Design of Integrated Monitoring and Early Warning System of Urban Rail Transit Train Running State ()
1. Introduction
With the high-speed development of urban railway, the train operation control, traffic safety, running real-time monitoring and fault diagnosis, rapid and efficiency of train trouble shooting become the key elements of the development of the industry. It is the new trend to design the monitoring system which is more conducive to the healthy development of the industry and provides more reliable transport service for traveler [1].
Comprehensive monitoring system of train safety is a complex systematic project; it needs taking the train control and management measures for various factors of train operation safety [2]. But it has not formed a complete integrated architecture to monitor the traffic operational conditions from multi-dimensions and multi-levels, and most of the existing train monitoring system analyzes only based on parts such as the collection, transmission, reliability evaluation, fault diagnosis and early warning of the equipment state, which is still in a scattered and immethodical state of system. These problems will be the bottleneck of restricting rapid development of urban rail transit. It is imperative to build advanced comprehensive intelligent monitoring system by intelligent decision technology, information processing technology, communication technology, and emerging technologies in the beginning of large-scale urban rail construction.
The characteristic of comprehensive monitoring system of train safety in urban mass transit is the large amount of integrated and interconnected sub-systems which are of big differences, complicated field devices with quick technique development, high automation grade with requirement for safety, stability and reliability. Comprehensive monitoring system of train safety in urban mass transit is developed from manual, separated system to integrated supervision control system. Today IMEWS is the main form adopted in domestic subway construction and will trend towards deep integration and traffic control center.
This article analyzes the characteristics of integrated monitoring and early warning system of urban rail transit train running state and puts forward that we need to create a targeted, adaptive integration architecture based on the existing integrated system. The state of the critical systems, the train running status and the train group state are monitored and analyzed in real-time through sensor network around the train to realize the exact location of the fault, the timely warning of security risks and provide the train emergency decision-making for OCC and drivers according to the information of expert database.
The mastery of the holographic train running status provides support for the managers and users. This system adopts the large-capacity train-ground wireless communication system, whose characteristics such as large-capacity, wireless and immediate guarantee the real-time monitoring, help managers understand the status of the entire urban rail transit in real-time intuitively and accurately and support the management effectively The system enhances the utilization efficiency of the device, reduces the operating costs urban rail and improves the decision-making level of managers to provide a safe traveling environment for passengers by monitoring and early warning of urban rail train running status effectively. The system realizes the service standard of urban rail transit with high-security, high-efficiency and high-quality. This paper will discuss the design of service framework, system framework, the system functions and the introduction of critical technologies.
2. Service Framework Analysis
In this paper, the designation of service framework of IMEWS of urban rail train running state should be started with analyzing user demand of urban rail operation enterprises by means of “top-down” and “bottom-up” mixed technique. On the basis of comprehensive demand analysis, merge similar demand, mining potential demand, form a clearly specific services division and service function on comprehensive monitoring early warning system. The research process is as follows.
2.1. Definition of System User Principals
Definition of system user principals is the prerequisite and foundation for demand analysis and customer service definition. Combined with the specific situation of domestic urban rail transit, the user principals of IMEWS can be divided into four main categories: enterprise management decision making department, train dispatching department, maintenance scheduling and system maintenance department.
2.2. User Requirements Analysis
Through demand analysis of the above four type of user principals, requirements of management department of enterprise for comprehensive monitoring system can be described as the table 1.
2.3. Definition of Comprehensive Monitoring and Early Warning System Services
According to the result of demand analysis, merge and arrange the same content and get service framework of comprehensive monitoring and early warning system shown in the table 2.
3. Integrated Monitoring and Early Warning Framework
System integration is the organization method of system structure essentially to combine different function module of software system with the data into a new system for the end user, the integration is not simple superposition of various software modules, but the individual components are integrated by using different methods at different levels in order to obtain the synergetic benefits and form a complete application for users, which can realize timely information exchange, comprehensive utilization, resources sharing, and unity of command and ensure monitoring and early warning system to be efficiency and timely and accurately on emergency [3]. So it is necessary to establish a comprehensive, adaptable overall framework of system which can dig hidden danger (see Figure 1).
