Hydration of Portland Cement in the Presence of Highly Reactive Metakaolin ()
1. Introduction
Metakaolin is a fine aluminosilicate material having pozzolanic activity. It is formed by calcination of kaolinite clays at temperature in the range of 650˚C - 750˚C [1] [2] . The varieties of metakaolin obtained from the purest grades of kaolinite are characterized by rather narrow limits of chemical composition (SiO2 50 - 55 wt%, Al2O3 40 - 45 wt%) and contain minor amounts of impurity components (Fe2O3, CaO, MgO) and phases (rutile, feldspars, quartz). The particles size of metakaolin is predominately in the range of 2 - 10 μm and the specific surface is of 10 to 25 m 2 /g.
The partial substitution of cement by metakaolin allows for increasing compressive strength of cement pastes, mor- tars (concretes) along with reducing their porosity and permeability [1] -[3] . This contributes to better cyclic freeze- thaw stability of the material, as well as its resistance against sulfates, chlorides, acids and alkalis [1] [2] [4] .
The influence of metakaolin on the hydration of cement and the formation of solid structure is based on the high specific surface of its particles and its pozzolanic properties [5] . In accordance with the literature data, within the first 24 hours after the hydration begins, metakaolin microparticles serve essentially as microfiller to densify the structure of cement paste, as well as nucleation centers for the main product of cement hydration, which is (C-S-H) [6] [7] . The pozzolanic properties of metakaolin, i.e., its ability to interact with Ca(OH)2 to form a C-S-H, which helps for further densification of the microstructure of cement paste, mortar or concrete, appear in the subsequent period (3 - 7 days on). Besides C-S-H, the products formed by metakaolin and Ca(OH)2 interacting are calcium aluminate hydrates (CAH13 and C3AH6) and hydrogelenit (C2ASH8).
In Russia, an interest in metakaolin as pozzolanic additive used to partially replace cement in concretes and mortar mixes has increased significantly in recent years. This is largely due to the establishing of several major domestic manufacturers of metakaolin using kaolinite deposits in Chelyabinsk region as raw materials sources.
The pozzolanic activity of metakaolin depends on the content and the structural features of its main constituent―metakaolinite [5] [8] [9] , its particles fineness (specific surface area) [9] [10] , the chemical nature and amount of impurity components. These characteristics of metakaolin are determined, in turn, by the composition of raw materials and processing parameters. Therefore, the varieties of metakaolin by different manufacturers may differ quite considerably in terms of pozzolanic activity. Thus, the study of the peculiarities of transformation of metakaolin being a part of cement paste is of a practical importance. This information is necessary for both interpreting the physical and mechanical properties of Portland cement materials supplemented with metakaolin and for estimating its optimal dosage.
When studying the pozzolanic activity of metakaolin, a solid-state 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy is of a great use [11] -[14] . This method allows the investigation of the following quantitative characteristics: the percentage of aluminum ions in different states of coordination with oxygen (for preliminary estimation of the pozzolanic activity of metakaolin itself); the degree of conversion for metakaolin and hydration degree for Portland cement as well as to study the influence of metakaolin on structural features of C-S-H and other phases formed in hardening Portland cement metakaolin pastes.
The purpose of this work is to investigate the pozzolanic activity of metakaolin “MKJL” (ZAO “Plast-Rifei”, TU 5729-097-12615988-2013, Russia) introduced into Portland cement paste at various dosages, as well as its influence on the kinetics of Portland cement hydration and the formation of hydration products by means of 27Al- and 29Si-MAS NMR spectroscopy.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
According to the manufacturer, the content of Al2O3 and SiO2 in metakaolin MKJL is (42 - 43) and (53 - 54) wt%, respectively. The main phase is an amorphous metakaolinite (90% - 93%). The amount of particles below 40 μm is 99%, below 10 μm―50%. Pozzolanic activity determined by binding of Ca(OH)2 from its saturated solution is at least of 1400 mg of Ca(OH)2 to 1 g of metakaolin.
Portland cement (PC) CEM I 42.5 N with the following composition, wt%: C3S―(52 - 53), C2S―(18 - 20), C3A + C4AF―(20 - 22), gypsum (CaSO4∙2H2O)―(3 - 4), anhydrite (CaSO4)―1, CaCO3―2 was used.
2.2. Sample Preparations and Testing Methods
Portland cement metakaolin pastes (PC substitution rate is 0, 10 and 30 wt%) were prepared at water-to-solid ratio (w/s―weight of water/weight (cement + metakaolin)) of 0.5. Pastes prepared were molded in the form of tablets with diameter of 50 mm and thickness of 3 - 4 mm. The samples were stored at 20˚C and RH of more than 90%. For NMR spectroscopy analysis a small amount of cement paste (~2 g) was powdered, washed with acetone (3 × 30 ml), filtered and then dried under vacuum at ambient temperature; the samples are then stored at −18˚C prior to analysis if needed.
