Enzyme Biosensor for Detection of Organophosphate Pesticide Residues Base on Screen Printed Carbon Electrode (SPCE)-Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) ()
1. Introduction
Two classes of pesticides for fruits and vegetables are insecticides and fungicides. Three types of widely used insecticides are dizinon, dimethoate and chlorpyrifos; they are the classes of organophosphate. Organophosphate pesticides recommended by Department of Agriculture because organophosphate pesticides are easily lost in nature. Nevertheless organophosphate pesticide residues in humans can cause both acute and chronic poisoning; it is caused by the accumulative nature of organophosphate pesticide residues [1] . Maximum limit of pesticide residue in rice is 0.1 mg/kg and the vegetables of 0.5 mg/kg [2] . Therefore, we need some good control levels of toxic compounds, as although not deadly but that can accumulate in the body, which can cause dangerous diseases.
The conventional methods for organophosphate pesticide residue analysis are gas chromatography (GC) and High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). However, both methods have the disadvantage that the test sample and the preconditions need a relatively long time, and are less accurate if not all pesticides can be analyzed simultaneously [3] . Appropriate solution to address the lack of GC and HPLC are biosensors. Biosensor offers a variety of benefits; it has very high selectivity and rapid testing, it can be used repeatedly, and it is very easy to be used on the direct determination in real samples [4] .
Organophosphate pesticide biosensor is made based on the hydrolysis of organophosphates by organophosphate hydrolase (OPH) as a biocatalyst. Hydrolysis is resulted in H3O+ ions which can be detected by potentiometric, amperometric [5] [6] , and conductometric. This study used a conductometric transducer, because it has several advantages; it uses a smaller electrode, and needs a low voltage and low-cost production [7] .
Using conductometric transducers have been developed based on reaction inhibition acetilcholinesterase on cholesterol [8] [9] . Conductometric biosensor using a modified Pt electrode—nata de coco has also developed for the detection of uric acid [10] . Biosensor performance is affected by the pH and the amount of the enzyme, so that the research was conducted by the amount of enzyme and the pH optimization.
Conductivity measurements based on reaction [11] :
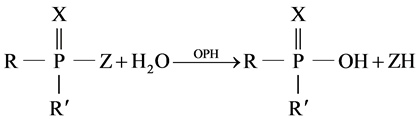 (1)
(1)
R and R' aromethoxy groups, Z is phenoxy groups, and X is O or S
 (2)
(2)
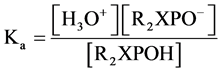 (3)
(3)
Initial concentration of R2XPOH linear with organophosphate concentration so:
 (4)
(4)
The conductivity of the solution generated by the hydrolysis of organophosphate, that can be calculated according to the following equation:
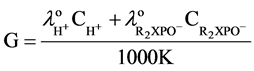 (5)
(5)
Because the OPH optimum performs at pH 7.5 - 9.5, the organophosphate pesticide dissolved in tris-HCl buffer which has very low conductivity.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
Organophosphate hydrolase was isolated from Speudomonas putida. Bovine serum albumin (BSA), Tris, and diazinon were purchace from Sigma Aldrich (USA). Tris-HCl buffer was made in steril distilate water . Fresh stock solutions were made in Tris-HCl buffer. Diazinon (O,O-Diethyl O-[4-methyl-6-(propan-2-yl) pyrimidin-2- yl] phosphorothioate; CAS [333-41-5]; Mw = 304.35 was used as a standard organophosphate insecticide. Screen Printed Carbon Electrode (SPCE) was purchace from QUASENSE Thailand
2.2. The Design of Biosensors Organophosphate
On the 1 × 5 mm2 of SPCE surface drops of 10 mL BSA (bovine serum albumin) 5%, and 0.1% glutaraldehyde 10 μL. Then, dried at 40˚C for 1 hour. Furthermore, 5, 10; 15; 20 and 25 µL of OPH solution (7 µg/µL) injected on the SPCE-BSA surface and that stored for 24 hours at 4˚C. Before it is used, SPCE washed with Tris-HCl buffer pH 8.
2.3. Measurement of Solution Organophosphate Conductivity
Biosensor immersed in a solution of Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5; 8.0, 8.5; 9.0 and 9.5) to obtain readeble conductivity. That repeated every measurement of solution conductivity. Then, the biosensor immersed into a solution of diazinon (appropriate pH) and conductivity recorded after the display indicates a readeble value.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Organophosphate Hydrolase
The concentration of the enzyme is one of the affecting factor to the rate of reaction, so that affects to the performance of biosensors. The results showed that the highest sensitivity of biosensor at OPH 70 and 105 μg, but the best correlation coeffcient was in 105 μg OPH (Table 1). The OPH more than 10 μg, the sensitivity and correlation coefficient are decreases. This is caused by limitations of the surface area of SPCE. With a size of 1 × 5 mm, surface of SPCE only accommodate 105 μg OPH, because enzymes cannot be immobilized completely. SPCE surface has been coated by BSA-glutaraldehyde, that has a varied pore sizes, Figure 1. The pore size which can be immobilizing enzymes that are have a fits size with the OPH, thus the immobilized OPH cannot be increased by OPH mass. Other possibility, the OPH accumulated on the electrode surface and that blocking of

Table 1. The sensitivity of biosensors in various of OPH mass.

