Do GMOs Accumulate Formaldehyde and Disrupt Molecular Systems Equilibria? Systems Biology May Provide Answers ()
1. Introduction
The safety assessment of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is a particularly contentious subject. The study, herein, provides, to the authors’ knowledge, the first systems biology analysis for assessing the safety of GMOs. In this research, a promising computational systems biology method [1] is utilized to couple the dynamics of known perturbations caused by the genetic modification (GM) of CP4 EPSPS in soybean, also known as Roundup Ready Soya (RRS) [2] with an integrative model of C1 metabolism and oxidative stress (two molecular systems critical to plant function), derived from previously published research [3] -[5] . Specifically, five biomolecules, including four enzymes―ascorbate peroxidase, catalase, glutathione reductase and superoxide dismutase, as well as one reactive oxygen species (ROS)―hydrogen peroxide, are known to perturb in RRS [6] -[8] .
Glyphosate-based herbicides, such as Roundup, inhibit 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase (EPSPS), a critical enzyme that is absolutely necessary for plant survival, as the enzyme is essential to catalyze the final step in the shikimate pathway’s biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids [9] . Roundup Ready (RR) plants contain the gene, which codes for a glyphosate-insensitive form of EPSPS, obtained from Agrobacterium sp. strain CP4 [9] . When GM occurs, the CP4 gene is incorporated into the plant genome to produce the enzyme CP4 EPSPS, which is insensitive to glyphosate, thus enabling the plant’s resistance to glyphosate [10] .
To date, regulatory authorities in twelve countries have approved the environmental (commercial) use of CP4 EPSPS GM in at least a total of seven plant species including Beta vulgaris L. (sugarbeet), Brassica napus L. and Brassica rapa L. (oilseed rape and turnip rape, respectively, although both can be referred to as canola), Gossypium hirsutum L. (cotton), Medicago sativa L. (alfalfa), Zea mays L. (maize), and Glycine max L. (soybean) [10] . The substantial advantages of such crops to be glyphosate-tolerant have resulted in rapid adoption: 94% of soybean, 91% of cotton, and 89% of corn planted in the United States, as of 2014, are glyphosate-tole- rant varieties [12] . However, concerns about the potential health and environmental safety of GMOs have limited the acceptance of such seed lines and food products, particularly in Europe and Japan [10] .
The results from this study suggest a substantial difference in the molecular systems of non-GMO and GMO versions of soybean, as observed in the temporal dynamics of two biomarkers, formaldehyde and glutathione, which predict metabolic disruptions in C1 metabolism. In non-GMO plants, formaldehyde, a known toxin, remains at near zero levels, as it is naturally cleared through a process of formaldehyde detoxification, a molecular system resident in all plants, bacteria and fungi [3] [4] . Concomitantly, glutathione, a known anti-oxidizing agent, in non-GMO plants, is naturally replenished and remains at non-zero steady state levels, to support such system detoxification of formaldehyde [4] . However, in the GMO case of soybean, or RRS, there is a significant accumulation of formaldehyde and a concomitant depletion of glutathione, suggesting how a “small” and single GM can create “large” and systemic perturbations to molecular systems equilibria.
The results of this research are particularly relevant, as the United States White House on July 2, 2015 has ordered a review of rules for GM crops [11] . The computational systems biology approach, herein, and the resultant predictions, may inform regulatory agencies in their efforts for “Improving Transparency and Ensuring Continued Safety in Biotechnology” [11] , to adopt a systems biology approach using a combination of in silico, computational methods used herein, and subsequent targeted experimental in vitro and in vivo designs, to develop a systems understanding of “equivalence” using biomarkers, such as formaldehyde and glutathione, which predict metabolic disruptions, as criteria for modernizing the safety assessment of GMOs, while fostering a much-needed transparent, collaborative and scientific discourse.
1.1. The Current Discourse on GMOs
A scientific discourse is particularly important as GMOs are a controversial topic [13] -[15] . Supporters of GMOs claim that due to the growing world population and shrinking resources such as arable land, there is a dire need for deploying GMOs to keep food production in pace [16] -[18] . This claim has been refuted by scientists and members of the sustainable agricultural community who assert that practices such as organic, biodynamic and indigenous farming methods, done within local and small farm ecosystems, can provide more than enough food to feed the world’s population while avoiding risks to human and environmental health caused by GMO foods and their reliance on man-made pesticides and factory farming methods [19] [20] .
Proponents of GMOs assert there is no safety concern since GMOs are approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) framework of substantial equivalence [21] (also referred to as “material difference” [22] ), a concept used for assessing “equivalence” or “difference” of GMOs and their non-GMO counterparts, and further argue humans have been plant breeding, a form of “genetic modification”, over many millennia. Anti-GMO activists counter that GMOs are unsafe since substantial equivalence is itself unscientific, and contend that targeted GM of specific genes are far different than plant breeding.
There are many aspects of this debate, which span emotional, economic, psychological, political, spiritual, and historical realms [14] [23] -[25] . The methodology for identifying the specific and relevant criteria, used in substantial equivalence, however, appears to be the objective and tangible cause of contention [19] . There is a growing and convergent consensus that new solutions and scientific methods are needed to select the relevant criteria for substantial equivalence [26] [27] .
1.2. A Systems Biology of GMOs
This research aims to provide a rational scientific framework, founded in principles of systems science and molecular systems biology, to discover such criteria to advance safety assessment of determining “equivalence” and/or “difference” of GMOs and their non-GMO counterparts [26] [28] . Systems biology, a new discipline emerging from the post-genomic era, provides a much-needed scientific and systems-based framework to explore how genetic modifications, small or large, may affect emergent properties of whole organisms [29] [30] . Computational methods emerging from systems biology are used in this study to explore critical molecular pathways and regulatory molecules, involved in critical plant function, as an approach to potentially discover key biomarkers that reflect disruptions to molecular systems equilibria and may be used as more relevant biological criteria for determining substantial equivalence.
Genetic engineering, like the splitting of the atom, is a significant human technological achievement. However, modern safety assessment methods for GMO’s have lagged. Systems biology methods, such as CytoSolve, the computational systems biology approach used in this study, emerging out of research from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (M.I.T.), one of the leading institutions that pioneered critical advancements in genetic engineering [31] , now provides a systematic methodology to integrate known molecular pathway knowledge and to mathematically model such information to understand the complexity of biological organisms, towards assessing safety of a GMO with its non-GMO counterpart. Moreover, systems biology approaches can aid in biosafety questions of GMOs in scientific risk assessment for decision-making [32] .
The computational systems biology methods employed in this effort provide a framework for not only making predictions but also for informing intelligent in vivo and in vitro experimental designs to verify the predictions observed in this research. This framework aims to foster open, transparent and collaborative scientific discourse, now possible through a combination of in silico, computational methods used herein, and subsequent targeted experimental in vitro and in vivo designs to develop a systems understanding of “equivalence” of GMOs and their non-GMO counterparts, not only in soybean but also across all plants.
1.3. Need for Standards for In Vitro and In Vivo Testing of GMOs and Non-GMO
The results from the in silico computational systems biology methods used in the study, suggest a substantial and material difference in a soybean GMO versus its non-GMO counterpart; in particular, the analysis suggests that GMOs in plants lead to significant changes in concentrations of the two biomarkers: formaldehyde and glutathione, suggesting deleterious biological impacts. The next logical phase of this study would be to conduct in vitro and in vivo experiments to verify these predictions.
However, such in vitro and in vivo tests are untenable for at least two reasons. First, it is difficult to acquire source material in an objective and independent manner, while maintaining compliance with existing legal constraints on the use of such GMO source material. Second, given the current environment of debate and controversy, any isolated experiment, done by either proponents of GMOs or those against GMOs, will be vigorously contested, since there are no agreed upon industry standards for conducting such testing to compare a GMO with its non-GMO counterpart.
Given the significant difference in levels of the two biomarkers of formaldehyde and glutathione, across GMO and non-GMO soybean, predicted from the in silico computational results of this research, and given the need to perform such in vitro and in vivo experiments, it becomes imperative to develop such objective industry standards to perform the necessary in vitro and in vivo testing, to advance the current discourse, beyond debate and controversy.
The timely White House initiative for “Improving Transparency and Ensuring Continued Safety in Biotechnology” for reviewing rules concerning safety of biotechnology products [25] perhaps provides a unique opportunity for conducting such discourse to develop the much-needed industry standards for conducting objective in vitro and in vivo testing of a GMO and its non-GMO counterpart.
