1. Introduction
In recent years, super paramagnetic iron oxides nanoparticles (SPIONS) such as magnetite (Fe3O4) and maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) have attracted different areas of technology. Some of them include antitumor drug delivery [1] , removal of industrial pollutants from water [2] , manipulation of biomedical objects [3] .
In addition, they can be applied in solid-state-phase absorbents of human genomic DNA [4] , green catalysts [5] , thin film from protection corrosion [6] , gas sensors [7] , magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast optimization [8] and hyperthermia treatment [9] . In the case of maghemite nanoparticles, their surface can be modified (functionalization) and mechanically controlled by an external magnetic field, therefore they are promising in medicine such as drug deliverers for cancer therapy [10] .
Up to date, many reports have described different methods to synthesize magnetite and maghemite MNCs. Some of them include electrochemical method [11] , laser pyrolysis [12] , microemulsion synthesis [13] , and hydrothermal technique [14] . In this work, we report the preparation of γ-Fe2O3 nanocrystallites by co-precipitation chemical procedure. This method is chosen because of the lower temperatures required to the synthesis compared to other techniques such as hydrothermal technique [14] which require interval of temperature from 130˚C to 250˚C and high vapor pressure (from 0.3 to 4 MPa). On the other hand, in our previous report [15] , we studied the intermediate super paramagnetic relaxation effect of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles by Mössbauer spectroscopy at different temperatures. The relaxation process was broken by decreasing the temperature up to 4.2 K proving the single-phase formation of the MNCs fitting the spectrum with the corresponding two typical hyperfine fields of maghemite. In this work we characterize the obtained nanocrystallites by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), selected area electron diffraction (SAED) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) to confirm the purity and the formation of monophasic γ-Fe2O3 MNCs. Besides, for a more accurate calculation of the blocking temperature and the magnetic diameter, in this work we perform the magnetic measurements at different temperatures.
2. Experimental
Homogeneous maghemite γ-Fe2O3 MNCs were obtained by the coprecipitation technique following the next procedure. Initially, magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles precursor were prepared from ferric chloride and ferrous chloride with stoichiometric ratio of Fe2+/Fe3+ (1:2) in aqueous solution (basic medium of pH = 11 - 12) without surfactants or organic solvents. 0.85 mL of 12.1 N HCl and 25 mL of deoxygenated water were added.
Besides, 5.2 g of FeCl3 and 2.0 g of FeCl2 were dissolved in the solution under continuous stirring. The resulting solution was dropped wise into 250 mL of 1.5 M NaOH solution under vigorous stirring up to obtain a black precipitate with pH = 12. The paramagneticity was checked in situ by placing a magnet near the system. Purified deoxygenated water was added to the precipitate and this solution was decanted by centrifugation at 4000 rpm. After repeating the last procedures three times, 500 mL of 0.01 M HCl solution was added to the precipitate with stirring in order to neutralize the anionic charges on the nanoparticles. Immediately, the oxidation of Fe3O4 into γ-Fe2O3 was carried out by adjusting the pH = 3.5 with hydrochloric acid. The oxidation was controlled under magnetic stirring at about 80˚C for 30 min to get maghemite phase. The sample was dried at about 40˚C with the aim of getting a reddish-brown color, which is characteristic from maghemite MNCs [16] . The characterization was done by X-ray Diffraction (XRD) in a Bruker D8 equipment with radiation Kα1 of copper (l = 1.54056 Å) in the range from 8 to 80 degrees, with a step of 0.02 degrees, at room temperature (RT). The X-ray diffraction pattern was analyzed by the Rietveld Refinement method using the DBWS program, the peaks shape was modeled with a Pseudo-Voigt function and the crystallite size is related to the line width (Γ ) that was estimated with the use of the Scherrer formula. For TEM measurements, we have used the Titan 80 - 300 kV microscope equipped with a special high-brightness Schottky-field emission electron source. We have used the Gauss program, developed at the Cadiz University, Spain, for counting nanoparticles with spherical shape. Measurements of the magnetic moment as a function of applied fields were carried out in a DC MPMS-SQUID magnetometer (Quantum Design) in a range of −55 k Oe to 55 k Oe at different temperatures from 10 K to 300 K. Measurements of the magnetic moment as a function of the temperature in the range 10 - 300 K were carried out by applying three different magnetic fields in zero field cooling (ZFC) mode.
3. Results and Discussions
The XRD pattern of the sample is shown in Figure 1. It reveals a monophasic sample with wide peaks due to

Figure 1. Rietveld Refinement of the XRD pattern of the maghemite MNCs obtained by co-precipitation. The black line corresponds to the experimental data, the red line is the theoretical diffractogram obtained after several refinements and the green line is the difference between the experimental and theoretical data. The Miller indexes are indicated in the top by the blue lines, and they are fully written in the strongest peaks.
the nanometric size of the crystallites. The diffractogram fits very well with the cubic symmetry (space group P4132) of γ-Fe2O3 (PDF Card 39-1346).
