Background: The status of inquisition by the nursing students shall be determined as it will be utilized as a tool to measure their clinical performance expertise as future nursing practitioners. The element of scientific inquiry is essential in providing standard fillers to give meaning to the various practical nursing gaps in the actual field, the hospital ward to be specific.
Objective: This research study aims to establish the level of scientific inquiry and clinical performance of undergraduate Arab nursing students.
Methods: The researcher utilized descriptive-correlational study as the research design. This is a descriptive study because it describes the level of scientific inquiry and level of clinical performance of the undergraduate Arab nursing students.
Results: The finding of the study is that “the majority of the Arab student nurses demonstrate a guided inquiry in their scientific inquiry level”. Most of the Arab student nurses demonstrate a guided inquiry (
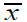
= 2.74, SD ± 0.99) in terms of their level of scientific inquiry. Largely, the Arab student nurses have proficient level in their level of clinical performance (
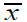
= 87.32, SD ± 12.36). Regression analysis revealed a no significant relationship (r
2 = 0.57; adjusted r
2 = 0.57; p > 0.005) between the level of scientific inquiry and clinical performance among Arab student nurses.
Conclusions: The study concluded that the majority of the Arab student nurses demonstrated a guided inquiry in their scientific inquiry level and a moderately proficient level of clinical performance. Furthermore, the study concluded that the level of scientific inquiry was not significantly related to clinical performance.