Research on the Complementarity and Comparative Advantages of Agricultural Product Trade between China and CEE Countries
—Taking Poland, Romania, Czech Republic, Lithuania and Bulgaria as Examples ()
1. Introduction
In 2008, the Department of Agriculture for the first time officially proposed agricultural foreign investment strategy, encouraging the overseas investment agricultural enterprises. Agricultural strategy of “going out” achieves substantial development. Central and Eastern European (hereinafter, CEE) countries are rich in agricultural resources, highly complementary with China’s agricultural products. Bilateral agricultural cooperation has great potential. The bilateral cooperation has profound impact on achieving mutual benefit and win-win progress and the implementation of China’s agricultural strategy of “going out”. It is an important part of realizing the common development of China and CEE countries in the new period. On November 26, 2013, Premier Li Keqiang pointed out that “to expand imports of high-quality agricultural products and other marketable products from CEE countries, and to enlarge citizens’ tourism consumption in central and Eastern Europe, taking a variety of ways to improve the trade imbalance” [1] . Thus, it is of great practical significance to research the complementarity and comparative advantages of agricultural product trade between China and CEE countries.
At present, domestic scholars have certain research on trade cooperation between China and CEE countries. CEE countries’ export to China and the direct investment of Chinese enterprises in CEE countries should be expanded by analyzing the market and goods structure of cargo trade between China and 12 CEE countries from 2001 to 2011 (SHANG Yuhong, 2012) [2] . China should import more from CEE counties and the bilateral cooperation field should be expanded, on account of China and CEE counties’ trade gravity model based on economies of scale, population scale, geographical distance, demand structure and institutional factors (GONG Jianghong, and CHEN Xuhua,2012) [3] . China should enhance investment in CEE countries based on the 12 measures to promote pragmatic cooperation between China and CEE countries proposed by Premier Wen Jiabao during his visit in CEE countries, based on studying the opportunities for Chinese investment in brought by the European debt crisis and the characteristics of current Chinese investment in CEE countries (LIU Zuokui, 2012) [4] . China and CEE countries are highly complementary in trade structure and have huge trade potential by analyzing the complementarity of cargo trade between China and 12 CEE countries (ZHANG Qiuli, 2013) [5] . To analyze the out of competition and trans effects and their forming reasons of 8 CEE countries’ trade to China (DOU Feifei, 2014) [6] . The export product competitiveness of CEE countries leads to changes of its market share in China, while China’s strong product competitiveness promotes the growth of its market share in 10 CEE countries (SHANG Yuhong, GAO Yunsheng, 2014) [7] . The literature about agricultural cooperation between China and CEE countries is less. The economy and population scale promote bilateral agricultural trade and it is in accordance with Linder’s “Theory of Preference Similarity” (ZHANG Haisen, XIE Jie, 2008) [8] . FAN put forward pragmatic policy suggestions by analyzing the agricultural trade and economic cooperation actuality between China and CEE countries in detail (FAN Liping, 2013) [9] . The existing literature shows that domestic research emphatically analyzes bilateral cargo trade while the study of bilateral agricultural products trade is still relatively lack. Hence, by analyzing the complementarity and comparative advantages of agricultural product trade between China and CEE countries, this paper aims to perfect research in this aspect and provide reference for the policy adjustment and formulation of bilateral agricultural trade.
2. The Research Range and Method
2.1. Research Range
According to the definition from Appendix I of Uruguay round agricultural agreement of the world trade organization (WTO), agricultural product includes chapter 1 to chapter 24 in UN Comtrade database, removing the fish and aquatic products. This is because that the WTO has a special organization to carry out statistic analysis for aquatic products. For the sake of the present situation of China’s agricultural product trade, agricultural product in this paper covers all products from chapter 1 to chapter 24 and from chapter 50 to chapter 53 (see Table 1). This paper adopts commodity classification of HS2002. Research data is mainly originated from the United Nations statistics. The form data are data in 2013.
