Bioequivalence Study of Two Oral Doxycycline Formulations (Doxysol® and Doxymed®) in Healthy Broiler Chickens ()
1. Introduction
Doxycycline is a semi-synthetic bacteriostatic tetracycline and a broad-spectrum antibiotic against Gram-nega- tive and Gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, Rickettsiae, Chlamydiae, Mycoplasmas and some protozoa [1] [2] . Pharmacokinetics properties of doxycycline are superior than older tetracycline, in terms of higher lipid solubility, complete absorption, better tissue distribution, longer elimination half-life and lower affinity for calcium [3] [4] . The in vitro antimicrobial activity of doxycycline is more effective than other tetracycline for the treatment of respiratory, urinary and gastrointestinal tract diseases [5] [6] .
The bioavailability and bioequivalence studies play an important role in determining therapeutic efficacy to register the generic drug products according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations [7] . Bioavailability is defined as the rate and extent to which an active drug ingredient is absorbed and becomes available at the site of drug action. In case of bioequivalence it is defined as statistically equivalent bioavailability between two products at the same molar dose of the therapeutic moiety under similar experimental conditions [7] [8] . The drug products are said to be bioequivalent if they are pharmaceutical equivalents or pharmaceutical alternatives and if their rate and extent of absorption do not show a significant differences statistically according to the FDA regulations [7] .
The aim of this study is to evaluate bioequivalence of two oral doxycycline powder (Doxysol® and Doxymed®) after oral administration of a single dose in broiler chickens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs
Doxysol®: is manufactured by Ascor Chimici, Italy. It is dispended as oral powder. Each 100 g contains 20 g doxycycline hydrochloride.
Doxymed®: is manufactured by Medmac Co., Amman, Jordan, as oral powder. Each 100 g contains 20 g doxycycline hydrochloride.
2.2. Broiler Chickens and Experimental Design
Twenty healthy broiler chickens (40 - 45 days old and weighing 2 - 2.30 kg) were chosen from Tanta Poultry Farm, Egypt. They were kept individually in cages, within a ventilated, heated room (20˚C), and 14 hours of day light. They received a standard commercial ration free from any antibiotics for 30 days before starting the experiment to insure complete clearance of any anti-bacterial substances from their bodies. Water was offered ad-libitum.
2.3. Bioequivalence Study of Doxysol® and Doxymed®
Twenty broiler chickens were used to study the bio-equivalence of Doxysol® and Doxymed® after oral administration. Broiler chickens were divided into two groups. The first group comprises ten broiler chickens to study the pharmacokinetics of Doxysol®. The 2nd group (10 broiler chickens) was used to study the pharmacokinetics of Doxymed®. Each broiler chickens in both groups were injected intravenously with 20 mg doxycycline standard activity/kg.b.wt. Broiler chickens were left for 15 days to ensure complete excretion of doxycycline from their bodies. Broiler chickens in the 1st group were administered orally (intra-crop) with Doxysol® in a dose of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt (1 gram of product/1 liter drinking water), while broiler chickens in the 2nd group were administered orally with Doxymed® in a dose of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt (1 gram of product/1 liter drinking water)/kg.b.wt.
2.4. Blood Samples
Blood samples were obtained from the wing vein (1 ml) and collected in test tubes immediately before and at 5, 15, 30 minute, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 hours after a single intravenous or oral administration (groups 1 and 2). Samples were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes and the obtained sera were used for the estimation of doxycycline concentration. The serum samples were stored at −20˚C until analysis, and the assay was performed within a week of obtainment.
2.5. Analytical Procedure
Arret et al. [9] described a rapid agar-diffusion assay for the quantitative determination of doxycycline in small volumes of blood by using Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6633). The used test organism for the microbiological assay was obtained from Microbiology Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt.
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
The pharmacokinetic parameters were determined for each individual sample according to Baggot [10] . Serum concentrations of the two formulations of doxycycline after a single oral administration were subjected to a non-compartmental pharmacokinetic analysis using computerized program, WinNonline 4.1 (Pharsight, USA). Values calculated were: AUC, area under the blood concentration (Cpt) time (t) curve to infinity, elimination rate constant (kel, calculated as the slope of the terminal phase of the serum concentration curve), terminal half-life (t0.5, where t0.5 = 0.693/kel), volume of distribution at steady state (Vd(ss)), body clearance (Cl(B)), the peak serum concentration (Cmax) and the time to peak concentration (tmax). The rate of absorption after oral administration was determined by comparing the area under the serum concentration curve (AUCoral) with that obtained following intravenous injection (AUCi.v.) in the same chicken.
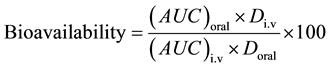
where: Div = Dose of i.v. administration .
Doral = Dose of oral administration.
The following equation according to FDA regulation [7] was performed to prove that the tested product is bioequivalent to the reference product in the study.
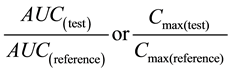
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Obtained data was analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA). The differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. All the data are expressed as mean ± SE.
3. Results
The mean serum concentration of doxycycline in broiler chickens were determined up to 24 h and were not detected in all chickens 48 h post single oral and intravenous administration. The mean blood concentrations-time profile (μg/ml) of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® after intravenous administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens are shown in (Table 1 and Figure 1).
