Interaction Mechanism and Strategy of Brand Relationship and Brand Extension ()
1. Introduction
Since the 21st century, enterprise faces increasing competition as the change of external environment. Introducing a new product or service is not only confronted with increasing advertising cost, but also a growing introducing risk. How to extend a brand? Scilicet on the basis of the existing brand, apply the existing brand to new products, thereby reduce the risk and cost of new products entering the market [1]. It has become a hot topic of concern to the industry.
Since 1979, when Tanber firstly brought forth the issues of brand extension, numerous scholars have made deep studies on this topic from different perspectives. The results of these studies can be divided into the following three categories:
Firstly, analyzing brand extension from the point of view of strategy: Smith and Park studied the strategy value of brand extension. Their results showed that introducing new products through brand extension strategy could bring more 8.3% of market share, and reduce advertising cost by 8.7% [2], compared to introducing a new brand.
Secondly, analyzing brand extension from the point of view of consumer awareness: Lots of studies show that brand image differences exist in the minds of consumers, which affect their choice and purchasing behavior. For example, Russell made a thorough research on consumer brand choice based on consumer preference matrix of different brands, and use consumer choice probabilities to different brands as the basis for brand positioning [3]. Some scholars have also studied the factors which will affect the attitude of consumer to extension brand.
Thirdly, studying brand extension mechanism from the point of view of enterprise and consumer. Boush thought that success of brand extension depends on two factors: First, similarity between the extension product and the core brand; second, consumer’s perception quality of the core brand [4]. The former relates to enterprise brand extension decision, the latter relates to consumer awareness.
Looking through the existing literatures, none of them considered the influence of brand relationship with brand extension. Brand relationship is the interaction of the consumer brand attitudes and the brand consumer attitudes [5], brand does not exist if there is no consumer. As a result, this article investigated the interaction mechanism between brand relationship and brand extension, and proposed related strategy about brand extension.
2. Interaction Mechanism of Brand Relationship and Brand Extension
Aggarwal held view that brand relationship underlines the interaction between brand and consumer [6]. From perspective of enterprise, in combination with Fournier’s brand relationship dynamic model [7], this article established a dynamic model of brand extension, shown as Figure 1, under the action of brand relationship.
Looking from a dynamic perspective, consumer purchase and use a product (including service and concept product), if dissatisfied, no brand association will happen, not to mention the brand relationship and brand extension. If satisfied, brand association will happen, forming a good brand relationship, consequently affect products extension of an enterprise. If the extended product is used with satisfaction, brand extension success, this success will enhance relationship between consumer and the brand, enrich brand association and improve brand image. On the contrary, when brand extension fail, the relationship will break down. At this time, if the enterprise adopt a crisis management, rehabilitate the brand relationship on its own initiative, brand relationship can return to their “companion” or “symbiosis” state, making the sustained and healthy development of the brand extension. This process constantly recycles.
Figure 2 described the interaction mechanism of brand relationship and brand extension, in which Figure 1 is the five level pyramid model of dynamically development of MBI brand relationship, Figure 2 is the Kapferer Model of brand extension.
In the MBI five level pyramid model, “existence” means unaided awareness, “correlation” means meeting certain kind of core consumer demand, “function” means product and performance, “merit” means unique competitive advantage, “link” means certain kind of affective relationship [8].