2. Substantial Equivalence
The concept of substantial equivalence, first appearing in a legislative amendment enacted by President Gerald Ford on May 28, 1976, enabled the FDA to compare the “equivalence” of newly developed medical devices with its traditional counterpart [21] (now also referred to as “material difference” [22] ). Substantial equivalence is based on the concept that existing products can serve as a benchmark for assessing the safety of new products. Using this concept, if a new product is found to be “equivalent” to its traditional counterpart, it is deemed safe. The intention of using this concept was towards fast-tracking the manufacturing of low and moderate risk medical devices to the market without the requirement of rigorous safety testing [28] .
With the advent of GMO crops, substantial equivalence was horizontally adopted from the medical systems and devices industry to the realm of agricultural systems and foods to become the mainstay for safety assessment of GMOs [27] . The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), one of the organizations along with the WHO and FAO focused on providing guidelines for safety assessment of foods derived from biotechnology, first mentioned the term “substantial equivalence” in the context of food safety in 1996 [27] . In 2001, the FDA issued a draft guidance for voluntary labeling of foods developed using bioengineering [22] . The draft guidance reiterates the FDA’s 1992 requirements for labeling products that have a significant change in nutrient content, contain a proven allergen, or have a “material difference” from the conventional counterpart. Using this concept, meta-level criteria were identified for substantial equivalence and/or material difference, relative to foods, in terms of: use, nutritional value, composition, nutritional effects, metabolism and level of undesirable substances [27] . In this application of substantial equivalence, foods derived from GMOs are considered “substantially equivalent” to their non-GMO and traditional counterparts if there are no intended or unintended alterations in the composition, if there are no adverse effects on dietary value, and if they pose no harm to the consumer and environment [27] .
The first instance of the application of the substantial equivalence concept to a GMO was for the safety assessment of Flavr Savr tomato in 1994, when it was proven that the GM tomato was equivalent to the wild type, in terms of molecular and chemical composition [27] . The newly introduced traits were further studied and certified by the FDA for safety [27] . Another report on the establishment of compositional equivalence includes details on GM corn and soybean [33] . In this case, the investigators put forth that the compositional variation between GM varieties and their conventional counterparts is encompassed within the natural variability of the crop, and only when there is a difference of >±20%, additional analyses are required [33] .
There is, however, significant disagreement concerning the application of substantial equivalence for safety assessment of GMOs even among the scientific community [34] . Anti-GMO activists argue that substantial equivalence is unscientific and outdated since it was originally developed in the 1970s for medical devices, which are not comparable to the complexity of biological systems. They also argue that by using substantial equivalence, industries could try to “have it both ways” [35] by stating that GM foods are novel in certain respects, which allow them to be patented, and in the same breath by using substantial equivalence, they can prove they are “not so novel” and “equivalent” to their non-GMO counterparts, thereby allowing them to mollify safety concerns as they pose no risks to health or environment [35] .
The concept has also been criticized as “pseudo-scientific” as it provides excuses for not conducting toxicological tests and prevents further scientific research into the possible risks of GMO-derived foods [34] . Per the current policy, as long as the GM food industries do not market GM foods with an alarmingly different chemical composition from those of foods already on the market, their new GM products are permitted without any safety or toxicological tests [36] . A counter to such views puts forth the position that substantial equivalence can be seen as, “…merely a regulatory shorthand for defining those new foods that do not raise safety issues that require special, intensive, case by case scrutiny”, and the principle itself is not intended to be a scientific formulation [35] . In addition, proponents of GMOs and supporters of substantial equivalence mention that critics of the concept have ignored many other quality assurance procedures that plant seeds undergo before sale [35] .
What is clear is that the criteria used for establishing substantial equivalence needs to be assessed more closely [26] , since criteria used to assess such equivalence may not be sufficient and refined to measure the effects of “small” genetic modifications on the complex and potentially “large” systemic changes in the end food product [34] -[36] . Moreover, since the methodology used in substantial equivalence plays a significant role in influencing the labeling of GM foods, if a GM food is determined to be substantially equivalent to its non-GM counterpart, based on using a uni-dimensional criteria such as nutritional standpoint alone, then there is no reason why the two sorts of foods should be distinctly labeled, and the freedom of choice among buyers is confused and limited [26] . Others argue that substantial equivalence needs to be adapted to situations where the composition of GMOs has been deliberately altered for novel traits [36] . This argument is based on the rationale that if the wrong cluster of properties or criteria is selected for comparison of GM and non-GM foods, the establishment of equivalence could be influenced [26] .
2.1. Beyond “Substantial Equivalence”: The Need for a Systems-Based Approach
Within the debate, there appears to be an emerging and directional convergence, including from the scientific community, starting in 2000, that perhaps other solutions and newer scientific methods are necessary for identifying criteria and methods for advancing the use of substantial equivalence in assessing safety of GMOs [27] [37] -[40] , as best exemplified in this statement:
“Establishing substantial equivalence is not a safety assessment in itself, but is a pragmatic tool to analyze the safety of a new food. It goes without saying that in the testing of new foods, use has to be made of the latest scientific methods,” [27] .
The field of systems theory and systems science may provide a foundational and beneficial perspective towards defining the characteristics of those “latest scientific methods”. In systems science, the definition of a “system”, originates from generalized systems theory (GST), which arose out of several disciplines, including biology, mathematics, philosophy, and the social sciences [41] . GST came into prominence in the 1950s [41] . Von Bertalanffy began thinking of GST in the 1930s; however, his ideas were not popular at the time and did not receive widespread attention until much later [42] . The aim of GST was to be a “...unifying theoretical construct for all of the sciences” [42] .
One broad definition of GST is, “... a set of related definitions, assumptions, and propositions which deal with reality as an integrated hierarchy of organizations of matter and energy” [39] . Another definition is, “... a collection of general concepts, principles, tools, problems, methods, and techniques associated with systems” [40] . From the context of GST, a generalized definition of a system emerges as: “An arrangement of certain components so interrelated as to form a whole” [40] .
Since the mid-1960s, systems science and systems thinking have evolved into a definitive discipline that is based on a holistic, systems-based approach, which recognizes that systems cannot be understood by taking them apart, and studying just their parts. The systems approach arose in contrast to the reductionism of the Newtonian method. In reductionism, a system or object is broken down into individual parts. To understand the system, the behavior of each part is studied individually, without considering the interactions among the set of parts [42] .
Such a reductionist approach, which focuses on the parts versus the interconnections, while valuable in understanding the individual part, is unable to account for complex and emergent behavior, denoted as emergent properties, which manifest as the parts of the system interact together [43] . From these interactions, new properties of the systems “emerge”―properties, which cannot be predicted from the properties of any individual part. Biological organisms and food, from a systems theory perspective, are themselves complex systems of interacting systems of interconnected molecular pathways.
Modifications to any component or to the interconnection of a food’s molecular system, given its complexity, will likely yield a new system with concomitant variations to its system dynamics and properties that can be wide-ranging depending on the nature of such modifications [43] .
2.2. The “Old” Biology: A Lesson in Misplaced Criteria of “Substantial Equivalence”
The field of biology is fundamentally an experimental science. Biologists execute many experiments to understand genes, proteins, protein-protein interactions. An example of perhaps the largest experiment in biology is the Human Genome Project (HGP), which began in 1990 and was completed in 2005. The HGP, when it began, was predicated on the hypothesis that what made humans different or non-equivalent to a nematode (or worm), was the number of genes. In some sense, the HGP used the criteria of number of genes to determine the “substantial equivalence” of complexity across organisms---the theory being that the number of genes equated to complexity.
Originally, it was estimated that a human had approximately 100,000 genes [44] . The HGP concluded that humans have only 20,000 to 25,000 genes, far less than what was originally theorized [45] , and near the same number of genes as the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, of approximately 19,000 genes [46] . The genome of the starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis, a delicate, few-inch-long animal in the form of a transparent, multi-tentacled tube has approximately 18,000 genes [32] .
The HGP revealed that whether, human or a worm (or sea anemone), they all have a similar number of genes, but a great difference in complexity of function as whole organisms. This contradiction led biologists to conclude that perhaps the number of genes in the genome is not connected or the basis of “equivalence” with the complexity of an organism, and that much of an organism’s complexity can be ascribed to regulation of existing genes by other substances (such as proteins) rather than to novel genes [47] .
What ironically emerged, therefore, from the HGP is that nature of being human is not predicated on the number of genes but rather by the complex interconnection of molecular interactions across the nucleus, cytoplasm and organelles. Being human is an “emergent property” of those specific interactions. Systems of intercom- nections, across myriad systems of molecular pathways, determine the difference between a human and a worm, not the number of genes. Therefore, equivalence in biological systems cannot rely on particular arbitrary criteria such as the number of genes but must be determined through a different and non-reductionist approach.