High-resolution solid-state NMR spectra have been obtained using AVANCE II-500WB (Bruker) spectrometer with “magic angle” spinning. Operating frequency for 29Si: 9935 MHz, 27Al: 130,32 MHz. Spectra were recorded by single-pulse excitation, the pulse duration: 3 μs (π/4) and 0.7 μs (π/12) with a delay of 6 s and 0.5 s, the number of scans were 10,240 and 2048 for 29Si and 27Al respectively. The samples were packed in zirconia rotors (diameter 4 mm) and rotated at 10 - 13 kHz. Chemical shifts are given in ppm relative to TMS (tetramethylsilane) and AlCl3・6H2O in solution as an external references for 29Si and 27Al, correspondingly. The assignment of the signals is accomplished in accordance to the published data [13] [14] . The deconvolution of spectra was done by means of Dmfit software. The spectra of metakaolin, Portland cement and PC-metakaolin mixes were also obtained in this way.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows the 27Al- and 29Si-NMR spectra of metakaolin MKJL. The 27Al-NMR spectrum has signals at 60, 30 and 5 ppm which belong to 4-, 5- and 6-coordinated Al atoms, respectively; their amounts are of 30.3, 35.4 and 34.4%, according to spectra deconvolution results. A wide signal in 29Si-NMR spectrum is an evidence of metakaolin amorphous structure. The position of the maximum at 105 ppm indicates the predominance of Q4 (1Al) type silicon atoms. As is well known, silicon atoms in kaolinite are of the same type, therefore, the conversion of kaolinite into metakaolin is accompanied by its amorphization, but slightly affects the polymeric state of Si. All transformations are mainly related to the change of the coordination state of Al (in kaolinite, aluminum is almost entirely 6-coordinated). It is known that the pozzolanic activity of metakaolin depends, among other things, on the content of aluminum ions in the unstable 5-coordinated state [11] . Metakaolins in which 5-coordinated Al is dominated possess high pozzolanic activity. The significant amount of 5-coordinated aluminum together with the appropriate phase composition suggests metakaolin MKJL to be a material with high pozzolanic activity.
Figures 2-4 show the results of solid-state 29Si-NMR spectroscopy for reference Portland cement paste and Portland cement metakaolin pastes at different ages.
Figure 5 is an example of the spectrum deconvolution. The signals between −(67 - 75) ppm belong to isolated SiO4 tetrahedra (signed as Q0) of PC silicate phases, which are alite and belite. Signals between −(78 - 85) ppm belong to C-S-H, where the main structural pattern is short silicate chains with some bridging AlO4 tetrahedra. The signal at −(84 - 85) ppm belongs to internal silicon nuclei in chain units (Q2), while −(78 - 80) ppm signal belongs to external ones (Q1). SiO4 tetrahedra connected with one SiO4 and one AlO4 (-Si-O-Si-O-Al-, Q2 (1Al)) are repre- sented by a signal at −(80 - 82) ppm and a peak with a maximum at 105 ppm belongs to metakaolin (Q4 (1Al)).
![]()
Figure 1. Metakaolin spectra: 1: 29Si-NMR, 2: 27Al-NMR. Along X is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
![]()
Figure 2. 29Si-MAS NMR spectra of PC (1) and Portland cement paste at the age of, days: 2: 1; 3: 7; 4: 28; 5: 90. Along X is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
![]()
Figure 3. 29Si-MAS NMR spectra of dry PC (90 wt%) metakaolin (10 wt%) mixture (1) and Portland cement metakaolin paste at the age of, days: 2: 1; 3: 7; 4: 28; 5: 90. Along X is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
![]()
Figure 4. 29Si-MAS NMR spectra of dry PC (70 wt%) metakaolin (30 wt%) mixture (1) and Portland cement metakaolin paste at the age of, days: 2: 1; 3: 7; 4: 28; 5: 90. Along X is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
![]()
Figure 5. An example of spectrum deconvolution (corresponded to the curve 5 in the Figure 4). Along X is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
During pozzolanic reaction, metakaolin undergoes the destruction and its components embed into the C-S-H structure and form aluminosilicate chains. The process of metakaolin breakage can go through the formation of intermediate aluminosilicate segments containing silicon atoms of Q3 and Q4 types, where there are variable numbers of aluminum ions in the neighbor environment [15] . As a consequence, there is not only the decreasing of the main signal of metakaolin, but also its extension to a weaker field due to the appearance of components with the chemical shift values exceeding −105 ppm.
Spectra deconvolution results are shown in Table 1.
