Brain as an Emergent Finite Automaton: A Theory and Three Theorems ()
1. Introduction
Our computational theory [2] of brain and mind includes two major parts rooted in the rich literature about biological brains [3] [4] : (A) dynamically emerging, motivation-free circuits and functions; and (B) motivation based on such circuits and functions.
The computation in the former (A) is carried out by target-precise neuron-to-neuron signal transmissions. Weng & Luciw 2012 [5] and Weng et al. 2013 [6] presented a computational theory for such brain circuits to process information spatial and temporal, respectively, using their distributed, emergent, and non-symbolic representations. As reviewed in those two articles, such brain circuits are also fundamentally different from many existing neural networks cited therein―the brain circuits are not only locally recurrent as many neural networks, but also globally recurrent in the sense that they all use motor as input concepts. As explained in Weng & Luciw [7] , the brain motors (or actions) correspond to all possible concepts that a human can learn and express from conception, through prenatal life, birth, childhood, infancy, and adulthood―such as location, type, scale, temporal context, goal, subgoal, intent, purpose, price, ways to use, and so on. These concepts are used by the brain circuits as states, like states in a Finite Automaton (FA) [8] , but such an FA is emergent and non-symbolic to be explained below.
The computation in the latter (B) is based on target-imprecise diffusion of neural transmitters that diffuse across brain tissue. Weng et al. 2013 [9] proposed a model for how reinforcement learning is carried out in such emergent brain circuits through two types of transmitter systems―serotonin and dopamine. Wang et al. 2011 [10] present a model about how individual neurons use two other types of transmitter systems―acetylcholine and norepinephrine―to automatically estimate uncertainty and novelty, so that each neuron can decide where it gets inputs from. These four types of neural transmitter systems―serotonin, dopamine, acetylcholine and norepinephrine―along with other neural transmitters but seemingly relatively less important than these four types [11] , amount to what we know as motivation. Various emotions are special cases of motivation [3] [4] .
This paper will not further discuss the motivation part of a biological brain and will instead concentrate on the former―(A) the basic brain circuits and functions. In other words, the theory below models any emotion-free brain. DNs with emotion such as pain avoidance and pleasure seeking will be only briefly discussed in Section 9.
This theory here does not claim that the FA-based brain model is indeed complete for an emotion-free brain, because there is no widely accepted and rigorous definition of a natural phenomenon such as a brain and therefore, there is always some limitation for any theory to explain a natural phenomenon. As such, as any theory can only approximate a natural phenomenon but can never exhaust such an approximation. The Newtonian physics is a good example because it is refined by the relativity theory.
All computational networks fall into two categories: Symbolic Networks (SNs) and Emergent Networks. The former category uses symbolic representations and the latter uses emergent representations. See the review for symbolic models and emergent models in Weng 2012 [12] which tried to clarify some common misconceptions on representations.
The class of SN [13] includes Finite Automata (FA), Markov Chains, Markov Models, Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDP), Belief Networks, Graphical Models, and all other networks that use at least some symbolic representations. The HMM and other probability-based models in the above list are symbolic because they add probability to the symbolic FA basis and therefore the basic nature of their representations is still symbolic―adding probability does not change the nature of symbolic representation. We will use FA as an example for SN because any SN includes FA as its basis.
The class of Emergent Network includes all neural networks that use exclusively emergent representations, such as Feed-forward Networks, Hopfield Networks, Boltzmann Machines, Restricted Boltzmann Machines, Liquid State Machines, and Reservoir Computing, and the newer Developmental Networks (DNs) [14] . However, traditional neural networks are not as powerful and complete as DN, because they do not have the logic of FA as explained first in [14] and we will be proved for DN in this paper.
The major differences between a Symbolic Network (SN) and a Developmental Network (DN) are illustrated in Figure 1.
Marvin Minsky 1991 [15] and others correctly argued that symbolic models were logical and clean, while connectionist models were analogical and scruffy. Neural networks are called emergent networks here because some networks were not emergent and partially symbolic. Michael Jodan 2014 [16] correctly raised fundamental questions that many researchers have not paid sufficient attention to. The logic capabilities of emergent networks are still unclear, categorically. This paper addresses some fundamental issues that Michael Jordan raised [16] recently.
Computationally, feed-forward connections serve to feed sensory features [17] to motor area for generating behaviors. It has been reported that feed-backward connections can serve as class supervision [18] , attention [19] , and storage of time information.
![]()
Figure 1. Comparison between a symbolic FA (or SN) and an emergent DN. (a) Given a task, an FA (or SN), symbolic, handcrafted by the human pro- grammer using a static symbol set; (b) A DN, which incrementally learns the FA but takes sensory images directly and produces motor images directly. Without given any task, a human designs the general-purpose Developmental Program (DP) which resides in the DN as a functional equivalent of the “genome” that regulates the development―fully autonomous inside the DN.
The work of Finite Automata (FA) played a major role in our theory about the brain. The work of Weng 2011 [14] and 2013 [20] was not the first to relate a network with an FA. Some researchers used neural networks to batch-com- pile a special kind of FA. Frasconi et al. 1995 [21] used a feed-forward network to explicitly compute the state transition function  of an FA. Their network requires: 1) a special canonical binary coding of the states so that the Hamming distance is 1 between any source state q and any target state
of an FA. Their network requires: 1) a special canonical binary coding of the states so that the Hamming distance is 1 between any source state q and any target state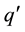 ; 2) an additional intermediate state is added if the source state q and target state q are the same; 3) the entire state transition function δ is known a priori so that their algorithm can directly compute all the weights as a batch (i.e., programmed, instead of learned incrementally). This compiled network uses a layer of logic-AND nodes followed by a layer of logic-OR nodes. Frasconi et al. 1996 proposed a radial basis function as an alternative batch-compiled feed-forward network for the above logic network [22] since a finite number of samples are sufficient for completely characterizing the FA due to its symbolic nature. Omlin & Giles 1996 [23] proposed a second-order network for computing the state transition function of a fully given FA. By second order, the neuronal input contains the sum of weighted multiplications (hence the second order), between individual state nodes and individual input nodes. There does not seem to be known evidence that a biological neuron uses such a product. The network Omlin & Giles 1996 is also statically “programmed” by a human programmer based on a fully given FA. They positively contributed to neural network studies.
; 2) an additional intermediate state is added if the source state q and target state q are the same; 3) the entire state transition function δ is known a priori so that their algorithm can directly compute all the weights as a batch (i.e., programmed, instead of learned incrementally). This compiled network uses a layer of logic-AND nodes followed by a layer of logic-OR nodes. Frasconi et al. 1996 proposed a radial basis function as an alternative batch-compiled feed-forward network for the above logic network [22] since a finite number of samples are sufficient for completely characterizing the FA due to its symbolic nature. Omlin & Giles 1996 [23] proposed a second-order network for computing the state transition function of a fully given FA. By second order, the neuronal input contains the sum of weighted multiplications (hence the second order), between individual state nodes and individual input nodes. There does not seem to be known evidence that a biological neuron uses such a product. The network Omlin & Giles 1996 is also statically “programmed” by a human programmer based on a fully given FA. They positively contributed to neural network studies.
The above studies aimed successfully compute the state transition function using a programmed network, but they do not generate emergent representations, do not learn from observations of FA operations, do not deal with natural input images (or patterns), and do not deal with natural motor images (or patterns), and not incrementally learn.
As far as we know, the DN in Weng 2011 [14] was the first general-purpose emergent FA that
1) uses fully emergent representations,
2) allows natural sensory firing patterns,
3) allows the motor area to have subareas where each subarea represents either an abstract concept (location, type, scale, etc.) or natural muscle actions (e.g., driving a car or riding a bicycle),
4) uses a general-purpose and unified area function that does not need interactive approximation and does not have local minima in its high dimensional and nonlinear but non-iterative approximation,
5) learns incrementally―taking one-pair of sensory pattern and motor pattern at a time to update the network and discarding the pair immediately after―and,
6) uses an optimization scheme in which every update of the network realizes the maximum likelihood estimate of the network, conditioned on the limited computational resources in the network and the limited learning experience in the network’s “life time”.
Explained in Weng 2012 [2] , the DN model is inspired by biological brains, especially brain anatomy (e.g., [24] [26] ) and brain physiological experiments (e.g. [19] [26] ). But we will use computational language in the following material, so that the material is understandable by an analytical reader.
In the following, we analyze how the DN theory bridges the symbolic school and the connectionist school in artificial intelligence (AI). First, Section 2 presents the algorithm for the Developmental Program (DP) of the DN. Section 3 gives a temporal formulation of FA to facilitate understanding the brain theory. Then, Section 4 proposes that the framework for FA is complete. All FAs in this paper are Deterministic FA. So, we call them simply FAs. How a DN learns incrementally from an FA is discussed in Section 5. The three theorems are presented and proved in Section 6 through Section 8.
