The correctional modification of inflammatory response at the experimental acute pancreatitis ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Acute pancreatitis is one of the most widespread diseases among time-urgent patients of the surgical profile. Nonetheless, the number of patients with acute pancreatitis doesn’t subside at present time, but is tending to increase [1-3]. The disease spectrum of acute pancreatitis ranges from mild and self-limiting disease (80%) to a rapidly progressive fulminant illness with morbidity rates up to 33% - 54% [1,4,5]. Total lethality rate constitutes 4% - 15% of AP cases [1,3,5-8]. Such high mortality, occasioned by acute pancreatitis, despite modern medical treatment necessitates a search of novel ways of fighting this disease.
It is known that the development of systemic inflamematory reaction underlies the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis irreverently of etiological factors. Thus, according to the Atlanta Symposium held in 1992, acute pancreatitis is defined as an acute inflammatory process of the pancreas that frequently involves peripancreatic tissues and/or remote organ systems [6,9,10]. However, the effectiveness of the existing anti-inflammatory preparations (antiphlogistics) may not secure essential, principal influence upon the severity of acute pancreatitis development.
Since the high anti-inflammatory efficiency of L-17 compound (from the group of substituted SR1, R62, 3, 4-thiadiazine-2-amins) had been asserted in our previous studies of a experimental cardiac infarction, which allowed to substantially circumscribe the area of inflammation reaction and to accelerate the reparation pro- cesses, here given outcomes enable to conclude that this compound may as well be applied for inflammatory process activity reduction in acute pancreatitis [11].
Thus, the objective of this experimental trial was to study the possibility of correction of inflammatory reaction in experimental acute pancreatitis with the L-17.
2. METHODS
2.1. L-17 Compound
L-17 compound of the group of substituted 5R1, 6H2-1, 3, 4-thiadiazine-2-amines was used to treat experimenttal pancreatitis in rats (Figure 1). This compound was synthesized in the Institute of Organic Synthesis, Ural Division of RAS, as part of a series of several active substances that affect metabolism and inflammation [12,13]. The compound is a registered invention (United States Patent No 6313111 of 6 November 2001, PCT RF Patent No 2259371 of 27 August 2005) [12,13]. The choice of this compound was due to the fact that compound L-17 is known to induce the replacement of exudative destructtion inflammation with cellular productive inflammation [11].
2.2. Animal Preparation and Anesthesia
The experiment was carried out on healthy sexually mature, nonlinear albino female rats. The animals used in the tests were quarantined in the vivarium of the Institute of Immunology and Physiology of the Ural Division of RAS (Ekaterinburg, Russia). The animals showed no symptoms of any disease. All animals were kept in equal conditions, and were fed according to customary schedule.
All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Institute of Animal Care and Use Committee at the Institute of Immunology and Physiology of the Ural Division of RAS and performed in accordance with the principles, formulated in the European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals used for Experimental and Other Scientific Purposes (Strasbourg, France, 18.03.1986), APS’s Guiding Principles in the Care and Use of Vertebrate Animals in Research and Training and in accordance with the Laboratory Practice Regulations of RF (Ministry of Public Health Order no. 267 from 19.06.2003) [14-16].
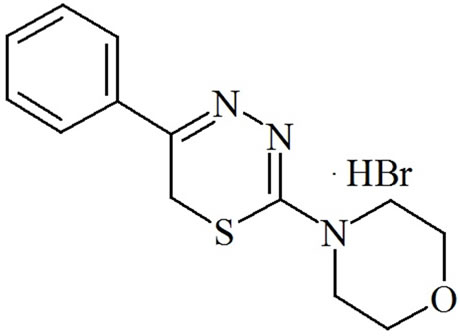
Figure 1. L-17 compound of the group of substituted 5R1, 6H2- 1,3,4-thiadiazine-2-amines.
All animals undergoing surgery received a similar level of care and attention. Surgery was performed using aseptic technique. Instruments were sterile.
For individual experiments, the procedure was as follows. After an overnight fast, the rats were anesthetized with ether and the peritoneal cavity was opened by a 2.5- to 3.5-cm midline incision. At the endpoints, all rats were anesthetized with ether and decapitated. Diazepam (2.5 mg/kg) was used to lessen the dose of a general anesthetic and to produce a smoother induction and recovery [15,16].
2.3. Experimental Protocol
The trial was carried out on 45 outbred female rats with the average body weight 180 - 240 g each. The animals were 8 - 16 weeks old. For getting statistically reliable results, the groups of 15 animals were formed. The animals of the same age, received from the rat farm at the same time formed the trial and the control sets.