With using NMR spectroscopy data, the hydration degree of Portland cement α in examined pastes was
![]()
Table 1. The connectivity distribution of silicon species in the investigated samples.
*QM is the signal of metakaolin which include Q4 (1Al) at 105 ppm and those components with chemical shift in the range of −(87 - 100) ppm.
calculated by the following formula:

where 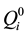 and
and 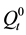 correspond to the initial amount of Q0-sites (%) and to the amount at the time t, respectively.
correspond to the initial amount of Q0-sites (%) and to the amount at the time t, respectively.
The degree of conversion of metakaolin ω was calculated by the formula:

where 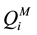 and
and  are the content of silicon atoms related to metakaolin in the initial state and at the time t, respectively.
are the content of silicon atoms related to metakaolin in the initial state and at the time t, respectively.
The average length of alumosilicate chains n in a mutual hydration product of PC and metakaolin as well as Al/Si ratio (Al/Si) and the total contribution of the inner silicon atoms m in aluminosilicate chains were calculated using formulae:
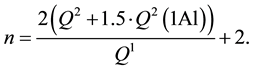
The results of these calculations are shown in Table 2.
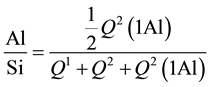
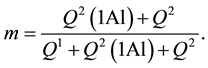
![]()
Table 2. Parameters of hydration in accordance with 27Si-MAS NMR data.
As it can be seen, in the case of low degree of cement substitution (10%), a metakaolin has not significant influence on the hydration rate of PC silicate phases at early stages of this process―the values of the cement hydration degree for the samples both with and without metakaolin are 23% and 26%, respectively; the difference between these values is below the instrumental error limit. However, in the case of high rate of substitution (30%), metakaolin promotes the hydration of silicate phases significantly (the hydration degree of Portland cement is about 33% at 1-day age). The observed acceleration of PC hydration in the presence of metakaolin is in agreement with literature data [1] .
Meanwhile, a slowdown of PC hydration in the samples with metakaolin at the late period is to be noted. After 7 days, a PC in the samples with metakaolin was less hydrated in comparison to the control sample of the same age, and the difference becomes even more significant over time. The possible cause for this retardation is the water deficit due to the competing processes-the hydration of cement and metakaolin pozzolanic reaction. In addition, spatial constraints may exist for deposition of cement hydration product caused by sealing of hardening paste structure voids by pozzolanic reaction products.
In as quick as 1 day, metakaolin partially gets involved in pozzolanic reaction, thus it confirm the assumption about its high pozzolanic activity. In accordance with spectral data, by this time, the amount of metakaolin reacted was up to 25% of its initial amount in the paste of low PC substitution (10%) and near 14% in case of high substitution (30%). The reducing in metakaolin conversion rate while increasing the degree of PC substitution is in accordance to [3] . Obviously, this effect is a consequence of replacing a certain amount of PC by additive, which leads to decreasing in concentration of alkali ions, OH− and Ca2+ ions in interstitial solution and reducing the heat of hydration for the mix.
At the age of 7 days, in the paste with 10% of metakaolin, the additive is completely consumed and its components get entirely included into the mutual product of cement hydration and pozzolanic reaction. In the 30% substituted cement paste, the content of metakaolin remains quite high (about 40% of the initial amount) even after 3 months of hydration and perhaps this value remains the same for any time thereafter.
The presence of metakaolin affects the polymeric state of C-S-H. This is largely due to the aluminum ions bridging silicate species. According to Table 2, in C-S-H formed by hydration of PC in the presence of metakaolin, the total contribution of the inner silicon atoms m is higher in respect to the reference C-S-H. Therefore, the product of mutual hydration of cement and metakaolin is characterized by a greater aluminosilicate chain length n compared with hydration product of the reference paste (Table 2).
At the early period of hydration (1 day), the average values of aluminosilicate chain length (n) of C-S-H in the pastes with metakaolin (10%) and without one are 3.4 and 3.5, respectively, i.e. one and the same. However, by the age of 7 days, the average chain length for the sample with metakaolin reaches 7 - 8; for the reference cement paste, it is only 5 over 3 months. Meanwhile, in the sample with 30%-substitution of cement by metakaolin this value reaches 4.9 in one day, and goes up to 11 - 12 thereafter.
