Oxygen uptake, heart rate, and work rate at ventilatory threshold for treadmill walking against a horizontal impeding force ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Level walking and cycle ergometer exercise are representatives of different modes of exercise for health and fitness. For a cycle ergometer exercise, the load determines the exercise intensity at a certain pedal frequency. In contrast, the intensity of level walking depends on velocity. In other words, the velocity, which is a factor of the “force-velocity relationship” during muscular contraction, controls the exercise intensity of level walking. However, during treadmill walking against a horizontal impeding force (horizontal load walking) at a constant velocity, an increase of load is considered as the increase of force in the force-velocity relationship.
Experimental studies of locomotion using a horizontal load on a treadmill began in order to determine the mechanical efficiency of movement. Lloyd and Zacks [1] estimated the mechanical efficiency (Apparent Efficiency, AE) during treadmill running on the basis of the rate of increasing energy expenditure for increment of work rate (load × velocity). Asmussen and Bonde-Petersen [2] also reported about the AE of walking and running using a similar technique according to Lloyd and Zacks [1]. Bijker et al. [3] compared the delta efficiency of running with that of a bicycle ergometer exercise. Furthermore, the AE of running was compared between adults and children [4], and the effect of footwear (Japanese wooden clogs) on the AE of walking was also evaluated [5]. In those studies, the horizontal load was gradually increased during consecutive exercise bouts (constant time interval), and the corresponding metabolic cost was determined. Recently, a ramp slope technique has been widely used with cycle ergometer tests as a means to incrementally increase the load. However, a horizontal load on a treadmill using this technique has not been developed.
In general, a ramp slope exercise test is a technique for imposing consecutive, sequential linear loads using an electrically-braked cycle ergometer, which is controlled by a computer. With this technique, subjects continue to exercise up to their maximal or sub-maximal levels, and medical and physiological parameters such as exercise electrocardiography readings, maximum oxygen uptake, and the ventilatory threshold (VT) can be determined. In particular, the VT is recognized as the level to safely improve cardio-respiratory function and endurance by physiologists and physical trainers, and is also known to minimize the discomfort associated with lactate accumulation during exercise [6]. Because it was clear that the energy cost increased linearly with the linear increment of a horizontal load in previous studies on efficiency, the VT during horizontal load walking may be detectable using a ramp slope technique.
Level walking is one of the moderate aerobic exercises that can easily be done by anyone. In addition, horizontal load walking does not require fast or quick movements even if the exercise intensity is increased because the walking velocity is constant. Therefore, it would be expected that aerobic conditioning at the VT level during horizontal load walking would be safe and useful for an exercise prescription. In contrast, several studies have found that the VT differed between different modes of exercise [7,8]. Therefore, it was assumed that the VT of horizontal load walking could be characterized by comparing it with that of a cycle ergometer exercise.
The purposes of this study were to determine the VT of horizontal load walking and to compare the VT of horizontal load walking with that of a cycle ergometer exercise.
2. METHODS
2.1. Subjects
Subjects were seven healthy male adults who had no history of orthopedic diseases that could affect walking and cycling (mean ± SD; age: 30.9 ± 7.0 years; height: 170.4 ± 8.8 cm; body weight: 66.1 ± 14.1 kg). The purpose, procedures, and risks of the experiment were explained before participating in this study, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. This study followed the principles outlined in the declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Procedures
On the basis of methods described in the previous studies, subjects performed horizontal load walking at 1.11 m/s (4 km/h) [2,5]. Horizontal loads were imposed using weights in a small basket that was connected to a wire, which was passed through a pulley and attached to a band around a subject’s waist (Figure 1). A ramp slope technique was used to load a sand bag weighing 0.16 kg in the basket every 6 seconds. The rate (slope) of the increment was 16.7 W/min. Subjects walked without loads for 3 min and the horizontal load by the ramp slope began to be imposed after unloaded walking. Loaded

Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental set-up.
walking was continued until subjects achieved up to 85% of their estimated maximum heart rates (HRmax, estimated by using the formula 220-age). The slope was preliminarily decided so as to reach 85% of HRmax during load walking for almost 10 min. Subjects also performed a cycle ergometer exercise at 60 rpm, and a ramp slope was imposed by an electrically-braked cycle ergometer (Combi, 75XLIIME, Japan). The slope was set at 20 W/ min by an automated program incorporated in the ergometer after 3 min of unloaded pedaling. Subjects also continued to perform pedaling up to 85% of their HRmax like a case of the horizontal load walking.
2.3. Measurement of Ventilatory Threshold
Expired gas during exercise was continuously collected by the breath-by-breath method. Ventilation ( ), oxygen uptake (
), oxygen uptake (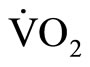 ), carbon dioxide production (
), carbon dioxide production (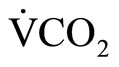 ), end-tidal pressure of O2 (PETO2), and end-tidal pressure of CO2 (PETCO2) were measured using a respiration gas analyzer (Minato Medical Science, AE300- SRC, Japan). Heart rate was monitored at the same time with a telemetry system (Nihon Kohden, LIFESCOPE6, Japan). VT was determined as the beginning of the nonlinear increase in
), end-tidal pressure of O2 (PETO2), and end-tidal pressure of CO2 (PETCO2) were measured using a respiration gas analyzer (Minato Medical Science, AE300- SRC, Japan). Heart rate was monitored at the same time with a telemetry system (Nihon Kohden, LIFESCOPE6, Japan). VT was determined as the beginning of the nonlinear increase in 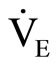 and
and 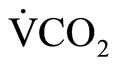 and an increase of
and an increase of  without an increase in
without an increase in 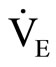 /
/ while PETO2 began to increase systematically without a decrease in PETCO2 [9-11]. Oxygen uptake (
while PETO2 began to increase systematically without a decrease in PETCO2 [9-11]. Oxygen uptake ( @VT, L/min and mL/kg·min), heart rate (HR@VT, beats/min), and work rate (WR@VT, W) at VT were compared between horizontal load walking and the cycle ergometer exercise. The VT during horizontal load walking was measured twice and the measured variables during each trial were averaged for comparisons.
@VT, L/min and mL/kg·min), heart rate (HR@VT, beats/min), and work rate (WR@VT, W) at VT were compared between horizontal load walking and the cycle ergometer exercise. The VT during horizontal load walking was measured twice and the measured variables during each trial were averaged for comparisons.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Paired t-tests were used to compare the results for each VT variable (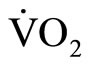 @VT, HR@VT, and WR@VT) between horizontal load walking and cycle ergometer exercise. Pearson’s correlation coefficient, the standard error of estimation, and a confidence coefficient were also determined for two trials of
@VT, HR@VT, and WR@VT) between horizontal load walking and cycle ergometer exercise. Pearson’s correlation coefficient, the standard error of estimation, and a confidence coefficient were also determined for two trials of  @VT during horizontal load waking. The confidence coefficient was based on the results of one-way analysis of variance [11]. A pvalue of <0.05 was considered significant.
@VT during horizontal load waking. The confidence coefficient was based on the results of one-way analysis of variance [11]. A pvalue of <0.05 was considered significant.
3. RESULTS
The VT during horizontal load walking could be determined for all our study subjects using the ramp slope technique, as shown in Figure 2. Table 1 shows a com-

Figure 2. A typical subject’s response to a ramp exercise test during horizontal load walking.

Table 1. Comparisons of oxygen uptake, heart rate, and work rate at ventilatory threshold (VT) between horizontal load walking and cycle ergometer exercise.
Values are Means ± SDs (n = 7). *p < 0.05.
parison of the VT results between horizontal load walking and cycle ergometer exercise.  @VT during horizontal load walking was significantly greater than that during the cycle ergometer exercise (p < 0.05), whereas the opposite was found for WR@VT (p < 0.05). In addition, HR@VT during horizontal load walking was slightly higher than that during the cycle ergometer exercise, although this difference was not significant. According to comparison among two trials for each subject, the correlation coefficient, standard error, and the confidence coefficient were 0.97, 0.097 L/min, and 0.96, respectively.
@VT during horizontal load walking was significantly greater than that during the cycle ergometer exercise (p < 0.05), whereas the opposite was found for WR@VT (p < 0.05). In addition, HR@VT during horizontal load walking was slightly higher than that during the cycle ergometer exercise, although this difference was not significant. According to comparison among two trials for each subject, the correlation coefficient, standard error, and the confidence coefficient were 0.97, 0.097 L/min, and 0.96, respectively.
4. DISCUSSION
Greater  @VT during horizontal load walking was observed as compared with that during a cycle ergometer exercise. This suggests that muscle mass recruited for exercise is much greater during horizontal load walking than during a cycle ergometer exercise because pedaling requires fewer muscles (lower extremities). It is well known that the maximal oxygen uptake depends on the muscle mass recruited for exercise [12-15]. Similarly, some reports showed that
@VT during horizontal load walking was observed as compared with that during a cycle ergometer exercise. This suggests that muscle mass recruited for exercise is much greater during horizontal load walking than during a cycle ergometer exercise because pedaling requires fewer muscles (lower extremities). It is well known that the maximal oxygen uptake depends on the muscle mass recruited for exercise [12-15]. Similarly, some reports showed that  @VT during rowing or running was greater than that during a cycle ergometer exercise [7,8]. It is plausible that whole body exercises as compared with partial exercises yield higher values for aerobic parameters. Furthermore, it was postulated that the greater metabolic cost was caused by the small output (WR@VT) during horizontal load walking.
@VT during rowing or running was greater than that during a cycle ergometer exercise [7,8]. It is plausible that whole body exercises as compared with partial exercises yield higher values for aerobic parameters. Furthermore, it was postulated that the greater metabolic cost was caused by the small output (WR@VT) during horizontal load walking.
The reliability of the VT during a cycle ergometer exercise has been questioned in previous studies. Davis et al. [16] reported that the correlation coefficient was 0.91 and the standard error of estimation was 0.085 - 0.131 L/ min for  @VT according to two trials for the same subjects (n = 9). Caiozzo et al. [11] also reported on the reliability of
@VT according to two trials for the same subjects (n = 9). Caiozzo et al. [11] also reported on the reliability of  @VT according to two trails (n = 20), which accounted for approximately 0.8 of the confidence coefficient. The results for the correlation coefficient, standard error, and confidence coefficient were comparable to those in previous studies (cycle ergometer exercises). This indicates that the VT during horizontal load walking is a reliable, practical index for aerobic conditioning.
@VT according to two trails (n = 20), which accounted for approximately 0.8 of the confidence coefficient. The results for the correlation coefficient, standard error, and confidence coefficient were comparable to those in previous studies (cycle ergometer exercises). This indicates that the VT during horizontal load walking is a reliable, practical index for aerobic conditioning.
5. CONCLUSION
The results of this study showed that horizontal load walking can be useful from the perspective of expending a greater metabolic cost than with a cycle ergometer exercise at the VT level. This physiological benefit suggests that horizontal load walking could be prescribed as an effective aerobic exercise.