Investigated the hospital utilization and medical resource usage of haemophilia A and B in Taiwan: 2001-2010 ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Hemophilia is a rare, devastating, inherited condition in which repeated bleeding leads to disability, pain and early death [1]. Hemophilia is an X-linked congenital bleeding disorder, with deficiency of coagulation factor VIII (hemophilia A, HA) or factor IX (hemophilia B, HB). Hemophilia patients often have hemarthrosis with severe joint pain, which results in joint immobility and subsequent muscle atrophy, joint contracture, and gait disturbance [2]. During the past 30 years, the life expectancy for individuals with haemophilia has significantly increased, largely because of the advances in medical care, the introduction and accessibility of factor replacement therapies, as well as improvements in the treatment of infectious diseases [3,4]. Although individuals with haemophilia have benefited from safer, more effective factor replacement products, these advances have been paralleled by substantial cost increases in the treatment for these patients [5].
In March 1995, Taiwan established a National Health Insurance (NHI) programmed, with approximately 23 million insured, covering over 99% of Taiwan’s population. The National Health Insurance Law defined haemophilia as a catastrophic illness, exempting patients from a copayment requirement and assuring patient’s access to adequate treatment. However, an optimal national treatment guideline has not yet been developed [6]. In Taiwan, the estimated mean prevalence (all severities) per 100,000 males was 6.7 ± 0.1 for HA and 1.2 ± 0.1 for HB, respectively, and showed a growth of 0.1 per 100,000 males every 2 - 3 year, respectively. The proportion of annually NHI medical expense for congenital abnormality of coagulation is around 0.4% - 0.5% [7]. As such, the care of hemophilic patients is costly [8,9], urgently needed to allow for newer insights, based on reliable data sources into resource allocation, cost-utility analysis in the treatment of haemophilia. The objectives of this study were to: identify and compare the overall cost and medical resource utilization of both treatments in order to provide a baseline model for Taiwan’s national insurance payment system and a reference for medical health-care policy in Taiwan and elsewhere.
2. METHODS
2.1. Database
The dataset was sourced from the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) for the period from 2001 to 2010. Initiated in 1995, Taiwan’s NHI program is characterized by a single plan with the government as the sole insurer, comprehensive benefits, low co-payments, and free choice of healthcare providers from a widely-dispersed network. The NHI had 23.34 million members (an over 99.5% coverage rate) at the end of 2012. The NHIRD is published annually by the Taiwan National Health Research Institute, and contains the original claim data and registration files for all the enrollees under the NHI program.
2.2. Study Sample
The study was designed as a retrospective study. In total, 2150 patients hospitalized with a discharge diagnosis of HA and HB (International Classification of Disease, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes 286.0 and 286.1) between January 2001 and December 2010 were selected from the NHIRD. Of these sampled patients, we identified 460 patients (27.2%) who had other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, according to the ICD-9-CM Clinical Modification code 710-739 (Co morbid disorders were identified at the enrolled hospitalization). If a patient had ≥2 hospitalizations within a 30-day period, they were regarded as the same episode and we only included the first hospitalization. The study cohort in terms of gender, age (<18, 18 - 30, 31 - 44, 45 - 64, and >65 years), urbanization level (5 levels; from 1 [most urbanized] to 5 [least urbanized]), a similar sex and age distribution. The mean age for these 2,150 patients was 30.2 (±23.0 years) years, with a range between 1 and 98 years.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
The SPSS statistical package (SPSS System for Windows, version 18.0). Pearson Chi-square tests were used to examine the gender, age, distributions of urbanization level, hospital level (Medical center, Regional hospital and Community hospital), and Division of both patients (HA and HB; Haemophilia with Musculoskeletal system and without musculoskeletal systems). We also performed a t-test survival analysis to medical expenditures and average length of stay (ALOS). A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. RESULTS
Taiwan HA and HB were included in the study sample. Haemophilia numbers during the study period included 219 in 2001, 213 in 2003, 233 in 2005, 217 in 2007, and 233 in 2010. The Length of hospital stays for 9 days, respectively. Hospitalization length decreased by 16% over the period studied. Table 1 illustrates the annual rise in total hospitalization costs for Haemophilia treatment during the 10-year period studied. Costs rose from NT $ 80.25 million in 2001 to NT $225.89 million in 2010 (Figure 1), with a total increase over the period of 181%.
