A series of ruthenium azopyridine complexes have recently been investigated due to their potential cytotoxic activities against renal cancer (A498), lung cancer (H226), ovarian cancer (IGROV), breast cancer (MCF-7) and colon cancer (WIDR). Thus, in order to predict the cytotoxic potentials of these compounds, quantitative structure-activity relationship studies were carried out using the methods of quantum chemistry. Five Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship (QSAR) models were obtained from the determined quantum descriptors and the different activities. The models present the following statistical indicators: regression correlation coefficient
R2 = 0.986 - 0.905, standard deviation
S = 0.516 - 0.153, Fischer test
F = 106.718 - 14.220, correlation coefficient of cross-validation
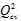
= 0.985- 0.895 and
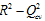
= 0.010 - 0.001. The statistical characteristics of the established QSAR models satisfy the acceptance and external validation criteria, thereby accrediting their good performance. The models developed show that the variation of the free enthalpy of reaction
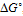
, the dipole moment μ and the charge of the ligand in the complex
Ql, are the explanatory and predictive quantum descriptors correlated with the values of the anti-cancer activity of the studied complexes. Moreover, the charge of the ligand is the priority descriptor for the prediction of the cytotoxicity of the compounds studied. Furthermore, QSAR models developed are statistically significant and predictive, and could be used for the design and synthesis of new anti-cancer molecules.