3. Systems Biology
Systems biology emerges from where the HGP ends, and provides such a non-reductionist approach to understand the complexity of biological systems. Reductionist thinking and the central dogma theory of Watson and Crick [48] had emphasized that genes alone are what make us who we are [49] . Systems biology rose in response to this reductionism and focuses attention not on just on one part, such as the genome, but on the complex interaction of systems of systems across genes, proteins, and complex molecular pathways, which are all influenced by an epigenetic layer [50] affected by both endogenous and exogenous systems including nutrition, environment, and perhaps, even thoughts [30] .
While systems biology, as a field, is only a decade old, building systems-level understanding of biology is not a new phenomenon. Over 5000 years ago, many traditional systems of medicine including Siddha, Unani, Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) proposed systems approaches to describing the whole human physiome [29] [51] . During modern times, starting in 1930s, with the concepts of homeostasis [52] , allostasis, and biological cybernetics [53] , attempts were made to understand biology from a systems level using the modern language of physics and control systems engineering.
Systems biology is now developing a system-level understanding by connecting knowledge at the molecular level to higher-level biological functions [54] . Previous attempts at system-level approaches to biology were primarily focused on the description and analysis of biological systems, limited to the physiological level. Since these approaches had little to no knowledge of how molecular interactions were linked to biological functions?a systems-based biology of connecting molecular interactions to biological functions was not previously possible [54] .
Modern systems biology, as a new field of biology, offers the opportunity, as never before, to link the behaviors of molecules to the characteristics of biological systems. This new field is enabling a description of systems of systems (SoS) of cells, tissues, organs and human beings within a consistent framework governed by the basic principles of physics [54] . This framework, therefore, provides a much needed scientific foundation in the current GMO debate to identify those “latest scientific methods” to evaluate “equivalence” of complex systems, such as GMOs and their non-GMO counterparts.
3.1. Computational Systems Biology: Modeling Molecular Systems
A grand challenge of modern systems biology is to develop tools that enable the analysis and modeling of complex cellular functions, including the whole cell, by considering molecular pathways as being the elemental modules of complex cellular functions. Biological systems are thought to have large number of parts almost all of which are related in complex ways [55] . Functionality emerges as the result of interactions between many proteins relating to each other in multiple cascades and in interaction with the cellular environment. By computing these interactions, it can be used to determine the logic of healthy and diseased states [56] . One way to model the whole cell is through a bottom up reconstruction. Such bottom up reconstruction, for example, of the human metabolic network, was done primarily through a manual process of integrating databases and pathway models [57] .
It is possible, for example, to regard signaling networks as systems that decode complex inputs in time, space and chemistry into combinatorial output patterns of signaling activity [58] . By treating molecular pathways as modules, our minds can still deal with the complexity [59] . In this way, accurate experimentation and detailed modeling of network behavior in terms of molecular properties can reinforce each other [60] . The goal then becomes that of linking kinetic models on small parts to build larger models to form detailed kinetic models of larger chunks of molecular pathways, such as metabolism, for example, and ultimately of the entire living cell [61] .
The value of integrating systems of molecular pathways is to demonstrate that the integrated networks show emergent properties that the individual pathways do not possess, like extended signal duration, activation of feedback loops, thresholds for biological effects, or a multitude of signal outputs [62] . In this sense, a cell can be seen as an adaptive autonomous agent or as a society of such agents, where each can exhibit a particular behavior depending on its cognitive capabilities.
Unique mathematical frameworks will be needed to obtain an integrated perspective on these complex systems, which operate over wide length and time scales. These may involve a multi-layered, hierarchical approach, wherein the overall signaling network, at one layer, is modeled in terms of effective “circuit” or “algorithm” modules [30] , and then at other layers, each module is correspondingly modeled with more detailed incorporation of its actual underlying biochemical/biophysical molecular interactions [63] . The mammalian cell may be considered as a central signaling network connected to various cellular machines that are responsible for phenotypic functions. Cellular machines such as transcriptional, translational, motility and secretory machinery can be represented as sets of interacting components that form functional local networks [64] .
As biology begins to move into the post-genomic era, a key emerging question is how to approach the understanding of how complex molecular pathways function as dynamical systems. Prominent examples include multi-molecular protein “machines,” intracellular signal transduction cascades, and cell?cell communication mechanisms. As the proportion of identified systems involved in any of these molecular pathways continues to increase, in certain instances already asymptotically, the daunting challenge of developing useful models ? both mathematical as well as conceptual-for how they work is drawing increased interest [65] .
The scientific methods that emerge from such computational systems biology may provide more resilient and sophisticated tools to explore the effects of modifications to the myriad systems of interconnected molecular pathways inherent in organisms and food itself. Such approaches are likely more relevant and meaningful in assessing “equivalence” of GMO and non-GMO foods rather than reliance on uni-dimensional criteria such as: nutritional value, composition, nutritional effects, etc., based on methods adopted for relatively simpler engineering systems such as medical devices nearly 40 years ago.
3.2. CytoSolve®: A Framework Modeling the Whole Cell and Complex Molecular Systems
One aspect of the grand challenge of systems biology is to create a platform to model the whole cell as well as complex molecular systems. This challenge led to the development of CytoSolve, starting in 2003 at the Massachusetts of Technology (M.I.T.) [66] . The development of CytoSolve recognized the siloed nature of biology, where biologists work in isolated and domain specific groups, to investigate, understand, and document particular molecular pathways. CytoSolve aggregates existing peer-reviewed scientific literature and mines this literature to extract molecular pathways of biological processes. The platform abstracts complex cellular functions as a plurality of such molecular pathways, each of which can be treated as individual models, as illustrated in Figure 1.
The CytoSolve platform computationally integrates the individual molecular pathway models, each of which mayspan multiple spatial and temporal scales, across compartments, cell types and biological domains [1] [59] to provide a computational architecture, as shown in Figure 2, for coupling individual molecular pathway models dynamically without the need to create a monolithic model.
This approach allows for an inherent scalability to build models of complex biological phenomena, not afforded by other known methods, since approach obviates the need to create one large monolithic model [1] , which can neither be modularly scaled nor maintained, given the dynamic nature of biological research.
![]()
Figure 1. CytoSolve provides a framework for integrating systems of systems of molecular pathway models [66] .
![]()
Figure 2. The CytoSolve software architecture framework for integrating systems of systems of molecular pathway models [66] .
More importantly, from a practical standpoint, the CytoSolve framework provides a mechanism not only for making predictions of complex molecular interactions and behavior but also for informing intelligent in vivo and in vitro experimental designs to verify such predictions.
4. Research Aim
In this research, CytoSolve is employed to integrate molecular pathway models of: 1) C1 metabolism, 2) Oxidative Stress, and 3) Dynamics of specific biomolecules perturbed by the CP4 EPSPS GM of soybean, to derive a modular computational model that predicts the effects of the GMO on regulatory molecules. The aim of this research is to use this resulting computational model to identify key biomarkers, which may serve as more definitive criteria to determine “equivalence” of GMOs and non-GMOs.
This research builds on three recent and specific efforts: 1) a systematic bioinformatics literature review of C1 metabolism [3] , 2) in silico modeling of the C1 metabolism system [4] , and 3) integrative modeling of oxidative stress and C1 metabolism [5] . A brief review of the results from that previous and recent research [4] [5] , is provided below as a contextual basis for the research aim herein. In particular, the review of this research provides the baseline for understanding the temporal dynamics of key biomarkers associated with plant metabolism in non-GMOs.
4.1. Identification of Key Regulatory Molecules: Formaldehyde and Glutathione
The previous work in in silico modeling of C1 metabolism [3] -[5] provides a cogent systems biology framework, which demonstrates that formaldehyde (HCHO) and glutathione (GSH) are two important regulatory molecules involved in the control systems of oxidative stress and C1 Metabolism. The temporal dynamics of formaldehyde and glutathione, in the non-GMO case, will be provided in section 4.2, as a baseline for comparing with the predictions for the GMO case in section 6.0.
4.2. Review of in Silico Modeling of C1 Metabolism
Recent efforts, using systems biology approaches in the field of plant sciences, have resulted in a comprehensive computational model of C1 metabolism [4] . C1 metabolism is one of the most important biological processes in living systems responsible for providing one-carbon units for proteins, nucleic acids, methylated compounds, and other biomolecules. The C1 metabolism system is mostly found in plants, bacteria, fungi, and mammals [67] [68] . A wide variety of important biomolecules are synthesized in C1 metabolism such as methionine, formylmethionine-tRNA, pantothenate, thymidylate, adenosine, and serine. More importantly, the C1 metabolism process provides the one-carbon units essential for DNA methylation, which controls plant growth and development, with a particular involvement in regulation of gene expression and DNA replication [69] .