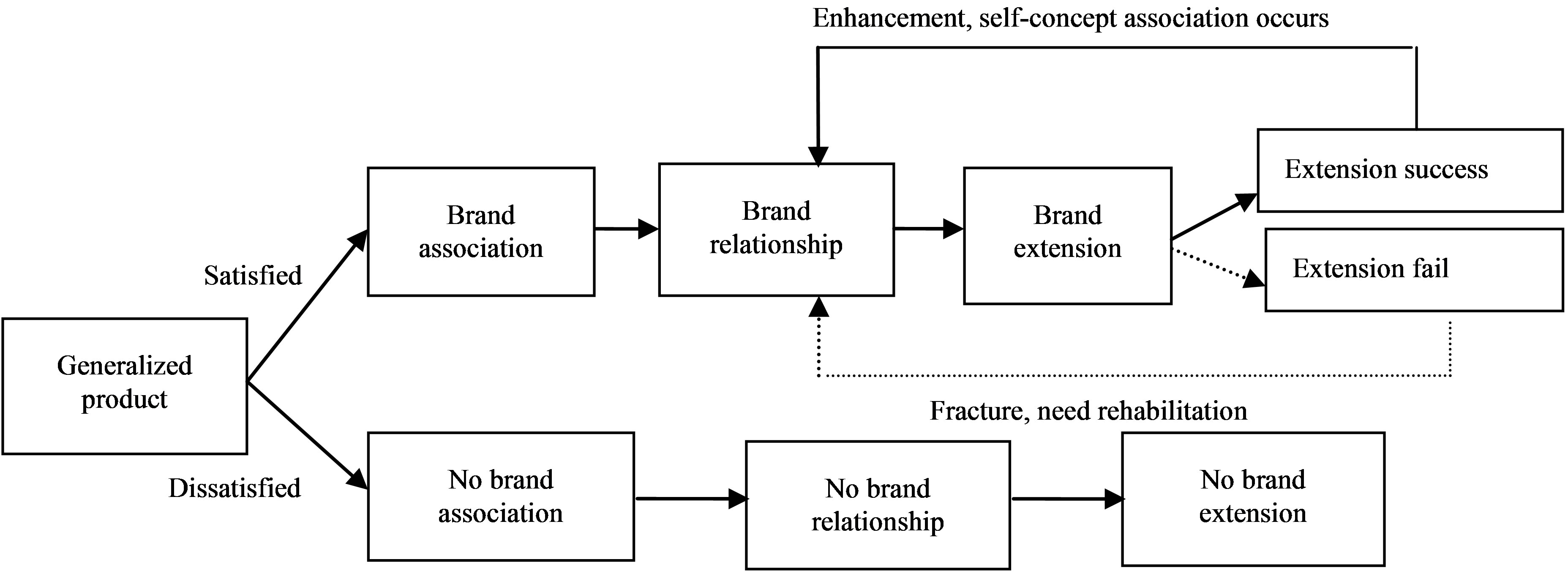
Figure 1. Dynamic model of brand extension under the action of brand relationship.
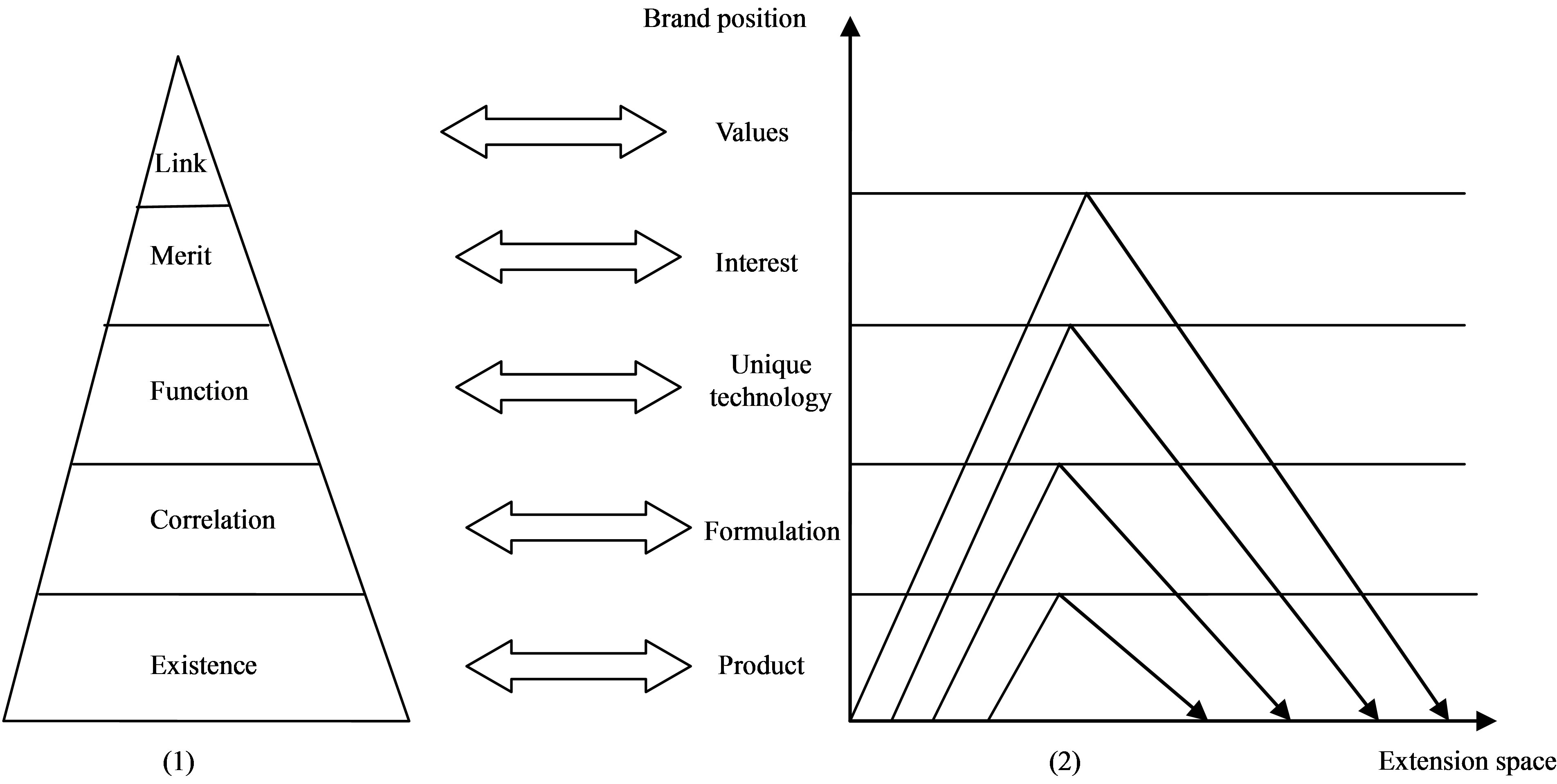
Figure 2. Interaction mechanisms of the five level pyramid model of dynamically development of MBI brand relationship and the Kapferer Model of brand extension.
Kapferer model indicated that when a product is located on itself, its function formulation, its unique technology, or other low level stage, the extension space of its corresponding brand will be limited. But when a product is located on brand culture or interest that taking values as nucleus, its brand extension space is larger. This model state clearly that in order to enhance the brand extension force, positioning of product core value should transfer from product, formulation, professional technology and etc. to interest type values.
3. Interaction Strategy Model
Following chapter will make a specific analysis of the interaction mechanism of brand relationship and brand extension, and deduce the strategy model of brand extension in every interaction stage between brand relationship and brand extension.
In Figure 2, when brand relationship stay in stage “existence” of model (1), i.e. the brand has no connection with consumer, enterprise only own a product but no popularity, brand extension is located in “product” stage of model (2), i.e. the first stage. By now, enterprise should skillfully use “4P” marketing theory to let consumer know and use the new product, then establish a mutual trust relationship. For example, although start from Children beverage, WaHaHa succeeded on fruit juice, tea beverage, purified water and even cookies exactly because they