Serotonin uptake rates in platelets from angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Platelets are derived from the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes and enter the circulatory system in an inactive form. An initial activation of platelets stabilizes them in hemostasis. Further platelet activation enlists more platelets at a fibrin-stabilized hemostatic area to form a thrombosis after associating with endothelium or with each other. The resulting thrombus is a leading cause of death for patients with hypertension and cardiovascular disease [1]. The type and the location of thrombosis are altered by factors that disturb the resting state of platelets and shift them to an active state. One disease that establishes an environment favoring pathophysiological activation of platelets is hypertension [2], and the platelets in blood of hypertensive subjects have an abnormal biological profile compared to platelets of normal subjects [1,2]. Additionally, the endothelium is also defective in hypertension, which promotes platelet activation and aggregation to form thromboses in the affected individuals. Increased thrombosis is associated with the development of high blood pressure, but this association may relate to a number of underlying vascular abnormalities including oxidant production and endothelial dysfunction rather than on platelet abnormalities [3,4]. It seems likely that preexisting vascular disease coupled to abnormalities in platelet activation and fibrinolysis may cause thrombus formation in hypertensive subjects [5-7]. Whether hypertension originating from different pathogenic origins differentially predisposes platelets to thrombosis also is not clearly defined.
In this regard, an activated renin-angiotensin system and its major biologically active component, angiotensin II (Ang II), contribute to hypertension [8]. However, whether Ang II-mediated hypertension is associated with a prothrombotic state of platelets remains controversial. Whereas some studies report a prothrombotic effect of Ang II [8-10], others report a protective effect of Ang II that is independent of its pressor effects [11-13] and may rely on elevated prostacyclin or nitric oxide to inhibit platelet aggregation [14,15]. Thus, a correlation between elevated serum Ang II and the adhesive properties of platelets remains elusive.
In the present study, we induced hypertension by subcutaneous infusion of Ang II in mice for one week to determine if elevation of circulating Ang II influences platelet aggregation. We reported earlier that the concentration of serotonin (5-HT) in plasma was higher in hypertensive than normotensive human subjects [15]. Notably, 5-HT is an independent risk factor for platelet aggregation and for thrombus formation in animals and humans [16-22]. Thus, pharmacological block of the 5- HT2A receptor in animal models of hypertension, which inhibits 5-HT-induced platelet activation, also reduces ex vivo platelet aggregation [23]. Additionally, selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) that lower the concentration of cytosolic 5-HT in platelets, predispose to platelet dysfunction and bleeding [16,23,24]. In an earlier study we showed that when 5-HT-infused mice were treated with paroxetine, an SSRI, the platelet content of 5-HT and markers of platelet activation associated with a pro-aggregation phenotype were reduced [16]. These studies strongly infer an involvement of 5-HT in platelet aggregation. 5-HT molecules are presumed to act as ligands for the platelet 5-HT2A receptor [25,26] and transporter (SERT) situated on the plasma membrane [16,27-29].
The goal of the current study was to determine the role of elevated circulating Ang II on in vivo platelet function using an Ang II-infused mouse model, and then define mechanisms by which Ang II influences platelet phenoltype using in vitro assays. Our findings support the hypothesis that Ang II can attenuate the aggregation response of platelets, an effect that appears to rely on stimulation of the angiotensin type I receptor resulting in loss of 5HT-uptake. Pretreatment with the Ang II recaptor blocker, valsartan, restores 5-HT uptake and platelet aggregation [16,27-29]. Thus Ang II contributes to the adhesive properties of platelets and their aggregability suggesting a potential clinical utility of our findings.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Animal Protocols
The SERT−/− (SERT KO) was provided by The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Maine) which has C57BL6 genetic background [30]. Mouse phenotype depends, to some extent, on their genetic background. To exclude this potential effect, in our proposed studies all experimental mice have been backcrossed into C57BL/6J background. The KO mice model demonstrated that 1) Mice thrived and reproduced in a slower rate than their wildtype counterparts; 2) Deficiency of SERT resulted in a 95% reduction of 5-HT in their platelet (Table 1); 3) Assay measuring the rate of platelet 5-HT uptake showed a 90% decrease in SERT−/− mice. Furthermore, comparing the expression levels of platelet plasma membrane proteins in wild-type (C57BL/6J) and SERT-KO (SERT−/− on C57BL/6J) mice confirm the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data by showing a 60% decrease on SERT expression on the plasma membrane in turn the 5-HT uptake rates of the platelets from SERT−/− (Table 1).
