Physiological effects of nickel chloride on the freshwater cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. IU 625 ()
1. INTRODUCTION
The formation of algal blooms is a serious concern around the world. Algal blooms can result from the use of pesticides, fertilizer, and waste [1]. The nutrient-enriched environments cause a dramatic increase in the cyanobacteria population. Many species of cyanobacteria secrete toxic metabolites [1,2]. These toxins have been linked to various diseases and are considered a factor in Alzheimer’s disease [2]. Monitoring of global water environments has become a human health imperative. The way cyanobacteria survive in heavy metal environments needs to be further evaluated.
The freshwater cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. IU 625 (S. IU 625) is a unicellular rod-shaped microorganism with a similar cell wall structure to gram-negative bacteria [3]. S. IU 625 is an ideal candidate to study heavy metal response mechanisms due to its fast growth, easy maintenance and cultural conditions [3]. The unique nature of cyanobacteria to grow in a wide range of environments conditions makes them ideal model organisms. Using S. IU 625 as a model, many biological processes can be assessed including cell biology, membrane transport and various molecular mechanisms.
Previous studies have shown that increasing concentrations of heavy metals can slow cell growth [3-13]. Nickel is an essential metal that plays an important role in cellular physiology for eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Nickel is a necessary cofactor for enzymatic function in prokaryotes [14]. High concentrations of nickel exposure could be potentially harmful. Nickel has been shown to cause detrimental damage to lung tissue [15,16] and is categorized as a potential carcinogen. It is also on the Environmental Protection Agency Target Analyte List [17]. In human cell lines nickel accumulates intracellularly and effects DNA methylation and iron-uptake systems resulting in iron deficiency [16].
Previous work has shown that S. IU 625 sequesters or utilizes an efflux mechanism to maintain homeostasis of heavy metals [3,18]. This study provides insight into the effects nickel chloride has on S. IU 625 and the response it utilizes to reduce nickel toxicity. Transcription of smtA, which encodes metallothionein, has been shown to increase heavy metal resistance.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Culture Maintenance
S. IU 625 stock cultures were maintained in an incubator shaker (Amerex Instruments Inc.) at 26˚C with continuous agitation at 100 rpm and constant fluorescent light. Five ml of cells were inoculated in 95 ml of sterilized Mauro’s Modified Medium (3M) [19] in 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks. The pH of the 3M medium was adjusted to 7.9.
2.2. Preparation of Nickel Chloride Solution
A nickel chloride (1%) stock solution was prepared using triple distilled water (Milli-Q Integral 5 Water Purification System, EMD Millipore, MA) in a sterile container from Sigma Aldrich. Solution was filtered with 0.45 µm Millipore membrane filters.
2.3. Growth of Synechococcus sp. IU 625 in the Presence of Nickel Chloride
Nickel chloride was added at varying concentrations (0, 10, 25, 50 mg/L) to exponentially growing cultures in four separate 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks. Cell growth was observed by: 1) Direct counts with hemacytometer; 2) Turbidity study, optical density (OD) was taken by using a spectrophotometer at 750 nm wavelength. Three repeatings of this experiment were carried out and the growth was monitored for 28 days. Mean and standard deviations were generated through GraphPad Prism.
2.4. Heavy Metal Distribution
Immediately after collection, samples were centrifuged and the supernatant placed into a different microcentrifuge tube and labeled. Adding dH2O to the cell pellet up to 1 mL resuspended the cells. Nickel concentrations in the cells and supernatant were determined by using an ELAN DRC-E ICP-MS following an ICP-MS protocol [20] at Naturex, Inc.
2.5. Microscopic Observations
One ml of culture was taken at each time point and used for analysis. Cells were immediately centrifuged for 1 minute and the supernatant discarded and then fixed with 12.5% formaldehyde in phosphate buffer. DAPI (4,6- diamidion-2-phenylindole) fluorescence was used to detect DNA. Two microgram per milliliter of DAPI was added to cells and incubated for 10 minutes in the dark and then added onto a 1% agarose pad. A Zeiss AxioVision microscope (with a Hamamatsu ORCA-ER digital camera) was used to observe cell morphology using differential contrast.
3. RESULTS
3.1. S. IU 625 Tolerates Up to 25 mg/L of Nickel Chloride
To determine the effects of nickel chloride on the growth of S. IU 625, cultures were grown in 3 M medium with increasing concentrations of nickel chloride (0, 10, 25 or 50 mg/L). Cells were monitored for 28 days to see the complete bacterial growth cycle. Collections were taken twice a week during each study. Growth curves indicate that cultures with increasing nickel chloride concentrations resulted in depressed growth until a certain nickel threshold concentration is reached (Figure 1).
