Patterns of salivary tumours at a university teaching hospital in Kenya ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Salivary gland tumours (SGTs) account for 3% of all tumours and 5% of head and neck tumours [1,2]. Rarity of these tumour types coupled with their complex and dynamic classification scheme over the years, makes diagnosis challenging. Further complicating the classification is the occurrence of SGT in major and minor salivary glands, and in addition there is an existence of benign and malignant entities and histological diversity in the same specimen [3]. According to the WHO classification neoplastic lesions are divided into 5 groups i.e benign and malignant epithelial tumours, soft tissue tumours, hemato-lymphoid tumours and secondary tumours [4].
Approximately 70% - 80% of SGTs originate in the parotid glands, 10% in the submandibular gland and 22% in the minor salivary glands [1,5]. In Africa, only few studies on SGT have been reported, mainly from Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Zimbabwe and Nigeria, reporting a prevalence from 2.8% to 10% of all head and neck tumours [6-10]. Although literature on SGT from the western countries is voluminous, there is paucity of data from the African continent. In this series data was collected from the department of Oral and Maxillofacial pathology, University of Nairobi over a 12-year period.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a descriptive retrospective study, data was retrieved from the histopathology records at the department of Oral Maxillofacial surgery and Oral Medicine Oral pathology Laboratory at the University of Nairobi Dental Hospital from 2000 to 2010. The department provides maxillofacial histopathology services not only for self reported and for referral patients from Nairobi and surrounding countries but, also from public and private practitioners’ country wide. Information on demographic characteristics, site of lesion and diagnosis was retrieved and recorded on a data sheet. The microscopic slides were re-examined by a pathologist for verification of the original results. For all the records whose diagnosis was equivocal, the slides were retrieved or fresh ones processed and re-evaluated. The study samples were fixed in 10% formalin and stained using Hematoxylin and Eosin (H & E). In categorization of these tumours efforts were made to closely adhere to the revised classification of SGTs [4]. The inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of SGT. Specimens with incomplete records, discordant diagnosis in addition to fine needle aspirates (FNA) were excluded from the study. The data was analysed using statistical program for social scientists (SPSS version 16.0) for windows and students T-test, and presented in tables, bar and pie charts.
3. RESULTS
One hundred and thirty two (5.4%) of the 2426 biopsy specimens processed had a diagnosis of SGTs. There were 75 (59%) females and 57 (41%) males. Most of the females were below the age of 60 years while, males were above that age. The age range was between 8 to 80 years (mean = 43.6 yrs) and the majority (68.9%) of the neoplasms presented between the 2nd to 5th decade. There was bimodal age distribution with increased frequency noted between the age groups of 20 - 29 and 50 - 59 years. Notably, the number of patients with SGT below the age of 10 years and above the age of 80 years were few (Figure 1).
There were 53 (40.2%) benign and 79 (59.8%) malignant SGTs. Benign SGT occurred a decade younger than the malignant ones. The numbers of SGT in minor salivary glands (67%) was twice that in the major type (33%). Of the major salivary glands, the most commonly affected was the submandibular (33%), followed by the parotid (10%) and the sublingual (7%). In particular the junction of the hard and soft palate (54%), was the most common site of all the SGT. Other sites involved were the buccal mucosa (8%), lips (4%) and tongue (1%). The palate was the site most commonly affected both for benign and malignant SGTs (Figure 2). From histopthological examination pleomorphic salivary gland adenoma (PSA) was the most frequent and the only type of benign tumour, with the number of females being twice that of males. The age range was between 8 - 68 years with a mean of 36.4 years. There were twice as many females presenting with benign SGT as males (M:F = 1:2) while for malignant type, the gender distribution was equal.
Among the malignant variants adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) (25%), adenocarcinoma (20.5%) and mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) (13.6%) were recorded respectively. Only one case of carcinoma expleomorphic adenoma was reported in the mandible of a 41- year-old male patient. MEC had a female predominance (M:F = 1:3.5), whereas ACC and adenocarcinoma had almost equal gender distribution. The lower limit of the age range of presentation of adenocarcinoma (16 - 80 yrs) and ACC (12 - 77 yrs) was a decade younger than MEC (21 - 76 yrs). The average age of those with adenocarcinoma (52.7 yrs) was a decade older than that of ACC (47.4 yrs) and MEC (44.7 yrs) (Table 1).

Figure 1. Distribution of SGTs by age and gender.
4. DISCUSSION
The annual incidence of SGT ranges from 0.4 to 13.5 cases per 100,000 population [11]. Due to the relatively few numbers of large scale epidemiological studies and in addition, to the considerable variation in the inclusion

Figure 2. Show the distribution of SGT among major and minor salivary glands.
criteria makes comparison difficult [12]. In our study SGTs consisted 5.4% of all the orofacial lesions whose biopsies were examined. Studies have reported prevalences of 6.3% in Tanzania, 6.3% in Nigeria, 9% in Uganda, 3% in Kenya while UK had a prevalence of 13.7% [6-8,13,14].