CEE countries in this paper refer to the 16 CEE countries in China’s diplomatic sense. In 2013, the total trade volume of agricultural trade between China reaches 1.07 billion US dollars. Among the 16 CEE countries’ agricultural trade to China, Poland accounts for 49.58%; second to it is Romania, accounting for 11.14%; followed by Czech Republic, Lithuania and Bulgaria, accounting for 7.86%, 6.12% and 4.91%, respectively. The proportions of the other 11 countries are all below 4%. The proportions of Macedonia, Montenegro, Slovenia and Bosnia and Herzegovina are less than 1%. Therefore, this paper mainly research the complementarity and comparative advantages of agricultural product trade between China and Poland, Romania, Czech republic, Lithuania and Bulgaria.
Data source: organized from UN Comtrade database, similarly hereinafter.
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Revealed Comparative Advantage
RCA, Revealed Comparative Advantage, mainly analyzing the comparative advantage of one country’s trade with other countries (Balassa, 1965) [10] . The computation formula is as follows:
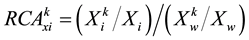 (1)
(1)
where 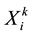 refers to the exports of i country’s product k,
refers to the exports of i country’s product k, 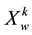 refers to the world’s total exports of product k, Xi means the total exports of all products in i country. Product can be divided into four categories by RCA values: product with very strong advantage (RCA > 2.5), product with strong advantage (1.25 ≤ RCA ≤ 2.5), product with moderate advantage (0.8 ≤ RCA < 1.25) and product with weak disadvantage (RCA < 0.8).
refers to the world’s total exports of product k, Xi means the total exports of all products in i country. Product can be divided into four categories by RCA values: product with very strong advantage (RCA > 2.5), product with strong advantage (1.25 ≤ RCA ≤ 2.5), product with moderate advantage (0.8 ≤ RCA < 1.25) and product with weak disadvantage (RCA < 0.8).
2.2.2. Trade Complementarity Index
As for the calculating convenience, this paper calculates the 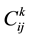 (Trade Complementarity Index, TCI), on the basis of revealed comparative advantage. In order to measure the complementarity between China and five CEE countries, the following formula is achieved by consulting YU Jinping’ s research method (HUO Weidong, and LU Xiaojing, 2003) [11] :
(Trade Complementarity Index, TCI), on the basis of revealed comparative advantage. In order to measure the complementarity between China and five CEE countries, the following formula is achieved by consulting YU Jinping’ s research method (HUO Weidong, and LU Xiaojing, 2003) [11] :
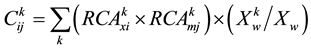 (2)
(2)
where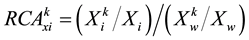 , meaning the export comparative advantage of product k in i country,
, meaning the export comparative advantage of product k in i country, 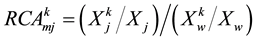 , indicting the import comparative advantage of product k in j country,
, indicting the import comparative advantage of product k in j country, 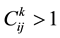 , the greater the
, the greater the 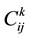 value is , the more highly the complmentarity is, and vice versa.
value is , the more highly the complmentarity is, and vice versa.
2.2.3. Intra-Industry Trade Index
Grubel, Llyod (1975) proposes Grubel-Llyod index, which is complement and development of comparative advantage (Huo Weidong et al., 2014). For further analyzing the comparative advantage of bilateral agricultural advantage, this paper uses Grubel-Llyod index to measure the intra-industry trade of agricultural products between China and five CEE countries. The computation formula is as follows:
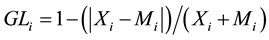 (3)
(3)
where Xi and Mi represent the exports and imports of product i respectively. When GLi tends to 1, it signifies that the trade of product i belongs to intra-industry trade; when GLi approaches 0, it means that the trade of product i belongs to inter-industry trade.
3. The Empirical Result Analysis
3.1. The RCA Indexes of Agricultural Products between China and Five CEE Countries
According to formula (1), the RCA indexes of agricultural products between China and five CEE countries can be reached (see Table 2). China’s agricultural products of chapters 50 and 53 have very strong comparative advantages; chapter 05, 16, 51 and 52 have strong comparative advantages; while the other 17 chapters of agricultural products don’t have product advantages. Poland’s 12 chapters of agricultural products have very strong and
strong advantages: chapter 02, 04, 05, 07, 08, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 and 24; while Czech Republic only has three chapters: chapter 01, 24 and 51. Except chapter 05, 13, 14, 20, 50 and 52, Lithuania’s other 22 chapters of agricultural products have product advantages, among which chapter 04, 07, 08, 10, 11, 24, 51 and 54 have very strong comparative advantages. Bulgaria’s agricultural products with very strong comparative advantages are chapter 10, 11, 12, 24 and 51. Table 3 lists the top five product categories among the agricultural products trade between China and five CEE countries. Combing Table 2 with Table 3, it’s clearly that there is big difference in the exporting agricultural products with comparative advantages and main agricultural products export category between China and five CEE countries. The bilateral agricultural product trades are highly complementary.
