Family Care Centre Model Could Decrease Anxiety Level among Family Members of Patients Who Have Been Undergoing in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) ()
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
The families of critical condition patient commonly have experienced in high level of anxiety, especially losing their beloved one. Due to such phenomenon, families typically experience fear associated with loss of control, uncertainty, and financial constraints. The accumulation of many stressful factors may lead to crisis condition that can threat family integrity and lose their ability to cope with their problem [1] [2] [3] .
It is necessary to concern about the family of criticial ill patients. It is a general consensus that involving families in the patient care is important and has positive effect on both families and patients. In this context, family members can have a great impact on the patients’ general well-being by providing psychological and emotional stability [4] [5] [6] . Therefore, the family members are the important people who should be involved in decision making and therapeutic process from the state of being well to diagnosis, treatment, and recuperation [7] .
Unfortunately, in the acute and critical care settings, nurses are highly focusing on the physiological and psychological impacts to the life-threatening illness of the patients. Limited attention and care have been given to family members. As a consequence, nurses do not provide appropriate nursing intervention to the family, especially to solve their high level of anxiety [8] [9] .
To alleviate the anxiety level of family and to help their families, they should be able to cope with this condition, and involving the family into nursing care process is vital. One theory that can be used to solve such problems is applying the Family care centre [10] [11] .
In this study, nurses and family members collaborate as a partnership to solve the anxiety problem. Commonly, this model is used in the pediatric care unit, but in the intensive care unit, FCC also can be used because the patient in the critical ill condition can’t make decision by theirselves or they mostly depend on the families. Therefore, the patients independency level would directly affect their family.
The study aims: “to analyze the responsiveness effect of the FCC model in decreasing anxiety level of family members of patients who have been hospitalized in the intensive care unit. Result of this study can be used to promote the positive roles of family members in the critical care setting in order to assist them to redeem their anxiety level.
1.2. Conceptual Framework of the Study

1.3. Definition of Term
Family care centre is an effort of counseling and mentoring done by researchers with the involvement of the family members who has been undergone hospitalization in ICU for facing the problem of their anxiety level, from assessing, planning, implementing FCC model and evaluating it within 3 days.
Anxiety levels of family members of patients who undergo hospitalization in the intensive care unit are signs and symptoms of both physical and psychological aspects that before and after the model is implemented by family care centre. It can be measured by Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, including: feelings of anxiety, tension, fear, sleeplessness, intellectual, somatic muscles, somatic sensory, signs of cardiovascular system, respiratory, digestive, urinary, autonomic, and changing behavior during the interview. The value range from 0 to 56, it means the higher the value, the bigger the anxiety level [12] .
2. Research Methodology
This study used a quasi experiment of pre and post test design with control group. It has been implemented since July to September 2015, offspring about 48 family members who were undergone in the ICU Dr. Hasan sadikin General Hospital Bandung, 24 family members were in the intervention group and the rest were the control group. The intervention group was the family members from general ICU (GICU), meanwhile control group was the family members from neurosugery ICU (NCCU). The data was obtained by using purposive sampling technique.
The family members who were selected based on inclusion criteria were responsible for and take care of; the patients every day, new admission in the ICU, and some them didn’t have experienced yet to take care of the patient in the ICU, cooperative, able to listen and speak clearly and sincerely to be a res- pondent. Meanwhile exclusion criteria were the family members who didn’t take care the patient every day, on the mild level of anxiety, and illiterate.
This study has ethical approved by ethical comission of Bandung Health Poly- technic, with the number: 60/KEPK-PKKB/6/2015 on the date June, 4, 2015 that signed by drg. RR. Megananda Hiranya Putri, M.Kes., as a head of ethical comission, and also has got permission by Director of HRD and education affair of Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung hospital, on the date July, 15, 2015.
Data collection was begun by identifying family members who meet inclusive criterion, then they were provided an informed consent and asked approval that was being the respondents. Subsequently measured that the respondent from intervention group and control group level of anxiety (pre-test), and then applied family care centre model within 3 days, based on thethree steps. In the first step, it focused to assess the cause of anxiety family members within 30 minutes, and then they were asked to provide nursing care plan including FCC model to solve the problem. The second step was implemented FCC model within 3 days by using education and consultation program, and empowering the family members accordingly to the cause of anxiety and to reduce anxiety level as well. This step was provided in 1 - 2 hours before visiting time, in order to prepare the family members can involve into nursing care when they met the patient in the visiting time. Third step was evaluating the implementation FCC model in the second step approximately in 30 minutes. After the family members completed the whole series of treatments then they directly measured the level of anxiety as a data post-test. Data processing was done by step: editing, coding, entrying, cleaning and processing, data.
3. Result
3.1. Univariate Analysis
Respondent characteristic of this study was focusing on age, education level, job, and previous experienced of taking care the patientin ICU of the family mem- bers and also relationship of the family to the patient. According to Table 1, half
![]()
Table 1. Respondent characteristic.
of the family (50%) in the intervention and control group is in the late adult- hood, most of them have low education level and jobless, and less likely about 41.7% of them didn’t have experience to take care of the patient in ICU as a spouse or as a parent (refer to Table 1).