Simulation results from the in silico model of C1 metabolism [4] provide new insights and predictions of temporal changes to formaldehyde, sarcosine and glutathione. The integrative model of C1 metabolism predicts that in normal, non-GMO plants, formaldehyde is evanescently produced and rapidly detoxified between ~1.5 to ~2 days [4] as shown in Figure 3(a). In non-GMO plants, glutathione levels are minimally affected and maintain a steady state 5,000,000 nM [4] as shown in Figure 3(b) (the log-scale version of this figure is in Figure B1 of Appendix B).
Finally, in that research, it was predicted that sarcosine is fully consumed during C1 metabolism [55] . Parameter sensitivity analysis of the C1 metabolism model revealed that variations in kGSH-HCHO, the binding rate constant of glutathione (GSH) and formaldehyde (HCHO), affect formaldehyde concentration in normal plants [55] . The sensitivity analysis demonstrated that even an order of magnitude variation in this parameter still results in complete formaldehyde detoxification.
4.3. Review of Integrated Model of Oxidative Stress with C1 Metabolism
Another related and recent work, concerning C1 metabolism [5] , the study employed computational systems biology approaches to explore how dysregulation to C1 metabolism may result from the influence of oxidative stress on C1 metabolism. The simulation results from the in silico modeling of integration of oxidative stress [5] with the fully integrative model of C1 metabolism [4] suggested that in non-GMO plants, oxidative stress causes accumulation of formaldehyde [5] as shown in Figure 4(a), and depletion of glutathione (GSH) [5] as shown in
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 3. (a) Temporal dynamics of formaldehyde in non-GMO plants; (b) Temporal dynamics of glutathione in non-GMO plants [4] .
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 4. (a) Temporal dynamics of formaldehyde in non-GMO plants undergoing oxidative stress; (b) Temporal dynamics of glutathione in non-GMO plants undergoing oxidative stress [5] .
Figure 4(b) (the log-scale version of this figure is in Figure B2 of Appendix B).
Parameter sensitivity analysis, in that study, relative to variations of the binding rate constant of formaldehyde (HCHO) and glutathione (GSH), kGSH-HCHO, demonstrated that formaldehyde accumulation, as well as glutathione depletion, remained [5] . Similarly, relative to variations of the rate of formation of sarcosine from glycine, VMTG, parameter sensitivity analysis demonstrated that formaldehyde accumulation, as well as glutathione depletion, remained [5] . Finally, relative to variations of the rate of superoxide production, kO2−, parameter sensitivity analysis demonstrated that formaldehyde accumulation, as well as glutathione depletion, remained [5] . In summary, there is a consistent accumulation of formaldehyde and depletion of glutathione in non-GMO plants, when they undergo oxidative stress.
5. Methods
In this effort, the CytoSolve® Collaboratory™ [3] -[5] is used to develop an in silico computational model to understand the effects to C1 metabolism as a result of GMO of soybean [3] -[5] .
First, a systematic bioinformatics literature review is conducted to discover any molecular mechanisms affected by GMO of soybean. Literature collection from an informatics standpoint is executed to ensure high recall to acquire the initial set. Based on the research question of “What effect does genetic modification have on C1 metabolism via oxidative stress?” 22 search criteria were developed and are listed in Supplementary Materials’ Appendix A. Online databases including PubMed and Google Scholar were searched using the search criteria. An initial set was produced as a result of 22 parallel independent searches. The initial set was searched by constraining the search criteria within the Titles or Abstracts to GM, oxidative stress, and C1 metabolism in plants to acquire the relevant set.
The papers from relevant set were reviewed by domain experts to determine the study set paper, from the relevant set, containing molecular pathway information such as:
1) cellular compartments containing species and reactions;
2) kinetics parameters oxidative stress pathways;
3) fold-changes in relevant enzymes and key molecular species concentrations.
In this detection process, priority was given to those articles which were the most recent and which contained information and/or studies on oxidative stress and maize or closely related grasses. The final result of this literature review was to discover the dynamics of key enzymes and molecular species, induced by GM, which affect the oxidative stress system.
Second, any dynamics of molecular interactions, induced by GM, identified from the literature review, are incorporated to expand the systems architecture for oxidative stress and C1 metabolism, developed in earlier work [5] .
Third, the updated systems architecture is used as the blueprint to create an integrative model of how GM of soybean affects oxidative stress and C1 metabolism.
Fourth, the resultant model is used to execute simulations to observe the effects of GM of soybean on the homeostasis of key regulatory molecules such as formaldehyde and glutathione. All simulations are executed for a simulation time period of 800,000 seconds (~9 days).
Fifth, parameter sensitivity analysis is performed on kinetic parameters of: 1. rate of formaldehyde production from methanol (VCAT), 2. binding rate constant of glutathione and formaldehyde (kGSH-HCHO), 3. rate of production of sarcosine from glycine (VGMT), and 4. rate of production of superoxide (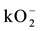 ) to estimate which of these kinetic parameters influence the key regulatory molecules of formaldehyde and glutathione.
) to estimate which of these kinetic parameters influence the key regulatory molecules of formaldehyde and glutathione.
Sixth, comparisons are made between the non-GMO and GMO cases relative to the temporal dynamics of key biomarkers to determine if there are any significant differences. For the non-GMO case, data exists from previous work, as reviewed in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
6. Results
The outcomes of this research are two-fold: 1) An integrative computational model which allows for the study of molecular mechanistic differences between GMOs and non-GMOs using GMO of soybean as a first use case, and 2) Simulation results using this integrative model, which suggests, that in the GM case of soybean, accumulation of formaldehyde as well as depletion of glutathione occurs. Specifically, there are six sets of results that emerge from this study.
The first set of results is a systematic literature review of effect of GM on C1 metabolism, described in section 6.1. The second set of results is an integrated computational systems architecture of C1 metabolism, oxidative stress and GM, in Section 6.2, which reveals the interfaces of the interactions between GM, oxidative stress system and C1 metabolism. The third and fourth sets of results are simulation outputs from the integration of GM and oxidative stress system separately with methionine biosynthesis and formaldehyde detoxification, in Sections 6.3.1 and 6.3.2, respectively.
The fifth set of results is the simulation output from the integration of GM and oxidative stress system with the entire model of C1 metabolism, in Section 6.4. Finally, the sixth set of results is the parameter sensitivity analysis, in Section 6.5, which provides a detailed understanding of which parameters are most sensitive to variations in the integrative computation of GM, oxidative stress and C1 metabolism.
6.1. Systematic Bioinformatics Literature Review of GMO Crops and Molecular Pathways
A systematic bioinformatics literature review is conducted for identification of molecular pathways involved in GMO crops, similar to the method used to identify the key molecular pathways of C1 metabolism [3] . Based on the framing of the research question and the application of the search criteria, in Appendix A, through a parallel strategy, the literature collection of an initial set of 107 papers is identified from online databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar. The final results of the systematic review are summarized in Figure 5, which identified four critical mechanisms which are affected by the GM of soybean, as well as five biomolecules that included four enzymes and one reactive oxygen species.
6.1.1. Identification of Altered Molecular Interactions from GM of Soybean
The 107 papers of the initial set from the systematic bioinformatics literature review yielded important insights, in particular, on the molecular interactions of GM of soybean relative to their effects on oxidative stress. For example, comparative studies of GM of CP4 EPSPS in soybean with non-GM plants reported differences in metal uptake ability and content, thereby, making the plant susceptible to oxidative stress [7] [8] .
The GM of CP4 EPSPS in soybean, in particular, has been found to be involved in four molecular mechanisms, as shown in Figure 6(a) and Figure 6(b), which upregulate four key enzymes such as superoxide dismu-
![]()
Figure 5. Systematic review results. There are 107 scientific papers (initial set), which met the search criteria. Of those, 34 papers (relevant set) appeared to be relevant based on the title and abstract. Upon further review, 11 papers (study set) were chosen as the study set upon which this systematic review is based. With this study set, 4 critical mechanisms (final set) in the oxidative stress pathways were identified that were affected by GM.
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 6. (a) Ascorbate-glutathione pathway. Enzymes affected by GM are circled in red [16] ; (b) Reactive oxygen species synthesis pathway. Enzymes and biomolecules affected by GM are circled in red [16] .
tase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase, and also affect hydrogen peroxide, a reactive oxygen species (ROS) across two important molecular systems in oxidative stress [70] : Ascorbate-glutathione pathway and Reactive oxygen species synthesis pathway. The specific kinetics, relative to the dynamics of these five biomolecules and their molecular interactions, are derived from the literature and provided in the Supplementary Materials in Table S1 along with the references.