Theorem 1 states that for any FA that operates in real time, there is an emergent DN that learns the FA incre- mentally. It observes one state-and-input pair from the FA at a time, learns immediately and becomes error-free for all the FA transitions that it has learned, regardless how many times a transition has been observed―one is sufficient but more results in better optimality in the real world. The DN is equivalent to the part of FA that corresponds to all transitions that have demonstrated so far.
Theorem 2 establishes that if the FA-learned DN is frozen―computing responses only but not updating its adaptive parts, the frozen DN is optimal in the sense of maximum likelihood when it takes inputs from infinitely many possible cases in the world.
Theorem 3 asserts that the FA-learned DN, if it is allowed to continue to learn from infinitely many possible cases in the world, is optimal in the sense of maximum likelihood.
Section 9 briefly discusses experiments of DN. Section 10 provides concluding remarks and discussion.
2. Algorithm for Developmental Program
The small DP algorithm self-programs logic of the world into a huge DN based on experiences in its physical activities. A DN has its area Y as a “bridge” for its two banks, X and Z, as illustrated in Figure 2(b).
Biologically, a DP algorithm models the collective effects of some genome properties of the cells of the nervous system―neurons and other types of cells in the nervous system [3] [4] [27] . Thus, in nature, the DP is a result of evolution across many generations of a species. The DP seems to be a more systematic way to understand natural intelligence than studies the response of a child or adult brain.
In artificial intelligence, a DP algorithm is the result of human understanding of the development of natural intelligence followed by a human DP design based such understanding. This approach, known as developmental approach [2] [28] , short-cuts the long and expensive process of cross-generation evolution.
Some parameters of DP (e.g., the number of cells in Y) could be experimentally selected by a genetic algorithm, but the DP as a whole seems to be extremely expensive for any artificial genetic algorithm to reach without handcrafting (e.g., see the handcrafted area function below).
Human design of DP algorithm [28] seems to be a more practical way to reach human-like mental capabilities and human-level performance in robots and computers for two main reasons: 1) Fully automatic development of intelligence (i.e., task-nonspecific and fully automatic learning) is the approach that the natural intelligence takes and has demonstrated success; 2) The design of the DP algorithm is a clean task, in contrast to traditional AI― modeling intelligence itself―which is a muddy task [2] [29] .
The quality in a human-designed DP, when the DP is widely used in the future, greatly affects all the capabilities in the developmental robots and computers that use the DP.
In the DN, if Y is meant for modeling the entire brain, X consists of all receptors and Z consists of all effectors―muscle neurons and glands. Additionally, the Y area of the DP can also model any Brodmann area in the brain and if so, the X and Z correspond to respectively, the bottom-up areas and top-down areas of the Brodemann area. From the analysis below, we can also see that the Y area of the DN can model any closely related set of neurons―Brodmann area, a subset, or a superset.
The most basic function of an area Y seems to be prediction―predict the signals in its two vast banks X and Z through space and time.
Algorithm 1 (DP) Input areas: X and Z. Output areas: X and Z. The dimension and representation
![]()
Figure 2. Conceptual correspondence between an Finite Automaton (FA) with the corresponding DN. (a) An FA, handcrafted and static; (b) A corresponding DN that simulates the FA. It was taught to produce the same input-output rela- tions as the FA in (a). A symbol (e.g., ) in (a) corresponds to an image (e.g.,
) in (a) corresponds to an image (e.g.,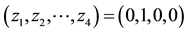 ) in (b).
) in (b).
of X and Y areas are hand designed based on the sensors and effectors of the species (or from evolution in biology). Y is the skull-closed (inside the brain), not directly accessible by the outside.
1) At time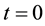 , for each area A in
, for each area A in , initialize its adaptive part
, initialize its adaptive part 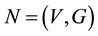 and the response vector
and the response vector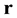 , where V contains all the synaptic weight vectors and
, where V contains all the synaptic weight vectors and  stores all the neuronal ages. For example, use the generative DN method discussed below.
stores all the neuronal ages. For example, use the generative DN method discussed below.
2) At time , for each A in
, for each A in  repeat:
repeat:
a) Every area A performs mitosis-equivalent if it is needed, using its bottom-up and top-down inputs  and
and , respectively.
, respectively.
b) Every area A computes its area function , described below,
, described below,
![]()
where ![]() is its response vector and
is its response vector and ![]() and
and ![]() are the adaptive part of the area defined above, before and after the area update, respectively. Note that
are the adaptive part of the area defined above, before and after the area update, respectively. Note that ![]() is not part of the domain of
is not part of the domain of ![]() because
because ![]() is the model for any area A, not just for an individual neuron of A. Thus,
is the model for any area A, not just for an individual neuron of A. Thus, ![]() does not use iterations, efficiently approximating lateral inhibitions and internal excitations.
does not use iterations, efficiently approximating lateral inhibitions and internal excitations.
c) For every area A in![]() , A replaces:
, A replaces: ![]() and
and![]() .
.
The DN must update at least twice for the effects of each new signal pattern in X and Z, respectively, to go through one update in Y and then one update in Z to appear in X and Z.
In the remaining discussion, we assume that Y models the entire brain. If X is a sensory area, ![]() is always supervised. The
is always supervised. The ![]() is supervised only when the teacher chooses to. Otherwise,
is supervised only when the teacher chooses to. Otherwise, ![]() gives (predicts) motor output.
gives (predicts) motor output.
The area function![]() , which is based on the theory of Lobe Component Analysis (LCA) [30] , is a model for self-organization by a neural area. Each area A has a weight vector
, which is based on the theory of Lobe Component Analysis (LCA) [30] , is a model for self-organization by a neural area. Each area A has a weight vector![]() . Its pre-response vector is:
. Its pre-response vector is:
![]() (1)
(1)
which measures the degree of match between the directions of ![]() and
and![]() .
.
To simulate lateral inhibitions (winner-take-all) within each area A, only top-![]() winners are among the
winners are among the ![]() competing neurons fire. Considering
competing neurons fire. Considering![]() , the winner neuron
, the winner neuron ![]() is identified by:
is identified by:
![]() (2)
(2)
The area dynamically scale top-k winners so that the top-k respond with values in![]() . For
. For![]() , only the single winner fires with response value
, only the single winner fires with response value ![]() and all other neurons in A do not fire. The response value
and all other neurons in A do not fire. The response value ![]() approximates the probability for
approximates the probability for ![]() to fall into the Voronoi region of its
to fall into the Voronoi region of its ![]() where the “nearness” is
where the “nearness” is![]() .
.
All the connections in a DN are learned incrementally based on Hebbian learning―cofiring of the pre- synaptic activity ![]() and the post-synaptic activity
and the post-synaptic activity ![]() of the firing neuron. If the pre-synaptic end and the post- synaptic end fire together, the synaptic vector of the neuron has a synapse gain
of the firing neuron. If the pre-synaptic end and the post- synaptic end fire together, the synaptic vector of the neuron has a synapse gain![]() . Other non-firing neurons do not modify their memory. When a neuron
. Other non-firing neurons do not modify their memory. When a neuron ![]() fires, its firing age is incremented
fires, its firing age is incremented ![]() and then its synapse vector is updated by a Hebbian-like mechanism:
and then its synapse vector is updated by a Hebbian-like mechanism:
![]() (3)
(3)
where ![]() is the learning rate depending on the firing age (counts)
is the learning rate depending on the firing age (counts) ![]() of the neuron
of the neuron ![]() and
and ![]() is the retention rate with
is the retention rate with![]() . Note that a component in the gain vector
. Note that a component in the gain vector ![]() is zero if the corresponding component in
is zero if the corresponding component in ![]() is zero.
is zero.
The simplest version of ![]() is
is ![]() which corresponds to:
which corresponds to:
![]() (4)
(4)
where ![]() is the firing time of the post-synaptic neuron
is the firing time of the post-synaptic neuron![]() . The above is the recursive way of computing the batch average:
. The above is the recursive way of computing the batch average:
![]() (5)
(5)
The initial condition is as follows. The smallest ![]() in Equation (3) is 1 since
in Equation (3) is 1 since ![]() after initialization. When
after initialization. When![]() , the initial value of
, the initial value of ![]() on the right side of Equation (3) is used for pre-response competition to find this winner
on the right side of Equation (3) is used for pre-response competition to find this winner![]() , but the initial value of
, but the initial value of ![]() does not affect the first-time updated
does not affect the first-time updated ![]() on the left side since
on the left side since![]() .
.