4.1. Age
The study done in the UK noted a much older age group (mean age = 60 yrs) affected by SGT’s, while, studies in China, Tanzania and Brazil show an average age in the 4th decade of life which is similar to our study [7,14-16] (Table 2). Reports from other countries for example Kenya, Zimbabwe, Nigeria, and Pakistan had an average in the 3rd decade [9,10,17]. In general the age profile in the African continent has been seen to be much younger than in the western countries where these tumours appear a decade or two later among the elderly [18,19]. A bimodal age peak as seen in this study has also been reported in Nigeria, Uganda and South Africa with peaks in the 2nd and 5th decades [20,21].

Table 1. Shows the age, gender and frequency of benign and malignant SGT.
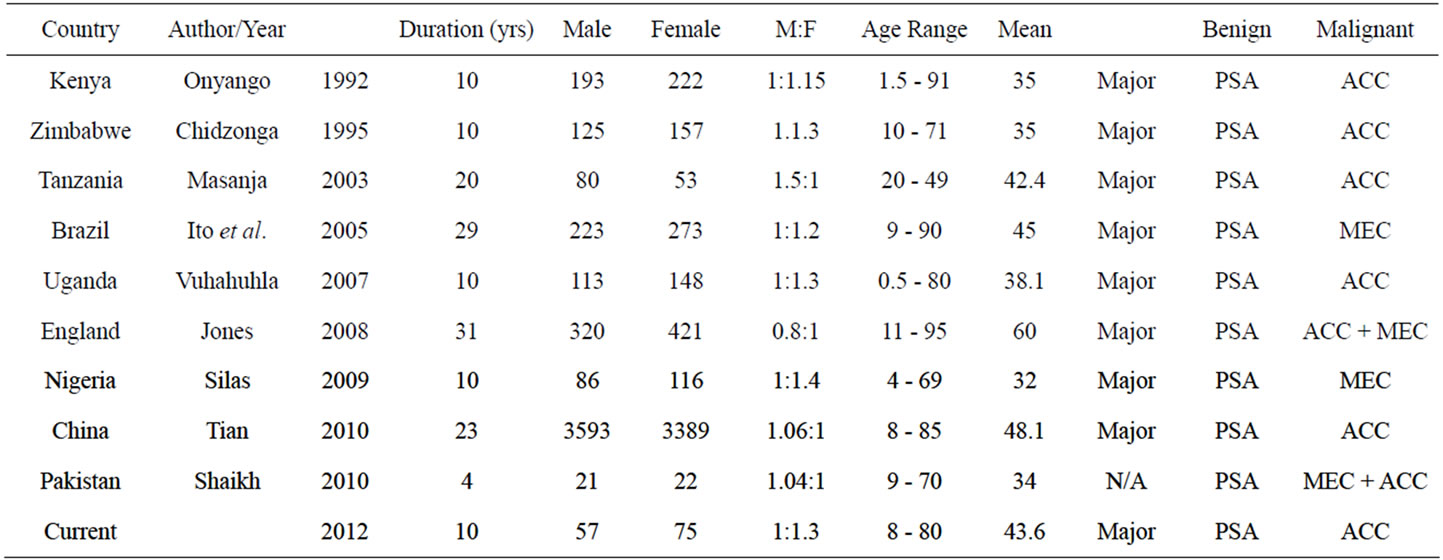
Table 2. Comparison of the pattern of SGTs in various countries.
4.2. Gender
There were more females than males with SGTs in this study population, which is similar to previous studies done in Nigeria, UK, Uganda, Zimbabwe and Kenya [6,9,10,14]. Equal gender distribution was recorded in Pakistan, Brazil and in another study in Nigeria [13,16,17] while, in Tanzania, there were more males with SGTs [7]. In Nigeria there was a slight male dominance in the benign tumours while, the females were three times more affected than males in the malignant SGTs [10]. In Zimbabwe and Brazil, malignant SGTs tumours had a male predominance whereas, there was female dominance in benign tumours [9,16]. In UK some studies showed had a female predominance in both malignant and benign SGT while in China, there were more males with benign SGT with equal gender distribution for the malignant types [14,15]. In Tanzania, where the gender was known, there was a male predominance for both the benign and malignant SGTs. It has been suggested in literature that malignant salivary gland tumours are more frequently diagnosed in female patients and our results support this finding [22] Table 1. In another study done in Kenya, by Onyango et al. at a major referral hospital reported equal gender distribution for both the benign and malignant SGT [6]. In our study, we had twice as many females as males presenting with benign SGT and as for the malignant the gender distribution was equal. There is gender variation in the SGT noted between countries however, the reason for this is not quite clear.