3.2. The Complementary Indexes of Agricultural Product between China and Five CEE Countries
Table 4 shows that the complementary indexes of China’s export and five CEE countries’ import are less than 1. The overall complementarity is not strong. In terms of agricultural product category, China’s export and Poland’s import are complementary in chapter 03, 05, 14, 20, 51, 52 and 53; China’s export and Romania’s import are complementary in chapter 05, 50, 51, 52 and 53; China’s export and Czech Republic’s import are complementary in chapter 05, 07, 16, 51 and 53;China’s export and Lithuania’s import are complementary in chapter 03, 05, 07, 08, 16, 50, 51, 52 and 53;China’s export and Bulgaria’s import are complementary in chapter 05, 16, 20, 50, 51, 52 and 53.
Based on the trade complementarity of five CEE countries’ export and China’s import, the trade complementarity indexes of exports of Poland, Czech Republic and Bulgaria and China’s import are all larger than 1. The trade complementarity of these three countries’ export and China’s import are generally strong. As far as agricultural product concerned, Poland’s export and China’s import are complementary in chapter 02, 04, 05, 12, 24, 51 and 53; Czech Republic’s export and China’s import are complementary in chapter 12, 51 and 53; Bulgaria’s export and China’s import are complementary in chapter 10, 11, 12, 14, 15 and 51. Both the trade complementarity indexes of Romania and Lithuania’s exports and China’s import are less than 1, indicating that the trade complementarity of their export and China’s import, on the whole, are not strong. In terms of agricultural product category, Romania’s export and China’s import are complementary in chapter 10, 12, 14, 24, 50, 51 and 53; Lithuania’s export and China’s import are complementary in chapter 03, 04, 07, 08, 10, 11, 12, 24, 51 and 53. Overall, China and five CEE countries are complementary in many agricultural product categories. China is surplus bilateral trade, i.e. five CEE countries are more dependent on China in agricultural product trade.
![]()
Table 2. The RCA indexes of agricultural products between China and five CEE countries.
Data source: organized and calculated from UN Comtrade database.
3.3. The Agricultural Intra-Industry Trade of China and Five CEE Countries
Table 5 shows the agricultural intra-industry trade indexes of China and five CEE countries in 2013. Intra-in- dustry trade and inter-industry trade is divided by GLi = 0.5. From the point of agricultural products in chapters, China and Poland’s trade demonstrates obvious intra-industry trade in chapter 04, 06, 17 and 22, for all the GL indexes are greater than 0.5. The GL indexes of chapter 05, 08, 09, 12 and 19 are greater than 0.2, presenting the tendency of intra-industry trade. The trades of the other calculable 11 chapters of agricultural products belong to inter-industry trade. In the agricultural products trade between China and Romania, the GL indexes of chapter 17, 19 and 24 are greater than 0.2, but less than 0.5, indicating a certain tendency of intra-industry trade. The trades of the other calculable 12 chapters of agricultural products present a strong characteristic of inter-industry trade. The GL indexes of chapter 19 and 21 in the agricultural products trade between China and Czech Republic are greater than 0.5, showing obvious intra-industry trade. Chapter 12, 13 and 52 reveal a certain tendency of intra-
![]()
Table 3. The top five product categories among the agricultural products trade between China and five CEE countries.
Data source: organized from UN Comtrade database, product category is expressed by HS code.
![]()
Table 4. The complementary indexes of agricultural product between China and five CEE countries.
Data source: organized and calculated from UN Comtrade database.
industry trade. The trades of the other calculable 7 chapters of agricultural products show obvious inter-industry trade. In the agricultural products trade between China and Lithuania, the GL indexes of chapter 08, 19 and 51 are greater than 0.5, presenting obvious intra-industry trade. Chapter 04 shows a certain tendency of intra-in- dustry trade. The trades of the other calculable 8 chapters of agricultural products present obvious inter-industry trade. In the agricultural products trade between China and Bulgaria, the GL indexes of chapter 08 and 17 are greater than 0.5, showing obvious intra-industry trade. Chapter 03, 18 and 53 indicate a certain tendency of intra-industry trade. The trades of the other calculable 11 chapters of agricultural products present obvious inter- industry trade.
