Antileishmanial Assay and Antimicrobial Activity on Crude Extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolus Barks and Leaves from Malaysia ()
1. Introduction
Antimicrobials (antibiotics) have played an essential role in decreasing morbidity due to infectious diseases. Antimicrobials are used for treatment of infections and for prophylaxis against infections in humans and animals, for growth promotion in food animal rearing and in agriculture. However, infectious diseases remain as the leading cause of death worldwide and bacteria has become more resistant to conventional antibiotic in recent years. The widespread use of these compounds is thought to further encourage the emergence of antimicrobial resistance [1] . The number of resistant pathogenic bacteria grows at an alarming rate worldwide and the search for novel antimicrobial agents from medicinal plants to combat such pathogens has become crucial for avoiding the emergence of untreatable bacterial infections [2] [3] .
Cancer, a cellular malignancy that results in the loss of normal cell-cycle control, such as unregulated growth and the lack of differentiation, can develop in any tissue of any organ, and at any time [4] .
Despite the therapeutic advances made in understanding the processes involved in carcinogenesis, cancer has become one of the most serious medical problems today. The worldwide mortality rate increases annually, with more than seven million deaths occurring per year. For this reason, cancer chemotherapy has become a major focus area of research [5] .
“Chemoprevention” is defined as a process to delay or prevent carcinogenesis in humans through the ingestion of dietary or pharmaceutical agents. This also implies the identification of chemical entities (specifically cytotoxic entities) that are effective against a range of cancer cell lines, although less active or non-toxic against the normal (healthy) cell population. The search for such anticancer agents from plant sources started in the 1950’s, and plant products have proven to be an important source of anticancer drugs [6] . This directly results from the biological and chemical diversity of nature, which allows for the discovery of completely new chemical classes of compounds.
The plant Melodinus eugeniifolus in Apocynaceae Family is a rare medicinal plant which has just been discovered in the Malaysia rain forest. The leaves and barks were extracted by hexane, chloroform and ethanol, respectively, and got six crude extracts. The present study was undertaken to screen the antileishmanial and antibacterial potential on Melodinus eugeniifolus. No such studies have been reported on this species to date.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The crude extracts were extracted from leaves and barks of Melodinus eugeniifolus Wall. ex G.Don with hexane, chloroform and ethanol.
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, R & M), MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) (Life Technologies), fetal bovine serum (for cell culture, Sigma), RPMI-1640 medium (for cell culture, Sigma), defined keratinocyte-SFM (Life Technologies), PBS (dulbecco’s phosphate buffered saline) (Sigma), trypan blue (for cell culture, Sigma), Trypsin EDTA (0.05% Trypsin, 0.53 mM EDTA.4Na) (Gibco), Penicillin-Streptomycin (liquid, 100 ml/pk) (Gibco). 96-well TC Plate (for mammalian cell culture, Orange Scientific), centrifuge tube (Orange Scientific), TC flask (Orange Scientific), minisart syringe filter (SSI), kit, pipette and tips are all from Dragon Med.
In vitro antimicrobial activity was examined for hexane, chloroform and ethanol extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolus. The following bacterial strains were employed in the screening: Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 11632), Bacillus cereus (ATCC 10876), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 43300) and Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli (ATCC 10536) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 10145).
2.3. Protocol
2.3.1. Anti-Leishmanial Assay
In vitro antileishmanial activity against Leishmania donovani promastigotes.
Antileishmanial activity of tested plant extract, against Leishmania donovani (strain MHOM/IN/1983/AG83) promastigotes, was evaluated by a quantitative colourimetric assay using MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) [7] . Amphotericin B (IC50 = 0.4 ± 0.1 µM) was used as the positive control in all the experiments. Promastigotes (5 × 105 cells/ml; 300 µl), were treated with and without tested samples at concentrations of 100 and 500 µg/mL, and incubated at 22˚C ± 2˚C. After 72 h, cells were harvested, and re-suspended in PBS (500 µl) containing MTT (0.3 mg/ml). Purple formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO and the optical density (O.D.) was measured at 570 nm in an ELISA reader (BIO-RAD; model 680, USA). The number of viable cells was directly proportional to the amount of formazan produced through the reduction of yellow MTT by the dehydrogenase enzymes present in the inner mitochondrial membrane of the living cells. The IC50 values (concentration of drug which inhibited at least 50% cell growth) for each compounds were determined from respective dose-responsive percentage inhibition curves with the help of Origin 5.0 software (Microcal Software, Inc., Northampton, MA, USA).