Adult C57BL/6J wild type or transgenic male mice (10 - 12 weeks old) were anesthetized with isoflurane (2.5% at 1.5 L/min oxygen) for implantation of subcutaneous osmotic mini-pumps (Alzet 2004, Durect Corporation, Cupertino, CA) containing angiotensin II (Ang II, Bachem, Torrance, CA, infusion rate: 2 ng/g/min) [31], or an equal volume of vehicle (0.9% saline) were implanted subcutaneously [16]. After recovery from anesthesia, mice were housed in individual cages and allowed free access to food and water.
Procedures involving animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were conducted in accordance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Table 1. Summary of platelet profiles in study groups of mice.
2.2. Blood Sampling and Platelet Preparation
After 24 hours of continuous infusion with either saline or Ang II, blood was withdrawn into a syringe containing 3.8% sodium citrate solution. Samples of platelet and plasma were prepared from the whole blood [16]. In biochemical studies, each assay was performed using the same number of platelets (300,000 platelets/µL blood).
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was measured in mice using tail cuff plethysmography using the CODA noninvasive blood pressure system by Kent Scientific Corp (Torrington, CT). Baseline SBP was calculated by averaging a minimum of 6 trials on 2 consecutive days prior to insertion of mini-pumps containing saline or Ang II. The SBP was recorded again by taking a minimum of 6 trials in each mouse after 24 hours of saline or 5-HT infusion and averaging the values daily for one week.
2.4. Platelet 5-HT Uptake Assay
Platelet pellets were quickly washed with phosphatebuffered saline (PBS) containing 0.1 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM MgCl2 (PBSCM), and then resuspended in PBS/CM with 14.6 nM 3H-5-HT at room temperature for 10 min, to include only the initial linear phase of 5-HT transport [16,17]. Platelets were collected by rapid filtration through Whatman GF/B filters and were washed twice with 5 ml of ice-cold PBS. Filters were placed in scintillation vials containing 5 ml scintillation cocktail and immediately counted.
Background accumulation of 3H-5-HT that occurred independently of SERT was measured in the same experiment using platelets incubated with the high-affinity cocaine analog, 0.1 µM 2β-carbomethoxy-3-tropane (β- CIT) (Chemical Synthesis Service, NIMH, Bethesda, MD). The value was subtracted from each experimental value to estimate 5-HT uptake mediated by SERT [32]. In parallel, the protein concentration of 0.2 × 106 (0.015 mg cellular protein) platelets was determined using the Micro BCA protein Assay Kit. 5-HT uptake rates were calculated as means of standard deviation values from three independent experiments.
2.5. Quantitative Measurement of 5-HT Levels by ELISA
The 5-HT levels in platelet and plasma which were prepared from the blood samples of each animal model were measured by a competitive ELISA technique following the manufacturer’s instructions (IBL ImmunoBiological Laboratories, Hamburg, Germany) [16,17]. Briefly, 5-HT in experimental and control samples were acylated with acetic anhydride in acetone and samples, controls, and standards were applied to 96-well microtitre plates coated with goat anti-rabbit IgG. Biotinylated 5-HT and rabbit antiserum to 5-HT were added to each well and incubated overnight at 4˚C. Para-nitrophenylphosphate in a diethanolamine solution was used as a substrate following the application of alkaline phosphatase conjugated goat anti-biotin antibody (Ab). Samples were read at 405 nm on an ELISA plate reader (Molecular Devices Union City, CA, USA). The amounts of 5-HT were quantified using standards supplied by the manufacturer and analyzed using Origin software (Microcal Software, Northampton, MA).