In general, China’s agricultural trade with Poland and the Czech Republic is given priority to intra-industry trade; China’s agricultural trade with Lithuania and Bulgaria present a general tendency of intra-industry trade; while its agricultural trade with Romania is inter-industry trade based. From the perspective of specific trade data of agricultural products, China is a net exporter of five CEE countries. China’s net exports of agricultural products to Poland is 0.12 billion US dollars, and the GL index is 0.78. Both the two data are the highest among five CEE countries. Therefore, bilateral agricultural product trade can be improved to a certain extent by raising the level of intra-industry trade between China and CEE countries.
4. Conclusions and Enlightenment
According to the characteristic analysis of trade of agricultural products between China and five CEE countries, the following conclusions can be reached: 1) The trade of agricultural products between China and CEE countries is relatively concentrated. China’s export mainly concentrates in Poland, Romania, Czech Republic, Lithuania and Bulgaria. China’s top three exporting products are fish, fruit and vegetable products and silk and its main importing products are meat and edible meat offal and edible animal products such as milk, egg, honey, oil seeds and feed; 2) There is a big difference in the comparative advantage of agricultural product export of China and five CEE countries. China’s major comparative advantage lies in labor intensive industry, while the rest agri- cultural products less competitive. The comparative advantages of agricultural products of Poland and Lithuania are obviously stronger than China. There exists a big difference in the comparative advantages of agricultural
![]()
Table 5. The agricultural intra-industry trade indexes of China and five CEE countries.
Note: “-” refers to data missing, “na” means only import or export data is available, incalculable.
products of five CEE countries and China. Bilateral agricultural products trades have great potential in complementarity; 3) China and five CEE countries are complementary in many product categories. The complementary indexes of Poland, the Czech Republic and Bulgaria’s export and China’s import are all greater than 1. The five CEE countries are overall more dependent on China. 4) The agricultural trade between China and five CEE countries shows both the characteristics of intra-industry and inter-industry trade, tending more to intra-industry trade. Bilateral trade of agricultural products presents both complemtarity and competitiveness, while the former is greater; 5) The main problems existing in current trade of agricultural products between China and CEE countries are: first, the bilateral trade volume is small and the trade dependence is low; second, China is a net exporter of CEE countries. The trade structure imbalance is serious; third, the trade categories of agricultural products are limited and bilateral trade comparative advantages are not fully explored.
Based on the above analysis and conclusions, several enlightenments can be obtained about bilateral trade of agricultural products. First, both sides should give full play to bilateral comparative advantage and to adjust the export advantage of agricultural products. Although bilateral trade scale is relatively small, China and CEE countries have many complementary agricultural products, indicting great potential in the trade of agricultural products. China can increase the export of products from labor intensive industry like aquatic products, fruit products and silk, paying attention to the extension of agricultural industrial chain and further strengthen its own comparative advantage. Second, they need to improve bilateral agricultural trade imbalance situation. China has been in the state surplus in bilateral agricultural trade for a long time and the surplus is expanding year by year, which is not conducive to bilateral long-term economic and trade cooperation. China should expand the import of products with strong comparative advantages of CEE countries such as milk and honey. It can satisfy the increasing domestic demand and explore the potential of CEE countries’ export. Third, on the whole, bilateral agricultural trade complementarity is given priority to complementary between industries. However, China and Poland show intra-industry complementary. China’s agricultural trade with Lithuania and Bulgaria presents a tendency of intra-industry complementary. Besides, the definition of “16 CEE countries” is a strategic concept put forward by China rather than a unified organization. China must consider the realities and lay emphasis on market subdivision when carrying out the trade of agricultural products with CEE countries. Finally, China should make full use of policy advantage, expanding field and pattern of bilateral agricultural trade cooperation. Under the background of agricultural “going out”, bilateral agricultural cooperation forum should be hosted and China’s direct investment in CEE countries should be supported, realizing mutual benefit and win-win result.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.