The Association of Psychological Stress Related Cytokines (TNF Alpha, IFN-Gamma) with Essential Hypertension in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region ()
1. Introduction
Essential hypertension is an important risk factor of a variety of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases [1], which are of the highest morbidity and mortality diseases [2-4], and the incidence trends to rise in recent years [5,6]. But the pathogenesis of essential hypertension is still unknown, which is also considered to be the result of a variety of environment factors in a certain genetic background.
Studies have shown that the essential hypertension was closely related to psychological factors, and psychological stress can not only cause transient rise of blood pressure, but also induce the formation of essential hypertension and contribute to its development. A great deal of research has shown that patients with essential hypertension were associated with different degrees of emotional disorder [7,8].
Along with the development of socio-economic, the acceleration of life pace, and the fierce of society competition, people are suffering from a wide range of psychological pressure. The issue of mental health increasingly attracts people’s attention. And scholars had paid more attention to the influence of the mental health on the occurrence, development and prognosis of the disease. The theory, about which psychologically related cytokines influenced the change of the blood pressure, had been recognized by many scholars.
With the rapid development of medical molecular biology technology, scholars studied the pathogenesis of hypertensive disease deeply, and more and more studies confirmed that hypertension was an inflammatory disease [9,10]. In recent years, the research of the association of immune inflammatory response with hypertension has gone beyond the bound of pure biology or pure psychology, and it was widely considered that psychological stress can impair immune function, result in the production of cytokines, and eventually lead to the occurrence of hypertension [11,12].
Our study was to study the relationship between the psychological stress-related cytokines and essential hypertension, as well as the role of the psychological stress and its related cytokines in the development of essential hypertension, to provide new ideas and guidance for the prevention and control of essential hypertension, and to further provide basic information for the study of pathogenesis of essential hypertension by surveying the status of mental stress and measuring the serum levels of psychological stress-related cytokines, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma).
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Subjects
We screened hypertension patients in six communities in Wuzhong City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, and chose the healthy people who had lived in the same community full 5 years as control group randomly.
Inclusion criteria were: 1) Hypertension patient who had been confirmed; 2) The control group participant was the healthy community population who had lived in the same community full 5 years, and who was the same sex and the same nationality as the case group, and age difference was in 5 years.
Exclusion criteria were: 1) Hypertension patient with severe hypertension complications; 2) Hypertension patient with family history of hypertension; 3) Hypertension patient with severe somatic diseases, secondary hypertension, neurological or psychiatric disorders; 4) Control group participant with other endocrine diseases which had similar etiology with hypertension.
Refer to relevant literature, our study adopted 1:1 matched case-control study. The formula for calculation of sample: , P =
, P = ,
,  ,
,
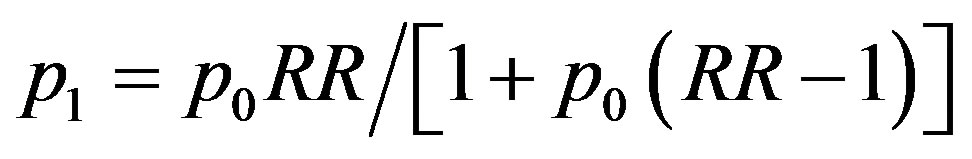 . The significance level was 0.05, the allowable error was 0.10, p0 = 55.9%, RR = 2.52, each of Hui and Han ethnic need 110 pairs of cases and controls. Finally, we selected 210 pairs of cases and controls randomly, including 108 pairs of Hui nationality and 102 pairs of Han nationality (50% male; 35 - 74 years of age).
. The significance level was 0.05, the allowable error was 0.10, p0 = 55.9%, RR = 2.52, each of Hui and Han ethnic need 110 pairs of cases and controls. Finally, we selected 210 pairs of cases and controls randomly, including 108 pairs of Hui nationality and 102 pairs of Han nationality (50% male; 35 - 74 years of age).