The 10 mg/L culture initially exhibited slower growth compared to the control but recovered after a few days. However, growth of the cells under 10 mg/L NiCl2 remained lower than the control. The 25 mg/L culture demonstrated a prolonged lag phase and did not fully enter exponential growth until day 11. The total cell count for the 25 mg/L NiCl2 remained lower than the control and 10 mg/L flasks by the end of the study. The 50 mg/L culture was incapable of entering the log phase, as growth of the culture was completely inhibited.
Between day 1 and day 8, a lighter pigmentation of green in the 25 mg/L NiCl2 culture was seen instead of the healthy dark green present in the control and 10 mg/L

Figure 1. Growth curves of S. IU 625 with or without nickel chloride stress: 0 (control), 10, 25 and 50 mg/L NiCl2, respectively. Triplicate cultures growth curves were plotted using GraphPad Prism. Top: Turbidity study with optical density at 750 nm of each culture plotted over the time course in days. Bottom: Direct count of cultures.
cultures. Increases in cell number should darken the green pigmentation of the culture as demonstrated by the 10 mg/L and control cultures. S. IU 625 has a photosystem similar to that of higher plants. Nickel ions can interfere with the electron transfer in this photosystem lowering the fluorescence [21]. This suggests a bleaching effect may be seen in the 25 mg/L during its delayed lag phase.
3.2. Initially Nickel Accumulates within S. IU 625 But Was Almost Completely Cleared by Day 11
Nickel concentrations in the supernatant and within the cells were determined by ICP-MS. The data was normalized against the control. The 10 mg/L NiCl2 culture accumulated 8% more nickel in the cells by day 5 and by day 11 it was reduced to control levels (0%). The 25 mg/ L culture accumulated less nickel by day 5 (6%) compared to the 10 mg/L culture. However, the 25 mg/L culture was not capable of fully driving all nickel into the supernatant. At day 15, 1% nickel still remained in the 25 mg/L culture compared to that of the control (Figure 2).
3.3. S. IU 625 Recovers from Nickel Chloride Induced Morphological Abnormalities
Increases in nickel chloride concentration induce more pronounced morphological abnormalities. Cultures are capable of recovering from these defects and grow in the nickel environments. Present defects include curved morphology and nickel concentration-dependent cell size changes (Figure 3). The 10 mg/L culture had an increase in curved cells and ectopic poles. After a week, the presence of these defects declined rapidly and most cells returned to a normal morphology. The 25 mg/L culture developed similar morphological defects as the 10 mg/L culture. An increase in the presence of dead cells (as seen by the lack of DNA stain with DAPI) was seen compared to that of the 10 mg/L or control cultures. After day 11, the 25 mg/L culture was capable of growing (Figure 1) with some minor morphological defects remaining throughout the rest of the study. The 50 mg/L culture had an increased prevalence of dead cells and a decrease in cell size. By the end of the study, microscopy suggested that nearly all of cells in the 50 mg/L culture were dead. The decrease in size could be an adaptive response to minimize the cells’ surface area exposed to nickel.
4. CONCLUDING REMARKS
In this study, we showed that S. IU 625 was able to tolerate nickel chloride stress up to 25 mg/L. Increasing concentrations of nickel had more pronounced effects on

Figure 2. Distribution of nickel during the growth of S. IU 625. Nickel dissociates from chloride in an aqueous environment. Raw ICP-MS data was generated examining the nickel concentration against a standard. The raw data was then standardized against the control. The percentage of nickel concentration on the y axis represents the increase in intracellular nickel over the control.
both the growth rate and defect prevalence. Nickel was transported almost entirely from cells to the supernatant by surviving cultures (10 and 25 mg/L). For cultures grown at 25 mg/L NiCl2, nickel was undetectable inside the cells at day 11, which also coincides with a rebound in the growth rate.
The initial qPCR data for smtA expression showed approximately a twenty-fold increase for the 25 mg/L culture up to day 11 (data not shown). Interestingly, there was no significant increase in smtA mRNA levels for the 10 mg/L culture but the nickel was still cleared from the cell based on the ICP-MS data. It suggested a possible alternative mechanism.
Future studies need to investigate other potential clearance mechanisms of nickel from the cell. Insight might be gained by identifying potential nickel resistance genes and utilizing knockout strains to examine the effects.