In addition, GM of CP4 EPSPS in soybean has been estimated to contain higher levels of hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde (MDA), indicative of lipid peroxidation [6] . During stressful conditions, such as a drought, it is well known that plants respond to such stressful conditions by altering their gene expression. In the case of GM of soybean with CP4 EPSPS, it has been reported that key enzymes such as catalase, involved in combating oxidative stress, are upregulated in comparison to their non-GM counterparts, indicating changes in cellular redox state [6] . Catalase has a feature of functioning in two modes: 1) the catalatic-mode: catalyzing the direct de- composition of hydrogen peroxide, or 2) the peroxidatic-mode: the utilization of hydrogen peroxide to oxidize organic substrates such as methanol, yielding formaldehyde [67] [70] . Upregulation of catalase enzyme due to oxidative stress could be a factor in increasing formaldehyde production through its peroxidatic activity.
Substantial literature exists that glutathione is an important anti-oxidizing agent that serves to maintain cellular redox homeostasis. Although in healthy cells, most of the glutathione (GSH) exists in its reduced state, the oxidative stress condition is characterized by the presence of higher amounts of the oxidized form, GSSG. In certain cases, upregulation of glutathione reductase, the enzyme catalyzing the conversion of GSSG to GSH to maintain glutathione homeostasis is insufficient to counter the GSH consumption [71] .
The literature review reveals that the action of sarcosine oxidase on sarcosine is also known to generate formaldehyde [67] . Formaldehyde is a toxic compound produced during plant C1 metabolism. The main sources of formaldehyde in plants are dissociation of 5,10-methylene-THF and oxidation of methanol [72] . Glutathione- dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase is the major enzyme involved in the detoxification of formaldehyde. It acts on a non-enzymatically formed adduct of GSH and formaldehyde [72] , indicating the crucial role of glutathione in the process.
Finally, relative to formaldehyde detoxification, previous research reveals that glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase also acts to detoxify products of lipid peroxidation generated during oxidative stress conditions [73] , thereby acting as a competing process to its usual function of formaldehyde detoxification. In addition, results from in silico modeling studies of C1 metabolism and oxidative stress [4] [5] conclude that oxidative stress perturbs formaldehyde detoxification in C1 metabolism.
6.2. Systems Architecture of GM, Oxidative Stress and C1 Metabolism
The literature review of the GM in soybean and its effects on molecular pathways, in previous section 6.1, provides valuable information on the interface of the GMO with oxidative stress. Earlier work on systematic review and modeling of C1 metabolism and oxidative stress revealed the systems architecture of interfaces between these two molecular systems for C1 metabolism [4] [5] .
In Figure 7, an integrative molecular systems architecture is presented by coupling the dynamics of the GMO molecular interaction in the heretofore known literature, accessible and aggregated by the authors, with the systems architecture of oxidative stress and C1 metabolism derived in earlier work [5] .
In Figure 7, GM, based on the literature review, interacts with oxidative stress pathways by interfacing with reactive oxygen species synthesis and ascorbate-glutathione pathways. In addition, the oxidative stress pathways interact, as reported in previous research [6] -[8] , with C1 metabolism by interfacing through the ascorbate-glu- tathione pathway, which interfaces with both methionine biosynthesis and formaldehyde detoxification pathways of C1 metabolism. These interfaces will be relevant in developing and testing the in silico modeling of the GMO’s effects on C1 metabolism.
6.3. Interaction of GM of Soybean with Oxidative Stress and Individual Molecular Pathways of C1 Metabolism
The integrative systems architecture of oxidative stress and C1 metabolism, in Figure 7, reveals that genetic modification interfaces with oxidative stress pathways which in turn, as shown previously [5] , interface with methionine biosynthesis and formaldehyde detoxification pathways of C1 metabolism.
Relative to the interface between genetic modifications and oxidative stress pathways, genetic modification
![]()
Figure 7. Systems architecture of GM, oxidative stress pathway and C1 metabolism.
increases the production of reactive oxygen species and upregulates the enzymes catalase, ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the oxidative stress pathways [74] .
Relative to the interface of oxidative stress with the methionine biosynthesis pathway, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a product of oxidative stress, is used to oxidize glyoxylate, in the methionine biosynthesis pathway, to create formate [75] .
Relative to the interface of oxidative stress with the formaldehyde detoxification pathway, glutathione, a main substrate for the antioxidant activity of glutathione reductase in the oxidative pathway [73] [74] binds with formaldehyde, which is the first step in clearing formaldehyde [76] . Additionally, catalase, an antioxidant enzyme from oxidative stress pathway, catalyzes the conversion of methanol to formaldehyde [70] .
6.3.1. Simulation Results from in Silico Modeling of GM of Soybean and Oxidative Stress with Only Methionine Biosynthesis System of C1 Metabolism
Herein, results from in silico modeling of the dynamics of GM of soybean and oxidative stress, with only the methionine biosynthesis system of C1 metabolism, are presented. The results obtained from this integrative model reveal the temporal dynamics of formaldehyde as shown in Figure 8. Glutathione is not observed since it is not a part of methionine biosynthesis system. The simulations are executed for a simulation time period of 800,000 seconds (~9 days).
The concentrations of formaldehyde, as shown in Figure 8, increase rapidly and reach a steady state at a concentration level of ~0.06 nM. This result is consistent since methionine biosynthesis is a source of formaldehyde, and the production of formaldehyde will be not affected by any of the byproducts of oxidative stress. For example, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is a product of oxidative stress, has no effect on the formation of formaldehyde in the methionine biosynthesis model, though H2O2 does affect oxidation of glyoxylate to formate [77] .
6.3.2. Simulation Results from in Silico Modeling of GM of Soybean and Oxidative Stress with Only Formaldehyde Detoxification System of C1 Metabolism
Herein, results from in silico modeling of the dynamics of GM of soybean and oxidative stress with only the formaldehyde detoxification system of C1 metabolism, are presented. The results obtained from this integrative model reveal the temporal dynamics of formaldehyde and glutathione (GSH), as shown in Figure 9(a) and Figure 9(b), respectively. The simulations were executed for a simulation time period of 800,000 seconds (~9 days). The results show an accumulation of formaldehyde concentrations (Figure 9(a)) and depletion of glutathione concentrations (Figure 9(b)) in the presence of oxidative stress with the GMO.
In Figure 9(a), the simulation results indicate the formaldehyde concentration increases after a simulation period of ~180,000 seconds (~2 days) and reaches a level of ~0.25 nM at 800,000 seconds (~9 days). This result can likely be explained by understanding the dynamics of interactions between oxidative stress due to the GMO
![]()
Figure 8. Simulation results of GM of soybean and oxidative stress on formaldehyde concentration in methionine biosynthesis model.
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 9. (a) Simulation results of GM of soybean and oxidative stress on formaldehyde concentration in formaldehyde detoxification pathway; (b) Simulation results of GM of soybean and oxidative stress on glutathione (GSH) concentration in formaldehyde detoxification model.
and formaldehyde detoxification. In the presence of oxidative stress due to the GMO, the synthesis of formaldehyde is increased and formaldehyde detoxification is lowered leading to accumulation of formaldehyde; however, there is a temporal delay in which the increases in formaldehyde concentrations become apparent.
This temporal delay of increased formaldehyde concentrations is likely because of the time evolution of two synergistic phenomena. The first phenomenon results from the accelerated consumption and depletion of glutathione (GSH) which results in reduced detoxification of formaldehyde. This is because there is a competitive need for glutathione (GSH) to be used: 1) to clear H2O2, a byproduct of oxidative stress, and, 2) to enable the detoxification of formaldehyde. The second phenomenon results from the increased production of formaldehyde from the increased conversion of methanol to formaldehyde by catalase, which is an important and integral enzyme of oxidative stress pathway [70] [76] . The coupling of oxidative stress due to genetic modification with formaldehyde detoxification exposes catalase, which was originally non-existent within the formaldehyde detoxification pathway alone. In summary, oxidative stress affects the formaldehyde detoxification pathway by increasing formaldehyde concentrations, synergistically through reducing formaldehyde clearance and increasing formaldehyde synthesis.
In Figure 9(a), the simulation results indicate that glutathione (GSH) concentration varies significantly in the presence of oxidative stress due to the GMO (the log-scale version of this figure is in Figure B3 of Appendix B). Without the presence of oxidative stress, glutathione levels remain at the steady state value of 5,000,000 nM [4] . In earlier work [5] , in the presence of oxidative stress, without GM, glutathione is depleted within ~180,000 s (~2 days). However, as Figure 7(b) shows, in the presence of oxidative stress, induced by GM, glutathione is completely depleted, nearly 300% faster, within ~50,000 seconds (~0.5 days). The significant acceleration in depletion of glutathione, in the GMO case, is because of increased ROS synthesis, far more than during normal oxidative stress.