2.2. Methods
1) The questionnaire: the questionnaire included name, gender, age, ethnicity, address, profession, marital status, educational qualification, telephone number, duration of time living in the community, how much they exercised, history of smoking, history of drinking, their dietary habits, state of interpersonal sensitivity, economic hardship, failure, and bereavement, prolonged illness, family history and personal history of hypertension.
2) Measurement of blood pressure, height and body weight: In accordance with the standard of “guidelines for management of hypertension in China (revised 2005)”, in the absence of antihypertensive drugs, people with systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg can be diagnosed as hypertension. Diagnosis of hypertensive patients must be multiple measurements of blood pressure while was maintaining in a state of quiet. All the participants were made to rest for at least 30 min in a sitting position, and then blood pressure of their right arm was measured with a desktop mercury sphygmomanometer. The participant with the systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg and/ or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg under quiescent condition or with previous history of hypertension can be diagnosed as hypertensive patient. Height and body weight were measured to calculate body mass index (BMI).
3) Blood sample collection: draw the morning fasting blood samples 3 milliliter, preserve them statically at room temperature for thirty minutes, and centrifuge them 3000 rpm for 15 minutes, then separate serum from blood for serum TNF-α, IFN-gamma, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC), fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test.
4) Assay: we used double antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method to determine the concentration of stress related factors, TNF alpha and IFN-gamma, and the ELISA test kit was purchased from Shanghai boatman company. Other serum index was tested by automatic biochemical analyzer OLYMPUS, AU2700 made in Japan.
5) Statistical analysis: SPSS 17.0 software was used for the statistical analysis. Quantitative data was expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) assuming Gaussian distribution. The comparisons of quantitative data between two groups were analysed with t-test. Risk factors were analysed using Logistic Regression. Correlation between variables was analysed by Pearson correlation. Multiple linear regression analysis was used for the multivariate analysis. Two-tailed significance values were given with P < 0.05 regarded as significant.
3. Result
3.1. Conditional Logistic Regression Analysis of Hypertension Psychological Stress Risk Factors of Hui and Han Ethnic Hypertension Group
Psychological stress risk factors of hypertension were presented in Table 1. Single-factor conditional Logistic regression analysis showed that, five aspects were the risk factors for Han hypertension group, and which were presented in Table 2. According to the results of single-

Table 1. The distribution of high blood pressure risk factor in Ningxia Hui and Han ethnic group.

Table 2. Single-factor conditional logistic regression analysis of Han ethnic hypertension group.
factor analysis, five factors had statistical significance (P < 0.05), and there were two factors filtered into the multifactor conditional logistic regression model (Table 3).
Single-factor conditional logistic regression analysis showed that six aspects were risk factors for Hui ethnic hypertension group, which were presented in Table 4. According to the results of single-factor analysis, and there were five factors filtered into the multifactor conditional Logistic regression model (Table 5).
3.2. Analysis of Psychological Stress Related Factors, TNF Alpha and IFN-Gamma in Hui and Han Ethnic
By paired t-test analysis, the results showed, the serum concentration of TNF alpha of hypertension group was higher than the control group, and the serum concentration of IFN-gamma of hypertension group was lower than the control group both in hui and Han ethnic respectively, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.01). The serum concentration of TNF alpha of Hui ethnic hypertension group was higher than the Han ethnic hypertension group, and the serum concentration of IFNgamma of Hui ethnic hypertension group was lower than the Han ethnic hypertension group, the difference had

Table 3. Multi-factor conditional logistic regression analysis of Han ethnic hypertension group.