The primary design goal of this system is to ensure the safety of train operation. The integrated system contains information and control systems, the various types of integrated systems need to maintain a high independence, to ensure system safety and reliability [4]. Considering the difference of the integrated system on design of system data, the time scale of the data and spatial scales are also very different, so the system is designed a high-capacity train-ground communication systems, which meets the requirements of large-capacity storage and timely transmission, and imports data to the corresponding database in artificial, automatic and TCP/IP way to achieve the data sharing and fusion [4]. The combination between the train safety monitoring system and the ground expert diagnostic system provides effective technology platform for the vehicle maintenance and also provides decision support for emergency response by monitoring and early warning platform integrate monitoring resources of application system, and fuse and process to realize the seamless connection of each monitoring application systems [5]. The platform contains three layers: the data access layer, the database layer, business presentation layer.
3.1. Ground Data Center
Ground data center is the base layer of a comprehensive monitoring platform. It has information interface of original monitoring subsystem and a database server for preliminary storage of data. This layer is the bottom of

Table 1. User requirements of urban rail transit operation enterprise management department.

Tale 2. Service framework of comprehensive monitoring and early warning system.
integrated framework, contains variety of data and its storage format like various business and alarm data and spatial data. Ground data center invokes data form monitoring subsystem, sent data into the integrated monitoring system platform at the same time [6].
Because data center contain a large number of spatial data, it has a variety of formats of spatial data, such as MapInfo, Arc Info, Oracle, Spatial, XML etc. The management of spatial data has two parts: spatial data model and spatial database. Spatial data model describes the spatial entity in real world and the relations among them and provides a basic method for spatial data organization and spatial database design. OGC proposed the standard of spatial data model based on GML, the major GIS vendors and database manufacturers have also developed product to support this specification and lay a good foundation for the spatial data sharing.
3.2. Data Access Layer
This layer sends the collected basic data into the database in different ways; realize the unified transmission and sharing of data source of different communication way and data formats. TCP/IP has the effective fault isolation and anti-interference measures. Data access layer is to detect the main interface equipment front-end processor (FEP) among systems, FEP completes conversion of all kinds of communication protocol and inserts multiple field control bus or network of each system.
3.3. Database Layer
Divide corresponding data table according to the monitoring system types and their purposes, which is convenient for foreground query and access, and also is full of benefits for maintenance and management of the back-

Figure 1. Overall framework of integrated monitoring and early warning.
stage. The data storage and management use the model of table space management of Oracle database. Data belonging to different monitoring methods are placed in a separate table space for management [7].
The integrated monitoring software generally uses the distributed database technology. In system not only the central server, domain server but also the I/O station and operator station is taken as server to provide some or all data access in real-time for the system. The real-time data distribute at all levels. Therefore, software application process can rapidly and effectively access the data. Distributed real-time database integrates the information from every station in a certain geographical range into a global database; any operator station can visit each server to complete the monitoring of local or remote.
3.4. Presentation Layer
When comprehensive monitoring system realized the data processing, system configuration, running status and operation record, it need to separate the business logic and user interface, then form a set of corresponding user interface. Presentation layer mainly use form and figure to display information of the critical equipments. Operator can observe the equipment’s parameter variation and fault information in running, and make the corresponding treatment timely and directly. System maintenance personnel is the vehicle maintenance personnel, they operate the interface to complete altering train information, setting parameter information, querying the historical data and the changing curve of data. These operations through the login authentication and identity can be. These operations can be finished by the login authentication. Decision-makers can assist the decision-making of equipment repair dispatching the disaster prevention, security and rescue, and operation plan, etc.
The presentation layer has two forms of terminal type: one is the standard WEB browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator, the client of the browser has the advantages of the low requirement for hardware, simple way of maintenance and upgrade mode and low cost, but this way make the server load in heavy, make the collection and said of complex information more difficult. Another is the traditional GUI client, compared with the browser, this way require higher to the hardware, client software needs to be installed on each of the machine, maintenance and upgrade costs higher, but it has rich graphics, timely user action response, etc. Different levels of security surveillance systems, the client can take different forms according to their functional requirements. In actual construction system, these two forms are sometimes combined, a system exists two expressions at the same time, using GUI technology to display and collect the complicated information, display and collect the simple information by using browser implementations.
