Piliostigma reticulatum is a native woody shrub found in cropped fields in the Sahel and has been shown to increase crop productivity and soil quality. Frequently occurring drying and rewetting cycles (DRW) may alter the soil quality beneath these shrubs. We investigated the effect of DRW cycles on microbial community in soil beneath and outside the
P.
reticulatum canopy and the roles of this shrub in the adaptation of the microbial community to abiotic stress. Soils were incubated in a climate controlled chamber for 45 days, after exposure to 10 consecutive days of DRW cycles at 75% of water holding capacity (WHC). Basal respiration,
β-glucosidase activity, microbial biomass carbon (MB
C), and available nitrogen (
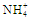
;
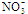
) were measured at 2, 30, and 45 days after soil exposed to the DRW cycles. MBC increased significantly two days after the DRW cycles and was greater for soil beneath the shrub canopy compared with soil outside the shrub canopy. PCA analysis based on basal respiration, microbial biomass carbon, available nitrogen, and
β-Glucosidase activity resulted in a tight clustering in the beneath shrub soil samples. Soils incubated for more than 30 days after DRW cycles had higher available nitrogen content than soils incubated for less than 30 days. Soil from beneath the shrub canopy significantly improved soil resilience based on β-glucosidase activity. Soil from beneath the shrub canopy also had higher nutrient levels and greater microbial activity even when subjected to DRW cycles, potentially improving the ability of crops to withstand in-season drought when they are adjacent to shrubs. The work should bring our scientific community into a more comprehensive assessment of potential effects of a crop-shrub intercropping that may allow for increased crop yields in semi-arid ecosystems under drought conditions.