The distribution of patients and hospital characteris-
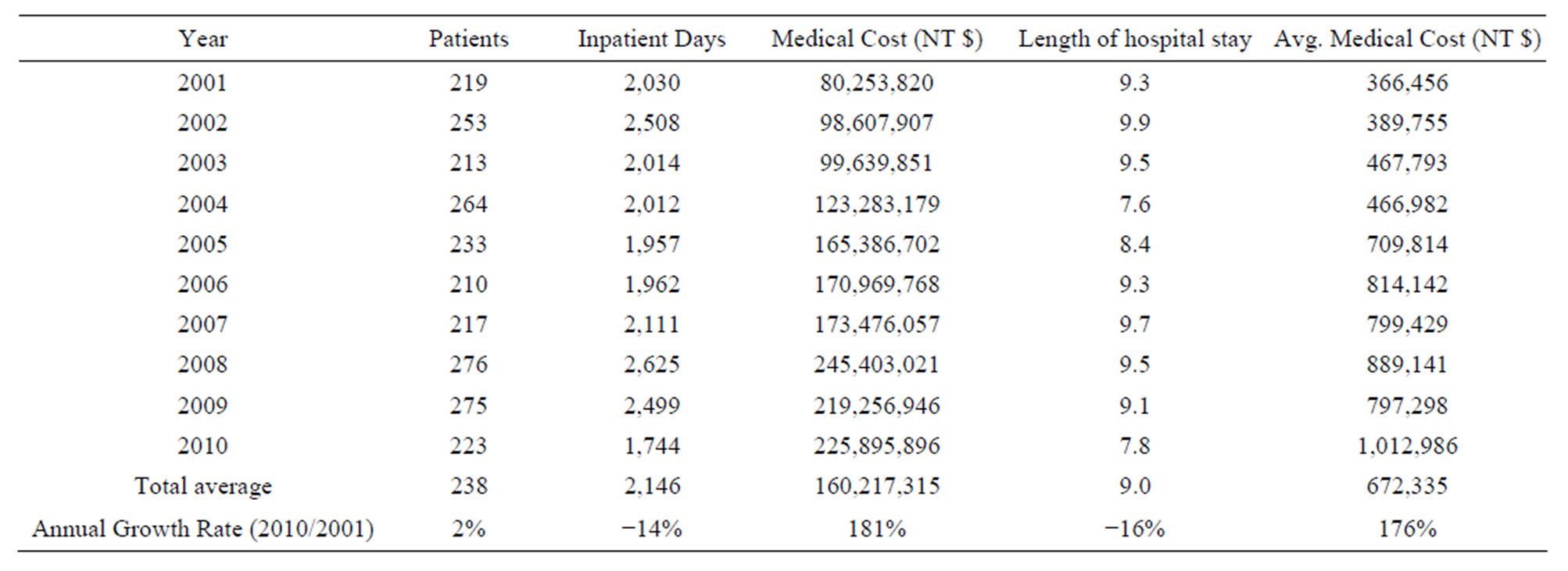
Table 1. 2001-2010 Medical Cost Statistics for Hemophilia patients under National Health Insurance programs.

Figure 1. Total costs of Hemophilia patients.
tics between the study cohort and comparison cohort is presented in Table 2. Overall, 1965 (91.4%) of the study participant were male and 185 (8.6%) were female (P < 0.05). This ratio supports the fact that the disease is more prominent amongst men. In terms of age, the average age of the participants was 30.2 (±23.0 years) years (P < 0.001) years. Most were in the <18 age groups. This finding supports the fact that the disease is more prominent amongst the juvenile and children., with a range between 1 and 98 years, Clinical division in general medicine (35.1%) and pediatrics (35.1%) at most primary (P < 0.05). No significant difference in the lowincome families, hospital level and urbanization level was detected between the study cohort and comparison cohort.
Total costs are shown in Table 3. 85.9% (patients 1847) to HA and only 14.1% (303 patients) to HB. In this study, we found the mean cost of cases being significantly higher during the HA that in the HB (NT $708,620 ± NT $1,414,988 vs. NT $422,322 ± NT $880,159, respectively, P < 0.001). Researchers categorized medical cost variables according to the Bureau of National Health Insurance guidelines as follows: diagnosis costs (including costs of inpatient diagnosis and consultation), ward costs (including ward and nursing costs), tube feeding costs, laboratory costs (including complete blood cell, glutei oxaloacetic transaminase, glutamic pyruvic transaminase, cholestero1, blood urea nitrogen, sodium, potassium, chlorine, cardiac catheterization and coronary angiography costs), X-ray costs (e.g., chest posterior to anterior costs), therapeutic procedure costs (including costs for therapeutic treatment, temporary pacemakers and electrocardiogram monitoring), blood/plasma costs, hem dialysis costs (including costs of hem dialysis and peritoneal dialysis), special materials costs, drug costs, dispensing service costs (e.g., unit dose dispensing costs) and injection service costs. The two classic types of studies in medical research are HA and HB, researchers found a significant statistical difference in diagnosis (95% CI = 339 - 1141), word (95% CI = 448 - 5848), laboratory (95% CI = 658 - 2010), X-ray (95% CI = 500 - 1522), blood/plasma (95% CI = 112 - 425), Hem dialysis (95% CI = 1007 - 2508), drug (95% CI = 157,905 - 391,158), Dispensing service (95% CI = 106 - 300), psychotherapy (95% CI = 17 - 90) and injection service costs (95% CI = 126 - 333) (P < 0.001). No significant difference in costs for tube feeding, therapeutic procedure, surgical, rehabilitation, anesthesia and special materials (P > 0.1). Medical costs such as those for HA were significantly higher than HB (P < 0.001).
Table 4 shows that there was no significant difference in two classic types of studies in medical research are Haemophilia with musculoskeletal system (21.3%) and Comparison patients (78.7%), researchers found a significant statistical difference in gender, age, diagnosis, tube feeding, laboratory, therapeutic procedure, surgical, rehabilitation, blood/plasma, anesthesia, special materials, drug and dispensing service costs (P < 0.001). No significant difference in costs for word, X-ray, hem dialysis, psychotherapy and injection service cost (P > 0.1), Medical costs such as those for Haemophilia with musculoskeletal system were significantly higher than comparison patients (P < 0.001).