2.3.2. Antimicrobial Assay. Disc Diffusion Assay
The principles of determining the effectivity of a noxious agent to a bacterium were well enumerated by Rideal, Walker and others at the turn of the century, the discovery of antibiotics made these tests (or their modification) too cumbersome for the large numbers of tests necessary to be put up as a routine. The ditch plate method of agar diffusion used by Alexander Fleming was the forerunner of a variety of agar diffusion methods devised by workers in this field. The Oxford Group used these methods initially to assay the antibiotic contained in blood by allowing the antibiotics to diffuse out of reservoirs in the medium in containers placed on the surface [8] .
With the introduction of a variety of antimicrobials it became necessary to perform the antimicrobial susceptibility test as a routine. For this, the antimicrobial contained in a reservoir was allowed to diffuse out into the medium and interact in a plate freshly seeded with the test organisms. Even now a variety of antimicrobial containing reservoirs are used but the antimicrobial impregnated absorbent paper disc is by far the commonest type used. The disc diffusion method of antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) is the most practical method and is still the method of choice for the average laboratory. Automation may force the method out of the diagnostic laboratory but in this country as well as in the smaller laboratories of many countries, it will certainly be the most commonly carried out microbiological test for many years to come [8] .
The Kirby-Bauer and Stokes’ methods are usually used for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, with the Kirby-Bauer method being recommended by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS). The accuracy and reproducibility of this test are dependent on maintaining a standard set of procedures.
NCCLS is an international, interdisciplinary, non-profit, non-governmental organization composed of medical professionals, government, industry, healthcare providers, educators etc. It promotes accurate antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) and appropriate reporting by developing standard reference methods, interpretative criteria for the results of standard AST methods, establishing quality control parameters for standard test methods, provides testing and reporting strategies that are clinically relevant and cost-effective [8] .
Interpretative criteria of NCCLS are developed based on international collaborative studies and well correlated with MIC’s and the results have corroborated with clinical data. Based on study results NCCLS interpretative criteria are revised frequently. NCCLS is approved by FDA-USA and recommended by WHO [8] [9] .
1) Preparation of Mueller Hilton Agar. Mueller Hilton Agar was prepared from a commercially available dehydrated base according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The agar solution was then autoclaved. It was then allowed to cool in a 45˚C - 50˚C water bath. The agar was then poured into plastic flat bottomed petri dishes on a level, horizontal surface to give a uniform depth of approximately 4 mm. This corresponds to 25 ml for plates with a diameter of 100 mm. The agar medium was then allowed to cool to room temperature and unless plate is used the same day, stored in a refrigerator (2˚C to 8˚C). A representative sample of each batch of plates was examined for sterility by incubation at 30˚C - 35˚C for 24 hr or longer.
2) Preparation of sample extracts, negative control and standard antibiotic solution. Sample extracts were dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 100 mg/ml and filtered. Negative control was DMSO. Standards used were ampicillin and streptomycin which were prepared at the concentration of 100 µg/ml.
3) Preparation of fresh/pure colonies of bacteria. Tryptic soy agar was prepared according to the manufacturers intructions. Agar was autoclaved and poured on petri dishes to 4 mm, approximately 25 ml to a 100 mm petri dish. Bacterias are streaked on the TSA plates in 4 density level around the plates. Plates are then sealed with a parafilm and incubated for 18 hr to obtain single colonies.
4) Preparation of disc with extracts, control and standards. About 10 µl of sample extracts was pipetted onto the disc in triplicates. Same was done for controls and standards. Impregnated discs are left to air dry overnight for 12 hr.
5) Inoculum Preparation. At least 3 - 5 well isolated colonies of the same morphological type are selected from an agar plate culture. The top of each colony was touched with a sterilized loop and the growth was transferred into the Bijou bottle containing TSB. This was repeated for each bacterium into each Bijou bottle. The broth culture was incubated at 35˚C for about 2 hr till it achieved the turbidity of 0.5 Mcfarland standard/625 nm to yield 1 × 108 cfu/ml. Using optical density at 625 nm, the reading below must be obtained for different bacteria, turbidity was adjusted with sterile normal saline.