2.6. Stirred Platelet Aggregation
For aggregation assays, platelets in plasma were prepared and platelet counts were normalized (300,000/µL) using a Hemavet 950 (Drew Scientific, Waterbury, CT). The response to collagen (3 µg/ml) as a platelet agonist was monitored by light transmittance (Chrono-log Corp., Havertown, PA) [16].
2.7. Flow Cytometry
The impact of Ang II on platelet activation was assessed using phycoerythrin (PE) labeled anti-αIIbβ3 (Jon/A) Ab developed to follow integrin activation on mouse platelets [16]. Platelets (300,000/µL) were incubated in the dark with PEJon/A (Emfret Analytics, Cat M023-2) and at the end of the incubation, 300 mL of 2% formaldehyde in PBS was added to stop the reaction. The samples were gated for single platelets based on forward and side scatter profiles and 20,000 events were recorded and read at the UAMS Flow Cytometry Core Facility. FITC labeled anti-P-selectin antibodies were provided from BD Pharmingen, Cat 553744.
2.8. Data Analysis
Nonlinear regression fits of experimental and calculated data were performed using Origin software, which uses the Marquardt-Levenberg non-linear least squares curve fitting algorithm. Each figure shows a representative experiment that was performed at least three times. The statistical analyses given in the Results section is from multiple experiments. Data with error bars are represented as mean ± SEM for triplicate samples. Data were analyzed by ANOVA (analysis of variance) to compare data sets and two-sided t-tests based on the ANOVA mean squared error.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Blood Pressure of Ang II-Infused Mice
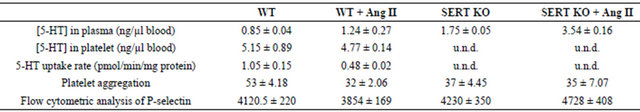
Adult C57BL/6J male mice were randomized to receive osmotic mini-pumps filled with isotonic saline or filled with Ang II. The baseline systolic blood pressure (SBP) was measured on 6 consecutive days prior to insertion of mini-pumps containing saline (control) or Ang II (24 µg Ang II/gram body weight) to achieve an Ang II infusion rate of 2 ng/g/min. Then, the SBP in each mouse was averaged from ≥6 trials each day for one week after saline or Ang II infusion (Figure 1). Ang II infused for one week elevated SBP from 101 ± 6 mm Hg to 180 ± 12 mm Hg, representing an average increase in SBP of 75%. Following confirmation of Ang II-mediated hypertension, mice were infused with 2 ng/g/min Ang II for one week in all future studies. No change in circulating platelet counts occurred in Ang II-infused animals (not shown).
3.2. Effect of Ang II Infusion on Platelet Activation, Aggregation and 5-HT Uptake Rate
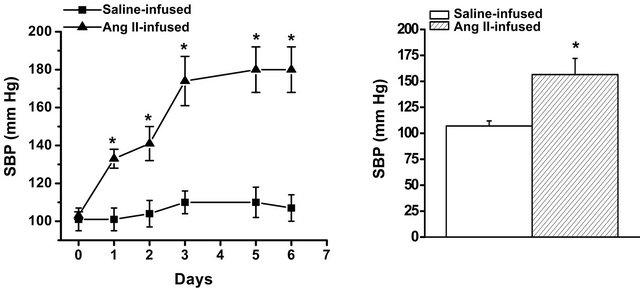
Platelets from saline-infused control mice, or from Ang II-infused hypertensive mice, were examined for two markers of platelet activation, P-selectin and integrin. Figure 2(a) shows no difference in the expression of surface P-selectin between platelet plasma membranes of control and Ang II-infused mice. Similarly, PEJon/A binding to surface integrin did not significantly differ between platelets of control and Ang II-infused mice. Thus, Ang II infusion did not activate platelets in the hypertensive mice.