applied “4P” marketing theory and strategies: choosing strategies of product, price, promotion and place which met consumers’ mind, and taken the first stage success of brand extension [9]. After success in first stage, consumers became familiar with the products, then come into stage “correction” in model (1) of Figure 2. In this stage, on the action of brand relationship, enterprise should upgrade its products to stage 2, “formulation” in model (2) of Figure 2 at the first opportunity. The suggested improving strategy is adopting deep research on consumers’ behavior and psychology when using the product, then adjusting product positioning, adding related core function. For example, one reason that the Ma’s Army rose suddenly in the world in the end of the 20th century is that their athletes took healthy oral liquid containing Chinese herbal medicines with a long term. In China, the traditional Chinese herbal medicine is famous as its good tonic and disease prevention function. In this context of traditional culture, the “Ma’s Army No. 1” health product extended from the physical brand “Ma’s Army” failed rapidly yet, because through preliminary scientific examination and users’ long-term use, the Ma’s Army No. 1 health product has no obvious core functions of physical enhancement, chronic diseases prevention, ageing delaying and etc., which are exactly the basis of expectation by which consumers accepted the “Ma’s Army” brand. In addition, the reason other healthy products like the Chinese Turtle Refine Products, Life Nuclear Energy, Brain Gold and etc. disappeared rapidly on market is also that the target consumers didn’t feel the expected core functions of these products.
