Using Spectroscopic Ellipsometry (SE), the optical
properties of Cu(In
1−xGa
x)
3Se
5 bulk compounds, grown by the Bridgman
method, were analyzed by varying x composition (0 ≤ x ≤ 1). Energy levels above
the gap in the band scheme were determined by measuring the complex dielectric
function
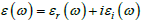
at
room-temperature for energies between 1.5 and 5.5 eV using a variable angle of
incidence ellipsometer. The transitions values
E1,
E2 and
E3 were observed above
the gap for different samples of Cu(In
1−xGa
x)
3Se
5 alloy. When a gallium atom replaces an indium atom, one assumes globally that
the levels related to selenium and copper are unchanged. Conversely, the levels
corresponding to the conduction band are shifted towards higher energies. Thus,
the gap increases as the composition of gallium increases. Spectroscopic
Ellipsometry (SE) gave evidence for the interpretation of the choice of gap
values which were compatible with that obtained from solar spectrum. Several
other characterization methods like Energy Dispersive Spectrometry (EDS), hot
point probe method, X-ray diffraction, Photoluminescence (PL), Optical response (Photoconductivity) were presented in this
paper. The Cu(In
1−xGa
x)
3Se
5 have an Ordered Vacancy Chalcopyrite-type structure with lattice constants varying as a function of the x composition. The
band gap energy of Cu(In
1−xGa
x)
3Se
5 compounds is found to vary from 1.23 eV to 1.85 eV as a function of x.