A Pure Mathematical Relationship between Pitch and Position for Stringed Instruments ()
Keywords
Stringed Instrument, Fret, Pitch, Mathematical Model

1. Introduction
Stringed instrument with frets is a big member in the stringed instrument family. In the west, we have guitar and mandolin, in China, Pipa, Liuqin and Ruan, in India, Sitar. It seems that, in the whole world, all the appearances of these stringed instruments are similar: the frets are not uniform distributed, whereas interval of adjacent frets decreases close to the plucking region. How about the frets distributed in mathematic?
Pure mathematical model is rare to be found, people tend to study the stringed instruments physically and acoustically as [1] -[4] . But this is so complex that only people who have relevant knowledge can understand well. So, in this paper, we proposed a novel point of view which is only based on the general musical knowledge and performing experiences.
2. Math Model
Right hand plays in the plucking region (in Figure 1), at the same time, left hand finger presses the string to touch a fret at 
 , then make a sound of pitch p, where p is the order number of corresponding pitch, as shown in Table 1, the pitch interval of each adjoining fret is half tone. The string strides over OZ, and pitch p rises from point O to Z, where OZ denotes the length of the entire string, OZ is a constant, d is the distance between the string and frets, which could be neglected. The pitch-position function
, then make a sound of pitch p, where p is the order number of corresponding pitch, as shown in Table 1, the pitch interval of each adjoining fret is half tone. The string strides over OZ, and pitch p rises from point O to Z, where OZ denotes the length of the entire string, OZ is a constant, d is the distance between the string and frets, which could be neglected. The pitch-position function 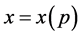 is the main task in this paper.
is the main task in this paper.
2.1. Basic Principles and Hypothesizes
2.1.1. Continuity Distribution of Pitch
The whole string is full of pitches just as the real number axis is full of real number. So, the principle could extend to stringed instruments without frets, such as violin and cello. The pitches in one octave are listed as Table 1 (take E string of guitar for example).
There are 13 pitches (labeled from 0 to 12) in one octave on E string of guitar. Pitch name is a musical name. According to 2.1.1, there are infinite pitch notes between “E” and “F”, “F” and “#F”, and so on.
2.1.2. Boundary Conditions
The pitch of the string played without left hand is called “free string”. When the left hand finger presses in the middle of the string, the pitch is one octave higher than free string. So, we can get two boundary conditions:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
2.1.3. Equal Ratio Hypothesize
For two tight strings of different length (see Figure 2), let free string pitches of string 1 and string 2 are respectively  and
and , pitches of finger pressing points are respective
, pitches of finger pressing points are respective  and
and , pressing positions are respective
, pressing positions are respective  and
and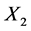 . This hypothesize is based on the performing experiences, that is, if
. This hypothesize is based on the performing experiences, that is, if , then
, then .
.

Figure 2. Two strings of different length.

Table 1. Pitch and its order number.
2.1.4. Key Position Hypothesize
The finger pressing position close to the plucking region determines the pitch. For example, in Figure 1, when a finger presses string at , the pitch played by right hand does not change whether
, the pitch played by right hand does not change whether  is pressed or not, because the string vibration part is
is pressed or not, because the string vibration part is . Distance between string and fret could be neglected as d = 0.
. Distance between string and fret could be neglected as d = 0.
2.2. Differential Equation
The pitches of three adjoining points P, Q, R are respectively ,
,  ,
, 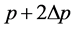 , in Figure 3, and their positions are respectively
, in Figure 3, and their positions are respectively ,
,  ,
, . Based on 2.1.3, we get
. Based on 2.1.3, we get , i.e.:
, i.e.:
 (3)
(3)
The deducting process is:

So, we have:

Let , so:
, so:
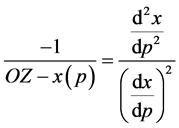 (4)
(4)
Fortunately, we can get the accurate solution according to (1), (2), (4):
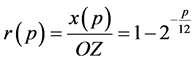 (5)
(5)
where  denotes the ratio:
denotes the ratio: .
.
And interval of fret could be expressed as:
 (6)
(6)
where r(p) and Dr(p) are respect the fret ratio-position and ratio-interval of the whole string.
Interestingly, based on Equation (5) and Equation (6), if , then
, then  and
and , which conforms to general knowledge.
, which conforms to general knowledge.

Figure 3. Fret positions of three arithmetic progression pitches.
3. Results
A real guitar is measured to get measurement results. Results of Equation (5) and Equation (6) are compared with measurement results, which are presented in Figure 4 and Figure 5 respectively, and the relative error is shown in Table 2. Where r1(p) is average value of twice measurements; the relative error is computed by .
.
4. Conclusion
What’s the mathematical relationship between pitch and position for stringed instruments? We answer this
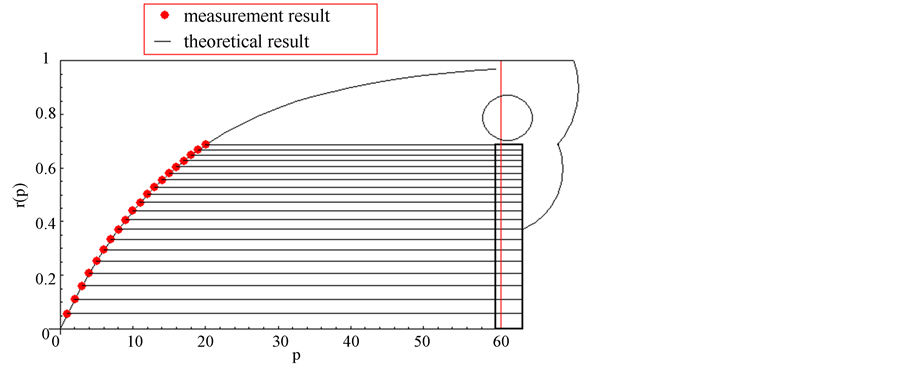
Figure 4. Comparison of measurement result and theoretical result. The curve is theoretical result of Equation (5). If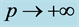 , then
, then . The red points are measurement results of 20 frets of a real guitar.
. The red points are measurement results of 20 frets of a real guitar.

Figure 5. The ratio-interval of adjacent frets. The curve is the theoretical result of Equation (6). ,
, .
.

Table 2. Theoretical result and measurement result.
question in this paper. The mathematical model is simple, direct and meaningful, only based on the general music knowledge and performing experiences. Measuring the pitch-position data from a guitar, the calculated values agree with the measurement values so well.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China Post-doctor Foundation No. 2012M520572, Tianjin Municipal Education Commission Grant No. 20120401 and Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission Key Grant (2014).
NOTES
*Corresponding author.