A comparison of the values of silicon nuclei Q1, Q2 (1Al) and Q2 signal intensities in samples with and without metakaolin allows for formal estimation of PC and metakaolin contribution to the mutual C-S-H. Thus, the contribution of metakaolin in the form of Q1 ![]() can be calculated by subtracting the contribution of PC hydration products
can be calculated by subtracting the contribution of PC hydration products ![]() from the total Q1:
from the total Q1:
![]()
where Q1 and ![]() are contents of Q1 species in cement pastes with and without addition of metakaolin, correspondingly, %;
are contents of Q1 species in cement pastes with and without addition of metakaolin, correspondingly, %; ![]() is the initial content of Q0 species in PC-metakaolin blend, %; α and αref are the hydration degree of PC in pastes with and without metakaolin, respectively (for the same age), %.
is the initial content of Q0 species in PC-metakaolin blend, %; α and αref are the hydration degree of PC in pastes with and without metakaolin, respectively (for the same age), %.
Similarly, one can estimate the contribution of metakaolin and PC to the content of Q2 and Q2 (1Al) species. Results of calculations of metakaolin contribution to C-S-H in the form of silicon nuclei of different con- nectivity are shown in Table 3.
As can be seen from Table 3, the contribution of metakaolin (M) to C-S-H upon the 1st day of hydration is already around 40% and after 7 days about half of C-S-H consists of material derived from metakaolin. Further- more, metakaolin mainly contributes to Q2 and Q2 (1Al) species, whereas PC does to Q1. Metakaolin effect on increasing of Q1 species is only significant at early stages of hydration. One of the examples in Table 3 has a negative value for the metakaolin contribution to Q1 species (−12.3). This is because the content of Q1 species in the presence of metakaolin was less than for pure PC. It is likely that silicon atoms of Q1 type issued by Portland cement are transformed into Q2 (1Al) with the participation of the aluminum ions issued by metakaolin. This goes to show that there is no border between “PC” and “metakaolin” C-S-H, and the estimation of the contribu- tion of metakaolin and cement into silicon species of C-S-H is uncertain.
As is known, an atomic ratio between aluminum and silicon in metakaolin is approximately 1 to 1. In this regard, it is interesting to establish in what proportion Al and Si migrate from metakaolin to C-S-H. As can be seen from Table 3, the Al/Si ratio in the “pozzolanic” product is much less than 1 at early stage of hydration. This means that part of the aluminum ions released from metakaolin may participate in the formation of other aluminum-bearing phases, besides participating of C-S-H formation. As hydration progresses (7 - 28 days), this ratio increases and reaches the values of 0.26 - 0.33.
Figure 6 shows the 27Al-MAS NMR spectra of cement pastes at the age of 1 day. There are signals assigned to aluminum ions in different coordination states that belong to PC, metakaolin and their hydration products. The narrow intense signal presented in all the spectra at 14.7 - 15.2 ppm belongs to ettringite. According to spectrum deconvolution, a ratio of ettringite content in the samples with 30 wt% metakaolin to pure PC one is of approximately 1.5 to 1.
The “shoulder” signal at 7 ppm observed on metakaolin containing samples spectra belongs to 6-coordinated Al in metakaolin. A wide signal at near 33 ppm observed only on metakaolin supplemented samples spectra as well belongs to 5-coordinated Al in metakaolin. The signal at 60 ppm are of 4-coordinated Al from aluminum- bearing cement phases and metakaolin. In area of 75 ppm on metakaolin containing samples spectra, there is a signal related to aluminum ions incorporated into aluminosilicate chains of C-S-H; the intensity of this signal increases with increasing of the metakaolin content. Thus, the 27Al-MAS NMR data confirms high content of aluminum in C-S-H at the very early stages of Portland cement hydration.
4. Conclusions
1) The conversion degree of highly reactive metakaolin within cement paste with 10% substitution of PC (water-to-solid ratio is 0.5) stored at 20˚C and more than 90% RH is about 25 and 100% at the ages of 1 and 7 days, correspondingly. In the case of 30% substitution, the conversation degree of metakaolin is about 14% after 1 day of hydration and about 50% after 28 days; the father conversation goes very slowly.
2) At high dosage (30%), metakaolin promotes the hydration of PC, but possesses no promoting activity when
![]()
Table 3. Contribution of metakaolin and cement to C-S-H.
![]()
Figure 6. 27Al-MAS NMR spectra of samples of 1-day age: 1: reference paste; 2 and 3: cement pastes with 10% and 30% metakaolin, correspondingly. Along X axis is a chemical shift δ, ppm.
taken at moderate dosage (10%). However, at the age of 1 - 3 months, the degree of PC hydration in the pre- sence of metakaolin is of 15% - 20% less than without it, probably, due to deficit of water or spatial restrictions.
3) C-S-H formed in cement paste in the presence of metakaolin is characterized by higher content of Q2 and Q2 (1Al) species in comparison with the reference cement paste, and hence has longer aluminosilicate chains as well.
4) After 1 day of hydration, an amount of ettringite in cement paste with high dosage of metakaolin is higher than that in pure PC paste. It may be due to the fact that aluminum ions liberated from metakaolin are taken into reaction to form ettringite.