Placenta Increta in Week 10 of Pregnancy with Consecutive Hysterectomy: A Case Report ()
1. Introduction
Placenta increta is a complication of pregnancy that can be life threatening for both mother and fetus [1]. The abnormally stiff attachment of the placenta might be due to poorly grown decidua in the lower uterine part [2].
Properly, the chorionic villi of the placenta accreta grow into the basal decidua within the uterus, whereas these villi in the placenta increta and the placenta percreta go into the musculature and the myometrium of the uterus respectively [3]. Then, infiltration in the serosa and even in the neighboring organs such as the urinary bladder and bowel can occur and so serious complication may arise [4].
2. Case Presentation
A 26 years old woman came to our hospital with chief complaint of vaginal bleeding. The admitted patient was gravida 3 and para 2 at 10 weeks of pregnancy with history of twice cesarean section and had two children that last delivery was 2 years ago.
The patient had been vaginal bleeding since one month previous time admission. Pelvic ultrasonography reported nonviable fetus with gestational age 10 weeks that suggest two differential diagnoses, i.e., missed abortion or molar pregnancy. The laboratory findings of the case was hemoglobin = 9/2 gr/dL and bHCG = 200,000 unit. The liver function test and thyroid function test were normal. Also vital sign of the patient in time of admission was normal.
3. Management
In spite of doing suction and curettage for miscarriage, the massive vaginal bleeding continued and hence we had to do the total abdominal hysterectomy for solve of this problem.
During operation bladder dome had been ruptured that repaired by urologist. Blood loss during operation was approximately three liter. So four units packed cell and two units FFP was transfused. During operation no vesicular changes was observed in the placenta. The lower segment of the uterine, at the site of scar of previous cesarean section, was very large and placenta increta was diagnosed (Figure 1).
Histological examination demonstrated the presence of placenta increta in the section of uterine specimen with normal endoand ectocervical mucosa (Figure 2). Typical invasive chorionic migratory cells and placental villi were demonstrated in outer layer of the myometrium.
4. Discussion
It was suggested that because of absent or inadequate formation of the decidua, the trophoblast may infiltrate the myometrium [5]. The abnormally stiff attachment of the placenta might be due to poorly grown decidua in the lower uterine part of the uterus [6]. Risk factors for an abnormal placentation include prior cervical dilatation and curettage, endometritis, submucous myomas and uterine scars defect after cesarean section [7-10]. The relationship between abnormal placentation and previous cesarean section was investigated by Clark et al. [11]. According in this study [11], the percentage risk for placental disorder, i.e. placenta previa, in pregnant woman without prior cesarean section is 0.26 percent and this percentage increased linearly with the number of previous section up to 70 percent at four or more. When a placenta previa is present, the probability of placenta accreta increased from five percent without previous cesarean section to 24 percent with one and up to 67 pre-