Table 2 showed the meanscore ofanxiety level of the family members in the intervention group before applied FCC model is 49.45 with standard deviation 4.43 and then after applied FCC model their anxiety level decreased to 18.79 with standard deviation is 3.84. Meanwhile in the control group their anxiety level in the pre test is 47.79 with standard deviation is 6.22 and decrease into 20.29 with standard deviation 4.12.
3.2. Bivariate Analysis
According to Table 3 that shown difference mean in the intervention group is 29.08 (Sd = 5.20), meanwhile the difference mean in the control group is 27.50 (Sd = 5.27). There are significant effect on the intervention and control group to decrease anxiety level of the family members who undergo in the ICU (p = 0.000).
To analyze effectivity of the implementation FCC model to decrease anxiety level on the family members who undergo in intensive care unit was used inde- pendent t-test, the result as shown in Table 4. Based on Table 4, Levene’s test
![]()
Table 2. The anxiety level in the intervention and control group before and after applying FCC.
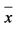 = means, Sd = Standard deviation.
= means, Sd = Standard deviation.
![]()
Table 3. Effect of applied FCC to decrease anxiety level both of intervention and control group.
![]()
Table 4. Effectivity of the implementation FCC model to decrease anxiety level family members who undergo in ICU.
show there are not significant difference mean between control group and inter- vention (p = 0.737), it means that there are no difference varians between control and intervention group or both group are homogen. Then, based on independent t-test that can be found the result, there are significant difference mean about 1.50 (Sd = 1.15, p = 0.0009). It means the implementation FCC model can decrease effectively anxiety level of family members who undergo in ICU.
4. Discussion
Stuart and Sandeen (1998) cited in Hawari (2008) defined that anxiety is an abnormal and overwhelming sense of apprehension and fear often marked by physiological signs (as sweating, tension, and increased pulse), by doubt concerning the reality and nature of the threat, and by self-doubt about one’s capacity to cope with it [13] . In this study the precipitating anxiety factors are patients who has been undergone to the ICU. Commonly patient who has be admitted to the ICU are in unstable condition. It was due to using any medical devices, and in life threatening event, so, it may cause negative effect to their family members, especially to get high level of anxiety.
Result of this study found that mean score of level anxiety in the intervention group before applied FCC model (pre test) is 49.45 (Sd = 4.43) and mean score after applied FCC model (post test) was 18.79 (Sd = 3.84). Meanwhile, the mean result of pre test was 47.79 (Sd = 6.22) or it was the highest level of anxiety, and the mean score of post test was 20.29 (Sd = 4.12). This result showed that the family members who were in the intervention and control group in the pre test for both of them was in the same lavel of anxiety, that was in the severe or high level. The result of post test anxiety level was the same level too, both of them was in the middle level of anxiety.
The result of this study is like as/similar to the previous study from Zahara Farhan (2014) about stress predictor of family members who undergo in ICU that found 95% family members reached the highest stress level when one of their family members have to be undergone in ICU [14] .
The result of this study is related to respondent’s characteristic, such as: education level, occupation, and relationship with the patient. According to Table 1 we can see that the majority of respondents have low education level. According to Notoatmojo (2005) cited in Desmita (2008), education is one of the factors that determine a person ability to access information. The higher the level of education, the easier the people of incurring information. Based on in this study, the majority of of respondents have low education level that has led to the lack of ability of these families to access information, especially information related to patient in ICU, which ultimately lead to severe anxiety [15] .
The highest meanscore of anxiety in this study because most respondents were not in paid (58.3% in the intervention group and 62.5% in the control group). This condition triggers the anxiety level. They do not have any satisfied source of income to covertheICUtreatment charges which is tooexpensive. Although there is BPJS program, they yet look for necessities as family nonetheless anxious because they have accommodation during period of accompanying waiting patient at the hospital.
The closeness relationship among patients’ relatives gives a negative impact on the level of the anxiety of the family members. In the intervention group, mostly family members were caring his or her spouse (41.7%), while the control group was responsible to his parents. Closely his emotional connection/psycho- logical with the patient against his spouse or parent is certainly preveil in a great pressure on anxiety levelcompared to these felt who have less emotional connection that is less a like. It was predominantly consideration, lovely feeling together with unreadiness yet to be left by his/her spouse.
Friedman (1998) stated that their family problems will affect other family members, in this study their family members who are sick and hospitalized in the intensive care is a source of stress for other family members to get trigger the anxiety level. If the anxiety is not addressed then the family will fall in a state of panic and can lead to destructive behavior [7] .
In that regard, it is one of the efforts to be made by nurses to reduce the impact of anxiety in the family is to involve the family in caring the patient through the implementation of a model of family care center (FCC) [16] .
Effect of apllying FCC model to reduce the anxiety level of family members who undergo in ICU.
