The Big Bang Started by the Creation of the Reverse Higgs Field ()
1. Introduction
In the conventional theory of the inflation and the Big Bang [1] , at the end of the inflation period, potential energy decayed into kinetic energy starting the Big Bang. This paper posits that at the end of inflation period [2] [3] , potential energy as rest mass was converted into kinetic energy by the creation of the reverse Higgs field as the massless particle (kinetic energy)-generating field derived from the absorption of the interuniversal void outside of the universe in the reversible multiverse. During the Big Bang, the creation of the reverse Higgs field was followed by the partial conversion of massless particles by the partial absorption of the Higgs bosons from the Higgs field generating massive particles. Photon remained massless in the partial conversion.
The Big Bang started by the creation of the reverse Higgs field provides the explanation for the origin of the digital space structure described in the previous papers [4] [5] . In the digital space structure, space is digitalized by 1 and 0 for attachment space and detachment space, respectively. Attachment space attaches to mass-energy continuously to account for rest mass, massive particles and reversible movement, while detachment space detaches adjacent mass-energy continuously to account for kinetic energy and massless particles. The digital space structure explains quantum mechanics, special relativity, gauge force fields, and dark matter [4] [5] . In this paper, the Higgs field is attachment space, while the reverse Higgs field is detachment space.
Section 2 explains the reversible multiverse, the Big Bang, the inflation, dark energy, and the cyclic universe. Section 3 explains the digital space structure.
2. The Reversible Multiverse, the Big Bang, the Inflation, Dark Energy, and the Cyclic Universe
The paper posits that the multiverse is reversible, forbidding any permanently irreversible phenomenon. A reversible cyclic universe containing temporarily irreversible phenomena is allowed. The collision of expanding universes is permanently irreversible due to the impossibility to reverse the collision of expanding universes, so the collision of expanding universes is forbidden. To prevent the collision of expanding universes, every universe is surrounded by the interuniversal void that is functioned as the permanent gap among universes. The interuniversal void has zero energy, zero space-time, and zero vacuum energy, while universe has non-zero energy, the inexhaustible resource of space-time, and zero or/and non-zero vacuum energy. To maintain the permanent gap among universes, the interuniversal void detaches the incoming mass-energy in the interuniversal void, so mass-energy stays permanently within universes only. Surrounded by the interuniversal void as the permanent gap among universes, an expanding universe with the inexhaustible resource of space-time expands without colliding with other universes. The detachment of the incoming mass-energy in the interuniversal void prevents the collision of expanding universes. As a result, the the properties of the interuniversal void include the detachment of mass-energy in addition to zero energy, zero space-time, and zero vacuum energy. On the other hand, the properties of universe include the attachment of mass-energy. The detachment and the attachment of mass- energy are equivalent to the repulsion and the attraction of mass-energy, respectively. In other words, the interuniversal void repulses (detaches) mass-energy, while universe attracts (attaches) mass-energy.
A zero-sum energy dual universe of positive energy universe and negative energy universe can be created in the zero-energy interuniversal void, and the new dual universe is again surrounded by the interuniversal void to avoid the collision of universes. Under symmetry, the new positive energy universe and the new negative energy universe undergo mutual annihilation to reverse to the interuniversal void immediately. Under reversible symmetry breaking, our dual universe has lasted a long time without reversing to the interuniversal void as described later.