In other words, any initialization of weight vectors will only determine who win (i.e., which newly born neurons take the current role) but the initialization will not affect the distribution of weights at all. In this sense, all random initializations of synaptic weights will work equally well―all resulting in weight distributions that are computationally equivalent. Biologically, we do not care which neurons (in a small 3-D neighborhood) take the specific roles, as long as the distribution of the synaptic weights of these neurons lead to the same computational effect. This neuronal learning model leads to the following conjecture.
Conjecture 1 In a small 3-D neighborhood (e.g., of a hundred nearby neurons), neural circuits are so different across different biological brains that mapping the detailed neuron wiring of brain is not informative at the level of individual neuron.
The NIH Connectome program aims to “map the neural pathways ... about the structural and functional connectivity of the human brain. ... resulting in improved sensitivity, resolution, and utility, thereby accelerating progress in the emerging field of human connectomics”. The DN theory and the above conjecture predict that such an NIH program is not as scientifically useful as the NIH program hoped in terms of understanding how the brain works and future studies of abnormal brain circuits. For the brain, “more detailed connectomics data” seems to be not as productive as more complete and clear theories.
3. FA as a Temporal Machine
In this section, we present an FA as a temporal machine, although traditionally an FA is a logic machine, driven by discrete event of input.
As we need a slight deviation from the standard definition of FA, let us look at the standard definition first.
Definition 1 (Language acceptor FA) A finite automaton (FA) M is a 5-tuple![]() , where Q is a finite set of states, consists of symbols. Σ is a finite alphabet of input symbols.
, where Q is a finite set of states, consists of symbols. Σ is a finite alphabet of input symbols. ![]() is the initial state.
is the initial state. ![]() is the set of accepting states.
is the set of accepting states. ![]() is the state transition function.
is the state transition function.
This classical definition is for a language acceptor, which accepts all strings x from the alphabet Σ that belongs to a language L. It has been proved [8] that given any regular language L from alphabet Σ, there is an FA that accepts L, meaning that it accepts exactly all ![]() but no other string not in L. Conversely, given any FA taking alphabet Σ, the language L that the FA accepts is a regular language. However, a language FA, just like any other automata, only deals syntax not semantics. The semantics is primary for understanding a language and the syntax is secondary.
but no other string not in L. Conversely, given any FA taking alphabet Σ, the language L that the FA accepts is a regular language. However, a language FA, just like any other automata, only deals syntax not semantics. The semantics is primary for understanding a language and the syntax is secondary.
We need to extend the definition of FA for agents that run at discrete times as follows.
Definition 2 (Agent FA) A finite automaton (FA) M for a finite symbolic world is a 4-tuple![]() , where Σ and
, where Σ and ![]() are the same as above and
are the same as above and ![]() is a finite set of states, where each state
is a finite set of states, where each state ![]() is a symbol, corresponding to a set of concepts. The agent runs through discrete times
is a symbol, corresponding to a set of concepts. The agent runs through discrete times![]() , starting from state
, starting from state ![]() at
at![]() . At each time
. At each time![]() , it reads input
, it reads input ![]() and transits from state
and transits from state
![]() to
to![]() , and outputs
, and outputs ![]() at time
at time![]() , illustrated as
, illustrated as![]() .
.
The inputs to an FA are symbolic. The input space is denoted as![]() , which can be a discretized version of a continuous space o input. In sentence recognition, the FA reads one word at a time. The number l is equal to the number of all possible words―the size of the vocabulary. For a computer game agent, l is equal to the total number of different percepts.
, which can be a discretized version of a continuous space o input. In sentence recognition, the FA reads one word at a time. The number l is equal to the number of all possible words―the size of the vocabulary. For a computer game agent, l is equal to the total number of different percepts.
The outputs (actions) from a language acceptor FA are also symbolic, ![]() which can also be a discretized version of a continuous space of output. For a sentence detector represented by an FA, when the FA reaches the last state, its action reports that the sentence has been detected.
which can also be a discretized version of a continuous space of output. For a sentence detector represented by an FA, when the FA reaches the last state, its action reports that the sentence has been detected.
An agent FA is an extension from the corresponding language FA, in the sense that it outputs the state, not only the acceptance property of the state. The meanings of each state, which are handcrafted by the human programmer but are not part of the formal FA definition, are only in the mind of the human programmer. Such meanings can indicate whether a state is an accepting state or not, along many other meanings associated with each state as our later example will show. However, such concepts are only in the mind of the human system designer, not something that the FA is “aware” of. This is a fundamental limitation of all symbolic models. The Developmental Network (DN) described below do not use any symbols, but instead (image) vectors from the real-world sensors and real-world effectors. As illustrated in Figure 2, a DN is grounded in the physical environment but an FA is not.
Figure 3 gives an example of the agent FA. Each state is associated with a number of cognitive states and actions, shown as text in the lower part of Figure 3, reporting action for cognition plus a motor action. The example in Figure 3 shows that an agent FA can be very general, simulating an animal in a micro, symbolic world. The meanings of each state in the lower part of Figure 3 are handcrafted by, and only in the mind of, the human designer. These meanings are not a part of the FA definition and are not accessible by the machine that simulates the FA.
Without loss of generality, we can consider that an agent FA simply outputs its current state at any time, since the state is uniquely linked to a pair of the cognition set and the action set, at least in the mind of human designer.
4. Completeness of the FA-in-DN Framework
The FA-in-DN framework is useful for understanding how a DN works. However, FA itself is handcrafted by a human teacher, or in other words, the behaviors of an autonomously developed human teacher.
It has been proved [8] that an FA with n states partitions all the strings in Σ into n sets. Each set is called equivalence class, consisting of strings that are indistinguishable by the FA. Since these strings are indistinguishable, any string x in the same set can be used to denote the equivalent class, denoted as![]() . Let Λ denote an empty string. Considering Figure 3, the FA partitions all possible strings into 6 equivalent classes.
. Let Λ denote an empty string. Considering Figure 3, the FA partitions all possible strings into 6 equivalent classes. ![]() as the agent does not know about “calculus” although it is in Σ. All the strings in the equivalent class [Λ] end in
as the agent does not know about “calculus” although it is in Σ. All the strings in the equivalent class [Λ] end in![]() . All strings in the equivalent class
. All strings in the equivalent class ![]() end in
end in![]() , etc.
, etc.
![]()
Figure 3. An FA simulates an animal. Each circle indicates a context state. The system starts from state z1. Supposing the system is at state q and receives a symbol σ and the next state should be q', the diagram has an arrow denoted as![]() . A label “other” means any symbol other than those marked from the out-going state. Each state corresponds to a set of actions, indicated below the FA. The “other” transitions from the lower part are omitted for brevity.
. A label “other” means any symbol other than those marked from the out-going state. Each state corresponds to a set of actions, indicated below the FA. The “other” transitions from the lower part are omitted for brevity.
From the above discussion, we can see that the key power of an FA is to lump very complex equivalent ![]() contexts into equivalent classes.
contexts into equivalent classes.
A Turing Machine (TM) [8] [31] is a 5-tuple T =![]() , where Q is the set of states,
, where Q is the set of states, ![]() and
and ![]() are the input and tape alphabets, respectively, with
are the input and tape alphabets, respectively, with![]() , q0 is the initial state, and
, q0 is the initial state, and ![]() is the transition function:
is the transition function:
![]()
where ![]() is the blank symbol not in
is the blank symbol not in![]() , h denotes the halt state, and R, L, S denote the head motion, right, left, and stationary, respectively. Consider the following two definitions:
, h denotes the halt state, and R, L, S denote the head motion, right, left, and stationary, respectively. Consider the following two definitions:
1) Define ![]() to include also the tape write action w and the head move action m:
to include also the tape write action w and the head move action m:
![]()
Each state in ![]() is a three tuple (q, w, m) where w and m can be empty.
is a three tuple (q, w, m) where w and m can be empty.
2) Let![]() .
.
The above transition function ![]() for TM becomes the transition function
for TM becomes the transition function ![]() of an FA:
of an FA:![]() .
.
Therefore, the controller of any TM is an FA. A grounded DN can learn the FA perfectly. It takes input ![]() from the real word and its action can include head write and head motion. A TM is not grounded, but the DN is grounded: A TM senses from, and acts on, a tape but a DN senses from, and acts on, its real-world physical environment.
from the real word and its action can include head write and head motion. A TM is not grounded, but the DN is grounded: A TM senses from, and acts on, a tape but a DN senses from, and acts on, its real-world physical environment.
The completeness of agent FA-in-DA can be described as follows. Given a vocabulary S' representing the elements of a symbolic world, a natural language L is defined in terms of S' where the meanings of all sentences (or events) in L are defined by the set of equivalent classes, determined by Q' of FA-in-DN. When the number of states is sufficiently large, a properly learned FA-in-DN can sufficiently characterize the cognition and behaviors of an agent living in the real physical world with vocabulary S'.