5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We deeply appreciated Naturex, Inc. (South Hackensack, New Jersey) for assisting the ICP-MS assays. This work was supported by Seton Hall University Biological Sciences Research Fund to T.C., NIH Grant
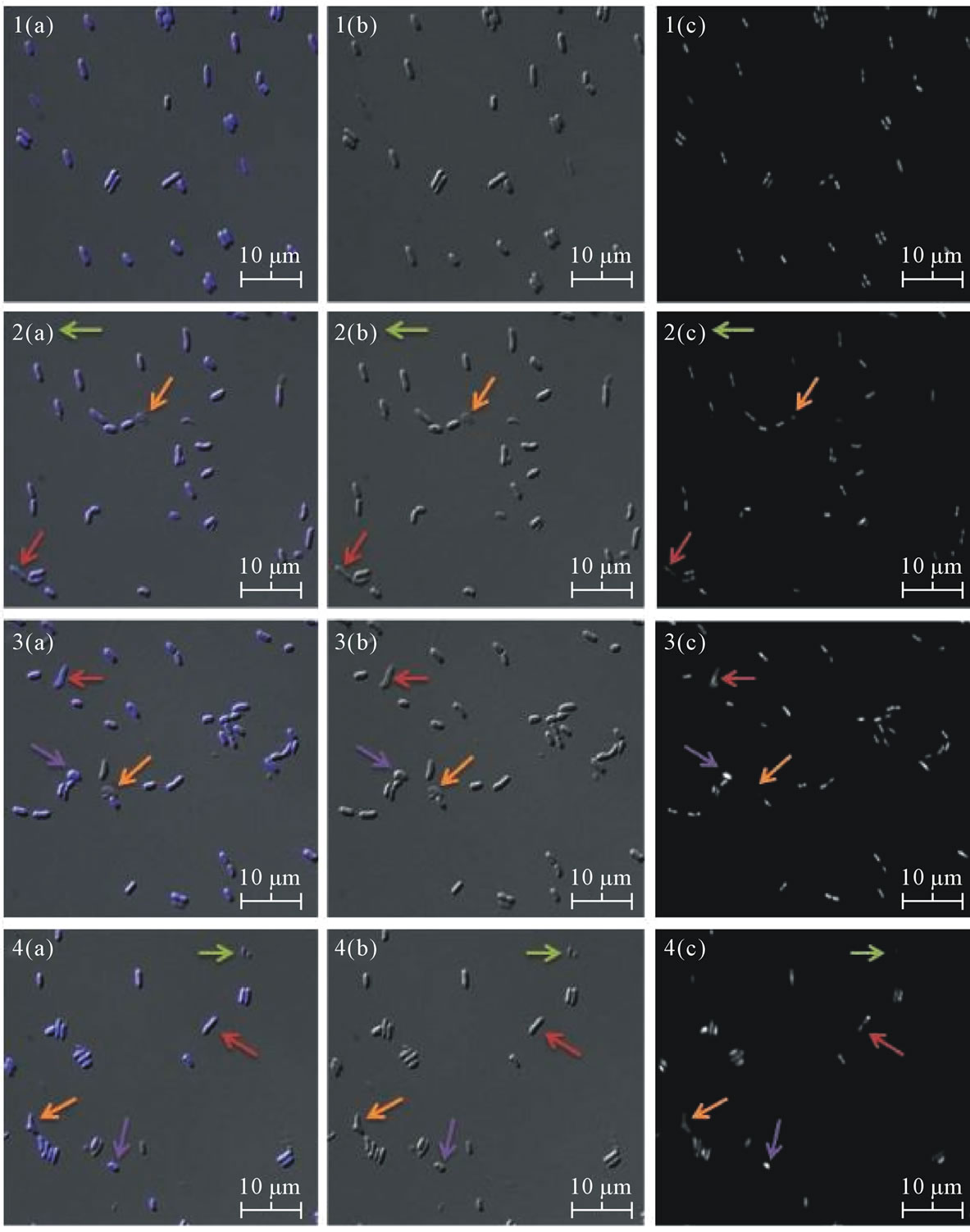
Figure 3. Microscopic observations of S. IU 625 with various nickel chloride concentrations at day 13. (a) Overlaid image; (b) DIC images; (c) DAPI-stained images. 1(a)-(c) 0 mg/L (control); 2(a)-(c) 10 mg/L; 3(a)-(c) 25 mg/L and 4(a)-(c) 50 mg/L NiCl2. Arrows indicate different morphological abnormalities. Green arrow: normal sized cells with no DNA; Red arrow: elongated cells with DNA; Orange arrow: abnormally shaped cells with DNA; Purple arrow: cocci-like, smaller cells, with DNA.
GM084860 to S.R.M., Montclair State University Faculty Scholarship Program to L.H.L., and CSUN IRIS support for B.T.N.