Next, the rate of aggregation was compared between platelets isolated from control and Ang II-infused mice. Platelets of Ang II-induced hypertensive mice were stimulated with collagen (3 µg/ml) to monitor their behavior in a stirred platelet aggregometer. Isolated plate-
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 1. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) profiles in salineand angiotensin II (Ang II)-infused mice. (a) Osmotic mini-pumps were filled with saline (control) or 24 µg Ang II/g mouse weight to achieve an Ang II infusion rate of 2 ng/g/min. SBP was evaluated using tail-cuff plethysmography [16]. SBP was measured daily for 6 days prior to the insertion of mini-pumps on Day 0. Basal SBP was not different between mouse groups and averaged 103 ± 2 mm Hg; (b) Seven days after mini-pumps were implanted, SBPs averaged 108 ± 8 mm Hg (saline-infused) and 151 ± 19 mm Hg (Ang II-infused). * = statistical difference between control and Ang II-infused mice (n = 6 each group).
lets from Ang II-infused mice showed a lower aggregation response to collagen than the platelets of saline-infused control mice (Figure 2(b)). Aggregation was decreased by an average of 39% in platelets from the Ang II-infused animals (53% ± 4% in Ang II-infused mice vs. 32% ± 2% in control mice; n = 6 each).
We recently reported an association between loss of the serotonin transporter (SERT) on the platelet surface and the pro-thrombotic influence of elevated plasma 5- HT. To evaluate this event as a potential mechanism for the decreased platelet reactivity in Ang II-infused mice, 5-HT concentrations in platelet and in plasma were determined by ELISA. The platelet 5-HT level was 5.15 ± 0.89 ng/µl for control animals (n = 6) and 4.77 ± 0.14 ng/µl for Ang II-infused animals (n = 5) (Table 1). The plasma to platelet distribution of 5-HT differed markedly between the two animal groups. Control mice showed a lower plasma concentration (0.85 ± 0.04 ng/µl blood) of 5-HT than Ang II-infused mice (1.24 ± 0.27 ng/µl blood). Next we compared 5-HT uptake rates between platelets from control and Ang II-infused mice. The 5-HT uptake rate of platelets isolated from Ang II-infused mice was 54% lower (P < 0.01) compared to platelets of control mice (Figure 2(c) and Table 1).
3.3. Effect of Ang II Infusion on Platelets of SERT KO Mice
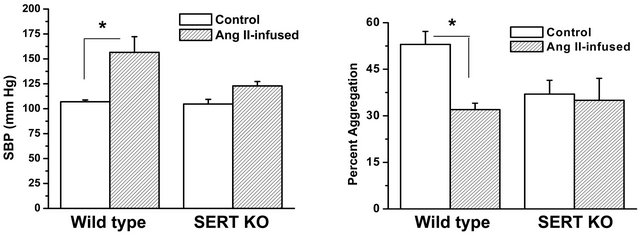
Collectively our data showed that elevation of Ang II in vivo causing hypertension in mice increases the plasma/platelet 5-HT ratio but reduces platelet aggregation. To further understand the involvement of 5-HT and SERT in Ang II-mediated hypertension, we compared blood pressure and platelet profiles between wild type (WT) and SERT knockout (KO) mice. Resting SBP was not significantly different between WT and SERT KO mice. However, infusion of Ang II for one week elevated the SBP of WT mice by 46% compared to a SBP rise of only 17% in SERT KO mice. We next evaluated the aggregation response of platelets from SERT KO mice to collagen stimulation. The aggregation response of platelets isolated from SERT KO or Ang II-infused SERT KO mice to collagen stimulation was not significantly different (Figure 3(b) and Table 1). Figure 3(c) shows that infusion of Ang II also did not alter the surface expression levels of P-selectin or integrin on platelets of SERT KO mice, suggesting no change in platelet activation status.
3.4. In Vitro Effect of Ang II on Platelets
Next, the effect of Ang II on platelet function was examined directly in an in vitro system. Isolated platelets from control (WT) mice were exposed to Ang II (50 or 100 pM) for 10 minutes before aggregation responses
 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 2. Effect of Ang II infusion on platelet function. (a) Surface expression of P-selectin, and integrin αIIbβ3 determined by flow cytometry as indices of platelet activation. Flow cytometry revealed no significant difference in expression levels of P-selectin or integrin between platelets of saline-infused (control) or Ang II-infused mice; (b) The aggregation response to 3 µg/ml collagen was significantly less in platelets from Ang II-infused mice compared to control mice; (c) The 5-HT uptake rate of platelets isolated from Ang II-infused mice was significantly lower compared to platelets of control mice. Assays in (a), (b) and (c) were performed in triplicate. * = statistical difference between control and Ang II-infused mice (n = 6 each).