Rietveld Refinement was performed which give a mean grain diameter of 6.4 ± 1 nm. The value of the uncertainty can be associated to the noisy background of the diffractogram commonly obtained in iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles [17] .
Table 1 summarizes the refined parameters obtained for maghemite structure. We observed from the Rietveld analysis the single phase of maghemite formed without any impurities. In addition, the obtained lattice parameters a = b = c = 8.3565 (Å) confirm the presence of the cubic structure and good crystallinity obtained during the chemical reaction.
Notably, the interplanar distance corresponding to 2θ = 43.284˚ is d(400) = 2.082 Å which is similar to the value reported by Hai et al. [18] . This value is helpful to differentiate between the XRD pattern of the maghemite (d(400) = 2.0886 Å, 2θ = 43.28˚) and magnetite(d(400) = 2.0993 Å, 2θ = 43.052˚) phases due to the shift at 2θ value. Figure 2(a) shows the bright TEM image of the maghemite MNCs. The sample consists on agglomerated particles with nearly spherical shape and diameter ranging from 6 to 10 nm.
The agglomeration could be prevented by using oleic acid [19] [20] . The top left inset of this figure shows the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern indexed with the cubic structure of the maghemite phase (JCPDS No. 39-1346). Note the presence of the plane reflection (400) remarked in the XRD above. The size distribution is presented in the bottom right inset of the figure. A mean diameter size of D = 6. 8 ± 0.1 nm is calculated which is close to that obtained by Rietveld Refinement above (6.4 ± 1 nm). Figure 2(b) shows a high resolution (HR) TEM image. The degree of agglomeration, size, round shape and grain bordering are better distinguished in this figure. Remarkably, the cubic structure of the maghemite phase obtained by the XRD above is confirmed by the fast Fourier transform (FFT) image which is shown in the top right inset of Figure 2(b) and revealing the (111), (220), (311) and (400) Miller indexes. The texture of the crystallites is better appreciated in the top left inset on this figure. The (111) indexes correspond to planes separated with d = 4.8 Å, whereas the (220) indexes to planes separated with d = 2.9 Å confirming the XRD analysis.
Table 2 summarizes and compares the values of these interplanar distances obtained by the XRD and HRTEM measurements. The corresponding FFT image of the zoomed area is also shown in the bottom left inset of the figure.
The magnetization dependence on magnetic field (M-H) loops of the maghemite MNCs measured at different temperatures are shown in Figure 3. The curves were fitted with the law of approach for high magnetic regions to estimate the saturation magnetization (MS) values [21] :

Table 1. Refined structural parameters for the γ-Fe2O3 phase, (RWP/Rexp = 1.12).

Table 2. Corresponding interplanar distances for the diffraction peaks (111) and (220) of maghemite MNCs obtained by XRD and HR-TEM techniques.
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 2. TEM analysis of maghemite MNCs. (a) Bright TEM: The insets show the indexed SAED pattern and the mean diameter value obtained by fitting the size distribution with a Gaussian function was D = 6.8 ± 0.07 nm; (b) HR-TEM: The top right inset shows the FFT image of the complete area, the top left inset shows a zoom image of an area revealing the crystalline planes and the bottom left inset shows the respective FFT image of this zoomed area.
 (1)
(1)
where the term chi × H represents the field-induced increase in the spontaneous magnetization of the magnetic domains, or forced magnetization. This term is really small at temperatures below the Curie transition point (Tc), thus it may be neglected. Importantly, Equation (1) is used just for values of temperatures below Tc. Besides, a and b are important parameters associated to the theoretical physics phenomena; a is related to inclusions and/or microstress, and b is related to crystal anisotropy [22] .
Where Keff is the effective magnetic anisotropy and MS is the saturation magnetization. Figure 4(a) and Figure 4(b) show the best fitting of Equation (1) to the experimental data of the M-H loops for T = 10 K and 300 K. Figure 4(c) shows the behavior of the saturation magnetization with the temperature. At RT the value of MS is near to that reported for bulk maghemite (60 emu/g) [23] . This indicates that eventual chemical residuals or dead layers formed on the surfaces of the MNCs [18] during the nucleation process are of minor influence proving a

Figure 3. M-H loops measured at different temperatures 10, 150, 250 and 300 K and under applied magnetic fields between −55,000 to 55,000 Oe. The inset shows the zoom plot of hysteresis loops obtained at different temperatures. We can regard the thermal dependence of the coercive field, which suggested the presence of superparamagnetism state at RT.
