a judicious choice of r combined with the appropriate LDR method, we can significantly reduce the feature dimension while still preserving the EMPC.
![]()
Table 7. Summary of singular values for the four competing LDR methods for the parametric bootstrap example.
9. Discussion
In this paper, while all population parameters are known, we have presented a simple and flexible algorithm for a low-dimensional representation of data from multiple multivariate normal populations with different parametric configurations. Also, we have given necessary and sufficient conditions for attaining the subspace of smallest dimension![]() , which preserves the original Bayes classification assignments. We have provided a constructive proof for obtaining a low-dimensional representation space when certain population parameter conditions are satisfied. Under a special case for the two-class multivariate normal problem with equal nonsingular covariance structures, our proposed LDR transformation is the LDF in [4] . Moreover, we have also extended our concept proposed in Theorem 1 to cases where the conditions in Theorem 1 are not satisfied through the application of the SVD given in Theorem 2.
, which preserves the original Bayes classification assignments. We have provided a constructive proof for obtaining a low-dimensional representation space when certain population parameter conditions are satisfied. Under a special case for the two-class multivariate normal problem with equal nonsingular covariance structures, our proposed LDR transformation is the LDF in [4] . Moreover, we have also extended our concept proposed in Theorem 1 to cases where the conditions in Theorem 1 are not satisfied through the application of the SVD given in Theorem 2.
We have presented several advantages of our proposed low-dimensional representation method. First, our method is not restricted to a one-dimensional representation regardless of the number of populations, unlike the transformation introduced by [14] . Second, our method allows for equal and unequal covariance structures. Third, the original feature dimension p does not significantly impact the computational complexity. Also, under certain conditions, one-dimensional representations of populations with unequal covariance structures can be accomplished without an appreciable increase in the EPMC.
Furthermore, we have derived a LDR method for realistic cases where the class population parameters are unknown and the linear sufficient matrix M in (7) must be estimated using training data. Using Monte Carlo simulation studies, we have compared the performance of the SY LDR method with three other LDR procedures derived by [14] [16] [19] . In the Monte Carlo simulation studies, we have demonstrated that the full-dimension EMPC can sometimes be decreased by implementing the SY LDR method when the training-sample size is small relative to the total number of estimated parameters.
Finally, we have extended our concept proposed in Theorem 1 through the application of the SVD given in Theorem 2 to cases where one might wish to considerably reduce the original feature dimension. Our new LDR approach can yield excellent results provided the population covariance matrices are sufficiently different.