This argument is based on the following observation: as long as the context state ![]() is properly learned so that it contains all the information that is necessary and sufficient for generating the following states, then
is properly learned so that it contains all the information that is necessary and sufficient for generating the following states, then ![]() with sensory input
with sensory input ![]() correctly selected from a cluttered scene should be sufficient to
correctly selected from a cluttered scene should be sufficient to
generate the next state:![]() .
.
As a simple example, an FA-in-DN can accept the context-free language![]() , the set of all
, the set of all
strings that consist of n a’s followed by the same number of b’s, by simulating how a TM works on a tape to accept the language L.
The Chomsky hierarchy [31] after the work of Norm Chomsky in particular and the automana and languages theory in classical computer science [8] [31] regard only Turing Machines as general-purpose programming machine because they mainly consider only the syntax of a computer language, not the rich semantics that a symbol can represent. However, a symbolic state q and an input symbol σ can practically represent any set of meanings. Yet, the meanings of general purpose with Turing Machines and FA-in-DN are different: with a TM, it means what kind of sequence of computations the TM program can represent. With the latter FA-in-DN, it means the richness of meaning any symbol (q and σ) can represent so that the FA-in-DN can represent any emergent state-based agent that has a finite memory.
In particular, it is important to note that a state can remember very early event [2] [6] : e.g. an event needed by ![]() can be contained in
can be contained in![]() ,
, ![]() , etc.
, etc.
But FA-in-DN goes beyond the symbolic AI, because it automatically develop internal representations― emergent.
5. DN Incrementally Learns FA
Next, let us consider how a DN learns from any FA. First we consider the mapping from symbolic sets S and q to vector spaces X and Z.
Definition 3 (Symbol-to-vector mapping) A symbol-to-vector mapping m is a one-to-one mapping![]() . We say that
. We say that ![]() and
and ![]() are equivalent, denoted as
are equivalent, denoted as ![]() if
if![]() .
.
A binary vector of dimension d is such that all its components are either 0 or 1. It simulates that each neuron, among d neurons, either fires with a spike ![]() or without
or without ![]() at each sampled discrete time
at each sampled discrete time![]() . From discrete spikes
. From discrete spikes![]() , the real valued firing rate at time t can be estimated by
, the real valued firing rate at time t can be estimated by
![]() , where T is the temporal size for averaging. A biological neuron can fire at a maximum
, where T is the temporal size for averaging. A biological neuron can fire at a maximum
rate around ![]() spikes per second, producible only under a laboratory environment. If the brain is sampled at frequency
spikes per second, producible only under a laboratory environment. If the brain is sampled at frequency![]() , we consider the unit time length to be
, we consider the unit time length to be ![]() second. The timing of each spike is precise up to
second. The timing of each spike is precise up to ![]() second at the sampling rate f, not just an estimated firing rate v, which depends on the temporal size T (e.g.,
second at the sampling rate f, not just an estimated firing rate v, which depends on the temporal size T (e.g., ![]() s). Therefore, a firing-rate neuronal model is less temporally precise than a spiking neuronal model. The latter, which DN adopts, is more precise for fast sensorimotor changes.
s). Therefore, a firing-rate neuronal model is less temporally precise than a spiking neuronal model. The latter, which DN adopts, is more precise for fast sensorimotor changes.
Let ![]() denote the d-dimensional vector space which contains all the binary vectors each of which has at most p components to be 1. Let
denote the d-dimensional vector space which contains all the binary vectors each of which has at most p components to be 1. Let ![]() contains all the binary vectors each of which has exactly p com- ponents to be 1.
contains all the binary vectors each of which has exactly p com- ponents to be 1.
Definition 4 (Binary-p mapping) Let![]() . A symbol-to-vector mapping
. A symbol-to-vector mapping ![]() is a binary-p mapping if m is one to one, that is, if
is a binary-p mapping if m is one to one, that is, if ![]() then
then ![]() implies
implies![]() .
.
The larger the p, the more symbols the space of Z can represent. However, through a binary-p mapping, each symbol ![]() always has a unique vector
always has a unique vector![]() . Note that different q’s are mapped to different directions of unit z’s.
. Note that different q’s are mapped to different directions of unit z’s.
Suppose that a DN is taught by supervising binary-p codes at its exposed areas, X and Z. When the motor area Z is free, the DN performs, but the output from Z is not always exact due to (a) the DN outputs in real numbers instead of discrete symbols and (b) there are errors in any computer or biological system. The following binary conditioning can prevent error accumulation by suppressing noise and normalizing the spikes as 1, which the brain seems to use through spikes.
Definition 5 (Binary conditioning) For any vector from![]() , the binary conditioning of z forces every real-valued component
, the binary conditioning of z forces every real-valued component ![]() to be 1 if the pre-response of
to be 1 if the pre-response of ![]() is larger than the machine zero―a small positive bound estimating computer round-off noise.
is larger than the machine zero―a small positive bound estimating computer round-off noise.
The binary conditioning must be used during autonomous performance as long as the Z representations use spikes, instead of firing rates. Machines zeros are noises from computer finite precision in representing a number. The binary conditioning suppresses the accumulation of such computer generated round-off errors. Because the Z representation is binary by definition, the binary conditioning forces the real numbers to become 0 or 1 only. However, the actual value of machine zero is computer dependent, depending on the length to represent a real number. In particular, the case of a constant Z vector of all ones will not appear incorrectly because all noises components that are meant to be 0 are set back to 0.
The output layer Z that uses binary-p mapping must use the binary conditioning, instead of top-k competition with a fixed k, as the number of firing neurons ranges from 1 to p.
Algorithm 2 (DP for GDN) A GDN is a DN that gives the following specific way of initialization. It starts from pre-specified dimensions for the X and Z areas, respectively. X represents receptors and is totally determined by the current input. But it incrementally generates neurons in Y from an empty Y (computer programming may use dynamic memory allocation). Each neuron in Z is initialized by a synaptic vector v of dimension 0, age 0. Suppose ![]() is the current synaptic vectors in Y. Whenever the network takes an input
is the current synaptic vectors in Y. Whenever the network takes an input![]() , compute the pre-resppnses in Y. If the top-1 winner in Y has a pre-response lower than 2 (i.e.,
, compute the pre-resppnses in Y. If the top-1 winner in Y has a pre-response lower than 2 (i.e.,![]() ), simulate mitosis-equivalent by doing the following:
), simulate mitosis-equivalent by doing the following:
1) Increment the number of neurons![]() ,
,
2) Add a new Y neuron. Set the weight vector![]() , its age to be 0, and its pre-response to be 2 since it is the perfect match based on Equation (1). There is no need to recompute the pre-responses.
, its age to be 0, and its pre-response to be 2 since it is the perfect match based on Equation (1). There is no need to recompute the pre-responses.
The response value of each Z neuron is determined by the starting state (e.g., background class). As soon as the first Y neuron is generated, every Z neuron will add the first dimension in its synaptic vector in the following DN update. This way, the dimension of its weight vector continuously increases together with the number c of Y neurons.
6. Theorem 1: DN Learns FA Perfectly
In this section, we establish the most basic theorem of the three, Theorem 1. First, we give an overview. Next, we establish a lemma to facilitate the proof of Theorem 1. Then, we present Theorem 1. Finally, we discuss grounded DN.
6.1. Overview
We first give an overview to facilitate the understanding of the proofs. Figure 4 is our graphic guide of this section. It has two parts, Figure 4(a) having a four-state and two-input FA as a small example of SN, and Figure 4(b) being a general purpose DN that can implement the FA in Figure 4(a) as only a special case but a DN can learn any FA autonomously from physically emerging patterns.
Although an FA is a temporal machine, the classic way to run an FA at discrete events that correspond to the time when the FA receives a symbolic input [8] . In order to explain how a continuously running DN learns an FA we run both FA and DN through discrete time indices.
An FA, such as the one in Figure 4(a) is handcrafted by a human programmer for a specific given task. However, a DN in Figure 4(b) can learn any FA, including the one in Figure 4(a). The DN observes one pair of symbol ![]() at a time from the FA but the DN only uses the physically consistent pattern
at a time from the FA but the DN only uses the physically consistent pattern ![]() corresponding to
corresponding to![]() , instead of
, instead of ![]() itself. By physically consistent, we mean, e.g., z is a muscle neuron firing pattern and x is an image in the eyes. Therefore, we say that
itself. By physically consistent, we mean, e.g., z is a muscle neuron firing pattern and x is an image in the eyes. Therefore, we say that ![]() is emergent (i.e., directly emerge from the physical world) but
is emergent (i.e., directly emerge from the physical world) but ![]() is not (i.e., handcrafted by the human programmer in the design document).
is not (i.e., handcrafted by the human programmer in the design document).