This result can likely be explained by understanding the dynamics of glutathione’s dual role in oxidative stress as well as formaldehyde detoxification. In this simulation, an initial and finite amount of glutathione is provided, which is not replenished. In the oxidative stress molecular system alone, where glutathione (GSH) is needed to clear H2O2, a byproduct of oxidative stress, glutathione levels will decrease over time.
In the formaldehyde detoxification system, where glutathione is needed to clear and detoxify formaldehyde accumulation, glutathione is used and replenished in a cycle with a temporal periodicity. The simulation reveals that for a finite and initial amount of glutathione, the integration of oxidative stress with formaldehyde detoxification will eventually lead to depletion of glutathione, notwithstanding any new sources of glutathione production. In summary, oxidative stress due to the GMO significantly perturbs the homeostasis of glutathione, in the formaldehyde detoxification system of C1 metabolism.
6.4. Simulation Results of in Silico Modeling of GM of Soybean and Oxidative Stress with Complete Integrative Model of C1 Metabolism
The previous section 6.3 provided simulation results from the integration of oxidative stress with only the formaldehyde detoxification system of C1 metabolism. In this section, we present the simulation results of the holistic integration of the molecular system of oxidative stress induced by GM of soybean, with the entire C1 metabolism system. The simulations are executed for a simulation time period of 800,000 seconds (~9 days).
The simulation results from the integration of oxidative stress, due to the GMO, with the complete C1 metabolism system reveal increases in formaldehyde accumulation and concomitant glutathione depletion, as shown in Figure 10(a) and Figure 10(b), respectively.
In Figure 10(a), the simulation of the integrative model of the GMO with oxidative stress and C1 metabolism indicate that formaldehyde concentration varies significantly in the presence of oxidative stress induced by the GMO. Without the presence of oxidative stress, formaldehyde does not accumulate in the C1 metabolism system [4] . In the presence of oxidative stress induced by the GMO, formaldehyde accumulates in the C1 metabolism system, starting at ~50,000 seconds (~0.5 days) and continues accumulating non-linearly to ~30 nM in 800,000 seconds (~9 day).
This simulation result is consistent with the previous integration of oxidative stress induced by the GMO in with formaldehyde detoxification alone, as shown in Figure 9(a). There are two key differences, however, in the temporal accumulation of formaldehyde in the integrative model of oxidative stress induced by the GMO and C1 metabolism (Figure 10(a)) versus the interaction of oxidative stress induced by the GMO with formaldehyde detoxification alone (Figure 9(a)). The first difference is that in the integrative model of oxidative stress due to genetic modification and C1 metabolism, formaldehyde accumulation begins nearly 4 times sooner at ~50,000 seconds (~0.5 days) versus at ~180,000 seconds (~2 days). The second difference is that at 800,000 seconds (~9 days), the formaldehyde concentration in the integrative model of oxidative stress and C1 metabolism is ~120 times higher at ~30 nM versus at ~0.25 nM.
These results indicate that in the integrative model of oxidative stress induced by the GMO and C1 metabolism, formaldehyde accumulation occurs faster and achieves a significantly higher level during the same temporal period. This is likely due to the fact that in the C1 metabolism model not only are the effects on the formaldehyde detoxification being considered, but also its coupled effects with methionine biosynthesis and the activated methyl cycle. The activated methyl cycle contributes to formaldehyde production from sarcosine [78] .
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 10. (a) Simulation results of GM of soybean and oxidative stress on formaldehyde concentration in C1 metabolism model; (b) Simulation results of GM of soybean and oxidative stress on glutathione (GSH) concentration in integrative C1 metabolism model.
In summary, oxidative stress induced by the GMO affects C1 metabolism by not only increasing the rate and quantity of formaldehyde concentrations through the activated methyl cycle, for example, but also by reducing the rate and quantity of formaldehyde clearance in the formaldehyde detoxification pathway.
In Figure 10(b), the simulation of the integrative model of the GMO with oxidative stress and C1 metabolism indicate that glutathione (GSH) concentrations vary significantly with the presence of oxidative stress induced by the GMO (the log-scale version this figure is Figure B4 of Appendix B). Without the presence of oxidative stress, glutathione levels remain at the steady state value of 5,000,000 nM [4] . In the presence of oxidative stress, without the GMO, glutathione is depleted within ~180,000 s (~2 days) based on previous research [5] . However, as show in Figure 10(b), in the presence of oxidative stress induced by the GMOs, glutathione is completely depleted 300% faster, within ~50,000 seconds (~0.5 days). The significant acceleration in depletion of glutathione in the GMO case is because of increased ROS synthesis, far more than during normal oxidative stress.
This simulation result is consistent with the previous integration of oxidative stress induced by the GMO in individual model of formaldehyde detoxification, in Figure 9(b). In this simulation, an initial and finite amount of glutathione is provided, which is not replenished. In the oxidative stress molecular system alone, where glutathione (GSH) is needed to clear H2O2, a byproduct of oxidative stress, glutathione levels will decrease over time. Simulation reveals that for a finite initial amount of glutathione, the integration of oxidative stress with C1 metabolism will eventually lead to depletion of glutathione, notwithstanding any new sources of glutathione production. The close similarity of this result (Figure 10(b)) with the previous result (Figure 9(b)) is because glutathione (GSH) directly affects and couples oxidative stress and formaldehyde detoxification, and is decoupled from methionine biosynthesis and the activated methyl cycle.
6.5. Parameter Sensitivity of GM of Soybean and Oxidative Stress with C1 Metabolism
The results from simulations of the molecular systems integration of oxidative stress and the C1 metabolism provide insights on two key biomolecular species: formaldehyde and glutathione. The integrity of literature reviewed and the kinetic rate constants used in the modeling is critical for the interpretation and usefulness of the simulation results. The relative significance of these critical parameters can be assessed by conducting a parameter sensitivity analysis.
Given the importance of formaldehyde synthesis and clearance in C1 metabolism, and central role of glutathione (GSH) in the oxidative stress homeostasis, the effect of four critical parameters was tested on formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations. These parameters are:
1) VCAT―Rate of formaldehyde production from methanol;
2) kGSH-HCHO―Binding rate constant of glutathione (GSH) and formaldehyde (HCHO);
3) VGMT―Rate of production of sarcosine from glycine;
4)![]() ―Rate of production of superoxide.
―Rate of production of superoxide.
Four sets of results emerge from the parameter sensitivity analysis of the four parameters itemized above. The first parameter that is analyzed is VCAT. VCAT is varied from 22 to 100 nM∙s−1 and the resulting formaldehyde and glutathione (GSH) concentrations are observed for the integrated oxidative stress induced by GM of soybean and C1 metabolism model in Figure 11(a) and Figure 11(b), respectively (the log-scale version of Figure 11(b) is in Figure B5 of Appendix B).
These results indicate that both formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations are not sensitive to changes in VCAT for the integrated oxidative stress induced by GM and C1 metabolism model. In all cases, formaldehyde accumulates to the same levels, and glutathione (GSH) is fully depleted.
The second parameter that is varied is kGSH-HCHO. kGSH-HCHO is varied from 0.000864 to 0.00864 nM−1∙s−1 and the resulting formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations are observed for the integrated oxidative stress induced by the GMO and C1 metabolism model in Figure 12(a) and Figure 12(b), respectively, (the
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 11. (a) Parameter sensitivity analysis of VCAT on formaldehyde in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism; (b) Parameter sensitivity analysis of VCAT on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism.
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 12. (a) Parameter sensitivity analysis of kGSH-HCHO on formaldehyde in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism; (b) Parameter sensitivity analysis of kGSH-HCHO on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism.
log-scale version of Figure 12(b) is in Figure B6 of Appendix B).
These results indicate that kGSH-HCHO is sensitive and affects formaldehyde concentrations. As Figure 12(a) illustrates, an order of magnitude variation kGSH-HCHO results in a non-linear variation at ~800,000 seconds (~9 days) of formaldehyde concentrations by ~six times. These results, relative to glutathione (GSH), in Figure 12(b) , however, indicate that kGSH-HCHO is insensitive and does not affect glutathione (GSH) concentrations. In all cases, formaldehyde accumulates though to varying levels, and glutathione (GSH) is fully depleted.