The main group (A), consisting of 15 animals with the average body weight 223 g each, got intraperitoneally the injection of L-17 compound, dozed 40 mg/kg in an hour after surgery. Later on, a 40 mg/kg doze of L-17 compound was repeatedly injected as often as once every 24 hours. The group B consisted of 15 animals with the average bodyweight 220 g, which also had the experimenttal pancreatitis induced, but no preparation was administered. The group C (intact) consisted of 15 animals. The animals were being taken out of the experiment after 24 hours, 120 and 168 hours.
2.4. Experimental Model of Pancreatitis
Modelling of pancreatitis in rats was performed in accordance with the author’s modification of ligation model of acute pancreatitis (RF Patent No 2259371 of 27/08/ 2008). After surgery, every rat was kept up in a separate, labeled cage.
The rundown of the methods. With ether anaesthetizetion administered, the midline 2 - 3 cm long laparotomy along the Sergent’s white [Hunter’s] line was executed, which practically averted any blood loss. The duodenum, mesentery and part of a stomach were delivered through the wound with subsequent transillumination of duodenum’s mesentery elements, enabling visualization of all its details, including the elements to be affected—pancreas ducts and marginal vessel of duodenum. With the use of an atraumatic needle the synthetic ligature (O in diameter), catching gland’s duct and marginal vessel of duodenum was performed. Consequently, the ligature ends were brought out to the abdominal cavity side wall, and ligature was being tightened, visually controlled to avoid capturing of intestines loops. Laparotomy incision was closed. The ligature exposure time approximated 50 - 60 minutes, whereupon it was taken off and removed from abdominal cavity altogether.
There has been no intraoperative lethality observed. Physiological parameters were in the normal range (temperature: 36.5˚C - 37˚C, heart rate: 250 - 370 beat/min, breathing: 60 - 90 breath/min) throughout the duration of the experiment. 40 minutes after the experiment, the animals completely resumed their preoperational condition in respect of behavioral pattern.
During initial 24 postoperational hours, the animals received only water, whereupon they were switched over to a routine regimen. Evaluating the animals’ behavior in 24 hours lapse—no changes or peculiarities in their behavioral pattern has been detected: the animals were active, displayed undelayed response to light and sound stimuli. No respiratory depression symptoms have been detected as well.
2.5. Methods
The pancreas was morphologically studied after fixation. In addition to visual assessment there was a light-optical examination. Paraffin blocks were made according to the common histological method. Series of 5 - 6 micron thick sections were stained with H&E after van Gieson and Weigert [17,18].
Serum activity of plasma creatinine, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate transaminase and amylase (before and in the process of experimental pancreatitis development were investigated at the same time intervals.
The blood (3 ml) for biochemical blood examination was drawn with subsequent centrifugation and blood serum separation. The analysis was implemented with the help of the “Immunochemistry Systems” “Beckman Coulter” (USA) biochemical analyzer.
2.6. Tolerability to L-17 Compound
Tolerability to L-17 compound in animals was estimated as being quite satisfactory: there were no detected cases of pain reactions or necrobiotic changes at injection sites, no postoperative wound infections and no pleural empyemas, except for slowing down of animals’ reactions to sound and light stimulation that was noted in 20 - 30 min after injections and lasted 40 - 45 min before the animals’ behavior was not different again from that of intact rats. Symptoms of respiratory insufficiency or food and drink intake disorders were also not seen.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
In statistical investigation, the Student’s test (t) was applied, when comparing the groups under the test the SPSS computer program was used for the data mathematical processing. All the data were expressed as mean ± SD. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. RESULTS
When analyzing laboratory counts, received in result of the experiment by the first 24 hours, the following alterations in the general blood count have been identified.
The experiment showed significant differences in complete blood counts (CBC) between the tested sets of animals. Thus, during the first 24 hours of the experiment, the animal group with experimental acute pancreatitis, which has not received treatment (group B), exhibited pronounced leukopenia (2.2 ± 0.62 × 103/µL) and lymphopenia (0.43 ± 0.12 × 103/µL) and thrombopenia (689.20 ± 29.28 × 103/µL) at the background of increased amount of neutrophils (1.72 ± 0.48 × 103/µL) and monocytes (0.08 ± 0.04 × 103/µL) as compared to group C and physiological standard for rats of this age and gender [7,17]. At the same time, during the first 24 hours the increase of leukocytes amount (4.64 ± 1.09 × 103/µL), and neutrophils (3.48 ± 0.92 × 103/µL) and monocytes (0.16 ± 0.13) was detected at the background of decrease of lymphocytes quantity (0.99 ± 0.38 × 103/µL) as compared to physiological requirement for rats of this age and gender [7,19]. In addition to that, a certainly less pronounced decrease of monocytes and thrombocytes amount as compared to hematological indicators of untreated animals with experimental acute pancreatitis was detected in this group.
