1. Introduction
This paper provides a novel quantum model of decision-making (QMDM) for mathematical economics. The model approach is based on recent neuroeconomic evidence [1] -[3] . This means that data such as neural activity is used to design a suitable alternative to the standard decision-making theory in economics [4] . Until today, the standard theory is the so-called expected utility theory (EUT) by von Neumann and Morgenstern [5] . Economists are reluctant in adapting or changing this model framework because they argue that only the outcome, i.e. the resulting choice, not the process of decision-making is relevant [6] . We disagree with this mainstream view because a scientific theory should be able to explain the right outcome with the true underlying processes. There is no doubt that human decision-making is probabilistic [7] . To address economic decision-making mathematically, it requires a model with stochastic processes. Obviously, this idea is inherent in a quantum model and thus provides a decent starting point for the QMDM.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. Section 2 presents a literature review. In Section 3, we describe the QMDM. This model enables us to get a better understanding of the role of the decision-making process. Section 4 concludes the paper.
2. Literature Review
Until today, the dominant decision-making model in economics is the EUT. Von Neumann and Morgenstern [5] developed this theory and it is still the workhorse model today. The cornerstone of this model is the so-called revealed preference assumption. This means that preferences have certain properties, such as completeness, transitivity, symmetry, reflexivity or irreflexivity [8] . Then the revealed preference relation, 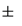 , and the expected utility function,
, and the expected utility function, 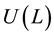 , is defined by the following two definitions.
, is defined by the following two definitions.
Definition 1 A revealed preference relation is defined as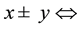 , there is a unique set of choices
, there is a unique set of choices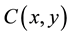 , for which
, for which .
.
Definition 2 The utility function  has an expected utility form if there is an assignment of numbers
has an expected utility form if there is an assignment of numbers  such that for every lottery L, defined as
such that for every lottery L, defined as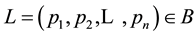 , we obtain
, we obtain
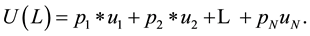 (1)
(1)
The function , defined according to Equation (1), is called a von Neumann-Morgenstern expected utility function.
, defined according to Equation (1), is called a von Neumann-Morgenstern expected utility function.
Despite its rigorous foundation and tremendous flexibility of the EUT, there are several caveats and unsolved issues. These limitations are illustrated by so-called decision-making paradoxes, for instance, the St. Petersburg paradox [9] , the Allais paradox [10] , the Ellsberg paradox [11] , the Kahneman-Tversky paradox [12] , and finally the Ariely paradox [13] . The discovery of these paradoxes stimulated the development of alternative theories of decision-making. The most famous alternatives are behavioral theories, such as the prospect theory [12] , the regret theory [14] , and the quadratic probability theory [15] . However, all existing alternatives do not sufficiently explain the paradoxes in a consistent manner.
Even more problematic, the standard and alternative theories are unable to explain the dynamic inconsistency paradox by Kydland and Prescott [16] . In addition more recently, the economic decision-making models are under pressure from neuroscience. Krajbich et al. [3] questions the workhorse model in economics because it does not fit empirical decision-making data [2] [17] . A new promising approach is the drift-diffusion model
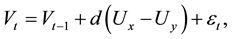 (2)
(2)
where x and y are the choice alternatives, 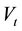 is the decision value in period t,
is the decision value in period t, 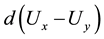 captures the distribution of the difference between both alternatives, and
captures the distribution of the difference between both alternatives, and 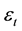 is a standard Gaussian error term with mean zero and volatility
is a standard Gaussian error term with mean zero and volatility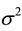 , such as
, such as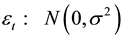 . On the other hand, a new line of research has been developed and concentrates on quantum models of decision-making. These models suppose that brain functions are based on quantum processes as almost all neuroscientific evidences suggest [17] - [19] .
. On the other hand, a new line of research has been developed and concentrates on quantum models of decision-making. These models suppose that brain functions are based on quantum processes as almost all neuroscientific evidences suggest [17] - [19] .