The third parameter that is varied is VMTG. VMTG is varied from 20 to 87 nM∙s−1 and the resulting formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations are observed for the integrated oxidative stress and C1 metabolism model in Figure 13(a) and Figure 13(b), respectively, (the log-scale version of Figure 13(b) is in Figure B7 of Appendix B).
These results indicate that VMTG is sensitive and affects formaldehyde concentrations. As Figure 13(a)) illustrates, a four times variation of VMTG results in a non-linear variation at ~800,000 seconds (~9 days) of formaldehyde concentrations by ~six times. In all cases, formaldehyde is shown to accumulate consistently, and is never depleted. These results, relative to glutathione (GSH), as shown in Figure 13(b), however, indicate that VMTG is insensitive and does not affect glutathione (GSH) concentrations. In all cases, formaldehyde accumulates though to varying levels, and glutathione (GSH) is fully depleted.
The fourth parameter that is varied is![]() .
. ![]() is varied from 20 to 100 nM∙s−1 and the resulting formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations are observed for the integrated oxidative stress and C1 metabolism model in in Figure 14(a) and Figure 14(b), respectively (the log-scale version of Figure 14(b) is in Figure B8 of Appendix B).
is varied from 20 to 100 nM∙s−1 and the resulting formaldehyde and glutathione concentrations are observed for the integrated oxidative stress and C1 metabolism model in in Figure 14(a) and Figure 14(b), respectively (the log-scale version of Figure 14(b) is in Figure B8 of Appendix B).
These results indicate that ![]() is sensitive and affects formaldehyde concentrations. As Figure 14(a) illustrates, a five times variation in
is sensitive and affects formaldehyde concentrations. As Figure 14(a) illustrates, a five times variation in ![]() results in a non-linear variation, at ~800,000 seconds (~9 days), of formaldehyde concentrations by ~ten times. These results indicate that
results in a non-linear variation, at ~800,000 seconds (~9 days), of formaldehyde concentrations by ~ten times. These results indicate that ![]() is highly sensitive and affects glutathione (GSH) concentrations. As Figure 14(b) illustrates, a five times variation in
is highly sensitive and affects glutathione (GSH) concentrations. As Figure 14(b) illustrates, a five times variation in ![]() results in an acceleration of glutathione depletion by a factor of six. In all cases, formaldehyde consistently accumulates to varying degrees and glutathione (GSH), concomitantly, is fully depleted, though temporally accelerated to varying levels.
results in an acceleration of glutathione depletion by a factor of six. In all cases, formaldehyde consistently accumulates to varying degrees and glutathione (GSH), concomitantly, is fully depleted, though temporally accelerated to varying levels.
7. Discussion
There are many important outcomes and conclusions that are derived from this research on what appears, to the authors’ knowledge, to be the first systems biology of GMOs.
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 13. (a) Parameter sensitivity analysis of VMTG on formaldehyde in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism; (b) Parameter sensitivity analysis of VMTG on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM, oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism.
First, a scalable and modular in silico computational systems biology framework for understanding GMOs, now exists, for not only making predictions but also for informing intelligent in vivo and in vitro experimental designs to verify the predictions observed in this research, using GM of soybean as a use case.
Second, this work, along with the previous work [4] [5] , now provides a methodology for comparative analysis of the dynamics of two key biomarkers, formaldehyde and glutathione, (and can be expanded to any number of biomarkers), between the non-GMO and GMO counterpart. In Figure 15, the comparative results of the temporal dynamics of formaldehyde in the non-GMO (Figure 15(a)) and GMO (Figure 15(b)) are shown. In Figure 16, the comparative results of the temporal dynamics of glutathione in the non-GMO (Figure 16(a)) and GMO (Figure 16(b)) are shown.
Without GM, as shown in Figure 15(a), formaldehyde begins at a peak of ~6 × 10−7 nM and is detoxified within 200,000 seconds (~2.5 days) and does not accumulate. With the GMO, as shown in Figure 15(b), formaldehyde is not detoxified, and begins to accumulate at 50,000 seconds (~0.5 days), and reaches a peak of ~30 nM at 800,000 seconds (~9 days). As discussed, the GMO induces oxidative stress, which forces formaldehyde accumulation, and more importantly, unlike normal non-GMO induced oxidative stress, as shown in Figure 4(a), the formaldehyde levels produced by the oxidative stress induced by the GMO, are different in two ways: 1) concentration levels of formaldehyde, at 800,000 seconds (~9 days), are slightly over two times higher in the GMO case than in the non-GMO case with oxidative stress, and 2) accumulation in the GMO begins ~three times sooner case than the non-GMO case with oxidative stress.
Without GM, as shown in Figure 16(a), glutathione remains at a steady state level of 5,000,000 nM and is maintained for 800,000 seconds (~9 days). With the GMO, as shown in Figure 16(b), glutathione is completely depleted within 50,000 seconds (~0.5 days). As discussed, the GMO induces oxidative stress that leads to glutathione depletion. More importantly, unlike normal non-GMO induced oxidative stress, as shown in Figure 4(b), the glutathione depletion caused by the oxidative stress induced by the GMO occurs ~4 times faster.
Third, the authors recognize that mathematical modeling, in general, is highly dependent on many variables and assumptions. The models developed and integrated herein are based on literature aggregated, by the authors, from the known and accessible scientific literature. In this study, the critical assumptions are as follows:
1) All the reactions used in the models discussed occur in a single cell and at the cell surface;
2) The cell was assumed to be a well-mixed reactor with uniform concentration of a given biomolecular species in the volume of the cell;
3) All the simulations were performed over a continuous time period without considering the effect of environmental factors such as solar cycle, temperature, and soil condition, for example;
4) The results predict the temporal dynamics of formaldehyde and glutathione in the non-GMO and GMO of soybean, but not the exact quantitative behavior as may be observed in subsequent in vitro and in vivo experiments;
NON-GMO GMO
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 15. The temporal dynamics of formaldehyde (HCHO) concentration levels in non-GMO [54] and with the GMO. In (a) is the non-GMO, and in (b) is the GMO case.
NON-GMO GMO
![]()
![]() (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 16. The temporal dynamics of glutathione (GSH) concentration levels in non-GMO [54] and with the GMO. In (a) is the non-GMO, and in (b) is the GMO case.
5) Most importantly, the results from this study are dependent on kinetic parameters and initial conditions of biomolecular species, information of which is based on the existing scientific literature.
The computational systems biology framework, afforded by CytoSolve, recognizes these limitations, and provides a promising methodology that is scalable and accessible in an open, transparent and collaborative manner, to continually integrate and update: a. new findings from publicly available literature, b. corrections to errors in previous research, and, c. proprietary information, to dynamically re-evaluate, expand and refine the models and publish new predictions.
Fourth, because the system is modular and allows for a “plug-and-play” type methodology for integrating molecular systems, as evidenced by the systematic integration of C1 metabolism with oxidative stress and then with molecular mechanisms of GM of soybean which induce oxidative stress, it is possible to continue to expand and refine this investigation by integrating other bio-molecular phenomena, and execute simulations under different conditions.
Fifth, the simulation shows that without GM, formaldehyde is produced and is detoxified to near zero levels. This allows one to understand why, in aggregate, normal, non-GMO plants always have a certain “background level” of formaldehyde, since at any point in time, there is a certain, very low, non-zero amount of formaldehyde, at that particular time, that is yet to be detoxified.
Sixth, concerning whether GMOs are “substantially equivalent” or “materially different” to non-GMOs, this work has focused the discussion on the criteria used for substantial equivalence and material difference, and whether such criteria are sensible and can truly capture the “difference” or “equivalence” between GMOs and non-GMOs. The underlying meta-level parameters, such as nutritional value, composition, nutritional effects, metabolism, etc., used in determining substantial equivalence are philosophically derived from performance parameters used for medical devices and hardware systems, which may not meet the needs for assessing the equivalence of biological organisms.
Seventh, as the Human Genome Project (HGP) demonstrated, attempting to establish substantial equivalence, based on meta-level parameters, such as the number of genes, to establish equivalence or differences between the complexity of two organisms is scientifically unsound. Had science used the number of genes as the criteria to determine the equivalence of organisms, then one would conclude that human beings are “equivalent” to a worm. The reality is humans are different from a worm, regardless of whether they have the same number of genes, because small differences in how genes interact, what proteins they upregulate, the interactions at the epigenetic level, etc., give rise to emergent properties and system dynamics, which ultimately define the difference between a human and a worm, and not the number of genes. Even a 0.01% difference in genetic matter can be “substantial” to making a big difference, depending, on where such differences lie in the genome, and what effects such difference have in the complex interactions of molecular pathways.