After success in this second stage, based on Figure 1, consumers’ core demand was met, their dependence on the product was enhanced, the relationship between brand and consumers was initially established. Then come into stage “function” in model (1) of Figure 2, i.e. the third stage. At this stage, consumers pay more attention to the overall feeling of products, such as: price, efficacy, quality assurance and etc. On the action of brand relationship, enterprise should upgrade its products to stage “unique technology” in model (2) of Figure 2 as soon as possible. The enterprise improving strategies in third stage include developing core product and expanding product lines. As well known, the “Master Kong” has a relative high recognition in China instant noodle market, as extension of this brand, the “Master Kong” pure water product came into market in 1998. After establishment of its core functionalities and recognizing by consumers, the company developed iced tea, oolong tea, crystal grape juice, plum juice and other drinks one after another, and paid great attentions to transfer of the overall product images in consumers’ minds, thus got great success.
After success in third stage, based on Figure 1, new product developed based on the core product of an enterprise came into market and was accepted by consumers, brand relationship was further strengthened. Then come into the fourth stage, “merit” in model (1) of Figure 2, by now enterprise has own unique competitive advantage, in consumers’ mind. On the action of brand relationship, enterprise should upgrade its products to stage “interest” in model (2) of Figure 2 as soon as possible. The enterprise improving strategy in fourth stage is that enterprise should highlight its unique ability, increase consumers’ interest and retain the “rational consumers” who seek interest-maximizing. “Coca-Cola” has always been the synonym of carbonated drinks, and has developed the Sprite, Fanta, through various forms of unique products information, for example, passing information to increase customer value through the advertisements “To those who cannot wait to go forward, 100 ml more harvest”; strengthening products interact with the young people through the “Fanta Dream Kingdom” series of marketing activities, and enhancing product loyalty of the target customers.
After success in fourth stage, based on Figure 1, then come into the fifth stage in model (1) of Figure 2, i.e. “link” stage. Consumers thought the brand has expressed self-sensation and became the projection of their undertaking and living, brand relationship came up to an optimal state. On the action of brand relationship, enterprise should upgrade its products to stage “values” in model (2) of Figure 2 as soon as possible. The enterprise improving strategy in this stage can be concluded as emotion maintain. Such as Marlboro, Marlboro successfully expanded its products from cigarette to jeans and other, not because of products similarity and channel resource sharing, nor because of its symbolized logo, but because its core brand value “brave, adventurous, enterprising” has been embedded in consumers’ mind. Consumers feel they are brave, adventurous and enterprising when consuming products of Marlboro, so they will show great forgiveness and lasting enthusiasm to the extension products under this brand.
In combined with Figures 1 and 2 and the above analysis, interaction and improving strategy model of brand relationship and brand extension can be deduced out. See Figure 3.