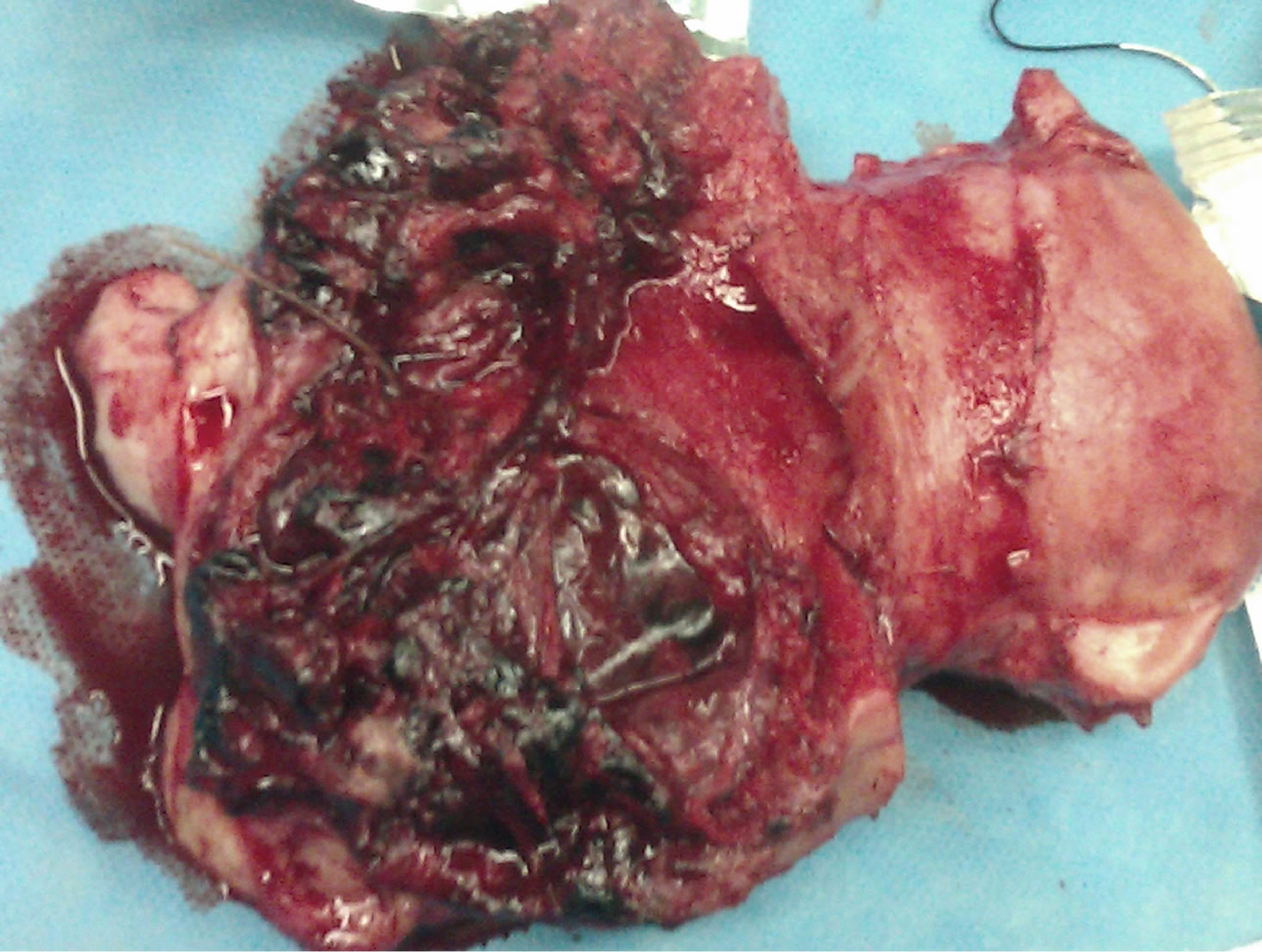
Figure 1. Pregnancy at the site of scar of previous cesarean section.
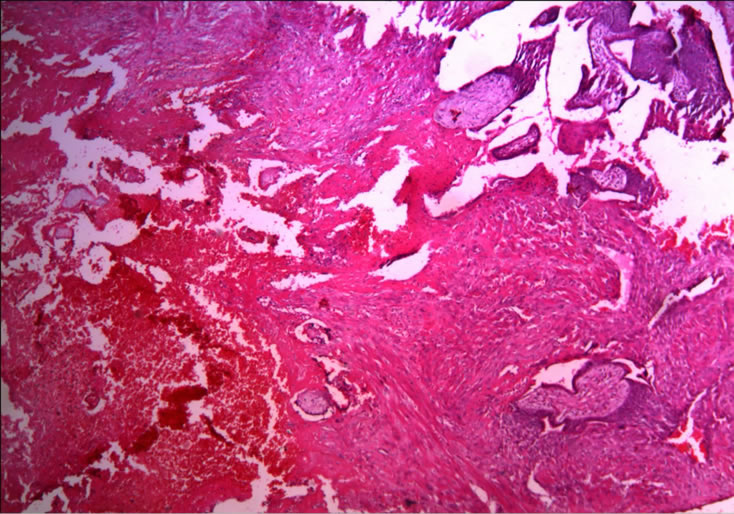
Figure 2. Placenta increta (penetration of chorionic villi into myometrium of the uterus).
sent with four or more prior section [11]. In a survey of the literature was found only a few cases of placenta increta and percreta in a similar early stage of pregnancy [12]. Monks et al. [13] reported a case of G4p3 with three previous cesarean section that at 10 weeks of gestation with the diagnosis of incomplete abortion that finally placenta accreta was diagnosed. Höpker et al. [4] reported a case of G3P2 with abdominal pain in left lower quadrant and diagnosis of incomplete abortion or molar pregnancy that suction curettage was had done for her and because of sever vaginal bleeding that not stopped finally total abdominal hysterectomy was done and histological examination was diagnosed placenta accreta. The simplest, safest and most accurate method of placental location is provided by transabdominal sonography [1]. According to the laying the average accuracy is 96% [14]. Transvaginal sonography improved diagnostic accuracy of placenta previa. MR imaging may help in surgical planning [1]. Levin et al. [15] compared the accuracy of MR imaging with abdominal and vaginal sonography and declared that the transvaginal sonography was adequate to diagnose six of seven cases accurately. Also Levin et al. [15] reported that the MR imaging to be helpful only in cases in which the placenta lay outside the range, for example posterior placenta accrete, for both transvaginal sonography or transabdominal sonography. Sonography is excellent to determine myometrial involvement [1]. Identification of placenta with bladder wall invasion is less accurate even though if both sonography and MR imaging are used.
5. Conclusion
According to increasing prevalence of repeated cesarean section in our country, it must suspect to impaire normal placenta in the cases that referred with abnormal vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain in the first trimester of pregnancy and also have risk factors for placenta accreta such as suction curettage history, history of repeated cesarean section or endometritis. It helps to decrease morbidity and mortality of these patients.
6. Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
7. Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the efforts of Fertility, Infertility and Perinatology Research Center for its support.
NOTES