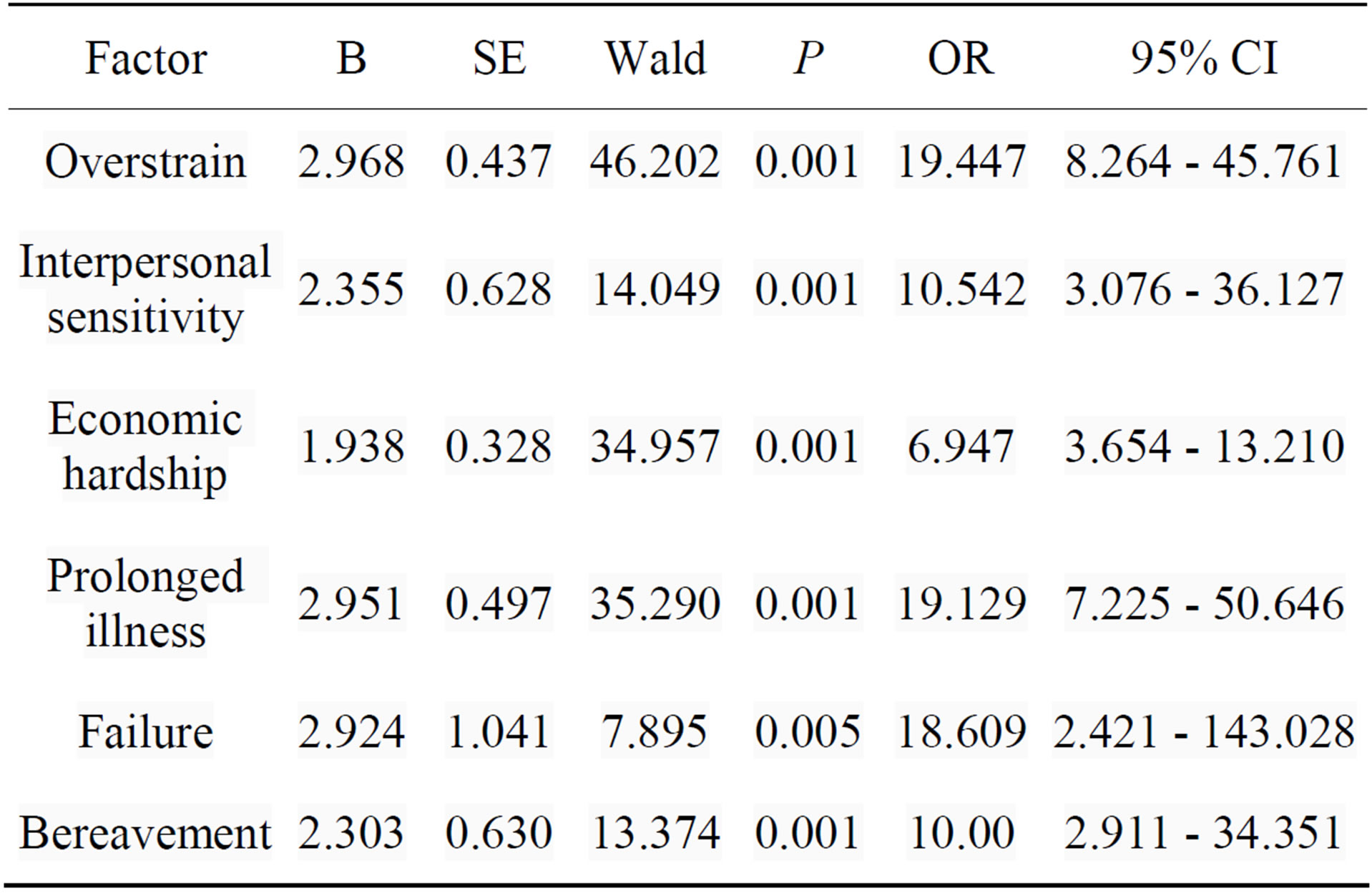
Table 4. Single-factor conditional logistic regression analysis of Hui ethnic hypertension group.

Table 5. Multi-factor conditional logistic regression analysis of Hui ethnic hypertension group.
statistical significance (P < 0.01) (Table 6).