A quantum model eases all problems significantly and the approach is backed by neuroeconomic evidence. The working of sophisticated quantum processes and networks was discovered already by Max Planck a century ago [20] . The working of the different brain functions was already studied by Schneider and Shiffrin [21] in the 1970s. Interestingly even von Neumann, the founding father of the EUT, mentions a quantum model as an alterative [22] . Recently, Yukalov and Sornette [18] [23] worked on those models, too.
The advantage of a QMDM is simple. First, it could be interpreted as a generalization of the EUT. Second, it solves the decision-making paradoxes and it is in line with recent research in neuroeconomics. The QMDM provides two innovative issues: First, it demonstrates why people sometimes choose or prefer low utility options; Second, the model considers the impact of groups and thus the interaction mechanism during the decision- making process. Consequently, the QMDM does not only tackle the present decision-making paradoxes, it explains the individual reasoning within groups, such as the unexplained error-attenuation effect.
3. The Model
In this section, we demonstrate the mechanism of the QMDM. In particular, we illustrate a solution to the following problem: people often choose an option with lower utility because they are more attracted to the alternative, however, this fact cannot be modeled within the standard EUT. The QMDM nicely solves this issue.
Let us consider a group of agents. Each agent A is a decision-maker, whose decisions are influenced by other group members. Agents choose among several choices, called lotteries or prospects. Each prospect is a vector in a Hilbert space![]() ; a kind of space of mind. Elementary prospects are represented by a set of vectors
; a kind of space of mind. Elementary prospects are represented by a set of vectors![]() . The elementary prospects are orthonormalized, so that the scalar product
. The elementary prospects are orthonormalized, so that the scalar product ![]() is a Kronecker delta. The orthogonality means that the prospects are independent. An agent’s space of mind A is defined as
is a Kronecker delta. The orthogonality means that the prospects are independent. An agent’s space of mind A is defined as
![]() (3)
(3)
where ![]() means spanning a space of all admissible elementary prospects. Such a space can be constructed for each member of the group. However, the states of mind of two distinct individuals are in general different. The space of mind for all other group members is denoted as
means spanning a space of all admissible elementary prospects. Such a space can be constructed for each member of the group. However, the states of mind of two distinct individuals are in general different. The space of mind for all other group members is denoted as![]() . Consequently, the total decision space is the tensor product and defined as
. Consequently, the total decision space is the tensor product and defined as
![]() (4)
(4)
This is a Hilbert space, or in economic terminology the decision space of the whole group. Usually, an agent A considers a set of prospect states, such as
![]() (5)
(5)
in the space of mind![]() . These prospect states are the final targets of the decision-maker in order to form a complete transitive structure. The decision-maker evaluates the set
. These prospect states are the final targets of the decision-maker in order to form a complete transitive structure. The decision-maker evaluates the set ![]() of these prospects
of these prospects ![]() by forming a complete and transitive preference relation.1 Based on a concept of a prospect operator, I define the prospect probabilities to be the average of the prospect operator. A prospect operator is each prospect
by forming a complete and transitive preference relation.1 Based on a concept of a prospect operator, I define the prospect probabilities to be the average of the prospect operator. A prospect operator is each prospect ![]() with the corresponding vector state
with the corresponding vector state ![]() in the Hilbert space of mind
in the Hilbert space of mind![]() . Thus, prospect probabilities are observable quantities. In addition, interacting agents are represented by a “group” prospect state
. Thus, prospect probabilities are observable quantities. In addition, interacting agents are represented by a “group” prospect state![]() . The observable quantities
. The observable quantities![]() , are defined as an expectation value over the statistical operator. With some algebra you can write the prospect probabilities as
, are defined as an expectation value over the statistical operator. With some algebra you can write the prospect probabilities as
![]() (6)
(6)
with the property of![]() . Consequently, we have
. Consequently, we have ![]() and the most favorable prospects correspond to the largest probabilities. This allows us to define two separate factors which determine the probabilities of a prospect. On one hand, the so-called utility factor
and the most favorable prospects correspond to the largest probabilities. This allows us to define two separate factors which determine the probabilities of a prospect. On one hand, the so-called utility factor
![]() (7)
(7)
and on the other hand, the so-called attraction factor
![]() (8)
(8)
These two elements have the property that the probability of a prospect ![]() is equal to the sum of both factors:
is equal to the sum of both factors:
![]() (9)
(9)
The utility factor ![]() is a weighting factor2 that can be normalized as
is a weighting factor2 that can be normalized as
![]() (10)
(10)
Respectively, the attraction factor satisfies the following property
![]()
1The ordering procedure is discussed in [18] .