 (a)
(a)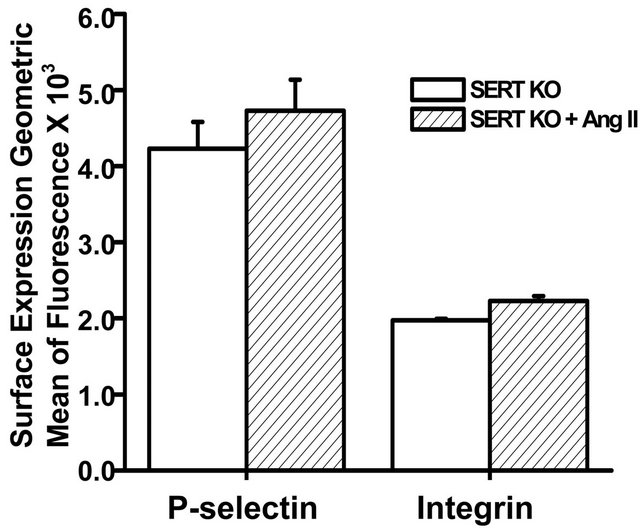 (b)
(b)
Figure 3. Effect of Ang II infusion on SBP and platelet function in wild type (WT) and SERT KO mice. (a) Resting SBP was not significantly different between WT and SERT KO mice. Ang II infusion (2 ng/g/min) increased the SBP of WT mice to 151 ± 19 mm Hg, which was significantly higher than the SBP of 122 ± 5 mm Hg achieved in SERT KO mice; (b) The aggregation response to collagen (3 µg/ml collagen) was blunted in platelets isolated from Ang II-infused WT mice, whereas the low aggregation response in isolated platelets of SERT KO mice was not significantly affected by Ang II infusion (n = 6 each group); (c) Results of flow cytometry revealed no significant difference in P-selectin or integrin αIIbβ3 expression between platelets isolated from salineand Ang II-infused SERT KO mice (n = 6 each group). Assays were performed in triplicate. * = statistical difference between saline-infused (control) and Ang II-infused mice.
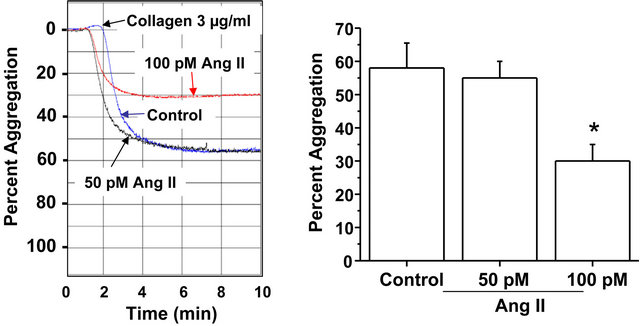
were recorded. The representative aggregation traces shown in Figure 4(a) reveal a reduced collagen-induced aggregation response of platelets exposed to 100 pM Ang II compared to untreated platelets. The bar graph in Figure 4(a) shows that the average aggregation response of platelets exposed to 100 pM Ang II was decreased by 48% compared to control platelets exposed to drug-free solution (30% ± 5% versus 58% ± 8%). Exposure of platelets to the lower concentration of Ang II (50 pM) did not alter aggregation.
The in vitro effect of Ang II on P-selectin, a marker of platelet activation, also was examined. The results from flow cytometry (Figure 4(b)) showed no significant effect of Ang II on P-selectin surface expression. Thus, exposure to Ang II coincides with a decreased platelet aggregation response to collagen without an apparent change in platelet activation.
3.5. In Vitro Effect of an Ang II Type 1(AT1) Receptor Blocker on Platelet Function
To determine if the effect of Ang II on platelet aggregation was mediated by the AT1 receptor, platelets were incubated for 10 minutes in 100 pM Ang II in the absence or presence of the AT1 receptor blocker, valsartan (5, 10 or 15 µM). Valsartan (15 mM) per se had no effect on the aggregation response of platelets (Figure 5). However, it reversed in a concentration-dependent manner the inhibitory effect of Ang II on platelet aggregation (Figure 5).