Because all three areas X, Y, Z in the DN all compute in parallel in Algorithm 1, we have two parallel computation flows in Figure 4(b):
1) The first flow corresponds to ![]() in the first column, y in the second column, and
in the first column, y in the second column, and ![]() in the third column.
in the third column.
2) The second flow has y in the first column, ![]() in the second, and y in the third.
in the second, and y in the third.
Both flows satisfy the real-world events, but for the FA logic here we let the second flow simply repeat (retain) the first flow. Therefore, due to these two flows, the DN must update at least twice for each pair ![]() for the effect of a new
for the effect of a new ![]() to reach the next
to reach the next![]() , once for the new y computation and once for the new
, once for the new y computation and once for the new ![]() computation. In the real world, DN should be updated as fast as the computational resources allow so as to respond to the real world as fast as it can.
computation. In the real world, DN should be updated as fast as the computational resources allow so as to respond to the real world as fast as it can.
The X area is always supervised by x as the binary pattern of σ.
The number of Z firing neurons depends on the number of different physical patterns required for Z, but we assume that the Z area uses binary representations. Each firing Z neuron, supervised by the current q from the FA as vector z, accumulates the firing frequency of the current single firing Y neuron as the corresponding Y -to-Z synaptic weights of the Z neuron. The incremental average in the Hebbian learning of Equation (4) is ex-
![]()
Figure 4. Symbolic Network (SN) and model the brain mapping, DN. In general, the brain performs external mapping ![]() on the fly. (a) An SN samples the vector space Z using symbolic set Q, and X using S, to compute symbolic mapping
on the fly. (a) An SN samples the vector space Z using symbolic set Q, and X using S, to compute symbolic mapping![]() . This example has four states
. This example has four states![]() , with two input symbols
, with two input symbols![]() . Two conditions
. Two conditions ![]() (e.g.,
(e.g., ![]() and
and![]() ) iden- tify the active outgoing arrow (e.g., red).
) iden- tify the active outgoing arrow (e.g., red). ![]() is the target state pointed to by the (red) arrow. (b) The grounded DN generates the internal brain area Y as a bridge, its bi- directional connections with its two banks X and Z, the inner products distance, and adaptation, to realize the external brain mapping. It performs at least two network updates during each unit time. To show how the DN learns a SN, the colors between (a) and (b) match. The sign
is the target state pointed to by the (red) arrow. (b) The grounded DN generates the internal brain area Y as a bridge, its bi- directional connections with its two banks X and Z, the inner products distance, and adaptation, to realize the external brain mapping. It performs at least two network updates during each unit time. To show how the DN learns a SN, the colors between (a) and (b) match. The sign ![]() means “image code for”. In (b), the two red paths from
means “image code for”. In (b), the two red paths from ![]() and
and ![]() show the condition
show the condition![]() . At
. At![]() , they link to
, they link to ![]() as internal representation, corresponding to the identification of the outgoing arrow (red) in (a) but an SN does not have any internal representation. At time t,
as internal representation, corresponding to the identification of the outgoing arrow (red) in (a) but an SN does not have any internal representation. At time t, ![]() predicts the action. But the DN uses internal
predicts the action. But the DN uses internal ![]() to predict both state
to predict both state ![]() and input
and input![]() . The same color between two neighboring hori- zontal boxes in (b) shows the retention of
. The same color between two neighboring hori- zontal boxes in (b) shows the retention of ![]() image in (a) within each unit time, but the retention should be replaced by temporal sampling in general. The black arrows in (b) are for predicting X. Each arrow link in (b) represents many connections. When it is shown by a non-black color, the color indicates the corresponding transition in (a). Each arrow link represents excitatory connections. Each bar link is inhibitory, representing top-k competition among Y neurons.
image in (a) within each unit time, but the retention should be replaced by temporal sampling in general. The black arrows in (b) are for predicting X. Each arrow link in (b) represents many connections. When it is shown by a non-black color, the color indicates the corresponding transition in (a). Each arrow link represents excitatory connections. Each bar link is inhibitory, representing top-k competition among Y neurons.
actly what is needed to compute this firing frequency. This firing frequency is equal to the discrete probability required for the optimality in the later Theorems 2 and 3.
The Y area of the GDN is empty to start with. Whenever there is a new input![]() , the DN automatically assigns a new Y neuron that memorizes
, the DN automatically assigns a new Y neuron that memorizes ![]() as its weight vector
as its weight vector![]() . Later, this Y neuron will not win in the top-1 competition unless when the same input
. Later, this Y neuron will not win in the top-1 competition unless when the same input ![]() appears again. The incremental average in the Hebbian learning of Equation (4) implies that every Y neuron never changes its weight vector after it is initialized using the input―average over the same vectors. Therefore, the number of Y neurons needed by the DN to learn an FA is equal to the number of different FA transitions.
appears again. The incremental average in the Hebbian learning of Equation (4) implies that every Y neuron never changes its weight vector after it is initialized using the input―average over the same vectors. Therefore, the number of Y neurons needed by the DN to learn an FA is equal to the number of different FA transitions.
With this overview, we are ready for Lemma 1.
6.2. Lemma 1
This subsection is a little long because of the detailed and complete proof, but I use the top-level Case 1 (new Y input) and Case 2 (old Y input) in the proof to organize the material. Each Case first considers Y and then Z. When we consider Z, we have Case ![]() and Case
and Case ![]() for the case where the Z neuron under consideration should fire and not fire, respectively, where i corresponds to 1 or 2 in the above Cases 1 or 2.
for the case where the Z neuron under consideration should fire and not fire, respectively, where i corresponds to 1 or 2 in the above Cases 1 or 2.
Lemma 1 (Properties of a GDN) Suppose a GDN simulates any given FA using top-1 competition for Y, binary-p mapping, and binary conditioning for Z, and update at least twice in each unit time. Each input ![]() is retained during all DN updates in
is retained during all DN updates in![]() . Such a GDN has the following properties for
. Such a GDN has the following properties for![]() :
:
1) The winner Y neuron matches perfectly with input ![]() with
with ![]() and fires, illustrated in Figure 4(a) as a single transition edge (red).
and fires, illustrated in Figure 4(a) as a single transition edge (red).
2) All the synaptic vectors in Y are unit and they never change once initialized, for all times up to t. They only advance their firing ages. The number of Y neurons c is exactly the number of learned state transitions up to time t.
3) Suppose that the weight vector v of each Z neuron is![]() , and Z area uses the learning
, and Z area uses the learning
rate straight recursive average![]() . Then the weight
. Then the weight ![]() from the
from the ![]() -th Y neuron to each Z neuron is
-th Y neuron to each Z neuron is
![]() (6)
(6)
![]() , where
, where ![]() is the number of times the
is the number of times the ![]() -th Y neuron has fired conditioned on that the Z neuron fires, and
-th Y neuron has fired conditioned on that the Z neuron fires, and ![]() is the total number of times the Z neuron has fired.
is the total number of times the Z neuron has fired.
4) Suppose that the FA makes transition![]() , as illustrated in Figure 4(a). After the second DN update, Z outputs
, as illustrated in Figure 4(a). After the second DN update, Z outputs![]() , as long as Z of DN is supervised for the second DN update when the transition is received by Z the first time. Z then retains the values automatically till the end of the first DN update after t.
, as long as Z of DN is supervised for the second DN update when the transition is received by Z the first time. Z then retains the values automatically till the end of the first DN update after t.
Proof. The proof below is a constructive proof, instead of an existence one. To facilitate understanding, the main ideas are illustrated in Figure 4. Let the X of the DN take the equivalent inputs from S using a symbol-to-vector mapping. Let Z be supervised as the equivalent states in Q, using a binary-p mapping. The number of firing neurons Z depends on the binary-p mapping. The DN lives in the simulated sensori-motor world X × Z determined by the sensory symbol-to-vector mapping: ![]() and the binary-p symbol-to- vector mapping
and the binary-p symbol-to- vector mapping![]() .
.
We prove it using induction on integer t.
Basis: When![]() , set the output
, set the output ![]() for the DN. Y has no neuron. Z neurons have no synaptic weights. All the neuronal ages are zeros. The properties 1, 2, 3 and 4 are trivially true for
for the DN. Y has no neuron. Z neurons have no synaptic weights. All the neuronal ages are zeros. The properties 1, 2, 3 and 4 are trivially true for![]() .
.
Hypothesis: We hypothesize that the above four properties are true up to integer time t. In the following, we prove that the above properties are true for t + 1.
Induction step: During t to t + 1, suppose that the FA makes transition![]() . The DN must do the equivalent, as shown below.
. The DN must do the equivalent, as shown below.
At the next DN update, there are two cases for Y: Case 1: the transition is observed by the DN as the first time; Case 2: the DN has observed the transition.