4. Overall Function Framework
4.1. Diagnosis Function of System
The diagnosis system is used to determine whether the working state of every part of comprehensive monitoring system is normal to provide security assurance for security monitoring of the train. The vehicle sensor system, fault diagnosis system, transmission system between vehicle and ground facilities, hidden trouble mining system and trackside system are integrated into the comprehensive monitoring and early warning platform where the information produced by each business system of urban rail can be checked, the working condition of systems can be diagnosed according to the examination of realtime data transferred from the data center, the data transferred from and into the data center change within the specified scope while the comprehensive monitoring system is under normal operation, when the received data is missing, or the data changes unusually over a period of time, it will be thought that the data transmission system or data center storage has problems, and then the operation station releases alarm information, and report the fault occurrence time, physical location of failure point, failure cause and type what will be displayed and be printed and logged to disk. Whether transmission system or data center storage has problems can be judged by using ping command to check the network
4.2. Monitoring of Running State of Train
4.2.1. State Monitor Function of Train Group
The condition monitoring of train group is mainly used to reflect running state of trains and provide the reference for vehicle center, the main monitoring content is: the interval train density; the driving distance. The operation safety of trains can be judged by monitoring the above information; the interval average running speed monitoring interval each average uplink and downlink direction train running speed and the interval average running time.
4.2.2. State Monitor Function of Train
State monitor function of train is to diagnose the train fault preliminary by testing the safety parameters of running trains, the main monitoring content is: running speed of trains; acceleration of trains; horizontal pendulum of running trains which is tested by monitoring the lateral acceleration; vibration condition of running trains, the working state between the pantograph and catenary can be reflected by monitoring vertical acceleration of vehicles.
4.2.3. Running State Monitoring of Critical System
The critical systems of trains mainly contain power system, brake system, running gear system, suspension system, vehicle door system and auxiliary inverter system. The system will carry on monitoring of all critical systems of trains. When the external business system is in failure or an error occurred in data transmission process, the monitoring system will alert users and display the current state of the trains.
4.2.4. Fault Warning Function of Running Trains
The information about hidden trouble will be sent to relevant departments before the critical systems in failure affect the running safety of trains. The decision-makers make relevant treatments to reduce the operation cost and improve the level of running safety. The specific function can be explained as that the fault alarm prompt is displayed on the comprehensive monitoring and early warning platform to remind relevant departments of the abnormal running state, and then the alarm details of the fault including alarm time, fault occurrence time, fault location, name and level will be displayed in the form of message box and shown to relevant departments.
4.2.5. Collaborative Emergency Treatment Work
Platform is responsible for the implementation of relevant monitoring resources deployment and command when there are abnormal events in daily work and management process. According to the overall integration requirements, the following functions are provided: monitoring and analysis of the various equipments and system status in real time; responding to the fault diagnosis information of train operation and according to the requirement of train fault emergency treatment work of the OCC staff; starting corresponding plans to provide technical support of emergency treatment for the OCC staff and producing relevant technical documents to improve the work efficiency of emergency response and handling when emergency happens. The content of collaborative emergency treatment work contains database management, emergency treatment advice and management of emergency treatment interface.
5. Critical Technologies of System
In order to improve the efficiency of the data utilization and realize data-sharing and centralized management and control of every subsystem, the information integration and functional integration of the monitoring and early warning system of train operation which can help operation and management personnel monitor the operation of trains on the line more conveniently and safely is needed. This paper summarizes the existing integration technology; get of the key technologies of comprehensive monitoring system implementation of urban rail transit
5.1. Interface Technology
The key of system integration is the application of open system and the seamless access of subsystems. In order to make the interface development standardization, IS015745 make regulation that the interface specification is represented by using the Application Interchange Profile (AIP), the interface should be developed according to AIP specification For the implementation of comprehensive monitoring system of urban rail transit, 422 RS and 485 RS are mainly used as serial data interface. The Ethernet topology structure complying with IEEE 802.3 standard and the TCP/IP network protocol are adopted in development of LAN data interface. The uniform interface platform for integrated industrial bus and system network is established in order to meet the communication requirements of field equipments and control.
5.2. Multi-Sensors Data Fusion Technology
In order to provide accurate real-time train running status information, the different kinds of data from multiple data sources should be fused for the reason that a variety of monitoring means and numerous sensors are used by comprehensive monitoring system implementation of urban rail transit. The data fusion processing model of the monitoring system mainly contains the following sections.