Eighth, systems biology and latest scientific methods, such as CytoSolve, now provide science with a capability and framework, though not perfect or complete, to acknowledge this complexity, and based on the known science, to integrate documented molecular pathway phenomena to predict, or at least know the bounds, of the range of effects that GMOs may have, and more importantly, to discover key regulatory mechanisms and critical molecules, which affect the regulation of these complex processes. Such methods can also be personalized to understand the specific behavior of particular GMOs by incorporating their unique biochemistries to discover other relevant and more specific biomarkers, beyond the two identified from this effort.
Ninth, in this study, through an important use case of GM in soybean, it has been demonstrated how a GMO can induce oxidative stress mechanisms, which then affect important molecular systems such as C1 metabolism, a pathway that is central to the functioning of all plants, bacteria, and fungi. This effort has resulted in the identification of two regulatory molecules, or biomarkers, glutathione and formaldehyde, whose levels vary significantly, in the GMO and non-GMO case.
Tenth, this approach may provide a generalized method for discovering molecular mechanistic criteria such as the concentration levels of formaldehyde (HCHO) and glutathione (GSH), found in this use case, which could perhaps, more systematically and rationally, address the equivalence or non-equivalence of GMOs and their non-GMO counterparts.
Eleventh, more recently, there is a growing confusion, even being promoted by eminent media outlets [17] [79] that GMOs are a “natural” process in “genetic modifications” resulting from human involvement in plant breeding. Such arguments point to plant breeding, done by indigenous people over millennia, as an example of this natural process. This research demonstrates that a GM is more akin to a targeted single molecule drug therapy, which can perturb molecular systems equilibria leading to side effects that can be enormous, uncertain and far-reaching. Even in the case of drug development, which is by no means perfect, the FDA requires significant testing and clinical trials, spanning upwards of fifteen years from the time of compound identification, to final approval. Moreover, plant breeding, unlike GM, was done over larger time spans and did involve “genetic modifications,” but such modifications were not just a single gene, but likely a choreography of “modifications” that resulted over time where many subsystems and genes were induced and modulated, by many external factors, thus, regulating side effects. At a minimum, given the potentially far-reaching effects of a single GM, as this research suggests for the GMO of soybean, at least a process, similar to the FDA clinical trials for single compound drugs, seems rational for GMO safety assessment and approval.
Twelfth, one important question that emerges from this effort is whether in vitro and in vivo testing should have been performed to verify the predictions. However, such testing is beyond the scope of this project for two reasons. First, it is difficult to acquire source material in an objective and independent manner, while ensuring legal compliance. Second, and more importantly, given the current environment, any isolated experiment, done by either proponents of GMOs or those against GMOs, will be vigorously contested since there are no agreed upon industry standards for conducting such testing to compare a GMO with its non-GMO counterpart.
The substantial and material difference in the levels of biomarkers of formaldehyde and glutathione, across non-GMO and GMO of soybean, predicted from this in silico systems biology analysis, however, demands such in vitro and in vivo testing. In order for the results of such testing to be broadly accepted by the scientific community, it is necessary to develop objective industry standards that define the exact protocols, processes and procedures, on how such in vitro and in vivo testing is to be performed. The timely White House initiative for “Improving Transparency and Ensuring Continued Safety in Biotechnology” to review rules concerning safety of biotechnology products [25] perhaps provides an unique opportunity for building consensus to develop these much-needed industry standards to conduct such in vitro and in vivo testing.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, systems science may provide the path forward in moving beyond the current debate and controversy, constrained by a reliance on reductionist approaches, to a new paradigm of systems biology that enables a systems understanding of “equivalence” and/or “difference” between a GMO and its non-GMO counterpart.
9. Future Direction
The methodology and results of this effort provide many areas of future research. There are four areas, in particular, that are relevant undertakings as logical and immediate next steps.
First, is to test the hypothesis that glyphosate action in endocrine disruption may likely be mediated through its upregulation of formaldehyde. The current framework is poised to conduct such in silico analysis.
Second, since C1 metabolism is present in gut bacteria of animals, it is possible to predict formaldehyde accumulation and glutathione depletion in the microbiome, and its subsequent effect on various disease models affecting the health of the host.
Third, to address the logical question why a GMO product survives and appears to maintain a phenotypic homeostasis, in spite of the deleterious biological impacts predicted from this research, future research can be conducted to demonstrate that it is likely that the GMO is in a perturbed state and has “adjusted” to an unnatural allostasis, a result of a significant disruption from its normal homeostasis.
Fourth, since little is known concerning the mechanism of methylation and how it affects the regulation of genes, future work can incorporate emerging research towards understanding how changes in the numbers of methyl groups modify methylation processes and how genes are targeted for methylation, affecting epigenetic phenomena in plants.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Warren Porter and Dr. Ray Seidler for their invaluable and critical feedback in the development of this manuscript.
Supplementary Materials
![]()
![]()
Table S1. List of parameters used in in silico models of oxidative stress.
Appendix A: List of Keywords
1. Genetic modificationoxidative stress signaling pathways
2. Agriculture AND genetic modification
3. Impact of GM CP4 EPSP induced oxidative stress
4. Population AND food security ANDgenetic modification
5. Kinetics of iron uptake in plants
6. Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione
7. Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione peroxidase in plants
8. Superoxide production AND photosynthesis
9. Perhydroxyl radical AND oxidative stress in plants
10. Fenton reaction AND oxidative stress in plants
11. Factors affecting formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity AND oxidative stress
12. Formaldehyde dehydrogenase acting on lipid peroxide
13. Lipid peroxide as substrate for formaldehyde dehydrogenase
14. ROS AND catalase expression in plants
15. Competitive inhibitors of formaldehyde dehydrogenase AND plant
16. Requirement of GSH for formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity
17. Glutathione depletion and formaldehyde dehydrogenase
18. Hydrogen peroxide levels AND ascorbate glutathione cycle
19. Iron AND oxidative stress AND glutathione level AND plants
20. EPSP synthase AND photosynthetic electron transport chain
21. Fffect of illumination on glutathione reductase activity in chloroplasts
22. Sarcosine oxidase activity graph versus sarcosine concentration
[1] Genetic modificationoxidative stress signaling pathways
[2] Agriculture AND genetic modification
[3] Impact of GM CP4 EPSP induced oxidative stress
[4] Population AND food security ANDgenetic modification
[5] Kinetics of iron uptake in plants
[6] Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione
[7] Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione peroxidase in plants
[8] Superoxide production AND photosynthesis
[9] Perhydroxyl radical AND oxidative stress in plants
[10] Fenton reaction AND oxidative stress in plants
[11] Factors affecting formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity AND oxidative stress
[12] Formaldehyde dehydrogenase acting on lipid peroxide
[13] Lipid peroxide as substrate for formaldehyde dehydrogenase
[14] ROS AND catalase expression in plants
[15] Competitive inhibitors of formaldehyde dehydrogenase AND plant
[16] Requirement of GSH for formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity
[17] Glutathione depletion and formaldehyde dehydrogenase
[18] Hydrogen peroxide levels AND ascorbate glutathione cycle
[19] Iron AND oxidative stress AND glutathione level AND plants
[20] EPSP synthase AND photosynthetic electron transport chain
[21] Fffect of illumination on glutathione reductase activity in chloroplasts
[22] Sarcosine oxidase activity graph versus sarcosine concentration
Appendix B: Log-Scale Figures for Glutathione (GSH) Temporal Dynamics.
![]()
Figure B1. Temporal dynamics of glutathione in non-GMO plants. Time is represented in log-scale.
![]()
Figure B2. Temporal dynamics of glutathione in non-GMO plants undergoing oxidative stress. Time is represented in log-scale.
![]()
Figure B3. Temporal dynamics of glutathione in GM of soybean and oxidative stress on glutathione (GSH) concentration in formaldehyde detoxification model. Time is repre- sented in log-scale.
![]()
Figure B4. Temporal dynamics of glutathione in GM of soybean and oxidative stress on glutathione (GSH) concentration in integrative C1 metabolism model. Time is represented in log-scale.
![]()
Figure B5. Parameter sensitivity analysis of VCAT on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism. Time is represented in log- scale.
![]()
Figure B6. Parameter sensitivity analysis of kGSH-HCHO on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism. Time is represented in log-scale.
![]()
Figure B7. Parameter sensitivity analysis of VMTG on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism. Time is represented in log- scale.
![]()
Figure B8. Parameter sensitivity analysis of ![]() on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism. Time is represented in log-scale.
on glutathione (GSH) in the integrated GM of soybean and oxidative stress model with C1 metabolism. Time is represented in log-scale.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.