Case 1: new Y input. First consider Y. As the input ![]() to Y is the first time,
to Y is the first time,![]() . Y initializes a new neuron whose weight vector is initialized as
. Y initializes a new neuron whose weight vector is initialized as ![]() and age
and age![]() . The number of Y neurons c is incremented by 1 as this is a newly observed state transition. From the hypothesis, all previous Y neurons in V are still their originally initialized unit vectors. Thus, the newly initialized
. The number of Y neurons c is incremented by 1 as this is a newly observed state transition. From the hypothesis, all previous Y neurons in V are still their originally initialized unit vectors. Thus, the newly initialized ![]() is the only Y neuron that matches
is the only Y neuron that matches ![]() exactly. With
exactly. With![]() , this new Y neuron is the unique winner and it fires with
, this new Y neuron is the unique winner and it fires with![]() . Its Hebbian learning gives age advance
. Its Hebbian learning gives age advance ![]() and Equation (3) leads to
and Equation (3) leads to
![]() (7)
(7)
As DN updates at least twice in the unit time, Y area is updated again for the second DN update. But X and Z retain their values within each unit time, per simulation rule. Thus, the Y winner is still the same new neuron and its vector still does not change as the above expression is still true. Thus, properties 1 and 2 are true for the first two DN updates within![]() .
.
Next consider Z. Z retains its values in the first DN update, per hypothesis. For the second DN update, the response of Z is regarded the DN’s Z output for this unit time, which uses the above Y response as illustrated in Figure 4. In Case 1, Z must be supervised for this second DN update within the unit time. According to the binary-p mapping from the supervised![]() , Equation (3) is performed for up to p firing Z neurons:
, Equation (3) is performed for up to p firing Z neurons:
![]() (8)
(8)
We can see that Equations (7) and (8) are the same Hebbian learning, but the former is for Y and the latter is for Z. Note that Z has only bottom input ![]() and the normalized vector
and the normalized vector ![]() is binary. That is, only one component (the new one) in
is binary. That is, only one component (the new one) in ![]() is 1 and all other components are zeros. All Z neurons do not link with this new Y neuron before the second DN update. Consider two subcases, subcase (1.a) the Z neuron should fire at the end of this unit time, and subcase (1.b) the Z neuron should not fire.
is 1 and all other components are zeros. All Z neurons do not link with this new Y neuron before the second DN update. Consider two subcases, subcase (1.a) the Z neuron should fire at the end of this unit time, and subcase (1.b) the Z neuron should not fire.
Subcase (1.a): the Z neuron should fire. All Z neurons that should fire, up to p of them, are supervised to fire for the second DN update by the Z area function. Suppose that a supervised-to-fire Z neuron has a synapse vector ![]() with the new
with the new ![]() just initialized to be 0 since the new Y neuron
just initialized to be 0 since the new Y neuron ![]() now fires. From the hypothesis,
now fires. From the hypothesis, ![]() ,
,![]() . But, according to the Z initialization in GDN,
. But, according to the Z initialization in GDN, ![]() for the new dimension initialization. Then from
for the new dimension initialization. Then from![]() , we have
, we have ![]() which is correct for
which is correct for![]() . From Equation (3), the c-th component of v is
. From Equation (3), the c-th component of v is
![]() (9)
(9)
which is the correct count for the new![]() , and the other components of v are
, and the other components of v are
![]() (10)
(10)
for all![]() , which is also the correct count for other components of the v synaptic vector. Every firing Z neuron advances its age by 1 and correctly counts the firing of the new c-th Y neuron. As Y response does not change for more DN updates within
, which is also the correct count for other components of the v synaptic vector. Every firing Z neuron advances its age by 1 and correctly counts the firing of the new c-th Y neuron. As Y response does not change for more DN updates within ![]() and the firing Y neuron meets a positive
and the firing Y neuron meets a positive ![]() weight to the firing Z neuron with age
weight to the firing Z neuron with age![]() , the Z area does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within
, the Z area does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within![]() .
.
Subcase (1.b): the Z neuron should not fire. All Z neurons that should not fire must be supervised to be zero (not firing). All such Z neurons could not be linked with the new Y neuron because the new Y neuron was not present until now. However, in computer programming or hardware circuits, each non-firing Z neuron must add a zero-weight link from this new Y neuron. Otherwise, the Z neuron never “sees” the new Y neuron and can never link from it when the Z neuron fires in the future. All these non-firing neurons keep their counts and ages unchanged. As Y response does not change for more DN updates within![]() , the Z area does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within
, the Z area does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within![]() , since the only firing Y neuron meets a 0 weight to the Z neuron.
, since the only firing Y neuron meets a 0 weight to the Z neuron.
The binary conditioning for Z makes sure that all the Z neurons that have a positive pre-response to fire fully. That is, the properties 3 and 4 are true from the first two DN updates within![]() .
.
Case 2: old Y input. First consider Y. To Y, ![]() has been an input before. From the hypothesis, the winner Y neuron j exactly matches
has been an input before. From the hypothesis, the winner Y neuron j exactly matches![]() , with
, with![]() . Equation (7) still holds using the inductive hypothesis, as the winner Y neuron fires only for a single
. Equation (7) still holds using the inductive hypothesis, as the winner Y neuron fires only for a single ![]() vector. Thus, properties 1 and 2 are true from the firstD N update within
vector. Thus, properties 1 and 2 are true from the firstD N update within![]() .
.
Next consider Z. Z retains its previous vector values in the first DN update, per hypothesis. In the second DN update, the transition is not new, we show that Z does not need to be supervised during the unit time ![]() to fire perfectly. From Equation (1), the Z pre-response is computed by
to fire perfectly. From Equation (1), the Z pre-response is computed by
![]() (11)
(11)
where ![]() is binary with only a single positive component and t is absent as Z does not have a top-down input. Suppose that Y neuron
is binary with only a single positive component and t is absent as Z does not have a top-down input. Suppose that Y neuron ![]() fired in the first DN update. From the hypothesis, every Z neuron has a synaptic vector
fired in the first DN update. From the hypothesis, every Z neuron has a synaptic vector![]() , where
, where ![]() counting up to time t, where
counting up to time t, where ![]() is the observed frequency
is the observed frequency
(occurrences) of Y neuron ![]() firing,
firing, ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the total number of times the Z neuron has fired. Consider two sub-cases: (2.a) the Z neuron should fire according to the transition, and (2.b) the Z neuron should not.
is the total number of times the Z neuron has fired. Consider two sub-cases: (2.a) the Z neuron should fire according to the transition, and (2.b) the Z neuron should not.
For sub-case (2.a) where the Z neuron should fire, we have
![]()
because the Z neuron has been supervised at least the first time for this transition and thus![]() . We conclude that the Z neuron guarantees to fire at 1 after its binary conditioning. From Equation (3), the
. We conclude that the Z neuron guarantees to fire at 1 after its binary conditioning. From Equation (3), the ![]() -th component of v is:
-th component of v is:
![]() (12)
(12)
which is the correct count for the ![]() -th component, and the other components of v are:
-th component, and the other components of v are:
![]() (13)
(13)
for all![]() , which is also the correct count for all other components in v. The Z neuron does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within
, which is also the correct count for all other components in v. The Z neuron does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within ![]() but still keeps firing. This is what we want to prove for property 3 for every firing Z neuron.
but still keeps firing. This is what we want to prove for property 3 for every firing Z neuron.
Next consider sub-case (2.b) where the Z neuron should not fire. Similarly we have![]() , from the hypothesis that this Z neuron fires correctly up to time t and thus we must have
, from the hypothesis that this Z neuron fires correctly up to time t and thus we must have![]() . Thus, they do not fire, change their weights, or advance their ages. The Z neuron does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within
. Thus, they do not fire, change their weights, or advance their ages. The Z neuron does not need to be supervised after the second DN update within ![]() but keeps not firing. This is exactly what we want to prove for property 3 for every non-firing Z neuron.
but keeps not firing. This is exactly what we want to prove for property 3 for every non-firing Z neuron.
Combining the sub-cases (2.a) and (2.b), all the Z neurons act perfectly and the properties 3 and 4 are true for the first two DN updates. We have proved for Case 2, old Y input.
Therefore, the properties 1, 2, 3, 4 are true for first two DN updates. If DN has time to continue to update before time![]() , we see that we have always Case 2 for Y and Z within the unit time and Y and Z re- tain their responses since the input
, we see that we have always Case 2 for Y and Z within the unit time and Y and Z re- tain their responses since the input ![]() retains its vector value. Thus, the properties 1, 2, 3, 4 are true for all DN updates within
retains its vector value. Thus, the properties 1, 2, 3, 4 are true for all DN updates within![]() .
.