high degree of purity of our sample as also confirmed with Rietveld Refinement and SAED patterns. Besides, the fitting of the thermal dependence of the coercive field (in the top right inset of Figure 4(d)) shows a behavior as a function of squared root of T for temperatures below T < 50 K which could be associated to low interparticle interactions [24] . Hence the fitting yields a mean value for the blocking temperature  = 62 ± 3 K. Note that there is a slight increment in the coercive field above 150 K. This unexpected behavior was also reported in other systems such as CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and can be associated with rotation of the magnetic moments from coherent to incoherent modes [24] . The mean blocking temperature can be also calculated from the ZFC signals (Figure 5(a)), assuming grains with the same diameter and following the relation:
= 62 ± 3 K. Note that there is a slight increment in the coercive field above 150 K. This unexpected behavior was also reported in other systems such as CoFe2O4 nanoparticles and can be associated with rotation of the magnetic moments from coherent to incoherent modes [24] . The mean blocking temperature can be also calculated from the ZFC signals (Figure 5(a)), assuming grains with the same diameter and following the relation:
 (2)
(2)
with 1.5 < β < 2 [25] . Taking a value of β = 1.6 and considering that Tmax = 105 ± 3 K (which is obtained from the curve with applied magnetic field of 500 Oe), we obtain 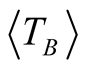 = 66 ± 3 K.
= 66 ± 3 K.
This value is in good agreement with the one determined from the temperature dependence of the coercive field above. Note that in the Figure 5(b) Tmax tends to shift to lower values when the applied magnetic field is increased [25] . The effective magnetic anisotropy is given by , where kB is the Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10−23 J·K−1) and
is the mean volume of the particles. Thus, K
eff = 1.6 × 10
4 J/m
3. Both values for K
eff obtained by the fit of the thermal coercive field and the ZFC relations at 500 and 100 Oeare similar. Nevertheless, these values are higher than that for bulk maghemite (4.7 × 10
3 J/m
3). This is because in the nanoscale, K
eff varies with size as 1/D
[26] .
, where kB is the Boltzmann constant (1.38 × 10−23 J·K−1) and
is the mean volume of the particles. Thus, K
eff = 1.6 × 10
4 J/m
3. Both values for K
eff obtained by the fit of the thermal coercive field and the ZFC relations at 500 and 100 Oeare similar. Nevertheless, these values are higher than that for bulk maghemite (4.7 × 10
3 J/m
3). This is because in the nanoscale, K
eff varies with size as 1/D
[26] .
The magnetic diameteris calculated with the formula [27] :
 (3)
(3)
where  is an initial susceptibility of the system, kB is again the Boltzmann constant, MS is the saturation magnetization calculated for T = 300 K (60 emu/g), and ρ is the density of the maghemite (4.87
is an initial susceptibility of the system, kB is again the Boltzmann constant, MS is the saturation magnetization calculated for T = 300 K (60 emu/g), and ρ is the density of the maghemite (4.87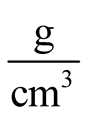 ).
).
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 4. Fitting of the M-H loop obtained at 10 K (a) and at 300 K (b), dependence of MS vs T (c) and temperature dependence of the coercive field (d) for maghemite MNCs obtained by co-precipitation. (The inset in (d) shows the fitting for the lowest temperatures).
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 5. Normalized ZFC magnetization curves obtained under Hext = 100 Oe, 500 Oe and 1 kOe (a) and Tmax dependence with the applied magnetic field (b) for maghemite nanoparticles prepared by co-precipitation.
An initial susceptibility obtained from M-H loop at 300 K (Figure 4(b)) is 0.02 emu/g Oe, yielding to a value of DMAG = 6.5 nm which is in good agreement with the mean values obtained by XRD and TEM analysis.
4. Conclusions
Magnetite with molar ratio Fe2+/Fe3+ 1:2 was oxidized to form maghemite MNCs by following the co-precipitation method. The average sizes of the particles estimated by Rietveld Refinement and HRTEM are 6.4 ± 1 and 6.8 ± 0.1 nm, respectively. The average size of the magnetic domains calculated from the magnetic measurements is 6.5 nm, confirming that the maghemite MNCs are constituted of single magnetic domains. Good crystallinity and single-phase formation are discussed and confirmed in detail by XRD (Rietveld analysis), TEM and SAED analysis. Additionally, coercive thermal dependence and M(T) measurements yield valuable and reliable information about the mean blocking temperature ( = 62 ± 3 K and
= 62 ± 3 K and  = 66 ± 3 K, respectively). The magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant is Keff = 1.6 × 104 J/m3 respectively. High magnetic saturation is obtained showing that not chemical residuals on the surface of the MNCs are formed during the chemical reaction, confirming once again the monophasic formation of MNCs. Therefore, co-precipitation is a reliable technique to synthetize homogeneous and pure maghemite nanoparticles.
= 66 ± 3 K, respectively). The magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant is Keff = 1.6 × 104 J/m3 respectively. High magnetic saturation is obtained showing that not chemical residuals on the surface of the MNCs are formed during the chemical reaction, confirming once again the monophasic formation of MNCs. Therefore, co-precipitation is a reliable technique to synthetize homogeneous and pure maghemite nanoparticles.
Acknowledgements
The work in Cambridge has been supported by the Engineering and Physical Science Research Council (EPSRC).
NOTES
*Corresponding author.