FCC model is a method that emphasizes the belief among health workers and family members in dealing with the problems faced by the patient and his relatives, started from planning, implementing and evaluating the care plan. In applying the model, there are 4 basic principles that should be considered, 1) their honesty and mutual respect among nurses, patient and his/her families, 2) there should be a sharing of information amongpatient, families and health workers; especially nurses, 3) the family involvement in caring the patient and 4) the collaboration among health workers in providing services to patient and family members [16] .
The result of this study shown in Table 3 indicated that the paired t-test analysis of both the intervention and the controlled group were statistically significant effect (p-value = 0.000) respectively. Furthermore, based on analysis using the independent t-test formula, shown in Table 4 was obtained p-value = 0.009, which means there are very significant result by applying the FCC model to decrease families members’ anxiety leevel whoundergo in ICU.
Hence, it indicates that the application of FCC model conducted by researchers by involving patient’s family member which in the implementation of nursing care, especially in dealing with anxiety issues starting from the stage of identification of the source of anxiety, planning in dealing with anxiety problems, then carried out efforts to overcome the problem by nurses to provide education and counseling to family members during visiting time that could prove successful in reducing the anxiety level of the patient’s family members. They seem to be more calm and able to control their emotion when visiting their patient.
The key succeed on implementing the FCC model in this study is influenced by the characteristics of respondents themselves as the intervention groups, based on the age of ranging from 41 - 60 years old was about 50% elderly. Generally they are mature, easy to give understanding, responses cooperative, and they have a sense of responsibility to think realistically [15] .
In addition, experience is considered as another factor that affect outcome of this study; more than half (58.3%) of respondents in the intervention group has already been experienced for more than 1 time caring aspatients in ICU, so they have already enough knowledges and experiences, able to control and to control their emotions easily, as a result that they can be more quickly to adapt the situation.
These results are similar to theresearch paper done by Puspita (2010), which showed a significant relationship between family support and the patient’s anxiety levels who has been being treated in ICU. It gave a positive effecttothe patient of decreasing anxiety with stand contrast to the family whom experiences were not theirs to decrease anxiety level (p = 0.001) .
Moreover, other researchers showed positive effect on family involvement at the time of implementing the nursing care. FCC was also considered as the most basic method to care of the patient, respect, collaboration and support them. Family involvement in caring of patients through applying FCC method was the strongest predictor in improvingthe feeling of respect, collaboration and support (OR = 1.66 and p-value = 0.001) [16] .
Positive effects on applying of FCC model towards elderly patient’s were also by obtained the research paper done by Anndale Mc Tavish and Cynthia Phillips (2014), it was about the experience of patient whom they weretreated by the application of FCC model in Kingston General Hospital, the results showed that the patientwho was treated in the hospital felt the quality of care and quality of life had been increased [17] .
Through application of the model FCC is the family seemed patient calm and ready emotionally when they came to visit patient on visiting time, this can be seen from the behavior of those who are no longer crying when dealing with the patients. Family members seemed unwilling to open communication with patient, support, and do some simple actions that do not endanger the patient. Therefore, with the involvement of the patient’s family members seemed quietly that the patient condition can be easily seen by the description of vital signs. It shows that between patient dan family has inner relationship closely, where the adaptive response of the family in the form of constructive coping directly to assist them during the recovery of physical patients condition and this can reduce the length of stay the patient.
5. Conclussions
1) Anxiety level in the intervention group before applying the FCC model is 49.46 or at the level of severe anxiety while after the application of the FCC model, the value decreases to 18.79 or in the middle level of anxiety.
2) Anxiety level in the control group in the pre-test is 47.79 or at the level of severe anxiety while the result of the post-test is 20.29 or in the middle level of anxiety.
3) Application of FCC is proven to significantly reduce anxiety level of family members of patients who undergo in the ICU in the intervention group compared with the control group (p = 0.009).
6. Suggestion
1) Related to this results and the previous study, the model FCC should be considered to be applied when caring patients in the ICU because patient who were undergo in the ICU, in general to those who some condition of dependence on others, unable to make decisions themselves and feeling depressed, so that the presence and involvement of the family members to be highly significant and important to be perceived by patient. In applying this model should also be noted patient condition and mental readiness of families to be involved in nursing care of the patient in order not to interfere with the work of nurses and other health team.
2) It is necessary to conduct further research related to the application with the FCC model of different methods e.g. by qualitative research to further explore the patient’s experience, families and caregivers about the effectiveness of model FCC. This research could also be more meaningful to further examine the characteristics of respondents to the success of FCC or can be developed by examining the different variables of the FCC’s influence.
Acknowledgements
Great appreciation is given to Director of Bandung Health Polytechnic who has supported and giving budget for this research project.We would also like to thank to the Director and the head of nurse of ICU Dr. Hasan Sadikin Bandung General Hospital who has givenus permission to conduct research. I am gratefully indebted for all of patients and family members who participated in this study.