Commentary on the Lamellar-Repulsive-Slippage Lubrication ()
ABSTRACT
In this article, we evaluated surface topographical images of the bovine (cartilage/cartilage) pair friction. In healthy joints, the cartilage (AC) surface coated with phospholipid multi-bilayers is activated by the lamellar-repulsive-slippage lubrication mechanism. Hydrophilic and negatively charged (-
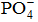
-) natural cartilage surface is covered by phospholipid bilayers. These phospholipids have been demonstrated to exert highly desirable characteristics on the surface of articular cartilage such as efficient lubrication, load processing, and semi-permeability for nutrient transport. We attempt to demonstrate phospholipids involvement in boundary lubrication of articular cartilage by: 1) the surface amorphous layer (SAL); 2) negatively charged surface; 3) lamellar-repulsive lubrication; and 4) lamellar-slippage mechanism in (cartilage/cartilage) pair lubrication. The secret of the super low friction and wear between the cartilage-bearing surfaces is lamellar-repulsive and slippage mechanism of lubrication. We also present the evidence that the superficial phospholipid bilayer covering the articular surface of cartilage has a primary function of creating a hydrophilic surface with wetting properties, and hence, of controlling interfacial properties under 7.4 pH values. We conclude that lamellar bilayers slippage, as well as the short-range repulsion between the interfaces of the negatively charged (-
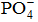
) cartilage surfaces, is a primary determinant of the low frictional properties of the joint.
Share and Cite:
Pawlak, Z. (2022) Commentary on the Lamellar-Repulsive-Slippage Lubrication.
Open Journal of Orthopedics,
12, 357-361. doi:
10.4236/ojo.2022.129035.
Cited by
No relevant information.