2![]() where
where ![]() is an expected utility function with a non-decreasing and concave, but positive function. x is a set of measurable payoffs and
is an expected utility function with a non-decreasing and concave, but positive function. x is a set of measurable payoffs and ![]() is the standard utility function.
is the standard utility function.
![]() (11)
(11)
According to recent neuroscientific research by Krajbich et al. [3] , Baumgartner [4] and Yukalov and Sornette [24] , the model requires a brain specific threshold that I define similarly by the quarter law. In other words, the average absolute value of the attraction factor is estimated by
![]() (12)
(12)
In summary, the prospect probability in Equation (9) consists of two terms: the utility and the attraction term. A prospect is more attractive if it provides more certain gain or less uncertain loss. In the end, the decision- maker chooses the most preferable prospect with the highest probability. Such a prospect is called the optimal prospect![]() , and defined as
, and defined as
![]() (13)
(13)
Let me demonstrate the working of the model with a simple example. Suppose prospect ![]() is more attractive than
is more attractive than![]() , or
, or![]() . According to the quarter law, we approximate the attraction factors as
. According to the quarter law, we approximate the attraction factors as ![]() and
and![]() . This implies that
. This implies that
![]() (14)
(14)
Since the utility factor is calculated with![]() , I obtain a quantitative estimate for the prospect probabilities. Given the final prospect probabilities, I choose the preferable prospect.
, I obtain a quantitative estimate for the prospect probabilities. Given the final prospect probabilities, I choose the preferable prospect.
Proposition 1 Let prospect ![]() be more attractive than
be more attractive than![]() , and let it be in line with Equation (14), then
, and let it be in line with Equation (14), then ![]() is preferred if
is preferred if![]() . The prospect is indifferent if
. The prospect is indifferent if![]() , and the prospect
, and the prospect ![]() is preferable if
is preferable if![]() .
.
Proof. Given that ![]() and
and ![]() is more attractive than
is more attractive than![]() , i.e.
, i.e.![]() , I obtain
, I obtain
![]()
and for![]() , then I obtain
, then I obtain
![]()
The proof for the indifference relationship follows respectively. ![]()
Thus, this model can disentangle the “economic utility” into an objective “utility factor” and a subjective “attraction factor”. However, the key difference of the QMDM is due to the attraction factor. This is definitely a novel element in the economic decision-making literature. Moreover, it allows computing the attraction factor with experimental data, such as
![]() (15)
(15)
Even the proponents of the drift-diffusion model find similar evidence. For instance, Krajbich et al. [3] explains that “(...) options that receive more attention also receive more evidence (...)”. Consequently, the QMDM holds great promise as a human decision-making model with preferences over risk, time, and social interaction, in the future.
4. Conclusion
All in all, the “Quantum Model of Decision-Making” (QMDM) demonstrates useful insights on the allocation and application of individual and group choices. I demonstrate that this model is an extension of the Expected Utility Theory (EUT) and thus the QMDM is just the generalization of the present workhorse model in economics. Consequently, the QMDM could be applied as a new framework in theoretical economics without changing the whole economic thinking. Moreover, the model enhances the modeling of choices while considering the present decision-making paradoxes and neuroscientific evidence. Even if, this model is not the final development in the ongoing debate, it is a tractable alternative and does not open the Pandora’s Box of rational choice theory in special and economic thinking in general.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank two anonymous referees for helpful comments and my IB-research assistants for editing the paper. Moreover, I gratefully acknowledge financial support from the RRI-Reutlingen Research Institute.