As it is evident from the given table (Table 1), the most comprehensive indicator, reflecting the degree of intensity of organism’s response to initial pancreas liaison was the pancreatic amylase. During the first 24 hours of the experiment, a pronounced fermentemia was observed in the untreated animals with experimental pancreatitis (group B). At the same time, the animals in the group with experimental pancreatitis at the background of L-17 compound introduction (group A) displayed a pronounced decrease in the activity of the ferments under observation. Thereby, the pancreatic amylase and creatinine level proved to be the most informative indicators of the degree of intensity of organism’s response to initial pancreas liaison.
Thus, the amylase level in blood of the animals of group A manifested a twofold decrease (6164 ± 208 U/mL) as compared to that of the animals of group B (13,935 ± 4613 U/mL). The creatinine level in blood of the animals of group A (30.50 ± 6.93 mg/dL) drastically differed from that of the animals of group B (49.20 ± 7.84 mg/dL).
3.1. Macroscopic Picture and Histomorphological Study
Macroscopically, 1 day after the impact on the pancreas

Table 1. Blood biochemical indicators of the first 24 hours of the experiment.
and on the duodenum marginal vessel, the animals of the experimental set (groups A and B) displayed occurrence of pancreas necrosis foci accompanied by hemorrhagic impregnation and symptomatic perifocal edema. By the 5th day the multiple nidi of steatonecrosis, serous-hemorrhagic bloody effusion, peritonitis symptoms and moderately marked enteroparesis were detected on parietal and visceral peritoneums of the abdominal cavity. By the 7th day the animals of the experimental set showed either a developing purulent common peritonitis or a peritoneal cavity abscesses forming. Therewith, the principal differences in the macroscopic picture manifested themselves by the 7th day of the experiment. Whereas, by the 7th day, the animals from the group B (experimental pancreatitis) manifested all signs of the development of acute pancreatitis’ complications; the animals treated with the L-17 compound (group A) displayed a picture of terminated inflammation process: no sweating in the abdominal cavity, no steatonecrosis and fibrinogenous overlays have been observed; the gland’s tissue betrayed signs of small size edema and infiltration.
The results of histomorphological study have matched the macroscopic picture. During the initial 24 hours, the untreated animals from the group B exhibited the necrosis nidus, represented by destroyed acinar structures of exocrine part of the gland; the diffusive infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and a pronounced trabecular vessels plethora were also identified (Figure 2).
The animals from the group A treated with L-17 compound showed the necrosis nidus with a destroyed acinar structure of exocrine part of the pancreas and partially of the islet apparatus. A marked exudative reaction, in the form of diffusive infiltration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and a pronounced trabecular vessels plethora were identified (Figure 3).
By the 5th day, the untreated animals from the group B showed the necrosis nidus in the shape of destroyed structures of several lobules of organ’s parenchyma; destruction of vessels’ walls of connecting tissue trabeculae was identified. In adjacent mesentery and peritoneum a diffusive neutrophilic infiltration of leukocytes with abscesses formation and signs of developing peritonitis were observed. By the 5th day, in the animals from the

Figure 2. Experimental pancreatonecrosis, 1 day. The signs of marked exudative inflammation with eosinophilic infiltration of organ’s stroma (A), destruction of pancreocytes and pancreatic islets (B) and dystrophic changes of acinar structures of exocrine part of the pancreas (C). Hematoxylin-eosin staining. Magnification 400.

Figure 3. Experimental pancreatitis, 1 day, at the background of L-17 compound administration. Abnormalities in the microcirculatory channel in the shape of sludge complexes in the vessel lumen (A), signs of interstitial edema (B) and nidal dystrophy of acinar structures of exocrine part of pancreas (C), cells of lymphoid line and macrophages (D) are prevalent in the infiltrate. Hematoxylin-eosin staining. Magnification 200.
group A the necrosis nidus got surrounded by demarcation bank, necrotic masses got blood soaked; formation of granulation tissue with proliferation of fibroblastic line of cells and signs of migration of immuno competent cells (lymphocytes, plasmatic cells and mastocytes) were observed. Hemosiderosis niduses were identified in trabecular structures.
By the 7th day of the experiment the group B of animals showed the signs of arrangement in the form of granulation tissue development, infiltrated predominantly by cells of mononuclear system. At the background of L-17 compound introduction, the necrosis area got substituted by areolar tissue, which contained functionally active fibroblasts and liberal quantity of immature connective tissue collagenous fibers.
3.2. Lethality
The most vivid indicator of L-17 compound efficiency was the level of lethality. By the 7th day the lethality in the group B amounted to 60%, whereas in the group A it comprised only 30%. The main cause of lethality was the development of polyorganic insufficiency at the background of pancreatitis and propagated peritonitis.