According to the principle of induction, we have proved that the properties 1, 2, 3 and 4 are all true for all t. ![]()
6.3. Theorem 1
Using the above lemma, we are ready to prove:
Theorem 1 (Simulate any FA as scaffolding) The general-purpose DP incrementally grows a GDN to simulate any given FA![]() , error-free and on the fly, if the Z area of the DN is supervised when the DN observes each new state transition from the FA. The learning for each state transition completes within two network updates. There is no need for a second supervision for the same state transition to reach error-free future performance. The number of Y neurons in the DN is the number of state transitions in the FA.
, error-free and on the fly, if the Z area of the DN is supervised when the DN observes each new state transition from the FA. The learning for each state transition completes within two network updates. There is no need for a second supervision for the same state transition to reach error-free future performance. The number of Y neurons in the DN is the number of state transitions in the FA.
Proof. Run the given FA and the GDN at discrete time t,![]() . Using the lemma above, each state transition
. Using the lemma above, each state transition ![]() is observed by the DN via the mappings
is observed by the DN via the mappings ![]() and
and![]() . Update the DN at least twice in each unit time. In DN, if
. Update the DN at least twice in each unit time. In DN, if ![]() is a new vector to Y, Y adds a new neuron. Further, from the proof of the above lemma, we can see that as soon as each transition in FA has been taught, the DN has only Case 2 for the same transition in the future, which means that no need for second supervision for any transition. Also from the proof of the lemma, the number of Y neurons corresponds to the number of state transitions in the FA.
is a new vector to Y, Y adds a new neuron. Further, from the proof of the above lemma, we can see that as soon as each transition in FA has been taught, the DN has only Case 2 for the same transition in the future, which means that no need for second supervision for any transition. Also from the proof of the lemma, the number of Y neurons corresponds to the number of state transitions in the FA. ![]()
If the training data set is finite and consistent (the same ![]() must go to the unique next state
must go to the unique next state![]() ), re- substitution test (using the training set) corresponds to simulating an FA using pattern codes. Theorem 1 states that for the GDN any re-substitution test for consistent training data is always immediate and error-free. Conventionally, this will mean that the system over-fits data as its generalization will be poor. However, the GDN does not over-fit data as the following Theorem 2 states, since the nature of its parameters is optimal and the size of the parameter set is dynamic. In other words, it is optimal for disjoint tests.
), re- substitution test (using the training set) corresponds to simulating an FA using pattern codes. Theorem 1 states that for the GDN any re-substitution test for consistent training data is always immediate and error-free. Conventionally, this will mean that the system over-fits data as its generalization will be poor. However, the GDN does not over-fit data as the following Theorem 2 states, since the nature of its parameters is optimal and the size of the parameter set is dynamic. In other words, it is optimal for disjoint tests.
6.4. Grounded DN
Definition 6 (Grounded DN) Suppose that the symbol-to-vector mapping for the DN is consistent with the real sensor of the a real-world agent (robot or animal), namely, each symbol ![]() for FA is mapped to an sub-image x from the real sensor, excluding the parts of the irrelevant background in the scene. Then the DN that has been trained for the FA is called grounded.
for FA is mapped to an sub-image x from the real sensor, excluding the parts of the irrelevant background in the scene. Then the DN that has been trained for the FA is called grounded.
For a grounded DN, the SN is a human knowledge abstraction of the real world. After training, a grounded DN can run in the real physical world, at least in principle. However, as we discussed above, the complexity of symbolic representation for S and Q is exponential in the number of concepts. Therefore, it is intractable for any SN to sufficiently sample the real world since the number of symbols required is too many for a realistic problem. The fact that there are enough symbols to model the real world causes the symbolic system to be brittle. All the probability variants of FA can only adjust the boundaries between any two nearby symbols, but the added probability cannot resolve the fundamental problem of the lack of sufficient number of symbols.
7. Theorem 2: Frozen DN Generalizes Optimally
The next theorem states how the frozen GDN generalizes for infinitely many sensory inputs.
Theorem 2 (DN generalization while frozen) Suppose that after having experienced all the transitions of the FA from time![]() , the GDN turns into a DN that
, the GDN turns into a DN that
1) freezes: It does not generate new Y neurons and does not update its adaptive part.
2) generalizes: It continues to generate responses by taking sensory inputs not restricted to the finite ones for the FA.
Then the DN generates the Maximum Likelihood (ML) action![]() , recursively, for all integer
, recursively, for all integer![]() :
:
![]() (14)
(14)
where the probability density ![]() is the probability density of the new last observation
is the probability density of the new last observation
![]() , with the parameter vector
, with the parameter vector![]() , conditioned on the last executed action
, conditioned on the last executed action![]() , based on its experience gained from learning the FA.
, based on its experience gained from learning the FA.
Proof. Reuse the proof of the lemma. Case 1 does not apply since the DN does not generate new neurons. Only Case 2 applies.
First consider Y. Define ![]() Voronoi regions in
Voronoi regions in ![]() based on now frozen
based on now frozen![]() , where each
, where each ![]() consisting of
consisting of ![]() vectors that are closer to
vectors that are closer to ![]() than to other
than to other![]() :
:
![]()
Given observation![]() , V has two sets of parameters, the X synaptic vectors and the Z synaptic vectors. They are frozen.
, V has two sets of parameters, the X synaptic vectors and the Z synaptic vectors. They are frozen.
According to the dependence of parameters in DN, first consider c events for area Y: ![]() falls into
falls into![]() ,
, ![]() partitioned by the c Y vectors in V. The conditional probability density
partitioned by the c Y vectors in V. The conditional probability density ![]() is zero if
is zero if ![]() falls out of the Voronoi region of
falls out of the Voronoi region of![]() :
:
![]() (15)
(15)
where ![]() is the probability density within
is the probability density within![]() . Note that the distribution of
. Note that the distribution of ![]() within
within ![]() is irrelevant as long as it integrates to 1.
is irrelevant as long as it integrates to 1.
Note that![]() . Given
. Given![]() , the ML estimator for the binary vector
, the ML estimator for the binary vector ![]() needs to maximize
needs to maximize![]() , which is equivalent to finding
, which is equivalent to finding
![]() (16)
(16)
since finding the ML estimator ![]() for Equation (15) is equivalent to finding the Voronoi region to which
for Equation (15) is equivalent to finding the Voronoi region to which ![]() belongs to. This is exactly what the Y area does, supposing
belongs to. This is exactly what the Y area does, supposing ![]() for top-
for top-![]() competition.
competition.
Next, consider Z. The set of all possible binary-1 Y vectors and the set of producible binary-p Z vectors have a one-to-one correspondence: ![]() corresponds to
corresponds to ![]() if and only if the single firing neuron in
if and only if the single firing neuron in ![]() has non-zero connections to all the firing neurons in the binary-p
has non-zero connections to all the firing neurons in the binary-p ![]() but not to the non-firing neurons in
but not to the non-firing neurons in![]() . Namely, given the winner Y neuron
. Namely, given the winner Y neuron![]() , the corresponding
, the corresponding ![]() vector is deterministic. Furthermore, for each Y neuron, there is only unique z because of the definition of FA. Based on the definition of probability density, we have:
vector is deterministic. Furthermore, for each Y neuron, there is only unique z because of the definition of FA. Based on the definition of probability density, we have:
![]()
for every ![]() corresponding to
corresponding to![]() . Thus, when the DN generates
. Thus, when the DN generates ![]() in Equation (16) for ML estimate, its Z area generates ML estimate
in Equation (16) for ML estimate, its Z area generates ML estimate ![]() that maximizes Equation (14).
that maximizes Equation (14). ![]()
8. Theorem 3: DN Thinks Optimally
There seems no more proper terms to describe the nature of the DN operation other than “think”. The thinking process by the current basic version of DN seems similar to, but not exactly the same as, that of the brain. At least, the richness of the mechanisms in DN that has demonstrated experimentally to be close to that of the brain.
Theorem 3 (DN generalization while updating) Suppose that after having experienced all the transitions of the FA from time![]() , the GDN turns into a DN that
, the GDN turns into a DN that
1) fixes its size: It does not generate new Y neurons.
2) adapts: It updates its adaptive part![]() .
.
3) generalizes: It continues to generate responses by taking sensory inputs not restricted to the finite ones for the FA.
Then the DN “thinks” (i.e., learns and generalizes) recursively and optimally: for all integer![]() , the DN recursively generates the Maximum Likelihood (ML) response
, the DN recursively generates the Maximum Likelihood (ML) response![]() : with
: with
![]() (17)
(17)
where ![]() is the probability density, conditioned on
is the probability density, conditioned on![]() ,
,![]() . And the
. And the ![]() has the pre-response vector
has the pre-response vector![]() , where
, where![]() ,
, ![]() , is the conditional probability for the
, is the conditional probability for the ![]() -th Z neuron to fire:
-th Z neuron to fire:
![]() (18)
(18)
The firing of each Z neuron has a freedom to choose a binary conditioning method to map the above the pre-response vector ![]() to the corresponding binary vector
to the corresponding binary vector![]() .