6) Inoculation of test plates. The bacterial broth was used within 15 minutes after the turbidity of the inoculum suspension was adjusted. Sterile cotton swab was dipped into the suspension and rotated several times and pressed firmly on the inside wall of the tube above the fluid level. This was to remove any excess inoculum from the swab. The dried surface of a Mueller Hilton agar plate was inoculated by streaking the swab over the entire agar at every 60˚. As a final step, the rim of the agar was swabbed.
7) Application of discs to inoculated agar plates. Each disc was pressed down on the agar to ensure complete contact according to prepared template. Plates were placed in 35˚C incubator within 15 minutes after discs are applied.
8) Reading plates and interpretation of results. After 18 hr of incubation, each plate was examined. Zone of inhibition was measure using sliding calipers to the nearest millimeters. The inhibition zones would thus include disc size of 6 mm. The experiment was done three times and the mean values are presented. Two samples with the best inhibition zone were chosen and test was repeated in triplicate with the concentration of 2 mg/disc using the same negative and positive controls to test dose/inhibition zones correlation [9] -[11] .
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Concentration-response curves were calculated using the Prism software package 5.00 for Windows, GraphPad Software, San Diego California USA, http://www.graphpad.com/ (GraphPad, San Diego, USA) and data were reported as mean and SD values obtained from a minimum of three determinations. Non-linear best fit was plotted with SD and 95% confidence interval.
Qualitative phytochemical analysis of the crude extract was determined as follows [12] [13] .
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Antileishmanial Assay
All the plant extracts, except the chloroform fractions of bark and leaf of Melodinus eugeniifolus, showed strong antileishmanial effect on the promastigotes of Leishmania donovani (IC50 < 500 µg/mL). (Table 1, Figure 1).
3.2. Antimicrobial Assay
The antibacterial activity of six extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolius was evaluated (Table 2). The extracts were screened for activity against Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA and Bacillus cereus) and Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) by agar disc diffusion method. All the extracts displayed remarkable antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria. The best sensitivity to the extracts (Figure 2 and Figure 3) at 2 mg/disc was respectively obtained against Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli.
3.3. Discussion
In the present study, six different extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolus (Apocynaceae) leaves and barks were

Table 1 . MTT assay of crude plant extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolus against Leishmania donovani (AG83) promastigotes.
BH: bark hexane extract; BC: bark chloroform extract; BE: bark ethanol extract; LH: leaf hexane extract, LC: leaf chloroform extract, LE: leaf ethanol extract.
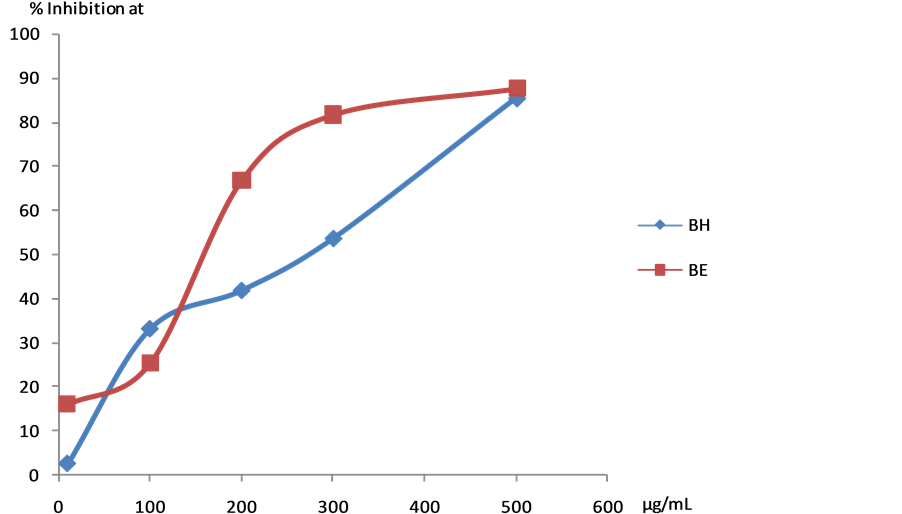
Figure 1. Detailed assay against Leishmania donovani (AG83) promastigotes on BH and BE extracts. BH: bark hexane extract; BE: bark ethanol extract.

Table 2. Antibacterial activity of Melodinus eugeniifolus. (1 mg/disc and 2 mg/disc) vs. ampicillin and streptomycin (1 µg/ disc) against 5 bacterial species tested by disc diffusion assay.