 (a)
(a)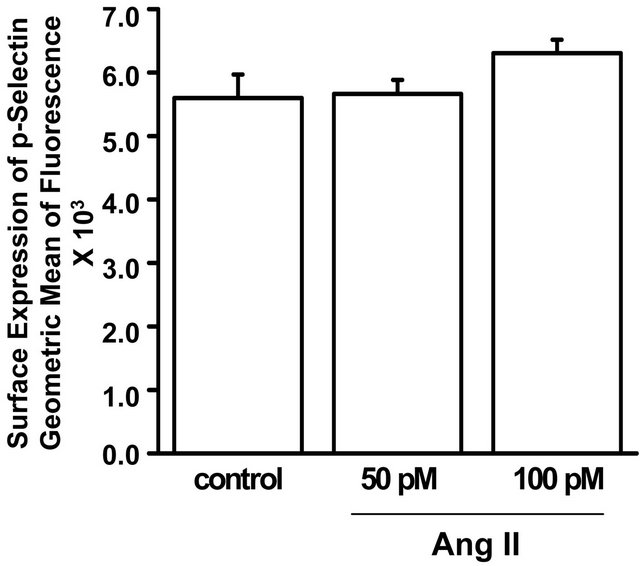 (b)
(b)
Figure 4. Isolated platelets of WT mice were untreated or exposed for 10 min to 50 pM or 100 pM Ang II. (a) Percent aggregation in response to collagen (3 µg/ml) of isolated platelets pre-incubated in drug-free solution (control) or Ang II (50 or 100 pM) for 10 min. The aggregation response to collagen was significantly less in platelets incubated in the higher concentration of Ang II (100 pM) compared to the lower concentration of Ang II (50 pM) or drug-free solution (control). * = statistical difference between control and Ang II (100 pM)-exposed platelets (n = 6 each); (b) Surface expression of P-selectin was not significantly different between isolated platelets pre-incubated in drug-free solution (control) or Ang II (50 or 100 pM).
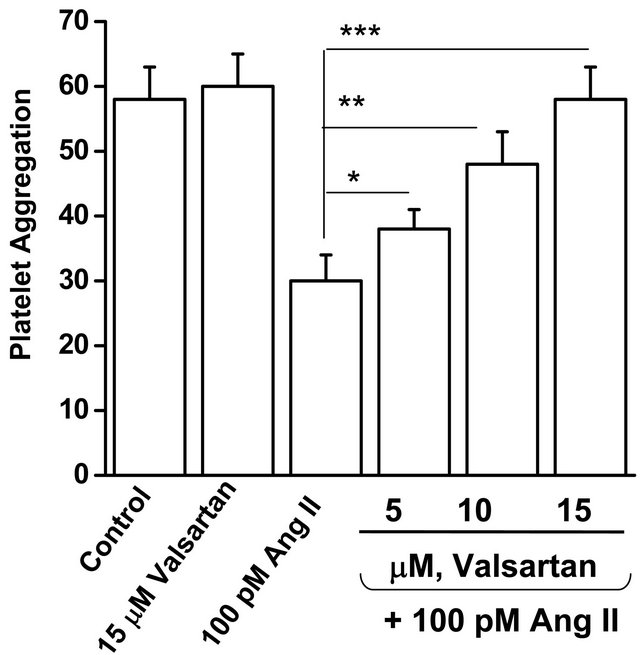
Figure 5. The Ang II receptor blocker, valsartan, reverses the blunted aggregation response of isolated platelets from WT mice incubated with Ang II. Isolated platelets from WT mice were incubated in drug-free solution (control), valsartan (15 mM), Ang II, or Ang II in the presence of valsartan (5, 10 or 15 mM) for 10 min. Valsartan (15 mM) reversed the inhibitory effect of Ang II on platelet aggregation. * = statistical difference between Ang II (100 pM) and – Ang II + valsartan exposed platelets (n = 4 each).