.
Proof. Again, reuse the proof of the lemma with the synaptic vectors of Y to be ![]() now adapting.
now adapting.
First consider Y. Equation (16) is still true as this is what DN does but V is now adapting. The probability density in Equation (15) is the currently estimated version based on past experience but V is now adapting. Then, when ![]() for top-k Y area competition, the Y response vector
for top-k Y area competition, the Y response vector ![]() with j determined by Equation (16) gives Equation (17). In other words, the response vector from
with j determined by Equation (16) gives Equation (17). In other words, the response vector from ![]() area is again the Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimate from the incrementally estimated probability density. The major difference between Equation (16) and Equation (17) is that in the latter, the adaptive part of the DN updates.
area is again the Maximum Likelihood (ML) estimate from the incrementally estimated probability density. The major difference between Equation (16) and Equation (17) is that in the latter, the adaptive part of the DN updates.
Next, consider Z. From the proof of the Lemma 1, the synaptic weight between the j-th Y neuron and the n-th Z neuron is
![]() (19)
(19)
The total pre-response for the n-th neuron is
![]()
since the j-th neuron is the only firing Y neuron at this time. The above two expressions give Equation (18). ![]()
The last sentence in the theorem gives the freedom for Z to choose a binary conditioning method but a binary conditioning method is required in order to determine which Z neurons fire and all other Z neurons do not. In the brain, neural modulation (e.g., expected punishment, reward, or novelty) discourages or encourages the recalled components of z to fire.
The adaptive mode after learning the FA is autonomous inside the DN. A major novelty of this theory of thinking is that the structure inside the DN is fully emergent, regulated by the DP (i.e., nature) and indirectly shaped (i.e., nurture) by the external environment.
The neuronal resource of Y gradually re-distribute according to the new observations in![]() . It adds new context-sensory experience and gradually weights down prior experience. Over the entire life span, more often observed experience and less often observed experience are proportionally represented as the synaptic weights.
. It adds new context-sensory experience and gradually weights down prior experience. Over the entire life span, more often observed experience and less often observed experience are proportionally represented as the synaptic weights.
However, an adaptive DN does not simply repeat the function of the FA it has learned. Its new thinking experience includes those that are not applicable to the FA. The following cases are all allowed in principle:
1) Thinking with a “closed eye”: A closed eye sets ![]() where u has 0.5 for all its components (all gray image). The DN runs where Y responses mainly to z as x has little “preference” in matching.
where u has 0.5 for all its components (all gray image). The DN runs where Y responses mainly to z as x has little “preference” in matching.
2) Thinking with an “open eye”: In the sensory input x is different from any prior input.
3) Inconsistent experience: from the same![]() , the next
, the next ![]() may be different at different times. FA does not allow any such inconsistency. However, the inconsistencies allow occasional mistakes, update of knowledge structures, and possible discovery of new knowledge.
may be different at different times. FA does not allow any such inconsistency. However, the inconsistencies allow occasional mistakes, update of knowledge structures, and possible discovery of new knowledge.
The neuronal resources of Y gradually re-distribute according to the new context-motor experience in![]() . The learning rate
. The learning rate ![]() amounts to equally weighted average for past experience by each neuron. Weng & Luciw 2009 [30] investigated amnesic average to give more weight to recent experience.
amounts to equally weighted average for past experience by each neuron. Weng & Luciw 2009 [30] investigated amnesic average to give more weight to recent experience.
In the developmental process of a DN, there is no need for a rigid switch between FA and the real-world learning. The mitosis-equivalent of Y neurons is gradually realized by gradual mitosis and cell death, neuronal migration and connection, neuronal spine growth and death, and other neuronal adaptation. DN can also switch between neuronal initialization and adaptation smoothly. The rigid switches between neuronal initialization and neuronal adaptation and between FA learning and the real-world learning above are meant to facilitate our understanding and analysis only.
The binary conditioning is suited only when Z is supervised according to the FA to be simulated. As the “thinking” of the DN is not necessarily correct, it is not desirable to use the binary conditioning for Z neurons. For example, a dynamic threshold can be used for ![]() to pass in order for the
to pass in order for the ![]() -th neuron to fire at value 1. This threshold can be related to the punishment and reward from the environment. In general, the threshold is related to the neural modulatory system.
-th neuron to fire at value 1. This threshold can be related to the punishment and reward from the environment. In general, the threshold is related to the neural modulatory system.
The thinking process by the current basic version of DN seems similar to, but not exactly the same as, that of the brain. At least, the richness of the mechanisms in an experimental DN is not yet close to that of an adult brain. For example, the DN here does not use neuromodulators so it does not prefer any signals from receptors (e.g., sweet vs bitter).
9. Experimental Results
Due to the focused theoretical subject here and the space limitation, detailed experimental results of DN are not included here. The DN has had several versions of experimental embodiments, called Where-What Networks (WWNs), from WWN-1 [32] to WWN-7 [33] . Each WWN has multiple areas in the Z areas, representing the location concept (Location Motor, LM), type concept (Type Motor, TM), or scale concept (Scale Motor, SM), and so on.
A learned WWN can simultaneously detect and recognize learned 3-D objects from new unobserved cluttered natural scenes [5] [34] .
The function of this space-time machine DN differs depending on the context information in its Z area [7] . If there is no Z signal at all, the WWN is in an (emergent) free-viewing mode and it detects any learned object from the cluttered scene and tells its location from LM, type from TM, and scale from SM. If the LM area fires representing a location (intent or context), the WWN recognizes the object near that intended location from the cluttered scene and tells its type from TM and scale from SM. If the TM area fires representing an object type (intent or context) the WWN finds (i.e., detects) an intended object type from the cluttered scene and tells its location from LM and scale from SM.
A WWN can also perform autonomous attention. If the DN suppresses the firing neuron that represents an object type in TM, the WWN switches attention from one object type to another object type that barely lost in the previous Y competition―feature-based autonomous attention. If the DN suppresses the firing neuron in LM, the WWN switches attention from one object location to another object location that barely lost in the previous Y competition―location-based autonomous attention.
The WWN has also performed language acquisition for a subset of natural language and also generalized and predicted [35] . For example, predict from one person Joe to his hierarchical properties such as male and human, and predict from Penguin to its hierarchical properties such as non-flying and bird.
The WWNs have versions that are motivated, such as pain avoidance and pleasure seeking, so that its learning does not need to be supervised [9] . The learned tasks include object recognition under reinforcement learning and autonomous foraging (wandering around) in the presence of a friend and an enemy.
However, the experimental results from such DN experiments are difficult to understand and to train without a clear theoretical framework here that links DNs with the well-known automata theory and the mathematical properties presented as the three theorems that have been proved here.
10. Conclusions and Discussion
Proposed first in Weng 2011 [14] , the DN framework seems to be, as far as I know, the first brain-scale computational and developmental theory for the brain and mind. By developing, we mean that the model regards brain areas should automatically emerge from activities, instead of fully specified rigidly by the genome. This view is supported by a great deal of cross-modal plasticity found in mammalian brains, from eye deprivation by Torsten N. Wiesel and David H. Hubel [36] , to the auditory cortex that processes visual information by Mriganka Sur et al. [37] , to the reassignment of modality―visual cortex is reassigned to audition and touch in the born blind as reviewed by Patrice Voss [38] .
Therefore, it appears that a valid brain model at least should not assume a static existence of―genome rigidly specified―Brodmann areas. This static existence has been prevailing in almost all existing biologically inspired models for sensorimotor systems. Instead, a brain model should explain the emergence and known plasticity of brain areas. DP enables areas to emerge in DN and adapt. The genome provides the power of cells to move and connect. The genome also plays a major role in early and coarse connections of a brain. However, fine connections in the brain seem to be primarily determined by the statistics of activities from the conception of the life all the way up to the current life time.
In conclusion, this paper provides an overarching theory of the brain and mind, although the complexity of the mind is left to the richness of the environment and the activities of DN―task nonspecific [28] . The paper also provides the proofs of the three basic theorems in an archival form. At this early time of the computational brain theory, we predict that the landscape of AI and understanding of natural intelligence would both fundamentally change in the future.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Hao Ye at Fudan University who carefully proof-read the proofs presented here and raised two gaps that I have filled since then. The author would also like to thank Z. Ji, M. Luciw, K. Miyan and other members of the Embodied Intelligence Laboratory at Michigan State University; Q. Zhang, Yuekai Wang, Xiaofeng Wu and other members of the Embodied Intelligence Laboratory at Fudan University whose work has provided experimental supports for the theory presented here.