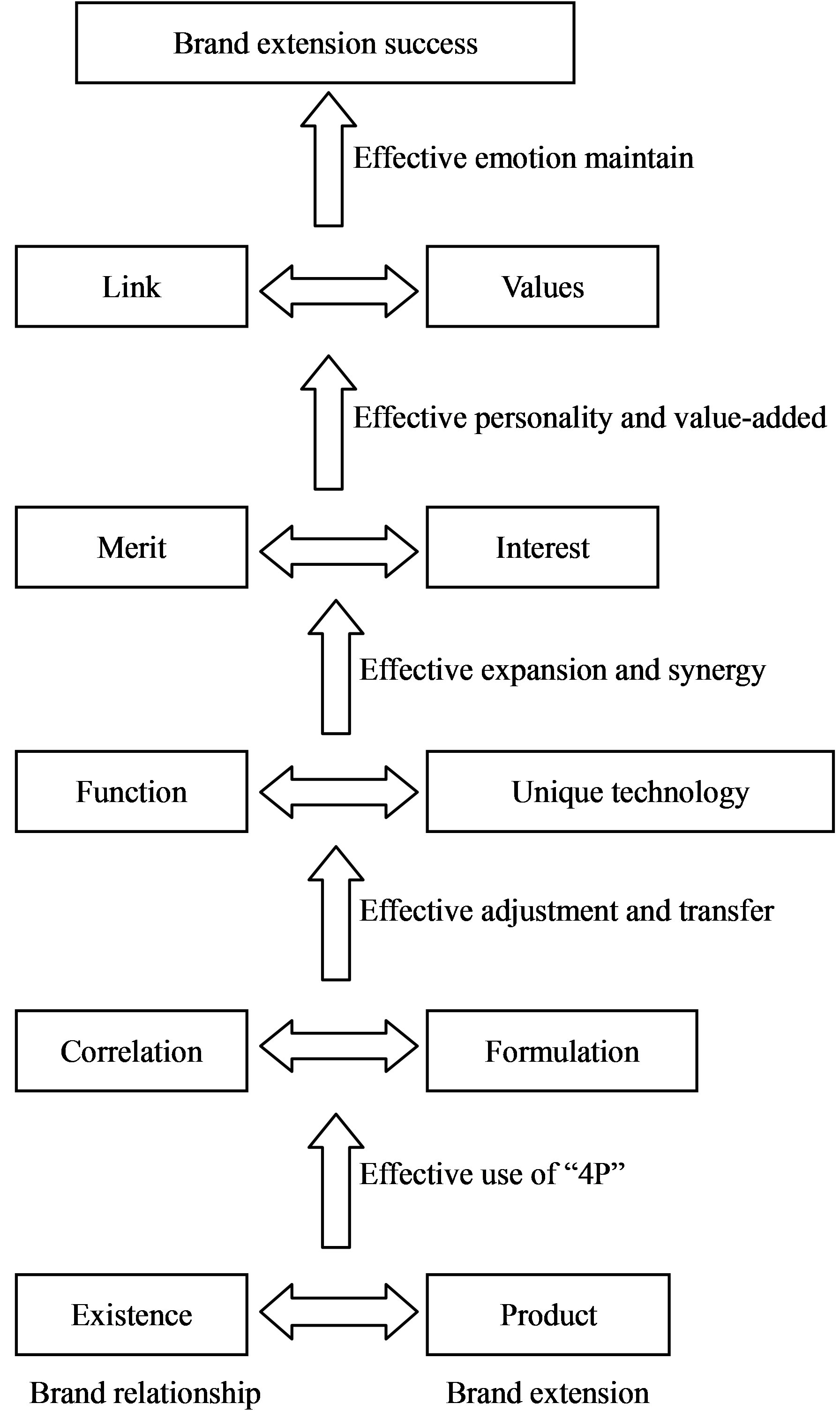
Figure 3. Interaction and improving strategy model of brand relationship and brand extension.
4. Conclusion
Brand extension will be affected by brand relationship. The stronger the relationship between consumers and brand, the easier the brand extension succeeds. With regards to this, through investigation of the interaction mechanism between brand relationship and brand extension, we can draw up the basic strategy that establishes a trust and interaction relationship between consumers and brand to increase success ratio of brand extension, consequently enhance the core competitiveness of enterprise.
NOTES