The universe before the Big Bang was the cold universe without kinetic energy [1] -[3] . In terms of the Higgs mechanism, the cold universe fully interacted with the Higgs field generating massive particles. The Higgs field provided the longitudinal component to generate massive particles. This paper posits that the Big Bang was started by the creation of the reverse Higgs field as the massless particle-generating field derived from the absorption of the interuniversal void. The Big Bang involved a two-step process. The first step of the Big Bang was the exchange process between the absorption of the interuniversal void outside of the universe and the desorption of the Higgs field inside of the universe. The absorbed interuniversal void was transformed into “the intrauniversal void” with space-time inside of the universe. Derived from the interuniversal void, the intrauniversal void had the same property of the detachment of mass-energy as the interuniversal void. Inside of the universe, the intrauniversal void with the property of the detachment of mass-energy detached adjacent mass- energy in the universe, resulting in the conversion of rest mass (massive particles) into kinetic energy (massless particles), so the intrauniversal void was the reverse Higgs field generating massless particles starting the Big Bang in the universe with the inexhaustible resource of space-time to expand. To complete the exchange process, the Higgs field inside was desorbed to become the external Higgs field outside of the universe. In terms of the Higgs mechanism, the reverse Higgs field derived from the interuniversal void desorbed the longitudinal component (the Higgs field) inside of the universe to become the external Higgs field outside of the universe, and generated massless particles. The equation for the first step of the Big Bang is as Equation (1)
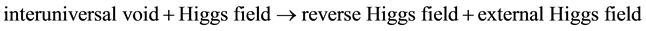 (1)
(1)
The diagram for the first step of the Big Bang is Figure 1.
The second step of the Big Bang was the exchange process between the partial absorption of the Higgs bosons (the mediating particles) from the external Higgs field and the partial desorption of the reverse Higgs field inside to become the interuniversal void outside of the universe. Under symmetry breaking, the second step was the partial reversal of the first step. In terms of the Higgs mechanism, the absorbed Higgs bosons provided the longitudinal components for massless particles to form massive particles, and desorbed the reverse Higgs field inside to become the interuniversal void outside to complete the exchange process. Photon without absorbing the Higgs boson remained massless in the partial conversion, and the unabsorbed Higgs boson became the observed Higgs boson [6] . The equation for the second step of the Big Bang is as Equation (2).
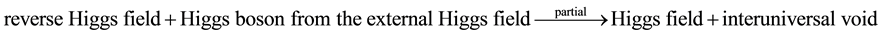 (2)
(2)
The diagram for the second step of the Big Bang is as in Figure 2.
In summary, the two-step process during the Big Bang included (1) the conversion of rest mass (massive particles) into kinetic energy (massless particles) by the creation of the reverse Higgs field derived from the absorption of the interuniversal void outside of the universe and (2) the partial conversion of massless particles into partial massive particles by the partial absorption of the Higgs bosons from the external Higgs field outside of the universe.
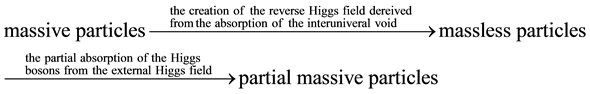 (3)
(3)
In the previous papers [2] [3] based on string theory with oscillating space-time dimension number between 11D (space-time dimension) and 4D, the vacuum energy of the universe is decreased with its oscillating space- time dimension number. The vacuum energy for 4D is zero, while 11D has the highest vacuum energy. The interuniversal void has zero vacuum energy, so during the Big Bang, the reverse Higgs field derived from the interuniversal void also had to have zero vacuum energy corresponding zero vacuum energy of 4D. Consequently, the absorption of the interuniversal void led to the transformation of the high space-time dimension universe with high vacuum energy into the 4D universe with zero vacuum energy as described in the cyclic universe [2]
![]()
Figure 1. The first step in the Big Bang.
![]()
Figure 2. The second step in the Big Bang.
[3] . In the cyclic universe, absorbing the interuniversal void, the 10D positive energy string universe was transformed into the 4D positive energy particle universe with the Kaluza-Klein structure which allowed space-time dimension number to change freely as described in Figure 3.
The strings have to be 10D, and cannot be transformed into 4D, so strings had to be transformed into particles that allowed the change of the number of space-time dimensions freely to accommodate the transformation from the 10D universe to the 4D universe driven by the absorption of the interuniversal void.