5.2.1. Data Collection
The data collected contains real-time data from various sensors and video.
5.2.2. Primary Filter
For the reason that the data which comes from various data sources is at different level, dimension and form, the primary filter processing should be made by adopting different means including filtering and digitalization before the data enter the host computer of monitoring system. The main treatment methods can be illustrated as image processing, digital filtering, etc.
5.2.3. Primary Treatment
A series of data operation including proofreading, recognition, correlation analysis and synthesis of the data or variable should be applied for the process of the digital data; some results can be directly imported into the data management system for the use of users, others have to be conducted in the secondary treatment.
5.2.4. Secondary Treatment
The system identifies and assesses the state of targets monitored to give the accuracy of evaluation result as soon as possible and provide the final results (alarm information, decision support information, etc.) for monitoring and operating personnel and all relevant departments by using various real-time data and original data and expert system knowledge within databases coordinately, the results will be sent to the data management system at the same time, and the various data will be dealt with the main treatment technologies including image recognition, fuzzy reasoning and expert system, etc, which is also supported by the database technology.
5.2.5. Man-Machine Interface
Monitoring and operation personnel provide alert information for relevant departments according to the information provided by the computer, and contact with each department timely and dispatch in failure.
5.3. The Technology Standards and Norms System of Monitoring and Early Warning of Urban Rail Train in Transit
Index system can be defined as a scientific and complete whole which is made up of a series of related and constrained indicators. Because the success of early warning depends on the proper index selection, and the key to the early warning research is to construct perfect index system.
Taking monitoring and early warning system of urban rail train in transit as the research object, the technology standards and norms system of monitoring and early warning of urban rail train in transit which is composed of the framework of technology standards and norms system, the overall index system, the standard system of Integrated application and the standard system of R&D is formed by combining the external constraint of system engineering application. The technology route is shown in the figure 2 [8].
5.4. Expert Database Based on Semantic Technology
So far, because the train fault in the operation state is
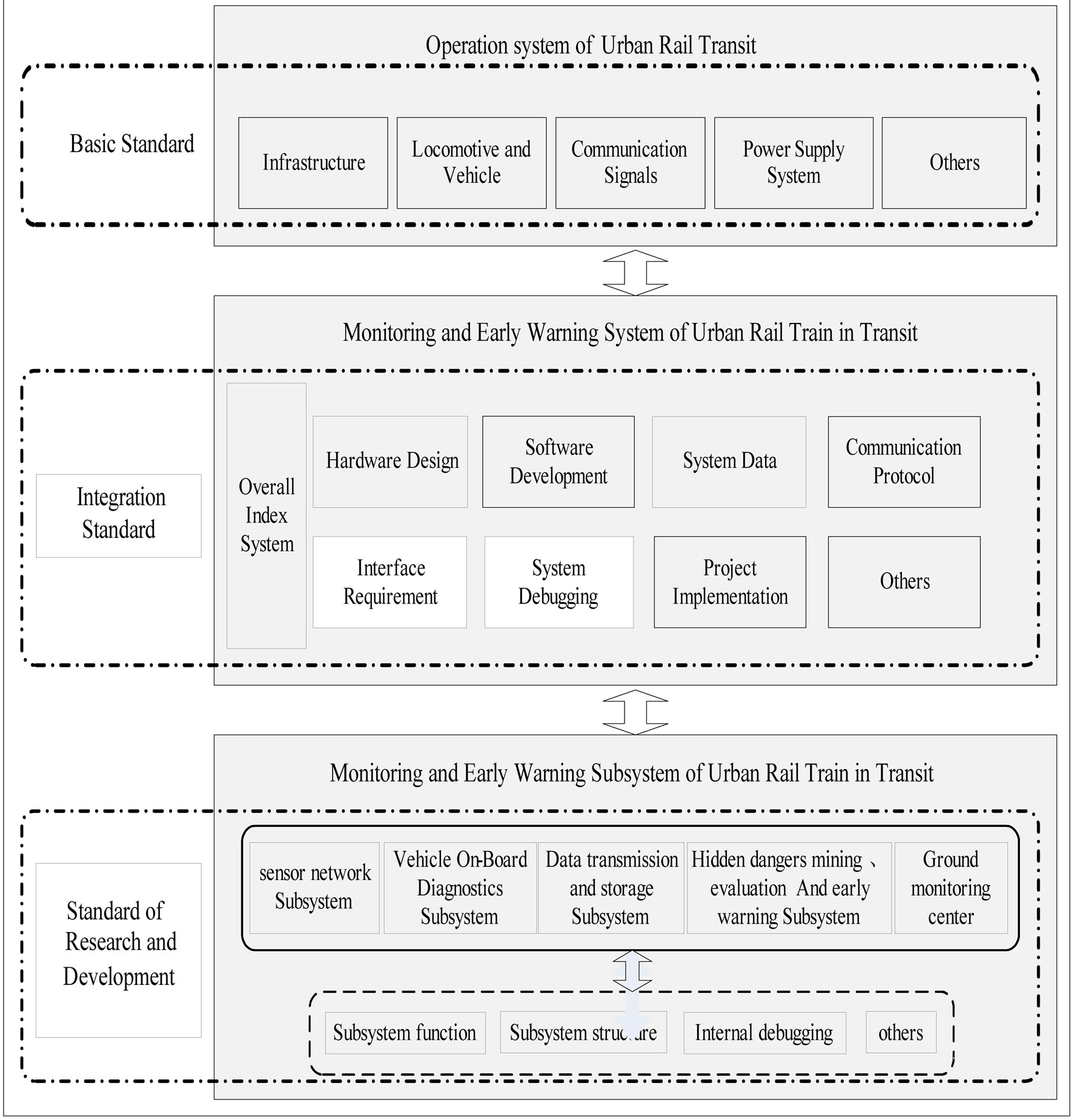
Figure 2. Technology route of the technology standards and norms system of monitoring and early warning of urban rail train in transit.