3.3. The Correlation Analysis of TNF Alpha and IFN-Gamma with Other Indicators in Hui and Han Hypertension Group
Pearson correlation analysis showed that the TNF-α of Hui hypertension group had a positive correlation with BMI, TC and TG, but had a negative correlation with HDL-C, and the TNF-α of Han hypertension group had a positive correlation with BMI, TC, TG and LDL-C. The IFN-gamma of Hui hypertension group had a negative correlation with age, BMI, TC and TG, and the IFN-

Table 6. Analysis of TNF alpha and IFN-gamma in Hui and Han ethnic.
△P < 0.01, the comparison of TNF alpha of Hui hypertension group with control group; ▲P < 0.01, the comparison of TNF alpha of Han hypertension group with control group; ▽P < 0.01, the comparison of IFN-gamma of Hui hypertension group with control group; ▼P < 0.01, the comparison of IFNgamma of Han hypertension group with control group; ☆P < 0.01, the comparison of TNF alpha of Hui hypertension group with Han hypertension group; ★P < 0.01, the comparison of IFN-gamma of Hui hypertension group with Han hypertension group.
gamma of Han hypertension group had a negative correlation with BMI, TC, TG, LDL-C and FPG (Table 7).
3.4. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis of TNF Alpha with Other Indicators in Hui and Han Hypertension Group
The TNF alpha of Hui and Han hypertension was dependent variable, and Age, BMI, TC, TG, LDL-C, HDLC and FPG were independent variable, the multiple linear regression analysis showed that the TNF-α of Hui hypertension group had a linear regression with Age, BMI, TC and HDL-C, and the TNF-α of Han hypertension group had a linear regression with BMI (Table 8).
3.5. Multiple Linear Regression Analysis of IFN-Gamma with Other Indicators in Hui and Han Hypertension Group
The TNF alpha of Hui and Han hypertension was dependent variable, and Age, BMI, TC, TG, LDL-C, HDLC and FPG were independent variable, the multiple linear regression analysis showed that the IFN-gamma of Hui hypertension group had a linear regression with age and BMI, the IFN-gamma of Han hypertension group had a linear regression with BMI (Table 9).
4. Discussion
Adverse psychological stress stimulates endocrine axis, which promotes the secretion of adrenal cortex hormones and pituitrin vasopressin, these hormones lead to heart rate elevating, vasoconstriction, blood pressure rising, that is the main influence of psychological stress on hypertensive disease [13]. SCL-90 symptoms self evaluation scale is internationally recognized scale, which can accurately depict mental health [14]. Our past study

Table 7. The correlation analysis of TNF alpha and IFNgamma with other indicators in Hui and Han hypertension group.
adopted SCL-90 scale to test the psychological stress condition of Hui and Han ethnicity in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, the results supported the view that psychological stress was one of the major risk factors in the genesis and development of hypertension [15,16].
Style stress theory pointed out that the whole process of the stress was triggered by stressor. Adverse life events stress was a kind of important stressor, and stressful life events may induce hypertension. The single-factor conditional logistic regression analysis results showed that overstrain, interpersonal sensitivity, economic difficulties and long illness were associated with hypertension [17]. The results of multifactor conditional logistic regression analysis showed that excessive anxiety and economic difficulties were significantly correlated with hypertension. The results suggested that different social economic pressure may be an important influence on hypertension [18,19].
Research suggests that psychological stress may be via the sympathetic nervous system and the catecholamine of blood circulation to cause many harmful effects. Sympathetic nerve excitement and the elevation of catecholamine levels in plasma can make platelet and macrophage active, and raise the expression of inflammatory molecules, which lead to endothelial dysfunction and the occurrence of hypertension [20]. TNF alpha is a kind of inflammatory cytokines which is produced by activation of mononuclear macrophage and has a variety of biological effects. TNF alpha plays an important role in immune regulation in chronic psychological stress, and its gene polymorphism also affects the level of psychological stress, and becomes the stress sensitive genes. Studies have found that a variety of psychological stress factors can induce the secretion of TNF alpha [21]. TNF alpha can not only damage blood vessels directly, but also cause its function disorder through increasing the gener-

Table 8. Multiple linear regression analysis of TNF alpha with other indicators in Hui and Han hypertension group.