Under reversible symmetry breaking, the positive energy universe absorbed the interuniversal void, while the negative energy universe did not absorb the interuniversal void. The positive energy universe started the abnormal expansion as the inflation-Big Bang, and at the same time, without the absorption of the interuniversal void, the coexisting negative energy universe started the normal gradual expansion from 10D to 4D dimension by dimension. The negative energy universe oscillates between 10D and 4D dimension by dimension. When the negative energy universe reaches 4D, without the absorption of the interuniversal void, the 4D negative universe without kinetic energy appears as dark energy to accelerate the universal expansion as described in Figure 3. According to the calculation in the cyclic universe [3] , dark energy started in 4.28 billion years ago in agreement with the observed 4.71 ± 0.98 billion years ago [7] . After the appearance as the dark energy, the negative energy universe will move back to D > 4 dimension by dimension, and disappear from the positive energy universe starting the contraction until the Big Crush followed by the deflation. Then, the universe will repeat the cycle starting the inflation-Big Bang or go back to the interuniversal void.
The multiverse can be considered as the digital multiverse consisting of +1 for positive energy universe, −1 for negative energy universe, and 0 for the interuniversal void. The sum of energy in the digital multiverse is 0, so the multiverse is the reversible digital zero-sum multiverse. In the reversible digital zero-sum multiverse, all phenomena have to be able to reverse back to the zero-energy interuniversal void. Through the asymmetrical absorption of the interuniversal void, the asymmetry between the 4D positive energy universe and the variable D negative energy universe allows the non-zero-energy universe and the irreversible phenomena to exist for a long period of time. The reversible digital zero-sum multiverse requires the asymmetrical non-zero-energy universe to be able to reverse back to the interuniversal void as in the Figure 3 of the cyclic universe.
3. The Digital Space Structure
The digital space structure described in the previous papers [4] [5] consists of 1 and 0 for attachment space and detachment space, respectively. In this paper, attachment space is the Higgs field, and detachment space is the reverse Higgs field. Attachment space and detachment space for mass-energy are equivalent to attraction space and repulsion space for mass-energy, respectively. During the Big Bang, the combination of the positive energy universe as 1 and the interuniversal void as 0 in the digital multiverse led to the digital space structure consisting of attachment space (the Higgs field) as 1 and detachment space (the reverse Higgs field) as 0 in the positive energy universe as in Equation (4).
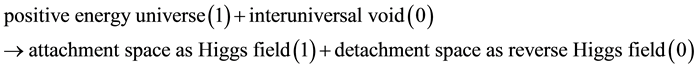 (4)
(4)
Derived from the space of the universe before the Big Bang, attachment space is the Higgs field, and attaches to mass-energy continuously and reversibly. Derived from the interuniversal void outside of the universe, detachment space is the reverse Higgs field, and detaches adjacent mass-energy continuously. Attachment space relates to massive particles, rest mass and reversible movement, while detachment space relates to massless particles and irreversible kinetic energy adjacent to detachment space continuously.
The combination of n units of attachment space as 1 and n units of detachment space as 0 brings about three different space structures: binary partition space, miscible space, or binary lattice space as below.
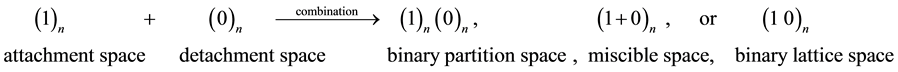 (5)
(5)
Binary partition space, 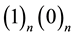 , consists of two separated continuous phases of multiple quantized units of attachment space and detachment space. In miscible space,
, consists of two separated continuous phases of multiple quantized units of attachment space and detachment space. In miscible space,  , attachment space is miscible to detachment space, and there is no separation of attachment space and detachment space. Binary lattice space,
, attachment space is miscible to detachment space, and there is no separation of attachment space and detachment space. Binary lattice space, 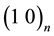 , consists of repetitive units of alternative attachment space and detachment space. As described before [4] [5] , binary partition space, miscible space, and binary lattice space explain the wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics, special relativity with miscible rest mass and kinetic energy, and gauge force fields and dark matter, respectively. The space structure based on the combination of binary partition space and binary lattice space explains superconductivity [5] and superstar without singularity to replace black hole with singularity [8] [9] . Singularity is permanently irreversible by losing information permanently, forbidden in the reversible multiverse.