The mean pharmacokinetic parameters of doxycycline (Doxysol® and Doxymed®) after intravenous administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens are shown in Table 2. The systemic bioavailability (F%) was 92.57 and 88.21% for Doxysol® and Doxymed®, respectively.
Doxycycline in both formulations after intravenous administration could be described in a two compartments- open model. Doxycycline intravenous administration in a dose of 20 mg/kg.b.wt. revealed a high volume of distribution (exceeded than one L/kg) calculated by extrapolation [VdB] and steady state [Vdss] method, which are factors made doxycycline is highly distributed in all body tissues. A factor revealed that doxycycline is the drug of choice for attacking the systemic infections caused by sensitive organisms.
The mean serum concentrations of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following oral administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens are shown in (Table 3 and Figure 2).
The mean pharmacokinetic parameters of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® after oral administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens are shown in (Table 4).
The disposition kinetics of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following oral administration of 20 mg doxycycline base/kg.b.wt. revealed that the maximum blood concentration [Cmax.] were 4.70 and 4.65 μg/ml and attained at [Tmax.] of 1.30 and 1.40 hours, respectively.
The 90% confidence intervals for the mean ratio of Cmax and AUC of the reference and tested formulations were within bioequivalence range and summarized in Table 5.
![]()
Figure 1. Semilogarthimic plot showing the serum concentrations-time profile of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following intravenous administration at a dose of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
![]()
Figure 2. Semilogarthimic plot showing the serum concentrations-time profile of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following oral administration at a dose of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
4. Discussion
Antibiotics are widely used as veterinary drugs or as feed additives to promote growth [11] -[16] . The pharma- cokinetics of doxycycline was reported in chickens following different routes of administrations [17] -[21] . However, the current study was designed to investigate pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of doxycycline of two powder formulations (Doxysol® and Doxymed®) after oral administration in broiler chickens.
Doxycycline in both formulations after i.v. administration could be described in a two compartments-open model. This indicated that, doxycycline distributed in the body of broiler chickens in two compartments; a central one which represent blood and highly perfused organs (kidney-liver-spleen-heart) and a 2nd peripheral compartment which represented by skin and connective tissues [6] . Doxycycline peak plasma concentration for both formulations was higher than the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for Mycoplasma gallisepticum (0.2
![]()
Table 1. Mean (X ± S.E) serum concentrations (µg/ml) of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following intravenous administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
![]()
Table 2. Mean (X ± S.E) pharmacokinetic parameters of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following intravenous administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
![]()
Table 3. Mean (X ± S.E) serum concentrations (µg/ml) of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following oral administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
![]()
Table 4. Mean (X ± S.E) pharmacokinetic parameters of doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® following oral administration of 20 mg doxycycline/kg.b.wt. in broiler chickens (n = 10).
![]()
Table 5. Bioequivalence between Doxysol® (reference) and Doxymed® (test) formulations.
BE: Bioequivalence.
Doxycycline in both formulations after i.v. administration could be described in a two compartments-open model. This indicated that, doxycycline distributed in the body of broiler chickens in two compartments; a central one which represent blood and highly perfused organs (kidney-liver-spleen-heart) and a 2nd peripheral compartment which represented by skin and connective tissues [6] . Doxycycline peak plasma concentration for both formulations was higher than the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for Mycoplasma gallisepticum (0.2 μg/ml) [22] , Mycoplasma pneumoniae (<0.5 μg/ml), Staphylococcus aureus (0.25 μg/ml) [23] , Streptococcus pneumoniae (<0.4 μg/ml) [24] and E. coli (1 - 4 μg/ml) [25] . However, doxycycline peak plasma concentration for both formulations was lower than the MICs for Pseudomonas aeruginosa (>64 μg/ml) [8] and Enterococcus fecalis (8 to 32 μg/ml) [26] . This emerge the therapeutic usefulness of doxycycline in control many susceptible bacteria. Doxycycline in Doxysol® and Doxymed® was eliminated with half-lives [t0.5(β)] equal to 17.32 and 13.86 hours, respectively. The long t0.5 is a clear characteristic of doxycycline in different species, which range from 4.2 to 16.6 h [1] [17] [18] [27] [28] .
The oral bioavailability of Doxysol® and Doxymed® indicated a good absorption from GIT. This is indicated that both products are advised to be given orally in case of acute bacterial attacks in blood and other organs [17] [18] . No significant differences were observed between the pharmacokinetics parameters of the two formulations; these results were showing the bioequivalence of the two formulations were according to the criteria established by FDA [7] .
Bioequivalence study is a test to assure the clinical efficacy of a generic versus brand drugs [7] . Bioequivalence refers to a comparison between generic formulations of a drug, or a product in which a change has been made in one or more of the ingredients or in the manufacturing process, and a reference dosage form of the same drug [29] .
The 90% confidence intervals for the mean ratio of Cmax and AUC of the reference and tested formulations were 98.93% and 89.30%, respectively. These values falls within the EMEA bioequivalence acceptance range of 85% - 125% for both Tmax and AUC and between 75% - 133% for Cmax [30] .
5. Conclusion
Based on the above pharmacokinetic and statistical results that calculated in the current study, we concluded that Doxymed® manufactured by Medmac-Jordan is bioequivalent to Doxysol® manufactured by Ascor Chimici-It- aly and both products can be used as interchangeable drug in veterinary medicine practice especially in poultry industrial sector.
NOTES
*Corresponding author.