BH: bark hexane extract; BC: bark chloroform extract; BE: bark ethanol extract; LH: leaf hexane extract; LC: leaf chloroform extract; LE: leaf ethanol extract; aInhibition zones are the mean including disc (6 mm); bAmpicillin and streptomycin at 100 µg/ml = 1 µg/disc. -: no activity noted i.e. inhibition zone of 6 mm.



Figure 2. Zone of inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus for all the extracts at 2 mg/disc. BH: bark hexane extract; BC: bark chloroform extract; BE: bark ethanol extract; LH: leaf hexane extract; LC: leaf chloroform extract; LE: leaf ethanol extract.



Figure 3. Zone of inhibition against Bacillus cereus for all the extracts at 2 mg/disc. BH: bark hexane extract; BC: bark chloroform extract; BE: bark ethanol extract; LH: leaf hexane extract; LC: leaf chloroform extract; LE: leaf ethanol extract.
screened for their in vitro antileishmanial and antibacterial activities, among the different extracts tested, the ethanol and hexane extract of barks showed significant antileishmanial activities with IC50 value of 159.9 µg/ml and 270.3 µg/ml. All the extracts displayed remarkable antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli.
The ideal chemotherapeutic agent has a high therapeutic index with selective toxicity, thereby resulting in lethal damage to pathogens through the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis or nucleic acid synthesis, as well as through the disruption of the cell membrane and the inhibition of certain essential enzymes. This results in selective disruption of the specific structure and/or function are essential to bacterial growth and survival, without causing similar effects to its eukaryotic host [14] .
The efficacy of antimicrobial agents is influenced by a number of factors. Firstly, it is of obvious importance that the antimicrobial agent reaches the site of the infection. This greatly depends on the stability of the drug, its lipophilic or hydrophilic nature, its absorption from a specific site and the presence of blood clots or necrotic tissue, the latter of which may protect the pathogen against the antibiotic. Secondly, the susceptibility of the pathogen to the particular chemotherapeutic agent is of utmost importance, as well as the specific growth phase in which the pathogen is in at that particular stage [14] .
Natural products have played a pivotal role in the discovery of antimicrobial drugs, with the drug either being completely derived from the natural product, or serving as a lead for novel drug discovery. Most antimicrobials discovered during the past 6 - 7 decades have been discovered through screening of soil samples, of which the antimicrobial efficacies were determined first in vivo and later in vitro [15] .
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram positive coccus bacterium that is a member of the Firmicutes, and is frequently found in the human respiratory tract and on the skin. Disease-associated strains often promote infections by producing potent protein toxins, and expressing cell-surface proteins that bind and inactivate antibodies [16] -[18] . Bacillus cereus is an endemic, soil-dwelling, Gram-positive, rod-shaped, beta hemolytic bacterium. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals. B. cereus bacteria are facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus Bacillus can produce protective endospores [19] [20] . Escherichia coli is a gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rodshaped bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms (endotherms) [21] [22] . Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common bacterium that can cause disease in animals, including humans. It is citrate, catalase, and oxidase positive. The symptoms of such infections are generalized inflammation and sepsis. If such colonizations occur in critical body organs, such as the lungs, the urinary tract, and kidneys, the results can be fatal. It is also able to decompose hydrocarbons and has been used to break down tarballs and oil from oil spills [23] -[25] .
Plants synthesize a diverse array of secondary metabolites, which play a key role in the natural defence mechanisms employed by the plant against predation by microorganisms and insects. It is thuds no surprise that these aromatic compounds have, in numerous instances, been found to be useful antimicrobial phytochemicals and, as a result, these compounds are now divided into different chemical categories: phenolics, terpenoids and essential oils, alkaloids, lectins and polypeptides, as well as polyacetylenes [26] . An increase in the isolation and identification of such compounds may thus contribute greatly to the success in antibiotic discovery.
It is known that nature is able to produce a wide variety of chemical entities of novel structure. Many of the new and novel compounds isolated from natural sources might otherwise have never been discovered, especially those of considerable complexity requiring the development of methods for the creation of new ring systems. Natural products appeared to be a promising source for new types of compounds with antitumor activity [27] .
4. Conclusion
Plant substances continue to serve as a wellspring of drugs for the world population and several plant-based drugs are in extensive clinical use [28] . Preliminary antibacterial screening of six extracts of Melodinus eugeniifolus showed that all the extracts displayed had promising growth inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. The results obtained suggest that further isolation studies can be performed on Melodinus eugeniifolus to identify the active constituents responsible for the antibacterial activities.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.