3.6. In Vitro Effect of Valsartan on 5-HT Uptake Rate and SERT Surface Expression
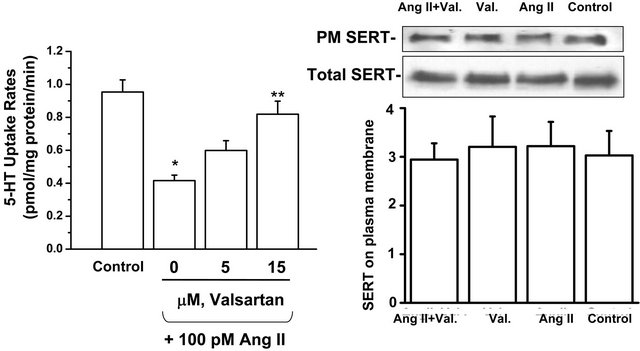
Finally we explored if Ang II directly regulates 5-HT uptake or expression of SERT molecules on the platelet surface. Figure 6(a) shows that isolated platelets exposed to 100 pM Ang II for 10 minutes showed a 54% decrease in the 5-HT uptake rate. Valsartan (5 or 15 µM) progressively reversed this effect. The prevalence of SERT in the platelet plasma membrane and cytoplasm was assessed by biotinylation of surface proteins, which were retrieved on streptavidin beads [34]. Then the SERT protein in bound and unbound fractions was assessed in Western blots probed with anti-SERT antibody (SERT-Ab). Figure 6(b) shows that Ang II did not change the density of SERT molecules on the platelet surface, implying that Ang II blocks 5-HT uptake as an independent receptor-mediated effect.
4. DISCUSSION
The role of Ang II in modulating platelet function during hypertension is controversial, and both a prothrombotic effect [8-10] and an anti-thrombotic effect have been described [11-15]. The findings in this study help to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which Ang II may favorably modulate platelet function. Notably, we explored the effects of Ang II on platelet biology using both in vivo and in vitro approaches, since efforts to define the direct actions of Ang II on platelets in vivo may be confounded by its pressor effect, impact on fluid and electrolyte balance, and other actions. For this reason, we also used in vitro assays to more directly assess the effect of Ang II on isolated platelets and thereby also eliminate in vivo influences exerted on platelets by blood pressure, circulating substances, endothelium-derived factors and other modulators of platelet function.
Our first new finding was that isolated platelets from Ang II-infused hypertensive mice failed to show markers of activation. These platelets showed reduced collagen-
 (a) (b)
(a) (b)
Figure 6. Valsartan restores 5-HT uptake in isolated platelets of WT mice incubated in Ang II and this effect occurs independently of changes in SERT expression. (a) Isolated platelets from WT mice were incubated for 10 min in drug-free solution (control) or Ang II (100 pM)-containing solution containing 0, 5 or 15 mM valsartan. Valsartan reversed the inhibitory effect of Ang II on 5-HT uptake in a concentration-dependent manner; (b) The expression of plasma membrane (PM)-delineated and total SERT was not significantly different between isolated platelets treated for 10 min with drug-free solution (control), valsartan (Val, 15 mM), Ang II, or Ang II and valsartan (n = 4 each group).
induced aggregation responses compared to platelets of saline-infused (control) mice. Thus, despite blood pressure elevation, our data suggest that chronic elevation of Ang II in vivo may exert a protective effect on the function of platelets that can persist even after isolation. Whether this favorable effect of Ang II on platelet aggregation can overpower the purported pro-thrombotic effects of Ang II during hypertension that includes oxidant generation and endothelial damage is unclear [31]. Further complexity is conferred by reports of Ang II’s stimulation of prostacyclin and nitric oxide (NO) [32,34,45] that also may exert anti-thrombotic effects. Nonetheless, our data suggesting that Ang II infusion confers an antiaggregation effect on platelets in vivo lend credence to earlier reports of its anti-thrombotic effect under other experimental conditions [11-15].