4. DISCUSSION
The author’s model of experimental pancreatitis has been applied in the study. It enabled receiving a prompt (already during the first 24 hours) picture of abnormalities, similar to the ones, observed in process of pancreatitis development in humans [10].
Thus, as early as initial 24 hours, the alterations of Arneth’s formula, typical for acute inflammatory process (signs of neutrophilesis at the background of a marked leucopenia) were found out, as well as over fivefold decrease of lymphocytes amount established. Along with that, the pronounced leucopenia argued the severity of the process, whereas the significant decrease of lymphocytes in blood during the first 24 hours was accounted for by the development of stress-induced reaction in process of acute pancreatitis formation [20].
The results of biochemical analysis, having identified the rise of blood amylase up to 13935 ± 2613 U/mL, alanine aminotransferase to –507.00 ± 89.61 U/l, aspartate transaminase to 558.3 ± 150.29 U/l., and of createnine up to 49.20 ± 7.84 mg/dL were the additional evidence of the severity of developmental process [8,20-22].
The given pattern of abnormalities, characteristic for pancreatitis, was confirmed by the outcome of histologycal study as well. Thus, during the first 24 hours of experimental pancreatitis in the necrosis nidus of exocrine part of the organ a pronounced phase of exudative inflammation without formation of leukocytal bank around injured area was identified. By the 5th day the necrosis area spread, covering a few segments of pancreas. By the 7th day the purulent-exudative inflammation spread over the adjacent mesentery and omentum structures.
Within the framework of the study, during the 1st day of experimental pancreatitis a single introduction of L-17 compound was executed. The data obtained in result of the experiment argue soundly the influence of the observed compound upon the nature of the developing inflammatory process (replacement of diffusive neutronphilic infiltration by lymphocytic one), as well as on the process evolution, according to histomorphological outcome.
Already during the 1st day of the experiment, at the animals from the group A, as compared to the group B, no leukopenia was observed (score of leukocytes grew higher to 4.64 ± 3.29 × 103/µL); and the signs of proliferative inflammation, characterized by a greater amount of immunocompetent cells (lymphocytes and monocytes) were observed.
Later, at the background of L-17 compound introducetion (5th day of the experiment) the necrosis area got surrounded by demarcation bank, and further on (by the 7th day) had been entirely replaced by granulation tissue.
Exactly the faculty of L-17 compound to depreciate the intensity of inflammatory reaction, showing in the limitation of lesion focus and acceleration of reparatory processes enables to limit lethality, caused by pancreatictis, since according to prevailing number of researchers the size of necrosis nidus soundly correlates the mortality rate [3,6,23]. Already in early 1980s, intraoperative findings revealed that the presence and the extent of intrapancreatic and extrapancreatic necrosis are essential determinants of complications, such as organ failure or pancreatic infections, as well as outcome in acute pancreatitis [6,24-26].
5. CONCLUSIONS
The previous investigations yielded the data, proving sufficiently high efficiency of L-17 compound application in treating myocardial infarction [11]. Thus there were data obtained that compound “L-17” of the group of substituted 5R1, 6H2-1, 3, 4-thiadiazine-2-amines significantly decreased the blood AST and CPK levels, and minimized the necrotic changes intensity along with reparation regeneration acceleration [11].
The data about histomorphological pattern of experimental acute pancreatitis under L-17 compound influence (the early granulation tissue formation and the smaller intrapancreatic and extrapancreatic necrotic areas), as well as lesser experimental animals lethality rate (twofold) resulted from this work, assert high efficiency of L-17 compound administration in case of acute pancreatitis. Of special interest is the antiphlogistic faculty of L-17 compound, consisting in depreciation of exudative-destructive processes intensity and activation of cellproliferative inflammation [11], this phenomenon being not dependant on intensity, localization and origin of inflammatory reaction at that.
6. SUMMARY
The use of L-17 compound in experimental acute pancreatitis results in replacement of destructive purulent inflammation by exudative-proliferative one, prevents lymphoand monocytopenia development, minimizes amylase and pancreatic ferments level during the first day of development of the disease and cuts down the lethality rate as result of pancreatitis complications twofold.
7. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Deepest gratitude is also due to the members of the Laboratory of Morphology and Biochemistry (RAS Institute of Immunology and Physiology, Yekaterinburg) whose knowledge and assistance has made this study successful. The authors would also like to convey thanks to the Ural Branch of the RAS for providing the financial underpinning and laboratory facilities.
This study was supported by a Special Research Grant of Interdisciplinary project of the Institute of Immunology and Physiology and the Institute of Organic Synthesis, Ural Branch of RAS (2009-2014).