4.3. Salivary Gland Type
In this study, among the minor salivary glands, the palate was the most commonly affected site (54%), unlike Zimbabwe, Nigeria, Pakistan, China, Uganda, Tanzania, Brazil and previous studies done in Kenya, where the parotid gland was the most affected with SGT [6-10,15,16]. Another study in Nigeria showed results that were similar to our findings with the palate being the most commonly affected site [13].
Clinicopathologic differences exist between SGTs in black African populations and white populations in Europe and USA [23,24]. These tumours tend to be more common in females than males and involving the submandibular and minor sublingual gland more than the parotid gland. The parotid and the minor salivary gland tumours are more likely to be malignant than those from the submandibular gland.
Warthin’s tumour is rare in the black African population [6,8,25-31]. Studies from Congo (Zaire), Nigeria, Malawi, South Africa, Kenya, Egypt and Uganda have recorded an almost equal involvement of the parotid, submandibular and minor salivary glands [6,24,26-30]. In most African series there is a higher incidence Submandibular gland tumours and a low incidence of parotid gland tumours compared to the western series [24,26,32,33]. The pattern has been the same in Kenya, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Tanzania and Nigeria [6-8,10]. In China, in keeping with the tradition of the pattern of 100:10:10:1 ratio for parotid, submandibular, minor salivary and sublingual tumours respectively, reported almost identical ratio indicating, a high incidence of minor gland tumours [8,15]. In Brazil and UK, the majority of the SGTs were located in the parotid gland, followed by the minor salivary and submandibular glands in tandem with large series of studies the only difference being there were no tumours recorded from the sublingual gland in Brazil unlike UK [16,19,34-36]. Several studies indeed, have not reported any SGT in the sublingual glands [16,17,36,37]. The sublingual gland is a rare site for tumours in both the Western and African series, the reported incidence is less than 5% of all SGT [8,24,38]. However, in our study we recorded 7% of SGTs in the sublingual gland. Minor SGTs tend to be more common in African studies; for example as reported for South Africa, Uganda, Malawi, and Nigeria [8,13,24,39]. In our study, 67% of the SGT were in them MiSGs (Figure 2). However, in Eastern Chinese, Zimbabwe, Tanzania and in the UK population, the most affected gland was the parotid, followed by the minor salivary gland (palate) then the submandibular gland [7,9,14,15].
4.4. SGT Histopathology
The ratio of benign to malignant was almost 2:1 in China, Nigeria and UK, whereas, in Kenya. Tanzania and Uganda it was 1:1 [6-8,10,14,15] There were far more benign than malignant SGTs both in Zimbabwe (3:1) and in Pakistan (4:1) [9,17]. Our findings of benign : malignant ratio of 1:1 and whereas a Nigerian study showed a ratio was 1:1.5. [13]. According to tumour types, the most frequent benign SGT tumour type recorded in this study was PSA (40.2%). A similar trend had been documented seen in Uganda (74.8%), Tanzania (44.4%), Nigeria (48.4%), Kenya 87%, Zimbabwe (73%), Pakistan 74.4% and in, UK (44.4%), China 69% [6-10,14,15,17]. Among the malignant variants, ACC was more frequently seen to occur in this study similar to other reports from China, Zimbabwe, Uganda, Tanzania [7-9,15]. Both MEC and ACC were reported to be common in UK and Pakistan. [14,17]. While MEC dominated the malignant SGT in Nigeria, ACC was more dominant in Kenya, Zimbabwe, Tanzania, Uganda and China as was the case in this study [6-9,15]. Warthin’s tumour is known to be very rare in Africa. This is evident in the fact that in our 12- year audit, not a single case was reported in this study, neither has it been reported across the African continent [31]. However, in China it is reported as the 2nd most frequent tumor type after PSA [15,31]. Eveson and Cawson found peak incidence of benign tumours in the 6th decade and malignant in the 7th decade. In general the SGT in our findings occur a decade younger with the benign presenting 10 years earlier than the malignant [34].
5. CONCLUSION
It can be concluded from this study that PSA and ACC are the most common SGT of the MiSG, with more females affected than males. As more than 50% of SGT in our study were malignant, any SGT should raise concern and be treated immediately. In addition the age at presentation was a decade younger which has been a common finding in the African continent. The results of this study skew towards those done in Africa, with differences noted from the Western and American literature There is a need for more research to elucidate some of the diversification linked to SGT. SGTs are diverse in their epidemiological patterns and therefore there is a need for SGT registry in all major hospitals to facilitate collection of data and explain the variations.
NOTES