Our second main finding was that platelets from Ang II-infused hypertensive mice showed blunted 5-HT uptake by SERT resulting in a loss of the primary mechanism for regulating plasma levels of 5-HT and depletion of 5-HT in the platelet cytosol. We were able to recapitulate this response in vitro by exposing isolated platelets directly to Ang II, which caused a decrease in 5-HT uptake. The suppressant effect of Ang II on 5-HT uptake was independent of changes in SERT expression and was reversed by the AT1 receptor antagonist, valsartan, a pharmacological intervention that also reversed the antiaggregation effect of Ang II. Based on these findings and supporting literature [11-15,32,34,36], we propose that AT1 receptor stimulation resulting in a loss of SERT activity and reduces platelet 5-HT signaling represents a newly identified mechanism by which Ang II attenuates aggregation responses. Indeed, findings by earlier investigators using mice with targeted deletion of key genes involved in 5-HT synthesis or signaling suggest loss of intracellular 5-HT can attenuate platelet aggregation. Thus, platelets of SERT KO mice shown to be nearly depleted of 5-HT [30,37] showed attenuated aggregation and Ang II did not further reduce this response. These results also resemble the behavior of platelets in blood samples of 5-HT-infused mice injected with the SSRI, paroxetine, to deplete intracellular 5-HT. Whereas the platelets of 5- HT-infused mice showed an enhanced aggregation response to collagen, lowering the 5-HT uptake rate of these platelets by paroxetine injection restored normal aggregation [16,18,19]. Similarly, isolated platelets of mice lacking the gene for tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), which is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of 5-HT in peripheral cells, demonstrated a dual requirement for intracellular 5-HT and Ca2+ for the release of a-granules during activation [27]. In these platelets, 5- HT stimulation accelerated the exocytosis of a-granules, which secrete their contents of procoagulant molecules into the plasma [27,28]. These molecules may include fibrinolytic regulators, growth factors, chemokines, immunological modulators, adhesion molecules such as Pselectin, von Willebrand factor, thrombospondin, fibrinogen, and fibronectin [38,39].
Finally, our finding that SERT KO mice show less blood pressure elevation in response to Ang II infusion than WT mice suggests that a link between Ang II and 5-HT signaling supports this pressor response. Whether SERT deletion in platelets per se or in another cell type accounted for the blunted rise in blood pressure in Ang II-infused SERT KO mice cannot be concluded here. However, the finding which platelets of SERT KO mice depleted of 5HT content show normal surface expression of activation markers but a reduced aggregation response to collagen mirrors the functional profile of platelets exposed to Ang II in vivo or in vitro. Thus, Ang II-induced or a gene-based loss of SERT-mediated 5-HT uptake resulted in an anti-aggregation effect, implying that an unrecognized pathway by which Ang II regulates platelet function may include down-regulation of plasma membrane SERT.
Importantly, clinical studies suggest that elevated plasma 5-HT enhances platelet activation [36-38], and plasma 5-HT may be increased in hypertension [17,39-44]. Our earlier studies also suggest that elevated plasma 5-HT is associated with an enhanced propensity for platelet aggregation [16]. By reducing the 5-HT uptake rate of platelets in the face of high plasma 5-HT, Ang II may exert a compensatory mechanism to support normal platelet aggregation rates by a SERT-dependent signaling pathway and confer protection from thrombosis during conditions of elevated blood pressure.
Additional studies are necessary to elucidate the precise mechanism by which Ang II attenuates 5-HT uptake by SERT, which our findings demonstrate relies on AT1 receptor signaling. It also may be important to evaluate if valsartan and other AT1 receptor antagonists alter in vivo platelet function, since our data suggest that valsartan reversed the anti-aggregation effect of Ang II. Our novel findings provide a basis for future studies by suggesting that Ang II confers an anti-aggregation platelet profile that may rely in part on reduced 5-HT uptake by SERT conferred by AT1 receptor signaling. The potential clinical utility of this finding will require further studies.
5. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge the UAMS Division of Laboratory Animal Medicine and Flow Cytometry Core. This work was supported by the American Heart Association [Grant 0660032Z] and by the NIH National Heart Lung and Blood Institute Grant HL091196-04 to FK.