1. Introduction
We previously reported two cases of birth defects in a farmer’s family including imperforate anus, growth hormone deficiencies, hypospadias, heart defect and micropenis [1]. This pattern has rarely been described and overlapped the Stratton-Parker syndrome whose aetiology remains to be discussed [2]. Other pathologies may be concerned such as the Cat-eye syndrome [3]. It is generally believed that they are from genetic origin, although promotion or initiation by environmental factors are possible, since phenotypic symptoms may not be associated to known chromosomal abnormalities. We wanted to know if the impregnation of the farmer by pesticides after spraying could be detectable, as well as in his family, how and when. The role of endocrine disruptors in embryonic development including epigenetic effects become to be well documented [4] and can be questioned in this case. We have previously demonstrated the endocrine disruption caused by a glyphosate-based herbicide (GBH) [5]. GBH are the major pesticides used by this farmer and can be relevant biomarkers of pesticide exposure. Here we tested whether the father was excreting GBH or not. GBH is a major herbicide used not only on this farm but all over the world. This was performed before, during and after spraying following usual agricultural practices. We also tested if the farmer wife and three children at a distance from the field were contaminated.
2. Methods
Urines samples were collected for 24 h the day before and 2 days after spraying. The day of spraying and the day after, urine was collected every 6 h. The farmer’s spraying methods and agricultural practices were observed. Glyphosate residues concentrations were measured by liquid chromatography-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. The chromatographic system consisted of a Shimadzu LC-10-AD-vp high-pressure pumping system and a SIL HTc autosampler (Shimadzu, Champs sur Marne, France). Chromatographic separation was performed on a SUPELCO Discovery C18, 5 µm (50 mm × 2.1 mm) column (St. Quentin-Fallavier, France). Mass spectrometry was performed using a ThermoFisher Scientific (San Jose, CA, USA) LTQ linear ion trap mass spectrometer equipped with an electrospray ionization source. Detection and quantification limits in urine were respectively 1 and 2 µg/L (ppb).
3. Results
The family lived 1.5 km away from the fields during this period. In total, 55 L of GBH were sprayed at various concentrations on 3 fields by the farmer. In addition, he sprayed 0.75 L of GBH with a hand sprayer. During the dilution of the formulation, he wore a mask and gloves but not while he was spraying from his tractor and moreover, he opened the window. When hand-spraying, he wore gloves but neither a mask nor a protective suit. After 4 h of handling pesticides, he went home to eat with his family and carefully washed his hands and changed his clothes. However, he did not take a shower. Glyphosate was easily detected (Figure 1) in the father’s urine, from the spraying up to two days thereafter. It reached a peak of 9.5 µg/L 7 h after the beginning of pesticide handling, corresponding to 3 h after the end of the manipulation. A plateau at 2 µg/L was evidenced two days after the pulverization. The mean concentrations of glyphosate in the father’s urine per 24 h were 4.35, 0.95 and 1.9 µg/L for day 0, 1 and 2 respectively. At this moment 2 µg/L of glyphosate was also found in one child. Aminomethylphosphonic acid, the main glyphosate metabolite, was not detected in any sample.
Glyphosate urinary concentrations were measured by HPLC-ESI-MS. Kinetic of urinary glyphosate was plotted for the father (solid line). No detectable levels of glyphosate were measured for the mother and two of the children. The third child presented a urinary concentration of 2 µg/L (ppb) of glyphosate two day after spraying (dotted line). Limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) were respectively 1 and 2 ppb.
4. Discussion
Here we evidenced a glyphosate contamination just after spraying GBH in a farmer who routinely handles pesticides. Two periods of glyphosate excretion were evidenced after one handling. A first peak 5 h after exposure could be explained by a rapid inhalatory or oral route [6] followed by elimination of detectable compounds. The second detectable increase, 24 h later, could be linked to dermal absorption [7] of a small part of the pesticide applied. This may explain the different intensity of the two times of excretions with different absorption rates of the pesticide [8]. This is a crucial element to consider in toxicokinetic studies; and to our knowledge we reported
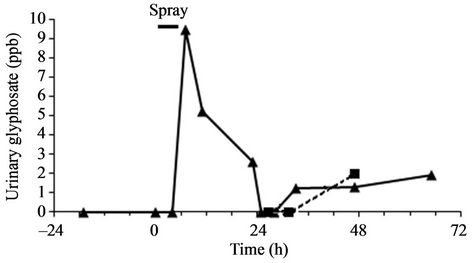
Figure 1. Glyphosate urinary concentrations the day before, the day, and two days after pulverization.
it for the first time for GBH human exposures. Oral administration of glyphosate in rats was followed by a peak 2 h after.
Surprisingly, one of his three children presented detectable glyphosate in urine even if he lived at a distance from the field. This could be due to prolonged contact with his father, for instance by skin. Glyphosate was already assayed in farmers and their families for pesticide exposure, showing that the whole family is exposed to the pesticide depending on their protective equipment [9,10]. The levels of GBH residues in this work correspond to urine concentrations after agricultural exposures, from a few ppb to 233 ppb (geometric mean 2.3 ppb) [9].
In our works, Roundup has cellular antiandrogenic effects from 0.2 ppm of glyphosate mixed with adjuvants, a concentration 20 times higher than those detected in these assays. However this occurred within 24 h, and did not take into account the bioaccumulation in tissues nor long term effects, as well as combined effects with other sprayed pesticides.
Paternal exposure is more and more recognized to be a cause of birth defects by pesticide mediated alterations of germ cells [11,12]. However, the lack of precautions taken by farmers also expose their family. In general, little precaution is given during GBH spraying and this is worldwide. The father answered that it was inconceivable to expose his family to pesticides by his practices because of the distance between the house and the fields. Informations and recommendations have to be improved for guiding farmers to protect health in agriculture production. In particular, the protections should be maximized even for GBH and showers after spraying are to be recommended, and clothes washing outside familial practices. Some mandatory training periods can be implemented. Also, we have described that plant extracts can protect human cells from GBH toxicity [13]. This can be an additional way of protection; it is a commercialized pharmaceutical drug. We ask for a more cautious monitoring of patients and their families during environmental chemical exposure.
NOTES