Figure 1. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) image of the electrode surface.
ions migration.
The sensitivity of biosensor at 70 µg OPH is good enough but the correlation coefficient is still not adequate, it may be caused by of OPH on the SPCE surface which is uneven, so that is difference in velocity of ion migration. If the OPH less than 70 µg, biosensor sensitivity is very inadequate, the signal is only generated by the migration of ions from buffer solution. Based on these results, we can conclude that the optimum mass of enzyme depends on the area of the electrode. Thus, the further research should be carried out optimization of SPCE area.
3.2. Biosensor Characterization
In this study, purpose of biosensor characterization is investigation of the working conditions of biosensors to obtain the maximum performance. The research studied of biosensor character is pH and response time. The pH optimum of biosensor is affected by pH of enzyme. The pH optimum of OPH at a range from 7.5 to 9.5, depend on the source of OPH, immobilized media, the type and concentration of buffer. Response time is a measure of the rate of reaction between the enzyme and the substrate, if the response time is too long, that indicate low enzyme purity.
3.2.1. Effect of pH Solution
Correlation equation of pesticide concentration and conductivity at various pH are shown in Table 2. The highest sensitivity of biosensors resulted at pH 9, but correlation of concentrations and the signal is not sufficient. This shows that although ions on the surface of the inside of SPCE are high, but not proportional to the concentration of pesticides in the solution. Biosensor sensitivity at pH 8.5 lower than at pH 9, but a correlation approximately 1, so it can be concluded that the optimum pH biosensor is at pH 8.5.
Performance of the biosensor at pH 7.5 and 8 are very low, because the OPH is not working optimally so that the hydrolyzed pesticides are not relevant with actual pesticide concentration, it is seen from the correlation is less good. Although theoretically, pH optimum of OPH at a range 7.5 to 9, but formation of ions from hydrolysable pesticide also dependent on the pH. Hydrolysis of organophosphate by OPH is generate a weak acids, so that ionization is strongly influenced by the pH at pH > pKa. It is not certain pKa values of pesticides hydrolyzed but it depends on the kind of pesticide.
Performance of OPH at pH 8.5 to 9.5 estimated similar, but the amount or type of pesticide hydrolyzed ion charge is different. In this study, diazinon is as the test solution. Diazinon structure is more complicated than the other organophosphate pesticides, and produced two simple compounds which are possible to perfectly ionization at different pH. Another possibility, the maximum number of ions formed at pH 9, but that not compatible with pores size which can be passed by ions, so that the probabilities become uneven. The biosensor performance is a like biosensor with chitosan membrane that has optimum performance at pH 9. It is possible there is little difference in the type of immobilization. More over chitosan pores have different sizes with BSA pores.
3.2.2. Response Time
The response time is defined as the time required by the device to interact with the sample to be resulted in the signal that can be read. Biosensor response time was only a few seconds, as if too long will allow the release of bioactive immobilized. The results showed that the response time affected by the concentration of pesticides, Figure 2. At this stage, the concentration of pesticide solutions are 0; 0.1; 0.3; 0.5; 0.7, and 1 ppm, according to the range of concentrations which can provide a linear relationship with the signal.
In Figure 2, it can be seen that the faster response time is achieved at higher concentrations of pesticides. That indicating the reaction rate of pesticide directly proportional to the concentration [12] . From this data it can

Table 2. Sensitivity of biosensor in various of pH solution.

Figure 2. Curve relationship between measurements time and the conductivity at various concentrations of pesticides.
be seen that the range of concentrations of pesticides which can be measured by the biosensor is less than Km [13] . This is important because an analytical biosensor will have a good sensitivity if the range of concentrations that can be measured is smaller than Km. Determine the exact response time from Figure 1 is very difficult because the signal for all concentrations tend to rise over time. Therefore, the regression equation was made at an all time measurements, Table 3.
Time measurement is the effect on the sensitivity of the biosensor despite all of the data showed a good sensitivity and a good correlation coefficient, there is a trend of increasing sensitivity. In the measurement of the 45 and 60 seconds biosensor sensitivity did not differ significantly. Thus it can be used 45-second response time. Researchers recommend that measurements to 15 seconds can be done, but on the condition of measurement time is the same for all samples, this can be done to extend the life of the biosensor.
From the characterization results, it can be concluded that the biosensors can be used to measure pesticide concentrations organophosphate in the range 0 to 1 ppm. Concentration range is smaller than Km, thus already eligible analytically. Optimum performance of biosensor generated if the sample is dissolved in the buffer solution of Tris-HCl at pH 8.5 and measurements were taken at 45 seconds.
3.3. Biosensor Performance
Performance of the biosensor is indicated by analytical detection limit and sensitivity. The regression equation was made of the average data repetition. The regression equation is y = 28.04x + 75.85, that obtained the sensitivity of the biosensor is 28.04 μS/ppm. Statistically determined also detection limit is 0.18 ppm. This means that the biosensor can be used to measure pesticide concentrations greater than 0.18 ppm. According to government regulations, maximum residue limits of pesticides in rice at 0.1 ppm and 0.5 ppm for vegetables. Thus pesticide biosensor can be applied only to measure pesticide residues in vegetables. Therefore, the biosensor is yet to be perfected in order to obtain a lower detection limit of less than 0.1 ppm.
This research also applications to real samples, the measured levels of pesticide residues in some vegetables, such as lettuce, cabbage, and spinach. However, because of the amount of each vegetable sample not representative enough so these results cannot be informed. Through this report only inform that developed a biosensor that can be applied to determine the levels of pesticide residues in vegetables. For further biosensor development required more testing of samples of agricultural products both fruits and vegetables
4. Conclusion
From the research, it can be concluded that the optimum biosensors resulted at 105 µg of OPH on SPCE size 1 × 5 mm2. The optimum performance of biosensors resulted at pH 8.5 by measuring response time 45 seconds. In optimum conditions the sensitivity of the biosensor is 28.04 μS/ppm with a detection limit of 0.18 ppm. To obtain a biosensor that can be mass produced it needs some development in terms of both conductivity cells and instruments.

Table 3. Sensitivity of biosensor at various time measurement.
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful to University of Brawijaya Research Institute, Malang Indonesia
NOTES
*Corresponding author.