, consists of repetitive units of alternative attachment space and detachment space. As described before [4] [5] , binary partition space, miscible space, and binary lattice space explain the wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics, special relativity with miscible rest mass and kinetic energy, and gauge force fields and dark matter, respectively. The space structure based on the combination of binary partition space and binary lattice space explains superconductivity [5] and superstar without singularity to replace black hole with singularity [8] [9] . Singularity is permanently irreversible by losing information permanently, forbidden in the reversible multiverse.
In the cyclic universe as shown in Figure 3, the force field in each of the four different universes, the positive energy 11D membrane universe, 10D string universe, 10D particle universe, and 4D particle universe, provided the prototype of each of the four different observed force fields, the strong force, gravity, the electromagnetic force, and the weak force, respectively, in the observed universe [2] [3] . The force field among the membranes in the 11D membrane universes provided the prototype of the strong force without charge among particles in our observed universe. The observed strong force was created during the Big Bang as a force field in binary lattice space around particles in the observed universe. The gravity in the bulk space of the 10D string universes provided the prototype of observed gravity as warping space in the observed universe. The observed gravity as warping space around particles was created in the observed universe during the Big Bang.
The absorption of the interuniversal void by the positive energy 10D string universe forced the 10D universes to be transformed from the 10D universes into the 4D universes, so strings had to be transformed into particles that allowed the change of its dimension number freely to accommodate the transformation from the 10D universe to the 4D universe driven by the absorption of the interuniversal void. The transformation of strings into particles came from the emergence of positive charge and negative charge that allowed the mutual annihilation of positively charged 10D strings and negatively charged 10D antistrings in the 10D string universes to produce positively charged 10D particles and negatively charged 10D antiparticles in the 10D particle universes. The force field involved in positive charge and negative charge provided the prototype of the observed electromagnetic force with charge. The observed electromagnetic force in binary lattice space around particles was created during the Big Bang.
The force field to represent the asymmetry between the positive energy 4D particle universe and the negative energy variable D particle universe provided the prototype of the observed asymmetrical weak force in the observed universe. The observed weak force in binary lattice space around particles was created during the Big Bang. As the result of the causality relationship between the 10D particle universe and the 4D particle universe, the electromagnetic force and the weak force were unified symmetrically as the electroweak force during the Big Bang. The symmetry breaking in the electroweak force occurred during the second step in the Big Bang.
4. Summary
This paper posits that the Big Bang was started by the creation of the reverse Higgs field as the massless particle-generating field derived from the absorption of the interuniversal void outside of the universe in the reversible multiverse. The interuniversal void surrounding every universe is to prevent the collision of expanding universes which have the inexhaustible resources of space-time to expand. The collision of expanding universes is permanently irreversible, forbidden in the reversible multiverse. To prevent the collision, the interuniversal void detaches the incoming mass-energy in the interuniversal void to keep expanding universes apart without collision. Inside of the universe, the absorbed interuniversal void with the property of the detachment of mass- energy was transformed into the reverse Higgs field that detached adjacent mass-energy in the universe, resulting in the conversion of rest mass (massive particles) into kinetic energy (massless particles) starting the Big Bang. During the Big Bang, the creation of the reverse Higgs field was followed by the conversion of massless particles except photons into massive particles through the absorption of the Higgs bosons. The absorption of the interuniversal void with zero vacuum energy also started the inflation by converting the high vacuum energy universe into the zero vacuum energy universe. The inflation followed by the Big Bang is a part of the reversible cyclic universe which explains the four force fields (the strong force, gravity, the electromagnetic force, and the weak force) and dark energy. During the Big Bang, the Higgs field and the reverse Higgs field produced the digital space structure consisting of attachment space (the Higgs field) denoted as 1 and detachment space (the reverse Higgs field) denoted as 0.