decided by the discussion of relevant decision makers and maintenance personnel, for users, how to make the right decisions in the shortest time is the key to improve the treatment efficiency, an effective way is to take similar fault disposal experience as reference in the past, but since the difference of participants of each failure event, many important decisions made under the state of emergency are not reorganized and analyzed specifically, so it is necessary to storage and manage the process of emergency disposal happened in the form of case to form expert database and provide reference for the decisionmaking of future similar events. The information issue in existing expert database refers to release information stored in the database through the web, the database is the data source of information release, its type is various and its standard is very complex. Developers need to master a variety of specifications to do development work; there is almost no reusability for dedicated program, the developers must modify the program once the database structure changes. There are many similarities among every information release, the repetitive work consumes developers a lot of time and energy [9].
Semantic technology can construct information release by itself on the basis of understanding user need, keep the developer free from a large number of repeated programming work and realize the software reuse, thus building expert database based on semantic provides quick fault information displaying and decision-making with help at the time of the accident [10].
5.5. Data Mining Technology
Based on data sharing platform of intelligent integrated monitoring and control system, carry on the analysis and comparison from a multidimensional angle to achieve reunification of the analysis method facing data and model and make full use of smart technology to extract the information hidden in the data to find the rule and knowledge behind the data and predict the future behavior. Thus decision support for dispatching and maintenance schedule is provided [11].
Decision tree, neural network, fuzzy statistics are the mainly used data mining techniques. Decision tree learning algorithm is mainly used for in-depth analyzing classification problems, is the main technique of classification and prediction. Compared with discriminate analysis, nonparametric statistics and clustering analysis algorithm. Decision tree really has flexible and convenient form, which made it have wider application space. Artificial neural network algorithm is abstract algorithms which simulate the human brain neuron structure. Knowledge expression and acquisition would be the main breakthrough to improve neural network algorithm.
6. Conclusions
This paper discusses the design of service framework, system framework and the system functions and introduces the critical technologies. This article puts forward a framework on how to establish comprehensive monitoring and early warning system of urban rail transit.
There are still a lot of details to be further studied. The proposed system is an intelligent monitoring system, which is based on automation system of computer industrial, computer communication network and communication equipment, so these key technologies must be studied intensively.
In addition, the construction of monitoring and early warning system need the professional, mechanical and electrical professional cooperation of computer and traffic engineering. The scientific and economic comprehensive monitoring system is established only in this way so as to realize the operation standards of urban rail transit with high safety, high efficiency and high quality service.
7. Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the ministry of science and technology of National High-Tech Research and Development Program of the People’s Republic of China (863 Program) under Grant No 2011AA110506.