Table 9. Multiple linear regression analysis of IFN-gamma with other indicators in Hui and Han hypertension group.
ate of blood vessel contraction factors and reducing the release of vasodilatation factors [22]. This study showed that, compared with control group, the serum TNF alpha level of Hui and Han hypertension group was higher, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.01), and which was in accordance with the past research results [23,24]. Previous study found that TNF-α was an important cytokine, which mediated inflammatory response and immune regulation, and played important role in the occurrence and regulation of vascular endothelial cells [25]. Abnormal function and structure of endothelial cells had close relation with hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, taking effective measures to control the level of serum TNF alpha may have the vital significance in alleviating or preventing the genesis and development of hypertension.
IFN-gamma was a kind of vascular endothelial cytokines, which was known as inflammatory cytokines associated with psychological stress, which had a wide range of pathologic physiology in the occurrence and development of hypertension, and played important role in the process of chronic psychological stress. This study showed that, compared with control group, serum IFNgamma level of Hui and Han ethnicity hypertension group declined significantly (P < 0.01). IFN-gamma was Th1-type cytokine, and mainly mediate cell immune. Significant reducing of serum IFN-gamma level suggested the reducing of cellular immune function, endocrine disorders, the blood pressure self-adjusting ability of body declines, which lead to the development of hypertension.
Our study also found that the concentration of TNF alpha of Hui ethnicity hypertension group was higher than Han ethnic hypertension group, but IFN-gamma concentration was lower than Han ethnic hypertension group, the difference had statistical significance (P < 0.01). The results indicated that the stress related cytokines TNF alpha and IFN-gamma were associated with Hui and Han ethnicity hypertension, and existed difference between Hui and Han ethnicity, this conclusion remained to be further research.
Multiple regression analysis showed that the TNF-α of Hui hypertension group had a linear regression with age, BMI, TC and HDL-C, the TNF-α of Han hypertension group had a linear regression with BMI; and the IFNgamma of Hui hypertension group had a linear regression with age and BMI, the IFN-gamma of Han hypertension group had a linear regression with BMI. Which suggested that TNF-α, IFN-gamma, age and BMI may together participated in the development of hypertension disease, and we should continue to conduct a prospective study in this aspect to explore the mechanism further.
From the previous literature and this study, we known that psychological stress was an important risk factor of the development of hypertension, and hypertension patents have poor psychology. So, while preventing or treating hypertension, people must improve the bad psychology. This study also showed that TNF-α and IFN-gamma had significant correlation with hypertension, therefore, taking measures to adjust the serum level of TNF-α and IFN-gamma may have vast importance to the intervention and treatment of hypertension.
5. What Is Known about the Topic
The psychological stress can not only cause transient rise of blood pressure, but also induce the formation of essential hypertension and contribute to its development. And patients with essential hypertension were associated with different degree of emotional disorder.
6. What Does the Study Add
TNF alpha and IFN-gamma were the important related cytokines between psychological stress and hypertension, and taking effective measures to control the level of serum TNF alpha and IFN-gamma may have the vital significance in alleviating or preventing the genesis and development of essential hypertension.
7. Conclusion and Limitations about This Investigation
This study explores the relationship between psychological stress-related factors and Hui Han Zu hypertension. It is difficult to illuminate genetic correlation. In the future research, we should carry out the study of the association between stress-related genes and hypertension, for further discussion of the differences of hypertension between different ethnic groups.
8. Acknowledgements
Source of Funding: This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China, the project was the association study between the expression and polymorphism of stress related genes, NPY, TNF-alpha, and metabolic syndrome, and the item number was 30860236.
NOTES
#Corresponding author.